Biology Chapter 10: Photosynthesis
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
the conversion of light energy to chemical energy
What is an autotroph?
an organism capable of producing their own food from simple substances in their surroundings
What is a heterotroph?
an organism incapable of producing their own food so they must rely on other organisms for fuel
Where was photosynthesis originated from?
prokaryotic organisms
What is cyanobacteria?
an early prokaryote that oxygenated the atmosphere of early Earth through photosynthesis
What is the foundation of Eukaryotic photosynthesis?
prokaryotic photosynthetic pathways
What is the primary location for photosynthesis in plants?
leaves
Which organelle does photosynthesis take place?
chloroplast
Chloroplasts are found in mesophyll; what is mesophyll?
the cells that make up the interior tissues of the leaf
What is the stomata?
pores in the leaves that allow CO2 in and O2 out
Do chloroplasts have double membranes or single membranes?
double membranes
What is the stroma?
aqueous internal fluid
What are thylakoids?
“plates” that form stacks called grana
What is chlorophyll?
green pigment in thylakoid membranes
What is the simplified formula for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy ——> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What are the reactants of photosynthesis?
6CO2 and 12H2O
What are the products of photosynthesis?
C6H12O6 and 6H2O and 6O2
Which molecule experiences a reduction in photosynthesis?
6CO2 gets reduced to C6H12O6
Which molecule experiences oxidation in photosynthesis?
6H2O gets oxidized into 6O2
What is a redox reaction?
a reaction where one or more electron partially or completely transfers from one reactant to another
Photosynthesis splits H2O into what?
H and O
Where does the electron transferred with the H+(from split H2O) go?
It is transferred to CO2 and reduced to sugar
What is OIL?
oxidation is loss (of electrons)
What is RIG?
reduction is gain (of electrons)
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
light reactions and calvin cycle
What is light?
electromagnetic energy that travels in waves and is made up of particles called photons
What is a wavelength?
the distance from the crest of one wave to the crest of the next
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
the entire range of wavelengths; 380nm to 750nm is visible light
The shorter the wavelengths the higher the energy therefore the longer the wavelengths the __________
lower the energy
What are the different ways light interacts with matter?
reflected, transmitted, absorbed
The color we see is from the _____________ wavelengths
reflected
What is chlorophyll a?
primary blue/green pigment involved in light reactions
What is chlorophyll b?
accessory yellow/green pigment
What are carotenoids?
yellow/orange pigment that broadens the spectrum of colors that drive photosynthesis
What is the purpose of photoprotection?
it prevents damage from chlorophyll or interactions with oxygen by using carotenoids to absorb and dissipate light energy
What do light reactions do?
convert solar energy into chemical energy
Where do light reactions take place?
in the thylakoid membrane in the photosystems

idk wtf this is but it’s important so learn it
What are the two forms of chemical energy?
NADPH and ATP
The cell converts light energy to chemical energy by using photons to _________________________
excite electrons
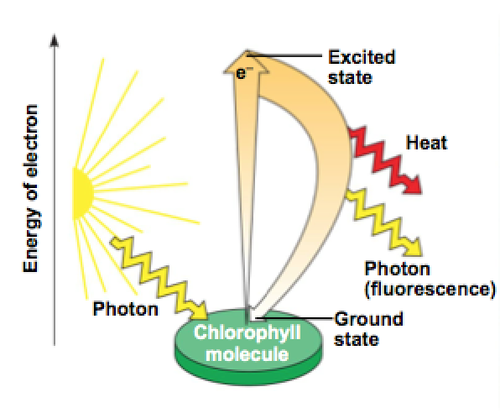
what is this
this is what happens when a chlorophyll absorbs a photon of light
an electron gets excited and becomes unstable so it goes back to ground state which releases heat and emits photons
What is a photosystem?
a reaction center and light capturing complexes
What is a reaction center?
a complex of proteins associated with chlorophyll a and an electron acceptor
What is a light capturing complex?
pigments associated with proteins; it’s like the antenna for the reaction centers
What are the two photosystems in the thylakoid membrane in order of function?
photosystem II
photosystem I
What is photosystem II?
a reaction center at P680 and absorbs light at 680nm
What is photosystem I?
a reaction center at P700 and absorbs light at 700nm
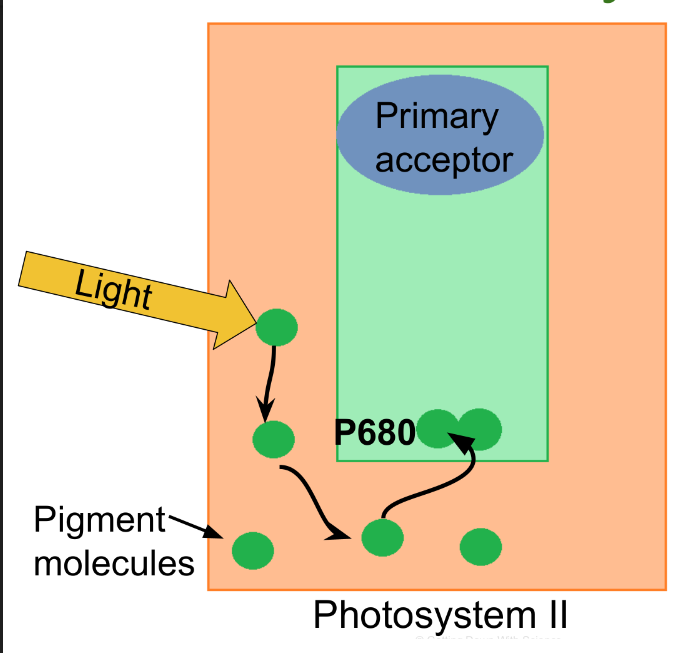
What happens in step 1 of photosystem II?
a photon will make an electron repeat going from an excited state to ground state until it reaches the P680
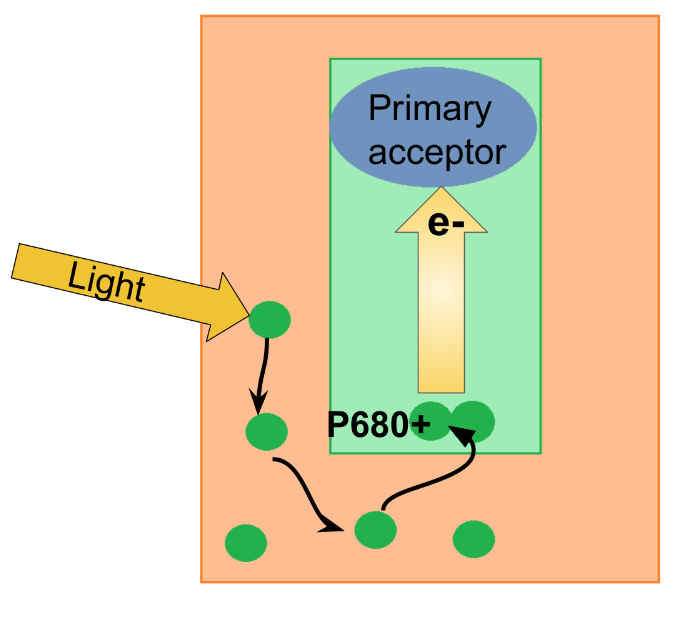
What happens in step 2 of photosystem II?
The electron is transferred to a primary electron acceptor which then forms P680+
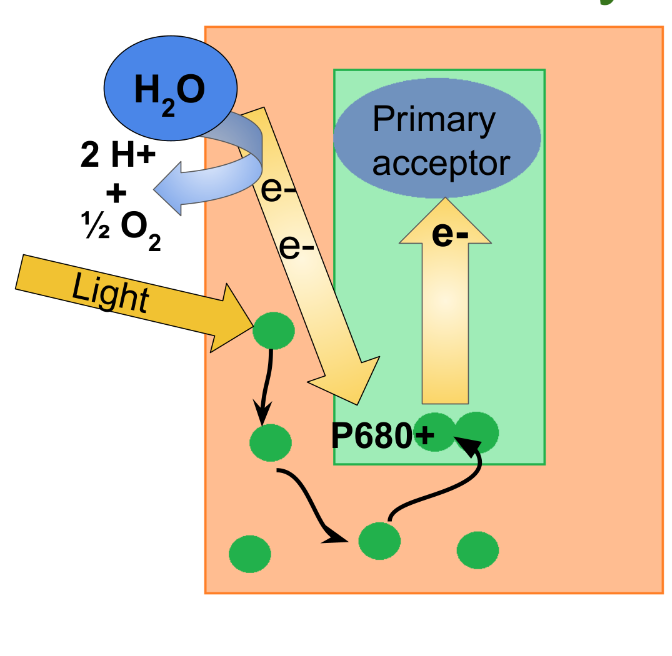
What happens in step 3 of photosystem II?
H2O is split into 2 electrons which reduce P680+, 2 H+ which is released into thylakoid space, and 1 oxygen atom which immediately bonds to another oxygen atom.
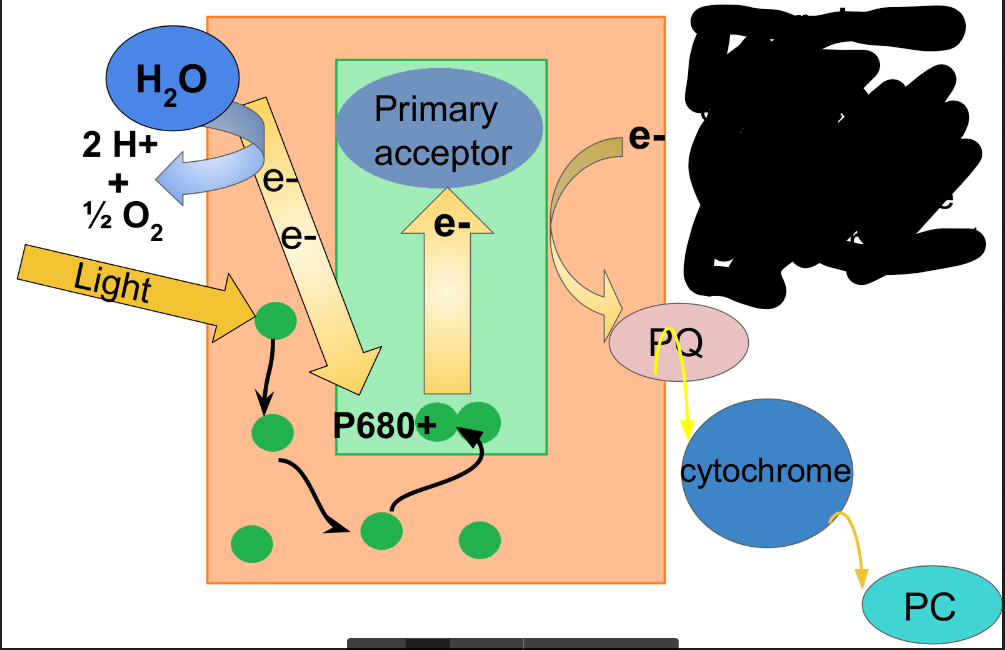
What happens in step 4 of photosystem II?
all excited electrons will pass from PSII to PSI through the electron transport chain; this is called linear electron flow
What happens between PS II and PS I to provide energy to form ATP?
the “fall” of electrons
The H+ gradient is a form of ____________ energy
potential
What does ATP synthase do?
it couples the diffusion of H+ to the formation of ATP
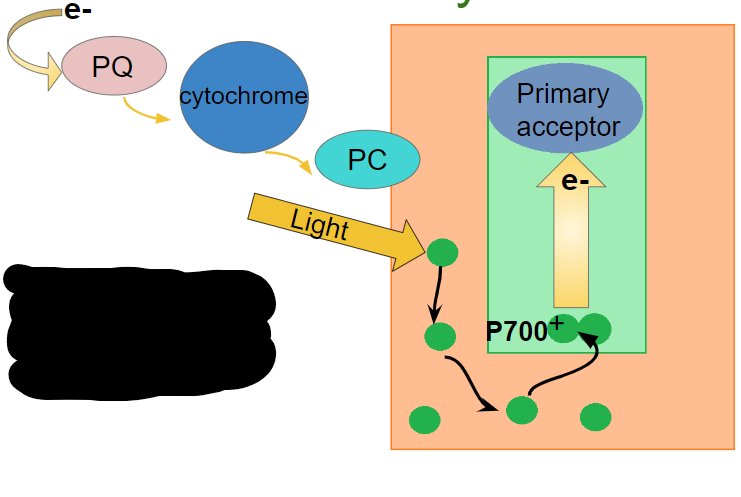
What happens in the first step of photosystem I?
light energy excites electrons in the P700 chlorophyll molecules and becomes P700+
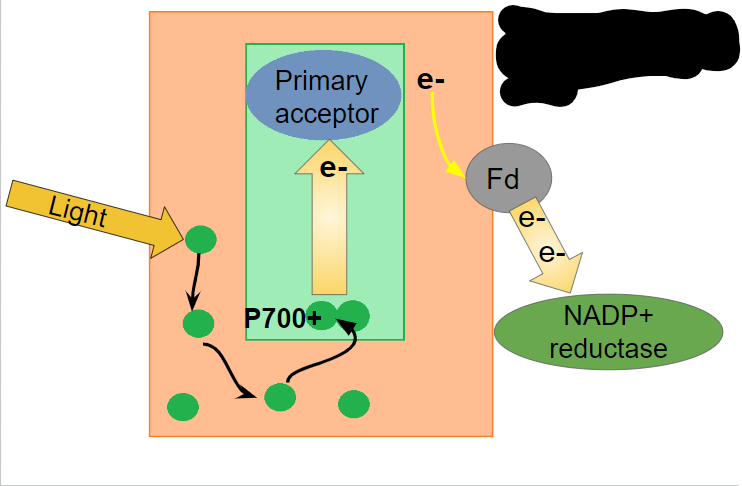
What happens in the second step of photosystem I?
electrons go down a second transport chain
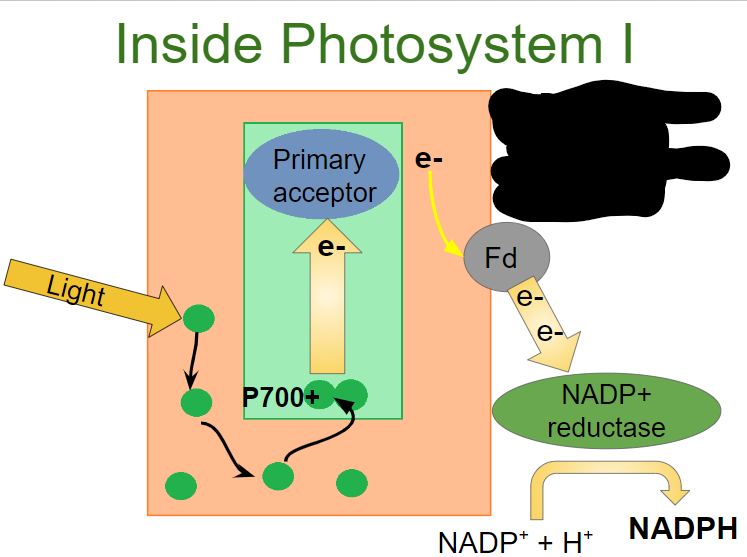
What happens in the third step of photosystem I?
NADP+ reductase catalyzes the transfer of electrons from Fd to NADP+
What are the inputs of light reactions?
H2O
ADP
NADP+
What are the outputs of light reactions?
O2
ATP
NADPH
What is the calvin cycle
cyclic electron flow
What does the calvin cycle do?
it uses ATP and NADPH to reduce CO2 to sugar (G3P)
For the net synthesis of 1G3P the cycle must take place __________ times.
3
What are the three phases of the calvin cycle?
carbon fixation
reduction
regeneration of RuBP
What happens in the carbon fixation in the calvin cycle?
CO2 gets incorporated into the cycle one at a time and attaches itself to RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate) which gets catalyzed by the enzyme rubisco and forms 3-phosphoglycerate (PGA)
What happens in the reduction in the calvin cycle?
All the PGA gets phosphorylated by 6 ATP and becomes one PGA and 6NADPH donates electrons to the PGA to reduce it to G3P; there are 6 G3P formed but only a net gain of 1 because the rest were used to generate RuBP
What happens in the regeneration of RuBP in the calvin cycle?
Use 5 G3P and 3 ATP to regenerate 3 RuBP and the cycle repeats to take in CO2 again.
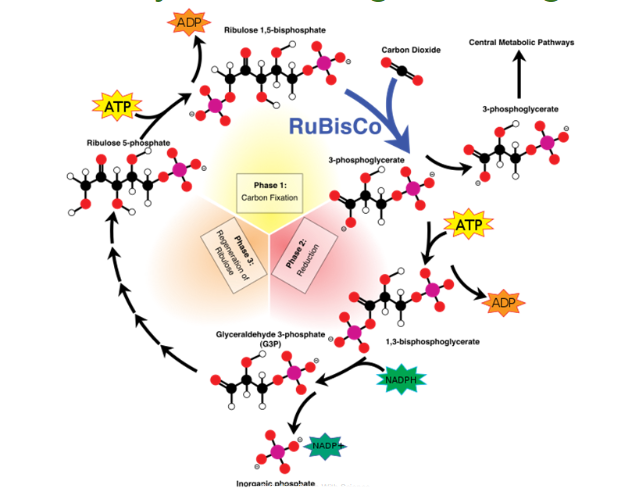
wtf is this
the calvin cycle
What are the inputs of the Calvin cycle?
3 CO2
9 ATP
6 NADPH
What are the outputs of the calvin cycle?
1 G3P
9 ADP
6 NADP+
What is photorespiration?
plants close their stomata to stop water loss on very hot days
Why is photorespiration bad for C3 plants?
There is less CO2 and more O2 so rubisco binds to the O2 and uses ATP producing more CO2 and no sugar
How did C4 plants adapt to combat photorespiration?
the stomata partially close to conserve water and mesophyll cells fix CO2 into a 4-C molecule and transfer it to sheath cells which releases CO2 to be used in the Calvin Cycle
What are CAM plants?
they open stomata at night and close during the day
What happens because of how CAM plants open their stomata?
CO2 is incorporated into organic acids and stored in vacuoles and then during the day, light reactions occur and CO2 is released from the organic acids and incorporated into the Calvin cycle