AP Micro Unit 1 - Basic Economic Concepts
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/57
Last updated 3:45 PM on 4/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
Microeconomics
* Branch of economics that focuses on the behavior of individual economic agents (households, firms, and consumers)
* Concerned with how economic agents make decisions and allocate limited resources to satisfy wants and needs
* Involves consumer behavior, consumer choice, and producers
* Concerned with how economic agents make decisions and allocate limited resources to satisfy wants and needs
* Involves consumer behavior, consumer choice, and producers
2
New cards
Macroeconomics
* Branch of economics that focuses on the overall level of economic activity and how it is affected by changes in policy and other factors
* Helps understand how the economy works and how it can be managed to achieve economic stability and prosperity
* Involves monetary policy, changes in fiscal policy, etc. and the effect they have on the economy
* Helps understand how the economy works and how it can be managed to achieve economic stability and prosperity
* Involves monetary policy, changes in fiscal policy, etc. and the effect they have on the economy
3
New cards
Scarcity
* There are not enough resources to produce everyone’s needs and wants
* There are infinite wants but limited resources
* There are infinite wants but limited resources
4
New cards
Opportunity Cost
* The next best alternative foregone as a result of a decision
* What you give up in place of another choice
* What you give up in place of another choice
5
New cards
Firm
* An individual business
6
New cards
Trade-offs
* The choices individuals and societies must make between two or more alternatives
* Often involves a sacrifice of one thing for another
* Often involves a sacrifice of one thing for another
7
New cards
Difference between Opportunity Cost and Trade-offs
* Opportunity cost looks at the next best alternative that is forgone in the place of another
* Trade-offs look at two or more alternatives that individuals/societies must chose between, often involving a sacrifice of one for the other
* Trade-offs look at two or more alternatives that individuals/societies must chose between, often involving a sacrifice of one for the other
8
New cards
Factors of Production (FOP)
* Tools we use to produce goods
9
New cards
Four Categories of Factors of Production
* Land
* Labor
* Capital
* Entrepreneurship
* Labor
* Capital
* Entrepreneurship
10
New cards
FOP: Land
* Natural resources and raw materials used to make products
* Examples: water, vegetation, oil, minerals, animals, etc.
* Examples: water, vegetation, oil, minerals, animals, etc.
11
New cards
FOP: Labor
* The effort, skills, and abilities individuals/employees devote to a task that they get paid for
12
New cards
FOP: Capital
* Physical Capital: The machinery, tools, and buildings used to produce goods and services
* Human Capital: Skills a worker has as a result of education, training, or experience that can be used in production
* Human Capital: Skills a worker has as a result of education, training, or experience that can be used in production
13
New cards
FOP: Entrepreneurship
* The ability of the individual to coordinate the other categories of resources to invent or produce a good or service
14
New cards
Three Economic Questions each economy asks
* What goods and services will be produce?
* How will goods and services be produced?
* For whom will the goods and services be produced?
* How will goods and services be produced?
* For whom will the goods and services be produced?
15
New cards
Economic System
* A set of rules, institutions, and practices that determine how a society produces, distributes, and consumes goods and services
* Like a framework society uses to allocate its resources and coordinate the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services
* Answers the three Economic Questions
* Like a framework society uses to allocate its resources and coordinate the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services
* Answers the three Economic Questions
16
New cards
Types of Economic Systems
* Traditional
* Command
* Market
* Mixed
* Command
* Market
* Mixed
17
New cards
Traditional Economic System
* Based on reliance on custom and tradition, simple methods of production, and a distribution of goods and services based on social and familial relationships
18
New cards
Command Economic System
* Central authority has complete control over production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services - makes all basic economic decisions
* Controls wages and prices
* Central authority determines answers to Three Economic Questions
* Can direct resources towards important social goals, BUT it can be inefficient and consumers won’t be able to express preferences through the market
* Controls wages and prices
* Central authority determines answers to Three Economic Questions
* Can direct resources towards important social goals, BUT it can be inefficient and consumers won’t be able to express preferences through the market
19
New cards
Market Economic System
* Production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services are guided by the laws of supply and demand
* No central planning body - freedom to produce and freedom to buy
* Can allow efficient allocation of resources, motivates innovation, BUT can lead to inequality and can become unstable and lead to market failure
* No central planning body - freedom to produce and freedom to buy
* Can allow efficient allocation of resources, motivates innovation, BUT can lead to inequality and can become unstable and lead to market failure
20
New cards
Mixed Economic System
* Combined form of command and market economies - government plays a role in regulation and providing certain public goods and services (can intervene), but the market is allowed to produce and sell goods for profit
* Allows for both efficiency and innovation, as well as address social goals and market failures, BUT can cause government interference and inefficiencies as well as conflict of interest between public and private sectors
* Allows for both efficiency and innovation, as well as address social goals and market failures, BUT can cause government interference and inefficiencies as well as conflict of interest between public and private sectors
21
New cards
Efficiency
* The ability of an economic system to produce a large quantity of goods and services with a minimum of resources
22
New cards
Equity
* The fairness of an economic system in distributing resources and opportunities
23
New cards
Stability
* The ability of an economic system to withstand several shocks and maintain a steady state
24
New cards
Production Possibilities
* The different combinations of goods and services that can be produced within the limits of an economy’s resources and technology
* How we can produce different amounts of different goods with limited resources
* How we can produce different amounts of different goods with limited resources
25
New cards
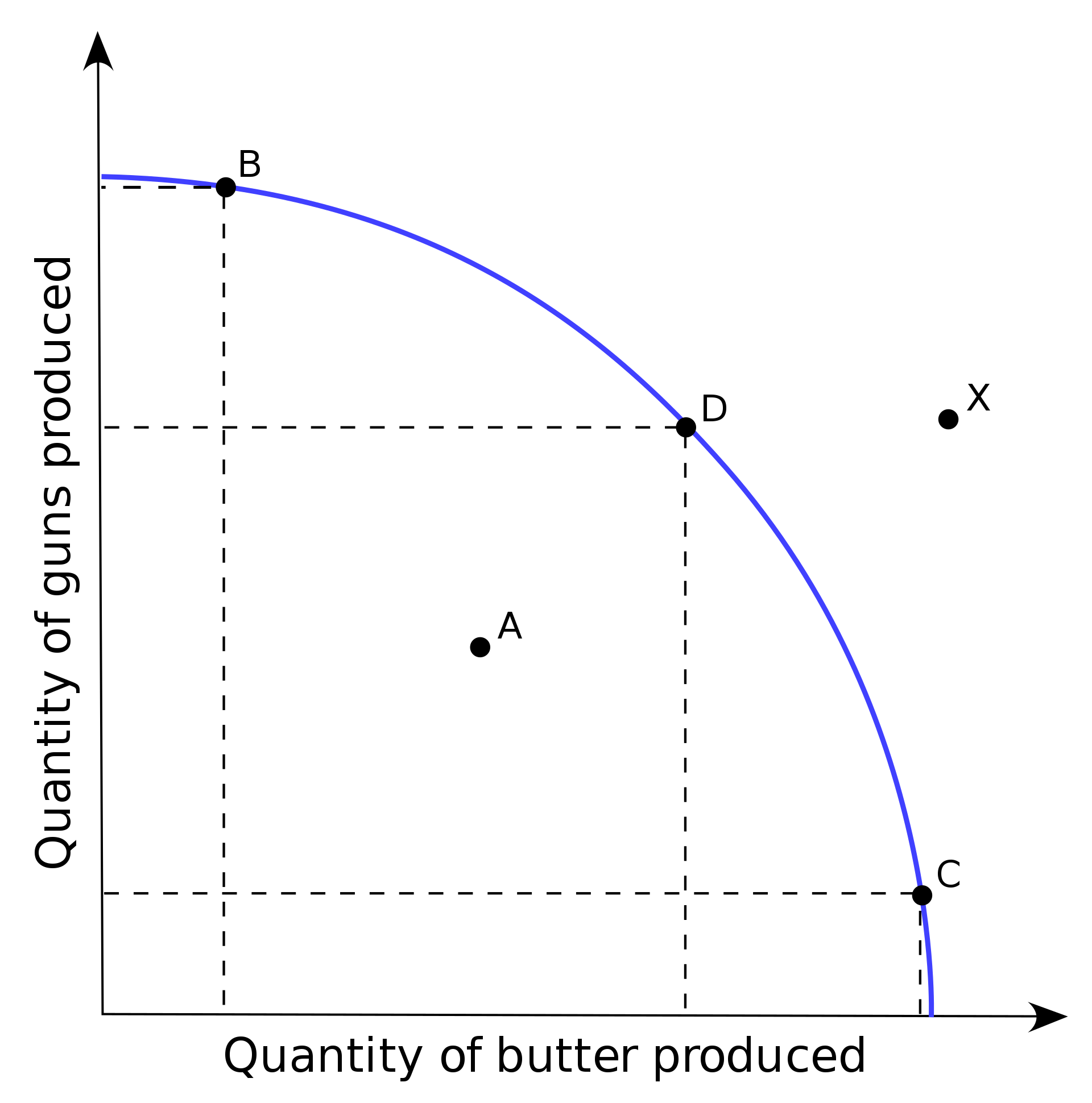
Productions Possibility Curve (PPC) - definition
* A visualization of production possibilities for two goods, with the assumption that:
* only two goods can be made
* resources are fixed
* technology is fixed
* only two goods can be made
* resources are fixed
* technology is fixed
26
New cards
Productions Possibilities Curve (PPC) - graph
27
New cards
Efficient Outputs (PPC)
* When we use all of our resources to produce a certain amount of a number of products
28
New cards
Underutilization of Resources (PPC)
* When we don’t use all of our resources to produce a certain amount of a number of products
29
New cards
Allocative Efficiency
* Production at the point society desires
30
New cards
Productive Efficiency
* Production at the point that minimizes costs
31
New cards
Benefits of PPC
* Helps calculate/measure opportunity cost
32
New cards
Drawbacks of PPC
* Assumes technology is constant - doesn’t account for different technological products being more efficient in producing one product than another
* Assumes resources are constant - doesn’t account for different resources making different products
* Assumes resources are constant - doesn’t account for different resources making different products
33
New cards
Increasing Opportunity Cost
* As we produce more of one thing, the amount we can produce of the other decreases faster and faster
* The steeper the PPC curve, the higher the opportunity cost
* The steeper the PPC curve, the higher the opportunity cost
34
New cards
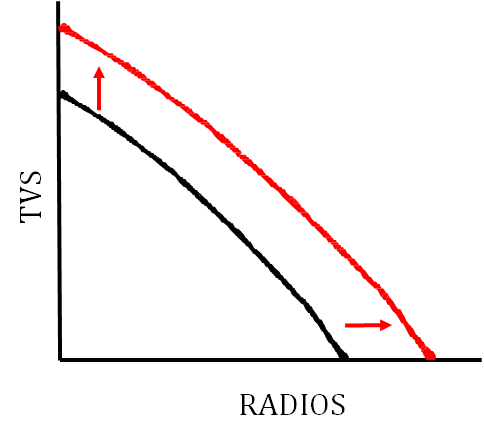
Economic Growth on PPC
* Shown by shift outwards (to the right)
35
New cards
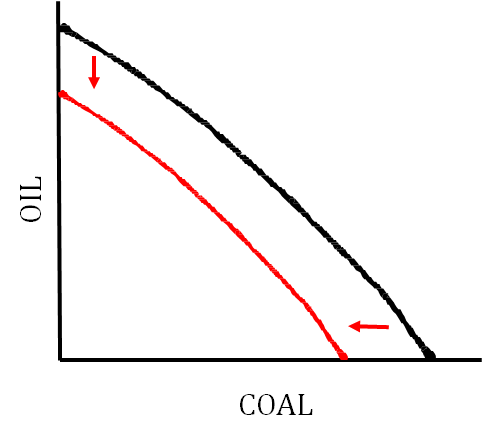
Economic Contraction on PPC
* Shown by a shift inwards (to the left)
36
New cards
What can cause the PPC to shift?
* Change in quantity or quality of resources
* Change in technology
* Trade
* Change in technology
* Trade
37
New cards
Absolute Advantage
* The ability to produce more of a good or service with a given amount of resources than someone else
38
New cards
Comparative Advantage
* The ability to produce a good at the lowest opportunity cost
39
New cards
Terms of Trade
* The rate at which one good can be exchanged for another
40
New cards
Specialization
* When a country stops producing one good to maximize production of another
* To get the other good, they trade with other countries
* To get the other good, they trade with other countries
41
New cards
Trade
* Exchange of goods and resources between countries, individuals, or businesses
* Leads to increased efficiency and higher levels of production and consumption
* Leads to increased efficiency and higher levels of production and consumption
42
New cards
Output
* How much is produced given a set amount of resources
43
New cards
Input
* How much of a resource is needed to produce one unit of a particular good or service
44
New cards
Calculating Opportunity Cost
* Output -- Output: Other Over (OOO)
* What you give up over what you gain
* Input -- Input: Other Under (IOU)
* What you gain over what you give up
* What you give up over what you gain
* Input -- Input: Other Under (IOU)
* What you gain over what you give up
45
New cards
Cost-Benefit Analysis
* Technique used to evaluate potential costs and benefits of a proposed project or policy
* Involves calculating the costs associated as well as the expected benefits it’ll bring
* Determine if the benefits outweigh the costs
* Involves calculating the costs associated as well as the expected benefits it’ll bring
* Determine if the benefits outweigh the costs
46
New cards
Explicit Costs
* Direct, monetary costs that a business incurs in the production of goods or services
* Easily identifiable and easily quantifiable
* Easily identifiable and easily quantifiable
47
New cards
Implicit Costs
* Indirect costs associated with using a particular resources
* AKA opportunity cost
* AKA opportunity cost
48
New cards
Total Benefit
* Total amount of benefit you gain from consuming a certain number of goods
49
New cards
Total Cost
* Total amount of cost you give up from consuming a certain number of goods
50
New cards
Utility
* Models the worth or value of something
51
New cards
Marginal Benefit
* The additional benefit we get from consuming just one more good or service
52
New cards
Marginal Cost
* The additional cost we incur from consuming just one more good or service
53
New cards
Constant Marginal Cost
* Each additional unit costs the same as more is consumed
* Set price
* Set price
54
New cards
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
* The additional utility or satisfaction from each additional unit will eventually decline
* Curve slows down until it goes back down with negative marginal utility
* Curve slows down until it goes back down with negative marginal utility
55
New cards
Cost-Benefit Maximizing Principle
* Total benefit is maximized at the quantity marginal benefit (MB) equals marginal cost (MC)
* MB=MC
* MB=MC
56
New cards
Marginal Analysis
* Allows us to explain how consumers make choices about what goods and services to purchase
* Examines the additional benefits against the additional cost by consuming one more unit
* Examines the additional benefits against the additional cost by consuming one more unit
57
New cards
Utility Maximization
* We want to attain the highest level of satisfaction from our economic decisions
* Utility is maximized at MU1/P1 = MU2/P2
* Utility is maximized at MU1/P1 = MU2/P2
58
New cards
Assumptions with Utility Maximization
* The consumer will spend all of their income
* The consumer will only buy two goods
* When choosing which good to buy next, the consumer will choose the good with the greatest Marginal Utility per Price (MU/P)
* When a consumer stops buying, the MU/P of the last unit of each good will be equal
* The consumer will only buy two goods
* When choosing which good to buy next, the consumer will choose the good with the greatest Marginal Utility per Price (MU/P)
* When a consumer stops buying, the MU/P of the last unit of each good will be equal