Blood and DNA Biology quiz
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the primary functions of blood?
Metabolizes substances, carries oxygen, removes waste, fights infection, and regulates body temperature
What color is human blood?
Always red.
What color can invertebrates' blood be?
Purple.
What color can beetles' blood be?
Yellow.
What color can some segments' blood be?
Green.
What color can horseshoe crabs' blood be?
Blue.
What is plasma and what does it contain?
Pale yellow fluid mostly made of sugar, water, lipids, waste, amino acids, hormones, and vitamins
What are erythrocytes and their main function?
Red blood cells that come from bone marrow, contain hemoglobin, transport oxygen and carbon dioxide, and make blood red
What are leukocytes and their role?
White blood cells that have a nucleus and are involved in the immune response.
What are the types of leukocytes?
Basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes
What are thrombocytes and their function?
Platelets that are cell fragments without a nucleolus, helping blood clot
What is preemptive testing in blood testing?
An initial test that checks if a sample is blood by interacting with hemoglobin.
What is confirmatory testing in blood testing?
A test that relies on blood properties like antigens to determine blood type.
What are the four types of blood in the ABO system?
A, B, AB, and O
How are blood types classified?
Based on the presence of certain antigens, A has A antigens, B has B antigens, AB has both, O has none
What does positive vs negative blood type indicate?
Positive means the presence of a certain protein (Rh factor), while negative means absence
What is the universal donor blood type?
O-.
What is the universal recipient blood type?
AB+.
What are antibodies and their function?
Proteins produced by B cells that attach to and attack pathogens, recognizing specific antigens
What are antigens?
Substances that produce an immune response.
What is agglutination?
Clumping that occurs when a corresponding antibody and antigen come into contact.
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid.
What is Chargaff's Rule?
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) and Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C).
What is the structure of DNA?
A double helix composed of two coiled strands of sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate, with nitrogen bases in the center
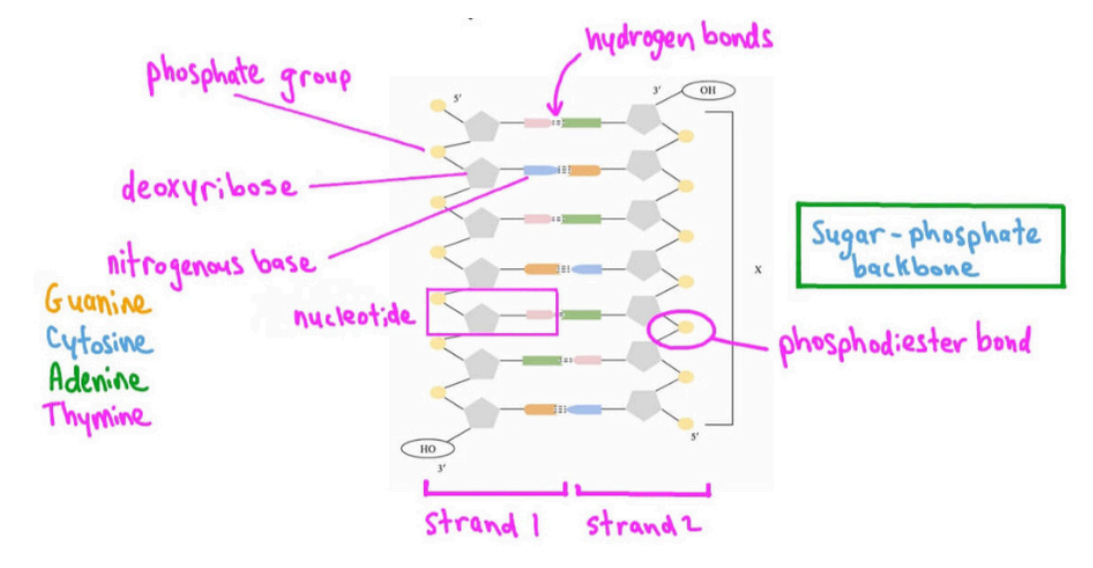
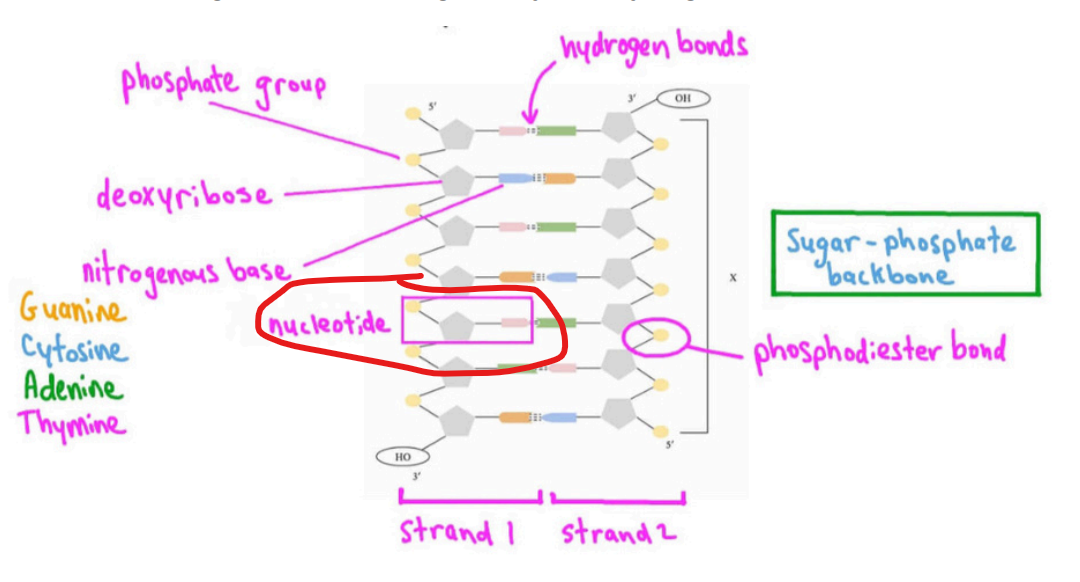
What are nucleotides?
Units of DNA that combine a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugars, and nitrogenous bases (A, T, G, C)
What are pyrimidines?
Nitrogenous bases Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C) that have a single ring structure.
What are purines?
Nitrogenous bases Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) that have a double ring structure.
What is a Kastle Meyers Test?
A preemptive test that identifies if it's blood or not