Patho Exam 2 - Hematology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is the percentage of blood that is plasma?
55%
What is the percentage of blood that is formed elements?
45%
Process of Hemostasis
Series of events that stop bleeding
Stages of Hemostasis
Primary and secondary hemostasis leading to clot formation and dissolution
Primary hemostasis
Formation of platelet plug to stop bleeding
Secondary hemostasis
Reinforcement of platelet plug with fibrin clot
Platelets
Cell fragments involved in blood clotting
Blood coagulation factors
Proteins in blood plasma that aid in clot formation
Fibrin clot
Insoluble protein mesh that stabilizes the platelet plug
Fibrinolysis
Process of breaking down the fibrin clot
Anemia - Definition
Functional inability of blood to supply tissues with adequate oxygen
Is anemia a disease?
Anemia is an expression of underlying disorder, not a disease
WHO criteria for Anemia
Hb < 13 in men, Hct < 41%; Hb < 12 in women, Hct < 36%
Revised WHO criteria for Anemia in malignancy
Hb < 14 in male, Hb < 12 in female
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Lab test measuring blood components
Hemoglobin (Hb)
Protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen
Hematocrit (Hct)
Percentage of blood volume occupied by red blood cells
Reticulocyte
Young red blood cell indicating bone marrow activity
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Average size of red blood cells
Mean cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
Hb concentration in red blood cells
How is anemia categorized?
Categorizing anemia based on cell size and Hb content
Mean corpuscular volumes for morphological classification
Microcytic - MCV < 80
Normocytic - 80 < MCV < 100
Macrocytic - MCV > 100
Generalized Symptoms of Anemia
Pallor
Dizziness
Leg Cramps
Headache
Insomnia
Oxygen deficit - Fatigue, tachycardia, SoB, decreased epithelial cell regeneration
Concentrating (difficulty)
Please Don't Leave Here In Orange Cars
Types of Anemia
macrocytic-normochromic
microcytic-hypochromic
normocytic-normochromic
Macrocytic Normochromic Anemia
Characterized by large stem cells and defective DNA synthesis. RNA processes at the normal rate
Macrocytic Anemia - Pernicious Anemia
Autoimmune condition causing B12 deficiency due to lack of intrinsic factor with neurological symptoms.
symptoms of pernicious anemia
Symptoms of anemia plus:
Paresthesia
Wobbly gait and difficulty walking
Sore tongue - smooth and beefy
"Lemon yellow" skin (sallow) - a combination of pallor and jaundice (icterus)
Dementia
Macrocytic Anemia - Non-autoimmune
Lack of intrinsic factor due to things like a gastric bypass.
Macrocytic Anemia - Folate Deficiency
Anemia due to inadequate folate absorption, common in alcoholics
Macrocytic Anemia - Diagnosis
Tests like antibodies against parietal cells and methylmalonic acid levels & homocysteine levels.
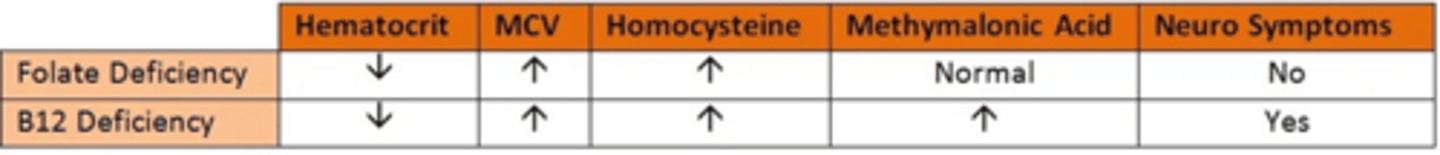
Macrocytic Anemia - Treatment
Lifelong B12 treatment for pernicious anemia, oral B12 for non-pernicious., take folic acid with B12
Folic acid supplements for folate deficiency
Folate deficiency
Condition characterized by a lack of folate in the body
examples: Crohn's Disease and Celiac (malabsorption/malnutrition)
Microcytic Hypochromic Anemia
Anemia characterized by abnormally small red blood cells with reduced hemoglobin
Iron deficiency - most common worldwide
Leading cause of anemia globally
Clinical presentation of iron deficiency anemia
weakness, fatigue, lightheadedness
PICA, SoB, pale ear lobes, palms, and conjunctiva
HgB decreased to 7 or 8 per dL
Progression of iron deficiency anemia
Koilonychia
Cheilosis, stomatitis, painful ulcerations in the mouth
Dysphagia
Evaluation of Iron deficiency anemia
Hemoglobin - decreased
Hematocrit - decreased
MCV - decreased
Serum ferritin - low
Serum iron / transferrin = iron saturation - low
peripheral blood smear
Bone marrow iron stain (Prussian blue/very invasive)
treatment for iron deficiency anemia
Iron replacement (ferrous sulfate) via PO, IM, or IV
Vitamin C to aid in absorption of iron
Side effects: constipation, black stool
Koilonychia
Clinical sign of iron deficiency anemia, where nails become brittle, thin, and spoon-shaped
Normocytic Normochromic Anemia
Anemia resulting from decreased erythropoiesis with normal cell size and hemoglobin content
Normo Normo etiology
Hemolysis - sickle cell disease, immune, transfusion (decreased RBC lifespan)
acute blood loss
bone marrow suppression - myeloma
anemia of inflammation or chronic disease
hypothyroidism
Anemia of Inflammation
Anemia associated with chronic inflammatory conditions, characterized by altered iron metabolism
Pathogenesis of anemia of inflammation
1. shortened RBC lifespan
2. suppressed EPO production
3. Ineffective bone marrow response
4. altered iron metabolism in macrophages
Anemia of inflammation initially is normocytic normochromic then becomes what?
Microcytic-hypochromic
Hemorrhage
Extravasation of blood from blood vessels
Hematoma
Accumulation of blood within tissues or externally
Can be benign or fatal (retroperitoneal hematoma)
Petechia
Tiny (1-2 mm) red or purple spots on the skin caused by minor bleeding
Purpura
Medium (3mm-1cm) red-purple skin lesion due to blood in tissues from breaks in blood vessels
Ecchymoses
Larger (1-2 cm) purplish patches on the skin caused by bleeding under the skin
Platelet Dysfunction
Impaired function of platelets leading to increased bleeding tendency
von Willebrand Disease
Most common inherited bleeding disorder characterized by a deficiency in von Willebrand factor.
Autosomal Dominant
vWF facilitates platelet adhesion -> causes mild or moderate bleeding
Coagulation Cascade Dysfunction
Impaired blood clotting process often due to factors like vitamin K deficiency or hemophilia
What can cause a vitamin K deficiency?
Antibiotic therapy and malabsorption
Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B characteristics
A - deficient in Factor VIII
B - deficient in Factor IX
X-linked recessive
prolonged bleeding time after minor tissue trauma
Possible hematuria and blood in feces
Diagnostics for hemophilia
Bleeding time and PT normal
PTT, aPTT, coagulation time prolonged
Serum levels for factor VIII are low
Diagnostic tests for bleeding disorders
•Prothrombin time (PT)
•International normalized ratio (INR)
•Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
•Bleeding time
•Thrombin time
•Complete blood cell count (CBC) with platelet count
•Peripheral blood smear
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Complex disorder where both clotting and bleeding occur simultaneously, often triggered by severe infections
Endothelial damage
Injury to the endothelial cells lining blood vessels that can initiate DIC
Consumptive coagulopathy
Condition where blood clotting factors are excessively consumed, leading to abnormal bleeding
Gram-negative bacteria
Type of bacteria with a distinct cell wall structure that can cause severe infections
Most common cause of disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC)