Chat is this Skibidi Science Rizz? By Aspooct :) Also the guy is mewing trust 🤫🧏♀️
Basic Questions:
Cell: A small living system with parts that work together to carry out tasks.
Organelles: Parts of a cell that make up the systems to keep a cell alive
Unicellular Organism: An Organism with 1 cell
Multicellular Organism: An Organism with more than 1 cell
The 5 Groups Of Organisms: Plants, Animals, Protists, Bacteria, Fungi
Ask Only What the title is
Whatever is written in white is the answer
Plants;
Examples Of Plants: Trees, Grass, Herbs, Flowers etc.
Energy For Plants: Plants Make their own energy by photosynthesis
Where Can Plants Live: Water or Land
Examples of Water Plants: Water Lillies, Elodea
Plants are multicellular
Animals;
Animals Can be Divided into Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Vertebrates: Animals With Backbones
Invertebrates: Animals Without Backbones
Are Animals Multicellular?: Yes
Are there more invertebrates or vertebrates: Invertebrates
How do we gain energy: By Eating
Fungi;
How does Fungi gain energy?: They gain energy from absorbing the dead or decaying matter
What process can't Fungi carry out; They can’t carry out photosynthesis
Can these organisms be both single-celled and multi-celled?: They can be unicellular or multicellular
Protists;
They are usually found in moist or wet environment
Protists can be unicellular or multicellular
They have the organelles of an animal cell
They can also have the organelles of plant cells
The ones with plant cell organelles, they can do photosynthesis
The ones with animal cell organelles only, they have to hunt in their environment for food
Bacteria;
Bacteria is Unicellular
It is the most basic organism
They don’t have a nuecleus
Some bacteria gather in colonies
The bacterium that causes strep throat is a bacterium colony
Unicellular Organisms;
These organisms need to be seen under a microscope
Unicellular Organisms are most often called micro-organisms
Nutrition;
Most unicellular organisms need to move around to find food and cant do photosynthesis
Some protists and some types of bacteria are the exception
Euglena is a protist with both animal and plant cell organelles, it can do photosynthesis
Fungi and bacteria interact with each other to gain nutrients
Paramecia;
These are animal-like protists
They live in aquatic environment
They have cilia all over their body that beat in unison, this creates water currents that they move in
The oral grove also has cilia to get food particles into it so it can take it in and make a food vacuole
The nutrients that are taken from the food particles in the food vacuole will be diffused into the cytoplasm
The waste goes out the anal pore
Amoeba;
These are animal-like protists
They must move around to find food
They use phagocytosis to feed on organisms
The food vacuole it creates acts as a digestion chamber and storage of food
When it needs nutrients, chemicals break down the food and take all the nutrients
Once all the nutrients are taken, it diffuses into the cell before exocytosis where it is removed
Steps of Phagocytosis;
The organism moves to the food particle and extends its pseudopods
It creates a food vacuole after fully incasing the food particle
Gas Exchange;
Most organisms need oxygen to survive
The chemical reactions needed for taking nutrients out of food requires oxygen and carbon dioxide as the waste product
In unicellular organisms, oxygen diffuses across the cell membrane into the cell, this means there is a steady exchange of gasses across the cell membrane
The carbon dioxide diffuses out of the unicellular organism when the concentration of carbon dioxide is more in the cell than outside the cell
Some micro-organisms such as fungi and bacteria can survive without oxygen
Responding To The Environment;
Humans have 5 senses to respond to the environment: Sight, Smell, Taste, Touch, Hearing
Unicellular organisms don’t have this ability
Some bacteria can detect chemicals in their area such as sugar and move accordingly
Photosynthetic protists can detect light in their area and move to it to gain energy
Movement and Locomotion;
Movement: A change in shape or figure of part or all of an organism
Locomotion: Movement that takes an object from one place to another
White blood cells use movement to take in harmful organisms and stop them using their pseudopods
Locomotion happens with unicellular organisms when they use flagella or cilia to create water currents to move
Multicellular Organisms;
The Douglas Fir tree is one of the largest organisms on earth, standing at 76 meters tall and almost 3 meters in diameter
Multicellular organisms use all its cells to perform life processes
Specialization And Differentiation;
All multicellular organisms start as one cell that duplicates over time
The number of cells determine the size of the organism
When a cell divides, it stays close to the other cells
As the number of cells increases, each cell becomes better at one particular job, they are specialized to do one job well to help the multicellular organism
Specialized cells are put into groups that do the same jobs as them, for example all the cells in the heart are made to pump blood and not digest food
Cell specialization takes place early on in a multicellular organism
There are 4 main types of cells; Nerve Cells, Muscle Cells, Fat Cells, Epithelial Cells
Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems;
Within multicellular organisms, differentiated cells are organized according to the function they perform
Tissues;
A group of cells with similar functions are called tissues
There are four basic Tissues: Muscle Tissue, Epithelial Tissue, Nervous Tissue, Connective Tissue
In plants, tissues are made up of thin plant cell walls and is commonly found in areas where water and nutrients are transported
Organs;
An organ is 2 or more specialized tissues that work together to do one or more functions in the organism
In plants, stems, leaves, flowers, and roots are the organs
Skin is the largest organ
Organ Systems;
Organs never work alone
Organ System: 2 or more organs that work together to do a certain function
Organ Systems overlap the use of certain organs
Organ systems are interdependent to the brain
Animal Organ Systems: Digestive System, Nervous System, Circulatory System, Respiratory System, Musculoskeletal System
Plants Organ Systems: Root System, Shoot System
Circulatory System;
The circulatory systems major function is to transport nutrients, gases, and waste to and from the cell in the organism
The major organs in the circulatory system are the heart and blood vessels
The circulatory system uses the epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscle tissues
Respiratory System;
The respiratory systems major function is to exchange O2 and CO2 between blood and the external environment
The major organs in the respiratory system are the lungs, windpipe, and blood vessels
The respiratory system uses the epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscle tissues
Digestive System;
The digestive systems major function is to break food particles down and takes the nutrients and then lets it get transported by the circulatory system
The major organs in the digestive system are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small and large intestines, and anus.
The digestive system uses the epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscle tissues
Musculoskeletal System;
The musculoskeletal systems major functions are to give structural support, keep internal structures safe from the outside, and help in movement and locomotion.
The major organs of the musculoskeletal system are the bones and muscles
The musculoskeletal system uses the epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscle tissues.
Nervous System;
The nervous systems major functions are to respond to the changes in or outside of the body and coordinates the function of all other organ systems.
The major organs in the nervous system are the brain, spinal cord, and sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, taste buds.)
The nervous system uses the epithelial, connective, and nervous tissues.
Multicellular Organisms Meeting Their Needs;
You have needs that must be met every day
You must respond to your environment to stay alive
Systems Working Together;
It is important for all systems in a multicellular organism to work together
The respiratory, digestive, and circulatory system help get us oxygen and nutrients, the two most important materials for energy in the body
An organism is only as strong as its weakest system
If an organ system is not doing its job properly, other organ systems that depend on it will also start to fail and it can affect the whole organism
Nutrition In Humans;
Food is taken down the digestive system to have the nutrients absorbed from it and the waste be exited out of the body
Digestive System Steps;
First the teeth and chemicals known as saliva in the mouth break down the food
Swallowing brings it to the esophagus where it is pushed down into the stomach
Cells in the stomach release chemicals to breakdown the food further
Then it is moved to the intestines where the nutrients are absorbed
Undigested food is passed out by the anus
Nutrition for Earthworms Steps;
They use the pharynx to suck in food
The esophagus moves it to the crop which stores its food and moistens it
Then it is moves to the gizzard which is a specialized stomach that contains small particles of gravel and sand that break down tough food
Then in the intestine, it uses chemicals to take in the nutrients and the waste is then passed out by the anus
Nutrition for Plants Steps;
Roots absorb nutrients and water from the soil
It then uses Xylem vessels to move those materials all across the plant
It moves it to the leaves where the stroma in the leaves take in carbon dioxide and sunlight to do photosynthesis
When it gets the sugar formed energy, phloem vessels transport it to the rest of the plant
The excess sugars are stored in the stem and roots for storage
Digestive System: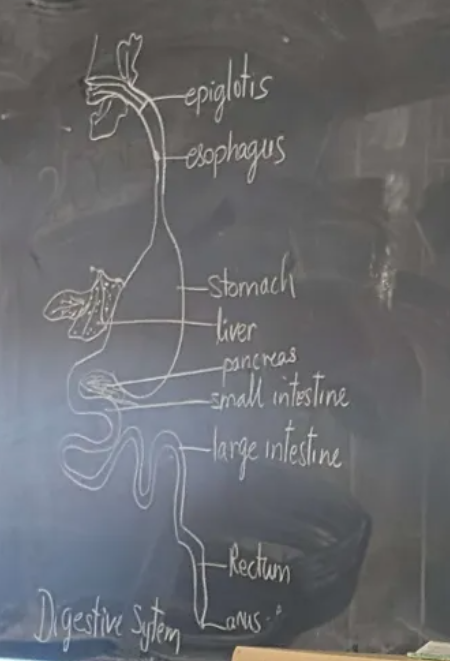
Section of a Leaf