Chemistry P1
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is matter?
Anything that occupies space and has mass
What is an atom?
Smallest unit of matter
What is physical properties?
Can be observed without changing the substance into something new; not changing its chemical formula
What are some examples of physical properties of matter
Colour, hardness, density, malleability, melting point
What are the 3 phases of matter?
Solid, liquid, gas
What is a phase change?
When matter changes from one state to another
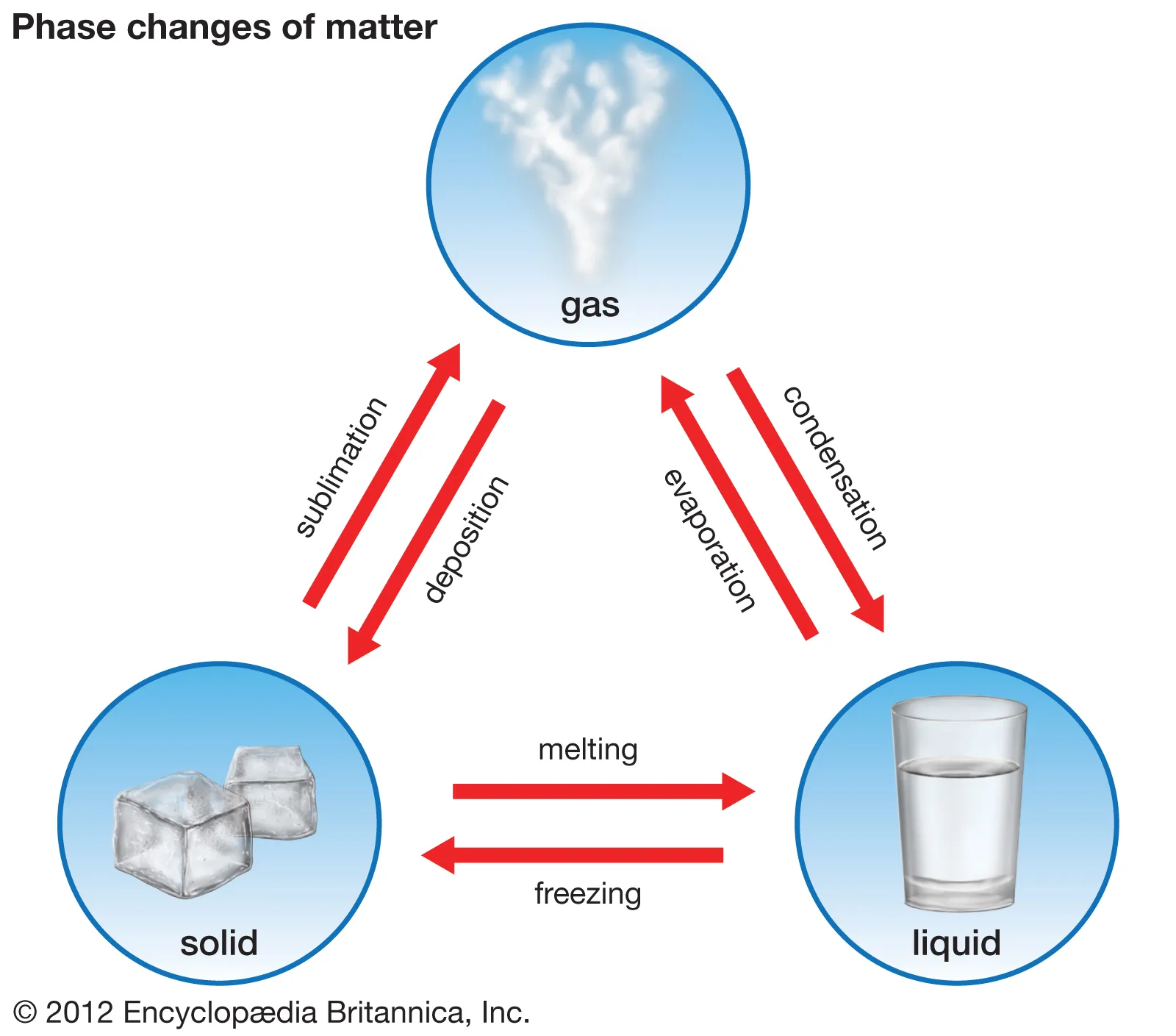
Describe solids
Fixed shape and volume
Describe liquids
No definite shape
Describe gases
No designed shape or colume
What is chemical propeties?
How a substance behaves when it reacts to form a new substance; changing its chemical formula
What are some examples of the chemical properties of matter?
Burning, toxicity, oxidation, etc
What is a pure substance?
Matter that is only made up of one substance and cannot be physically separated into any other matter; elements and compounds
What are the 2 types of pure substances and describe them
Elements - Can be found on the periodic table
ex)Helium, Hydrogen
Compounds - Found naturally, mix of elements together
Ex) H2O, NaCl
What is a mixture?
The physical mixing of 2 or more components; Homogenous and heterogenous
What are the 2 types of mixtures and describe them
Homogenous - Looks like one substance
Ex) Soda, Orange juice
Heterogenous - You can see the physical components it is made of
Ex) Salad, trail mix
What is the Dalton’s Billiard Ball Model?
The foundation of Atomic theory
Atoms are spherical like billiard balls
Each atom has its own unique properties
Atoms are indivisible; they are the building blocks of life
Atoms can combine in many ways to create a wide variety of elements/compounds
What is the Thomson’s Raisin Bun Model?
Thomson discovers the electron
The electron is 2000X smaller than the smallest atom and has a negative charge
Atoms must contain electrons
Electrons must be spread-out evenly throughout a positively charged atom like raisins in a bun
What is Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment?
Alpha particles from radioactive polonium were fired at a thin piece of gold foil
Most alpha particles pass through the gold undeflected
Atoms have a very small nucleus where almost all of the mass is located. Since the nucleus is so small, the alpha particles had a small chance of actually hitting it
Rutherford discovered the nucleus was made up of protons and neutrons
Electrons orbit the outside of the nucleus, like planets around the son. Most volume of an atom is empty space
What is the Bohr model of the atom?
Electrons exist at certain distances from the nucleus(called orbits, shells, or energy levels)
Max number for the 1st energy level = 2e-
Max number for the 2nd and 3rd energy level = 8e-
What is the Electrons cloud model of an atom(Schrodinger&Heisenberg)?
We can’t exactly know where an electron is at any given time, but electrons are more likely to be in specific areas
E- are in a cloud
Define elements
Made of atoms, atoms are made from subatomic particles
What is the charge, mass, symbol, and location of a Electron?
Charge - Negative
Mass - No mass
Symbol - e-
Location - Cloud, around the nucleus
What is the charge, mass, symbol, and location of a Proton?
Charge - positive
Mass - 1
Symbol - p/p+/H+
Location - In the nucleus
What is the charge, mass, symbol, and location of a Neutron?
Charge - No charge, neutral
Mass - 1
Symbol - n
Location - In the nucleus
What subatomic particle makes up most of the volume of an atom?
Electrons
What subatomic particles makes up most of the mass of an atom?
Neutrons and protons
What is the atomic number?
The # of protons and electrons in an element
What is the atomic mass?
The average weight of one element = protons and neutrons
What is an Ion?
When an electron is being added or taken away; an atom that has a positive or negative charge
Why is Hydrogen so special?
Because it doesn’t belong to a specific group
It’s a non-metal that acts like a metal
Describe metal and where is it located on the periodic table?
Located to the left of the “staircase” and typically gives electrons
Conductors of energy and heat
Malleable
Ductile
Luster
Describe Non-Metals and where is it located on the periodic table?
Located to the right of the “staircase” and typically accepts electrons
Poor conductors
Brittle
Not ductile
Lack luster
Describe metalloids and where is it located on the periodic table?
Is considered the “staircase” which separates metals and non-metals and typically gives electrons
What are periods in the periodic table?
The rows of elements from left to right.
Total of 7 periods
The row number is equivalent to the energy levels
What is groups/family in the periodic table?
The rows of elements from up to down
Total of 18 groups/families
Groups is numerical while family is names
The # of e- in the last energy level or valence e-, only works for g1-3, g13-18
What is group1 in the periodic table?
It’s called the Alkali Metals and are very reactive with H2O(water)
What is group2 in the periodic table?
It’s called the Alkaline Earth Metals and are less reactive with H2O(water)
What is group17 in the periodic table?
It’s called the Halogens and are very reactive non-metals
What is group18 in the periodic table?
It’s called the Noble Gases and are non-reactive
What are naturally diatomic elements?
Elements that are paired when alone'
H O N Cl Br I F
What are examples of polyatomic elements?
Sulfur has 8 and phosphorus has 4
What are valence e-
The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom
What can we learn about atoms from the Bohr energy level diagrams?
How many valence e- are in the last energy level
Tells us the reaction behavior of the atom; whether an atom is going to give or take e-
How are ions formed?
By gaining or losing e-
Describe and explain Ionic compounds
Bond between non-metal and metal
Transfer electrons
Solid at room temp
Can conduct in solutions as long as they can dissolve in water
Describe and explain molecular compounds
Bond between non-metal and non-metal
Share electrons
Solid, liquid, and gas at room temp
Low to no conductivity in solutions
What are compound subscripts?
They indicate the number of particular type of atom in the chemical formula for a molecule or a compound
What are compound coefficients?
Coefficients appear in front of a compound formula to indicate how many compounds of that type are
What are properties of ionic compounds?
High melting point
Retain their crystal shape
Vary in solubility
Are conductors when they dissolve in solutions. Ionic compounds that do dissolve and conduct electricity are called electrolytes
Form 3D grids called lattices
What does IUPAC stand for?
International committee of pure and applied chemist