Microeconomics Monster Vocab
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
allocative efficiency
A state of the economy in which production is in accordance with consumer preferences; in particular, every good or service is produced up to the point where the last unit provides a marginal benefit to society equal to the marginal cost of producing it
Ceteris Paribus
all other things held constant
Circular Flow
A model of the movement of goods, services, resources, and money in an economy.
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
complementary goods
Goods that are commonly used with other goods
absolute advantage
the ability of an individual, a firm, or a country to produce more of a good or service than competitors, using the same amount of resources
accounting profit
total revenue minus total explicit cost
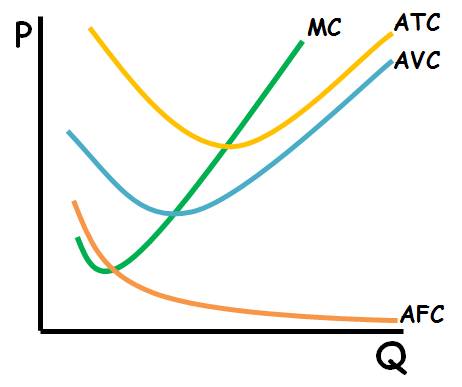
Average Fixed Cost (AFC)
fixed cost divided by the quantity of output
Average Total Cost (ATC)
total costs divided by quantity of output
Average Variable Cost (AVC)
total variable costs divided by quantity of output
consumer surplus
the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it
cross-price elasticity of demand
a measure of how much the quantity demanded of one good responds to a change in the price of another good,
deadweight loss
the reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium
derived demand
Business demand that ultimately comes from (derives from) the demand for consumer goods.
determinants of demand
the external factors that shift demand to the left or right
determinants of supply
factors other than price that determine the quantities supplied of a good or service
diseconomies of scale
the property whereby long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output increases
economic costs
explicit costs + implicit costs
economic profits
total revenues minus explicit and implicit costs
economies of scale
factors that cause a producer's average cost per unit to fall as output rises
explicit costs
The actual payments a firm makes to its factors of production and other suppliers.
free rider
a person who receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it
human capital
the knowledge and skills a worker gains through education and experience
implicit costs
Indirect, non-purchased, or opportunity costs of resources provided by the entrepreneur
income effect
the change in consumption resulting from a change in real income
inferior goods
Goods for which demand tends to fall when income rises.
law of demand
consumers buy more of a good when its price decreases and less when its price increases
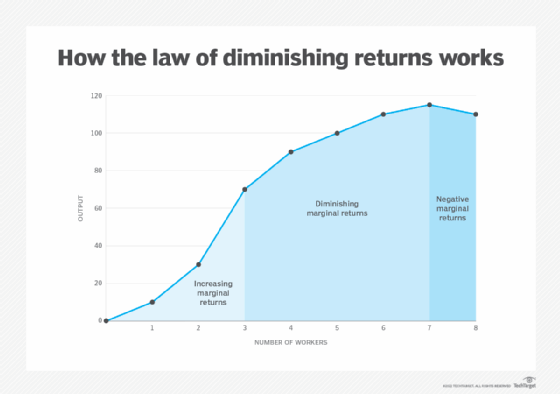
law of diminishing marginal returns
as more of a variable resource is added to a given amount of other resources, marginal product eventually declines and could become negative
law of diminishing marginal utility
the principle that consumers experience diminishing additional satisfaction as they consume more of a good
law of increasing costs
law that states that as we shift factors of production from making one good or service to another, the cost of producing the second item increases
law of supply
Tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price
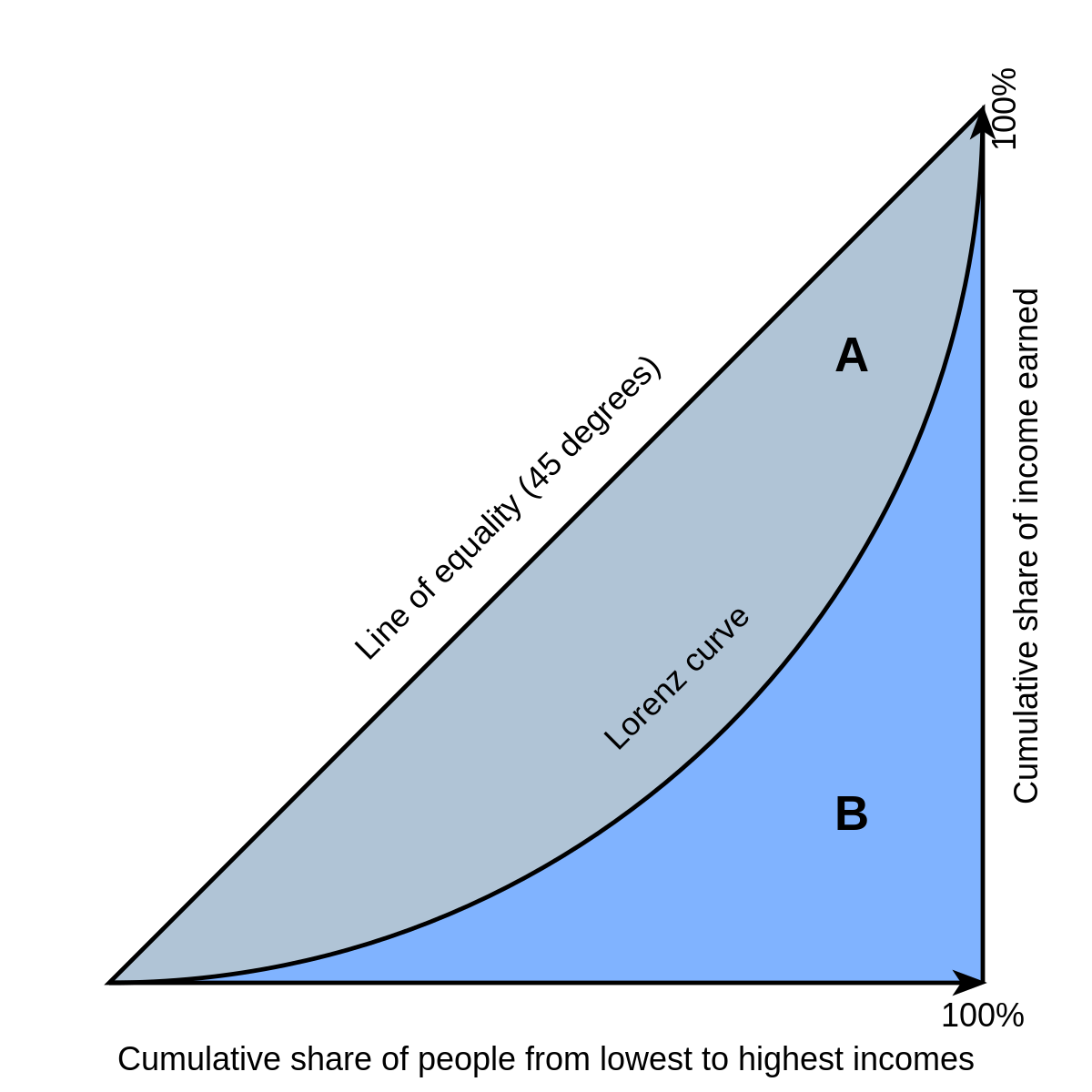
The Lorenz curve and Gini ratio
income gap (inequality of distribution)
Marginal Benefit
the additional benefit to a consumer from consuming one more unit of a good or service
marginal cost
the cost of producing one more unit of a good
Payoff Matrix (Game Theory)
strategies of one player against strategies of another player
marginal product of labor
the change in output from hiring one additional unit of labor
Marginal Resource Cost
The change in total cost caused by a one-unit change in an input.
marginal revenue product of labor
the change in a firm's revenue as a result of hiring one more worker
marginal utility
an additional amount of satisfaction
market failure
a situation in which a market left on its own fails to allocate resources efficiently
monopolistic competition
a market structure in which many companies sell products that are similar but not identical
monopoly
A market in which there are many buyers but only one seller.
Monopsony
a market structure in which there is only a single buyer of a good, service, or resource
natural monopoly
a market that runs most efficiently when one large firm supplies all of the output
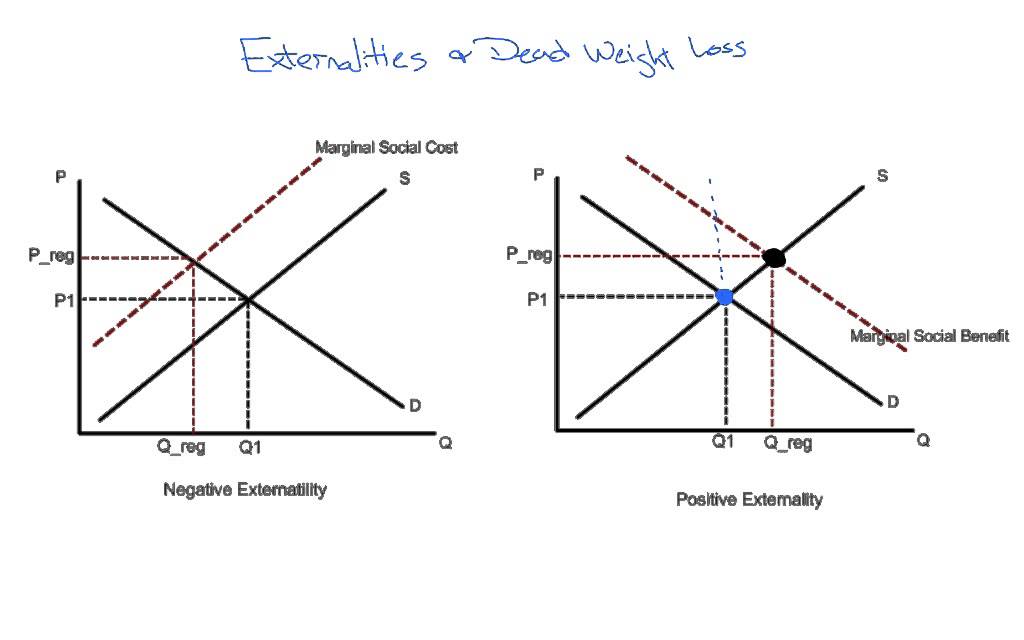
negative externality
the harm, cost, or inconvenience suffered by a third party because of actions by others
normal profit
the minimum income entrepreneurial ability must receive to induce it to perform entrepreneurial functions for a firm
Oligopoly
A market structure in which a few large firms dominate a market
opportunity cost
whatever must be given up to obtain some item
perfectly elastic
flat demand curve; consumers are perfectly price sensitive
perfectly inelastic
quantity does not respond at all to changes in price (E=0)
positive externality
beneficial side effect that affects an uninvolved third party
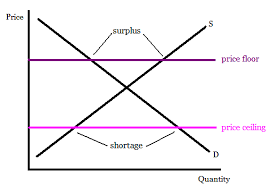
price ceiling
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold
price floor
A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold
Prisoner's Dilemma
a paradox in decision analysis in which two individuals acting in their own self-interests do not result in the optimal outcome.
producer surplus
the amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller's cost of providing it
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
a curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two products that may be produced with available resources and current technology
profit maximizing resource employment
The firm hires the profit maximizing amount of a resource at the point where MRP = MRC
progressive tax
A tax for which the percentage of income paid in taxes increases as income increases
proportional tax
A tax in which the average tax rate is the same at all income levels.
regressive tax
A tax for which the percentage of income paid in taxes decreases as income increases
resources
Land, Labor Capital
short run
the period of time during which at least one of a firm's inputs is fixed
substitute goods
Products or services that can be used in place of each other.
substitution effect
when consumers react to an increase in a good's price by consuming less of that good and more of other goods
Total Cost
the sum of fixed and variable costs
Total fixed costs
all the expenses that remain the same no matter how many products are made or sold
total product(TPL) of labor
The total quantity of output produced for a given quantity of labor employed
total revenue test
means for determining whether demand is elastic or inelastic.
total variable costs
Variable cost per unit x number of units sold
utility maximizing rule
equating the ratio of the marginal utility of a good to its price for all goods
Demand-Supply with Surpluses
PPC (Constant and Increasing)

Cost Curves (Fixed-Average-Total-Marginal)
Lorenz Curve
Diminishing Marginal Returns
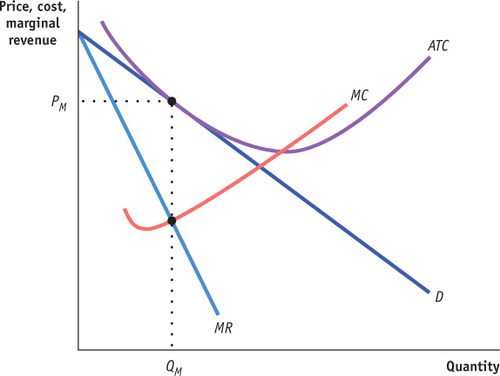
Monopoly
Externality with DWL (Negative and Positive)
Gov Set Prices (Ceilings and Flooors)
Monopolistic Competition
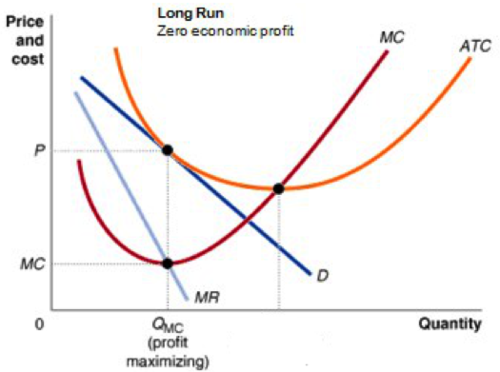
Product Market Perfect Competition
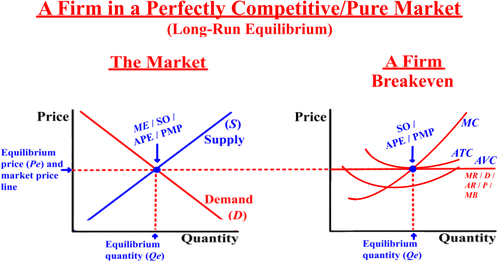
Factor Market Perfect Competition
Payoff Matrix (Game Theory)
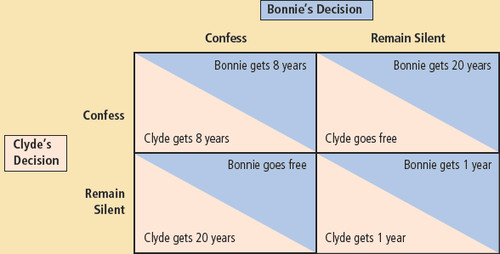
Monopsny