Biology: Topic 1.1 - 1.2
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Important properties of water
Polar solvent
Maximum density @ 4ºC
High specific heat capacity
Cannot be compressed
Adhesive (others) & cohesive (together)
High surface tension
What are nitrate ions used for?
To make DNA and amino acids
What are calcium ions used for?
To form calcium pectate for the middle lamellae
What are magnesium ions used for?
To produce chlorophyll
What are phosphate ions used for?
To make ATP and ADP
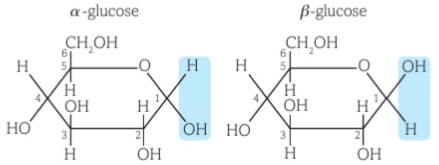
Alpha and beta glucose structures
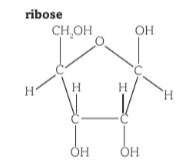
Ribose structure
Types of bonds in carbohydrates
glycosidic (condensation reaction)
Disaccharides components
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Lactose = glucose + galactose
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Starch - structure and function
Amylose (1,4 glycosidic bonds)
Amylopectin (1,6 glycosidic bonds)
Compact, not soluble in W, slow and quick E release
Glycogen - structure and function
Like starch but more 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Compact, quicker E release (humans)
Cellulose - structure and function
β glucose (1,4 glycosidic bonds/OH hydrogen bonds)
Rigid, lattice struct = strength (PPQ)
Lipids - structure and bonding
1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids
Ester bonds (esterification)
Functions of lipids
Energy store (3x more than carbs)
Hydrophobic (waterproofing)
Insulation
Buoyancy
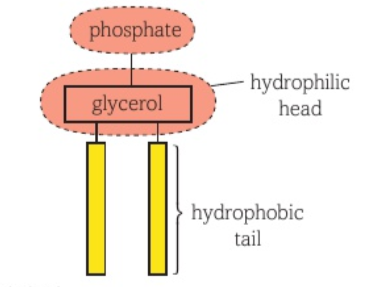
Phospholipids
Hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tail
(PO4³⁻)
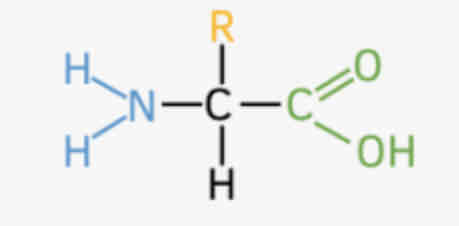
Proteins - structure and bonding
20 types of Amino acids
Peptide bonds
Bonds between AA:
Disulfide, Hydrogen, Ionic
Formation of proteins
1º struct - linear seq of AA
2º struct - α helix or β pleated sheet
3º struct - 3D folding (other bonds)
4º struct - more than 1 tertiary protein
Fibrous proteins
Collagen
α helix, triple helix
Insoluble and tough - connective tissue
Globular proteins
Haemoglobin / Amylase
Spherical
Water-soluble - used in transport
Conjugated proteins
Prosthetic group (PG)
Glycoproteins - Carb PG, hold water well so aren’t broken down easily - mucus
Lipoproteins - Lipid PG, bind w/ cholesterol and transport it