NS Fundamentals - Blood Brain Barrier
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
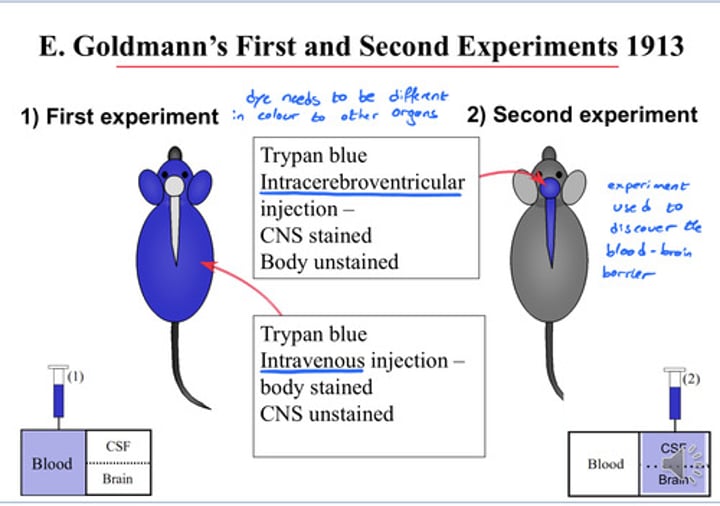
What did the Goldmann experiment of 1913 discover?
- Trypan Blue intracerebroventricular injection lead to CNS staining but body unstained
- Trypan Blue intravenous injection lead to body staining but CNS unstained
- ultimately discovered the Blood Brain Barrier
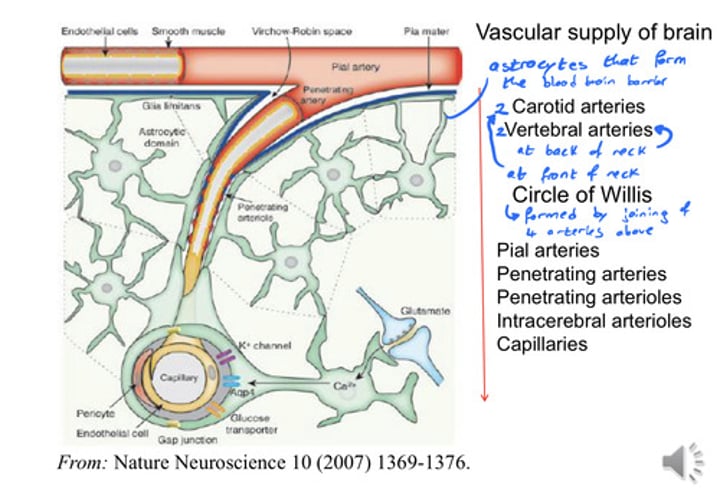
Describe the Vascular Supply for the brain.
- Astrocytes form the Blood Brain Barrier
- 2 Carotid (front of neck) and 2 Vertebral (back of neck) Arteries
- Joining of arteries to form the Circle of Willis
- Diverging off into Pial arteries
- Followed by arterioles and finally capillaries
What are characteristics of Capillaries in the Brain?
- The level of complexity in the capillary network of the brain is far greater than normal bodily tissues (no cell is far from capillary)
- Much higher density of capillaries in brain compared to normal bodily tissue (linking to above)
- Form a luminal membrane (barrier closest to capillary) and an abluminal membrane (barrier further out from capillary)
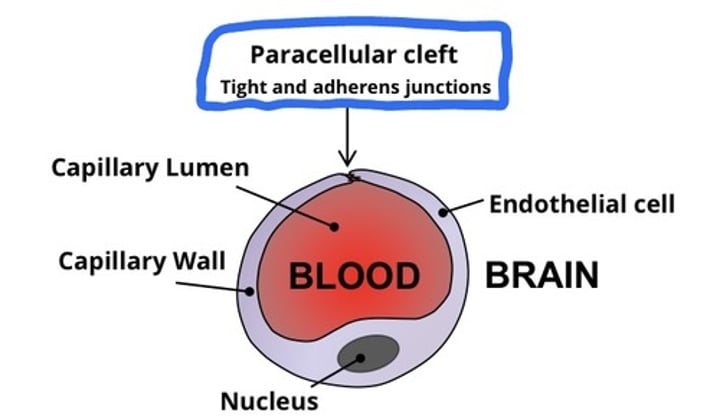
Describe the Vascular component of the Blood Brain Barrier.
- Capillary lumen is surrounded with a single endothelial cell, making up a mono-layer wall
- Paracellular Cleft is region where the endothelial cell joins itself via Tight and Gap (adheren) junctions
Describe the Neural components of the Blood Brain Barrier.
- Endothelial Basement Membrane = separates tissue and protects from mechanical stress
- Astrocytic Basement Membrane = same as above
- Glycocalyx = gel-like substance around cell, providing physical barrier against other substances
- Pericyte = maintain the blood vessels
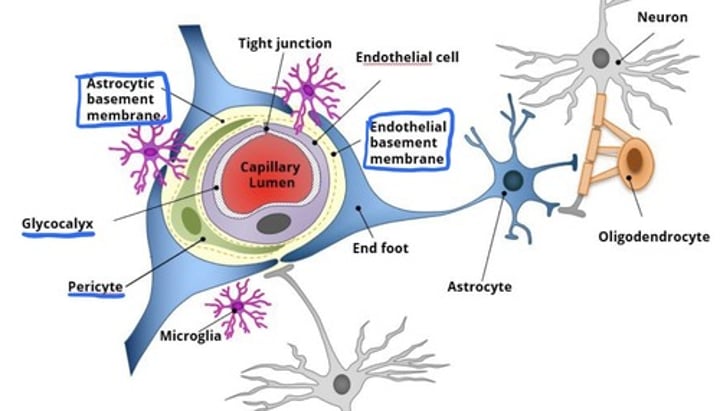
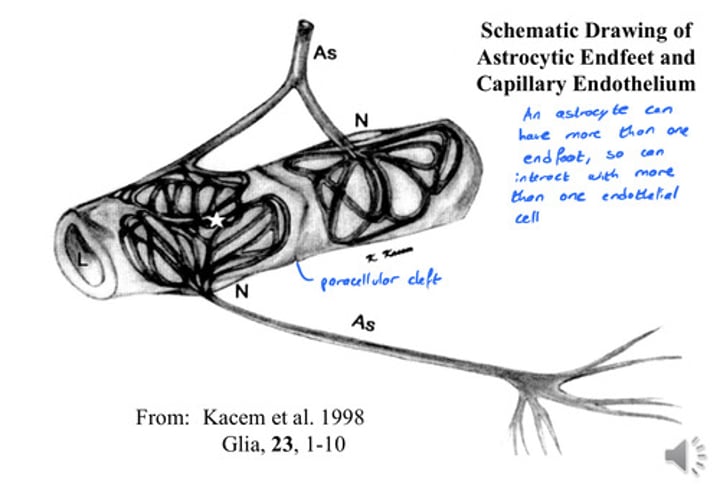
What are Astrocytic endfeet, and what do they do?
- A projection structure of an astroctye that covers the capillary endothelium, and an astrocytic may have more than one of these, so more than one interaction is possible
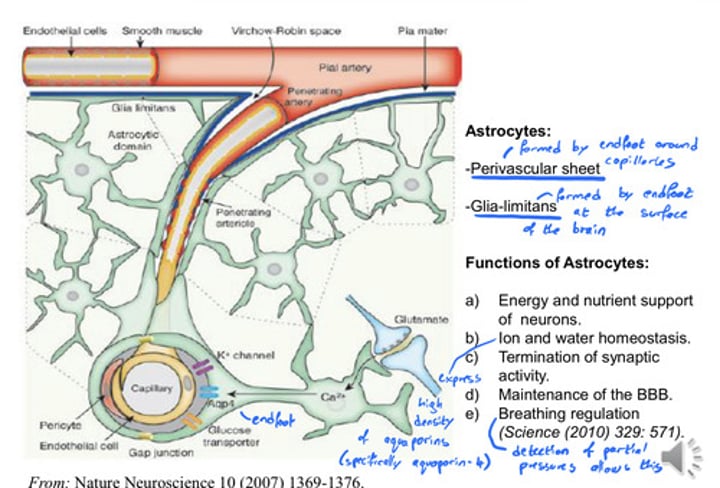
- Form Perivascular sheet with endfeet around capillaries
- Form Glia-limitans with endfeet at surface of brain
What are the functions of Astrocytes?
- provide nutrients for neurons
- ion and water homeostasis (expresses high density of aqauporins)
- Terminate synaptic activity
- Maintenance of Blood Brain Barrier
- Breathing regulation via partial pressure detection
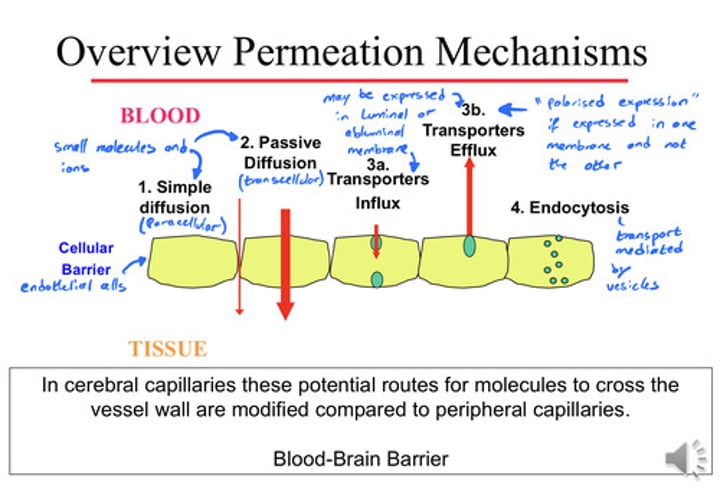
What are the different permeation mechanisms between blood and tissues?
- Simple (paracellular) and Passive (transcellular) diffusion
- Transporters influx and efflux (can be expressed in luminal and/or abluminal membranes - endothelium and astrocytes) ("polarised expression" is when transporters are expressed on one membrane and not the other)
- Endocytosis
Describe the composition of the Paracellular Cleft.
- Paracellular movement is mediated by Gap (adheren) and Tight Junctions, found mixed together throughout the paracellular cleft
- Gap junctions and Tight junctions both bind to the actin cytoskeleton on the cell
- Tight junctions prevent movement of ions and molecules between the intracellular space
What are the features of the cerebral capillary endothelium?
- Physical barrier formed via continuous strands of tight junctions at paracellular clefts
- Chemical barrier that is highly selective via high levels of transporters and reduced levels of vesicles or fenestrations
- Metabolic barrier via enzyme systems that metabolise foreign molecules attempting to move between the BBB
How does the BBB act as a physical barrier?
- It has continuous strands of tight junctions, increasing impermeability
- Electrical resistance is significantly higher for brain capillaries, contributing to ion impermeability
- Phospholipid bilayers mean mainly lipophilic molecules are able to pass the BBB
How does the BBB act as a chemical barrier?
- It has a high level of specific transporters, with a reduced level of vesicles and fenestrations
- Transporters found are for substances that are necessary for CNS function such as D-Glucose, or Amino acids
- ABC efflux transporters actively remove foreign substances that attempt to pass the BBB back into the capillary
How does the BBB act as a metabolic barrier?
- It has enzyme systems that metabolise molecules that attempt to enter the brain, and prevent further transport by making them less lipophilic
-
What are the functions of the BBB?
- To control the molecule influx into the brain Interstitial Fluid (provides optimal environment for neuronal function)
- To supply the brain with essential materials
- To mediate efflux of waste products
- To restrict ion and fluid movements (protects from ion fluctuations)
Why do drugs need to be able to pass the BBB?
- For treatment or prophylaxis of neurodegenerative conditions (cause degeneration of neuronal matter) or neurological conditions (cause malfunction of neuronal matter)