D202: Psychology Section One Terminology and Definitions
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
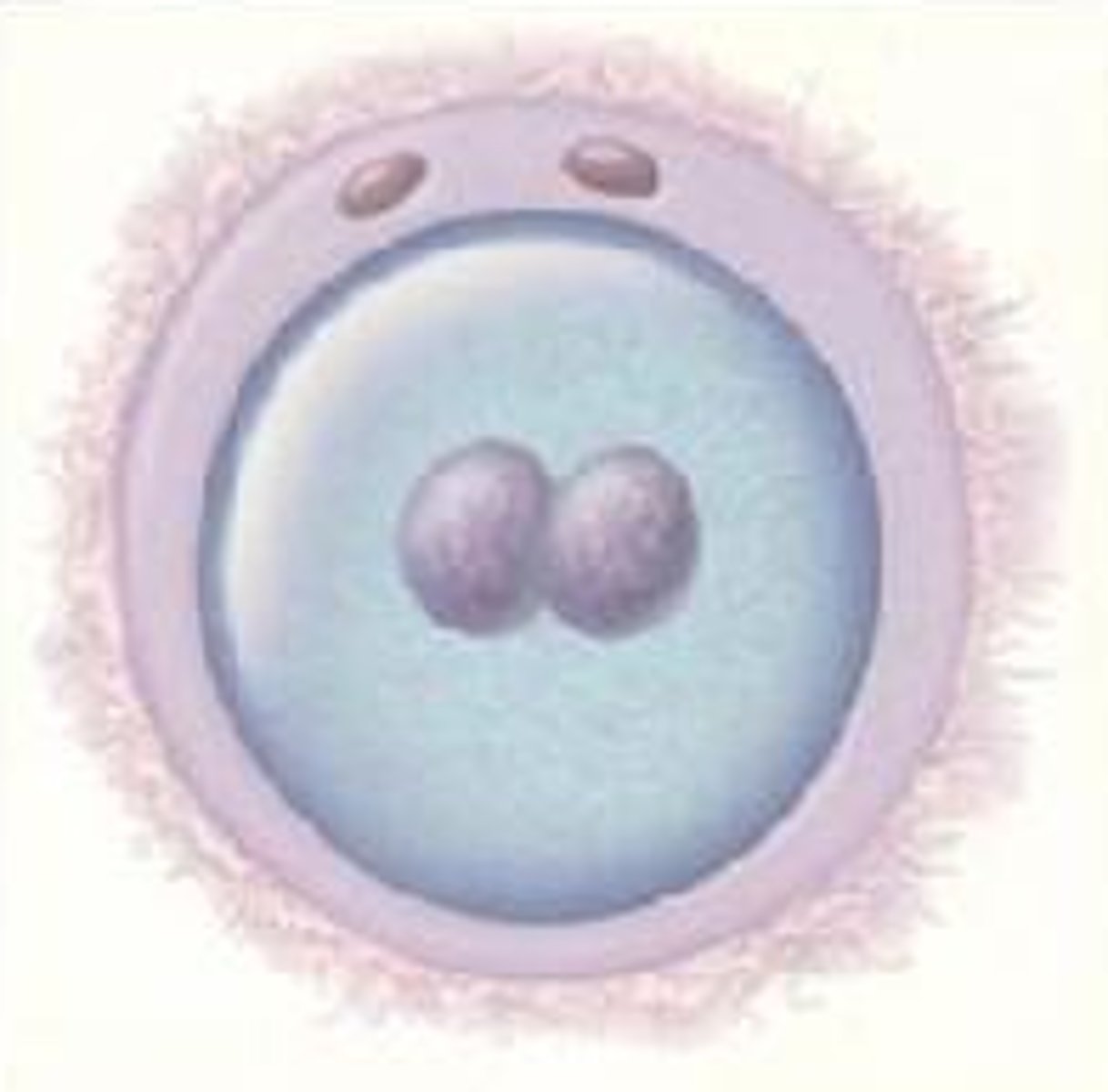
What are the key developments during the germinal period?
Implantation, fertilization, mitosis, blastocyst.
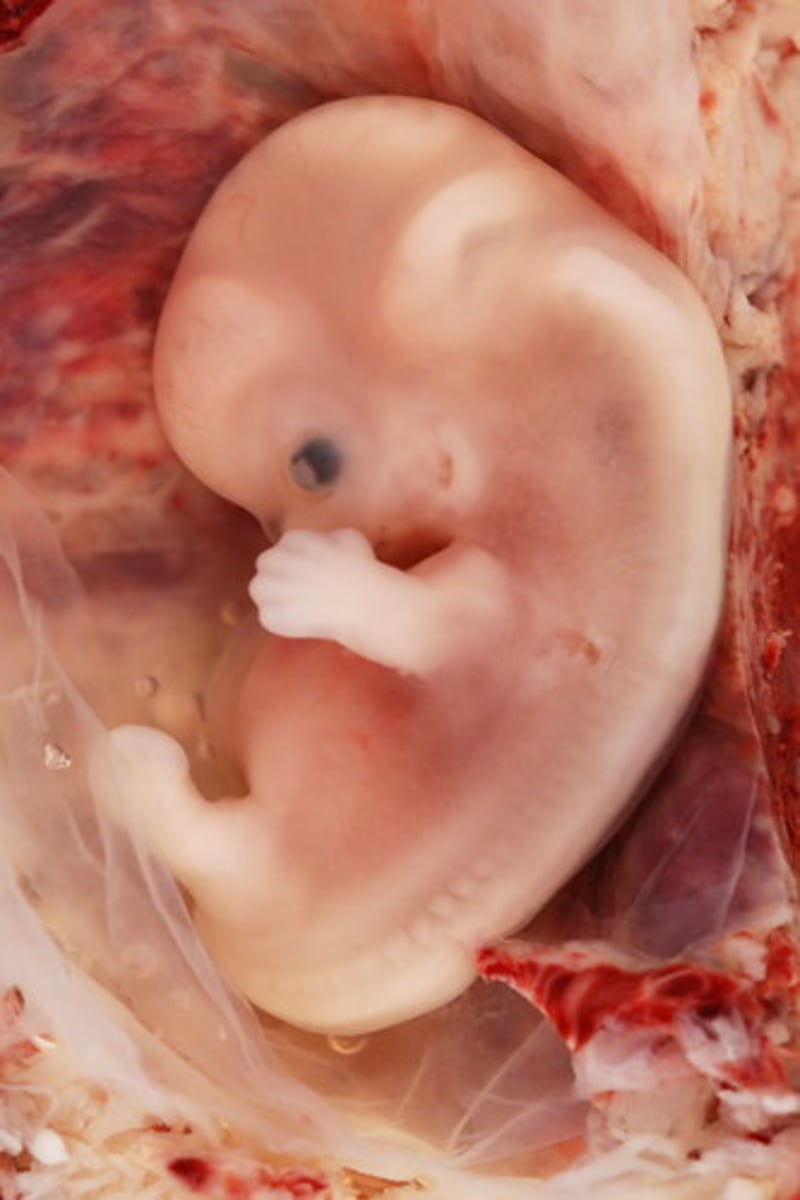
What are the key developments during the embryonic period?
Embryo, placenta, umbilical cord, & brain development
What are the key developments during the fetal period?
Fetus, viability, genitalia.
What is RH disease and what are the associated risks?
Rh disease is a dangerous kind of anemia.
This happens when the mother's blood is Rh-negative and her baby's blood is Rh-positive.
What is the 1st stage of labor?
Longest stage, cervix dilates, may have discharge
What is the 2nd stage of labor?
Baby passes through birth canal, head usually first, may need episiotomy
What is the 3rd stage of labor?
Mostly painless, delivery of placenta or afterbirth, possible stitches for episiotomy
What are the five measures assessed in the APGAR assessment?
Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity, Respiration
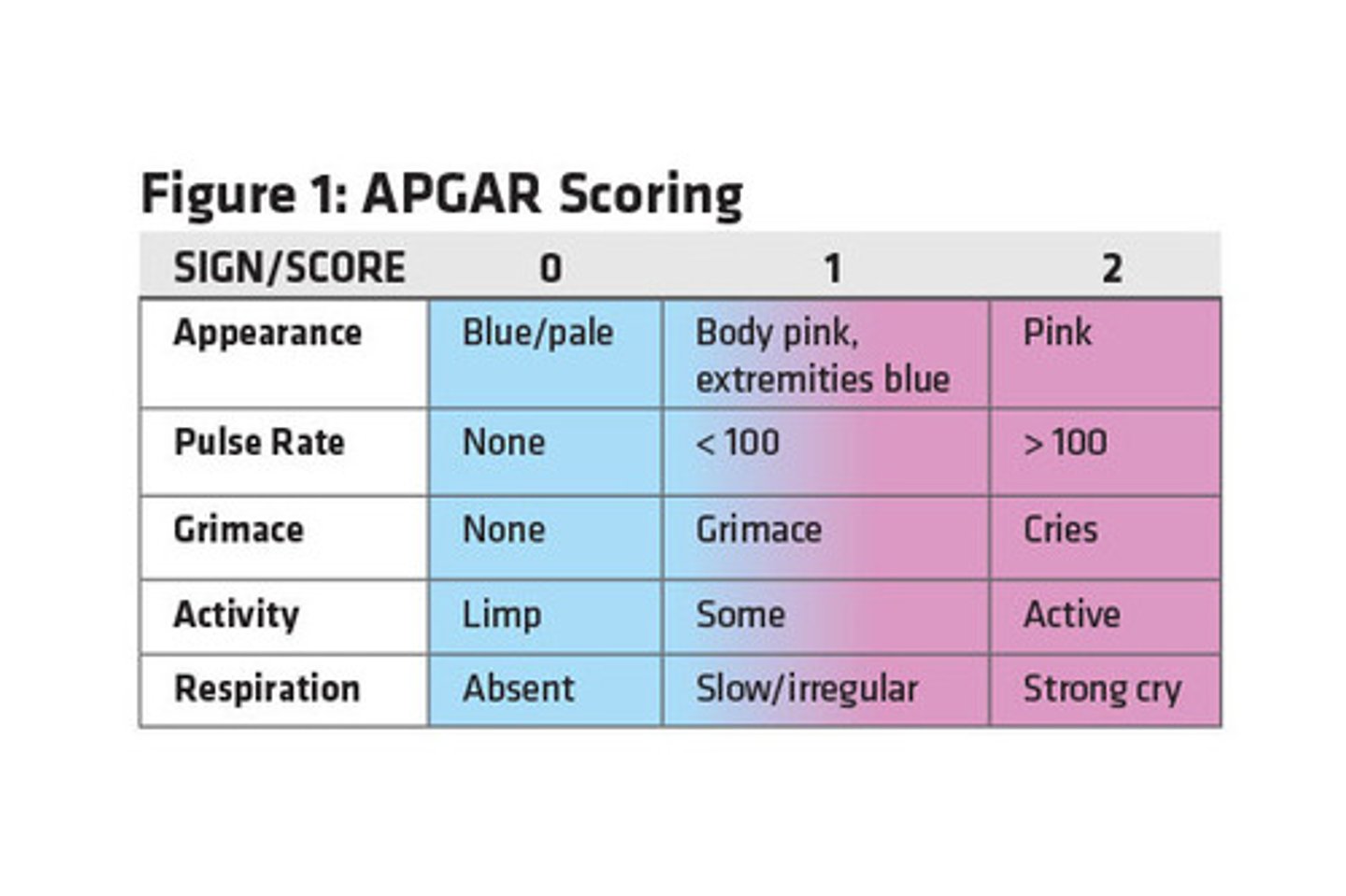
How is the APGAR scored?
Conducted between 1 and 5 minutes after birth. Each of the 5 categories is scored between 0-2. A score under 5 is cause for concern.
What are three possible symptoms of postpartum anxiety?
Heightened alertness, intrusive and horrifying thoughts of something terrible happening to the infant, and physiological arousal.
What hormone is associated with postpartum anxiety?
Oxytocin (bonding hormone).
What are the symptoms of postpartum depression?
Feelings of sadness, sleeplessness, and difficulty bonding with the newborn.
What are some common symptoms of baby blues?
Trouble sleeping, moodiness, and feeling letdown.
What are the key differences between baby blues and postpartum depression?
Baby blues are temporary and typically disappear within 10 days, while postpartum depression is more severe and can last longer.
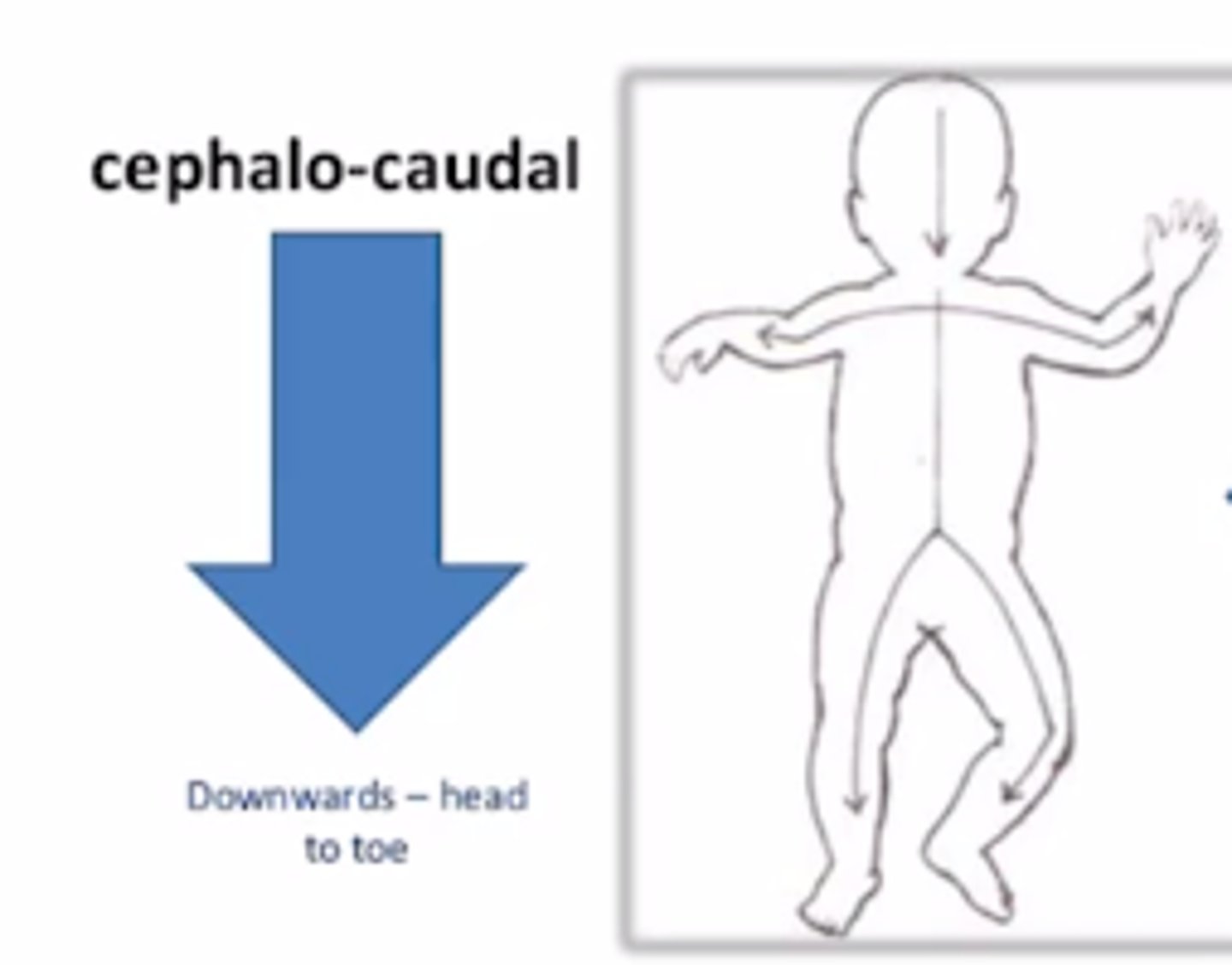
What is cephalocaudal pattern of growth?
Head to tail development. Ex: Hold head before sitting.
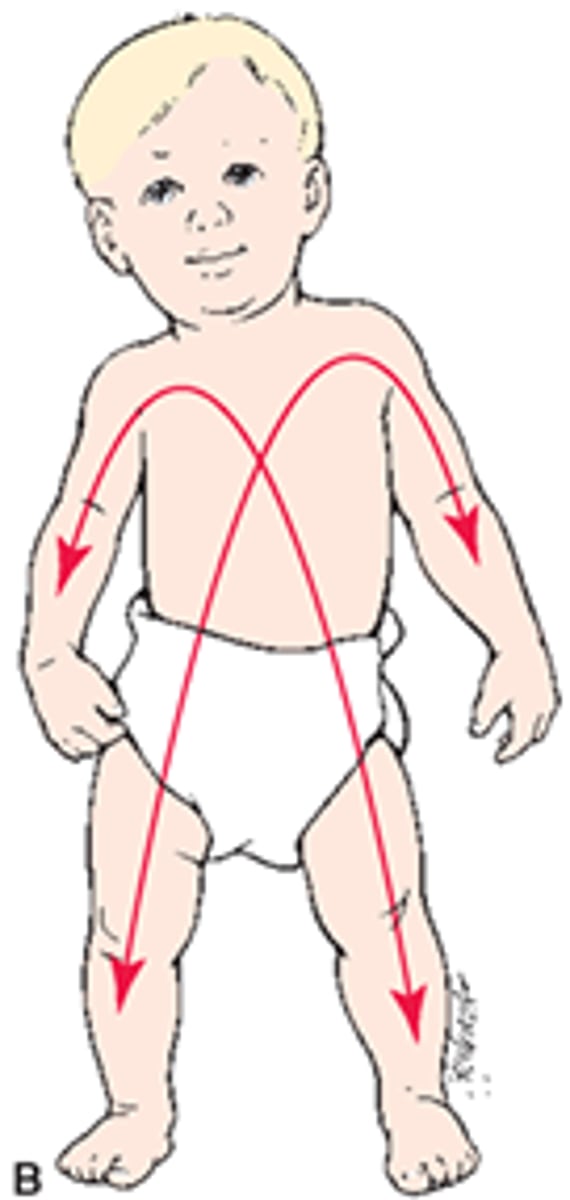
What is proximodistal pattern of growth?
Midline outward development. Ex. Sitting before walking.
What do infants prefer to look at?
Face-like stimuli
Summarize beneficial breastfeeding outcomes for the child.
Lower rates of childhood leukemia, asthma, obesity, diabetes, and SIDS
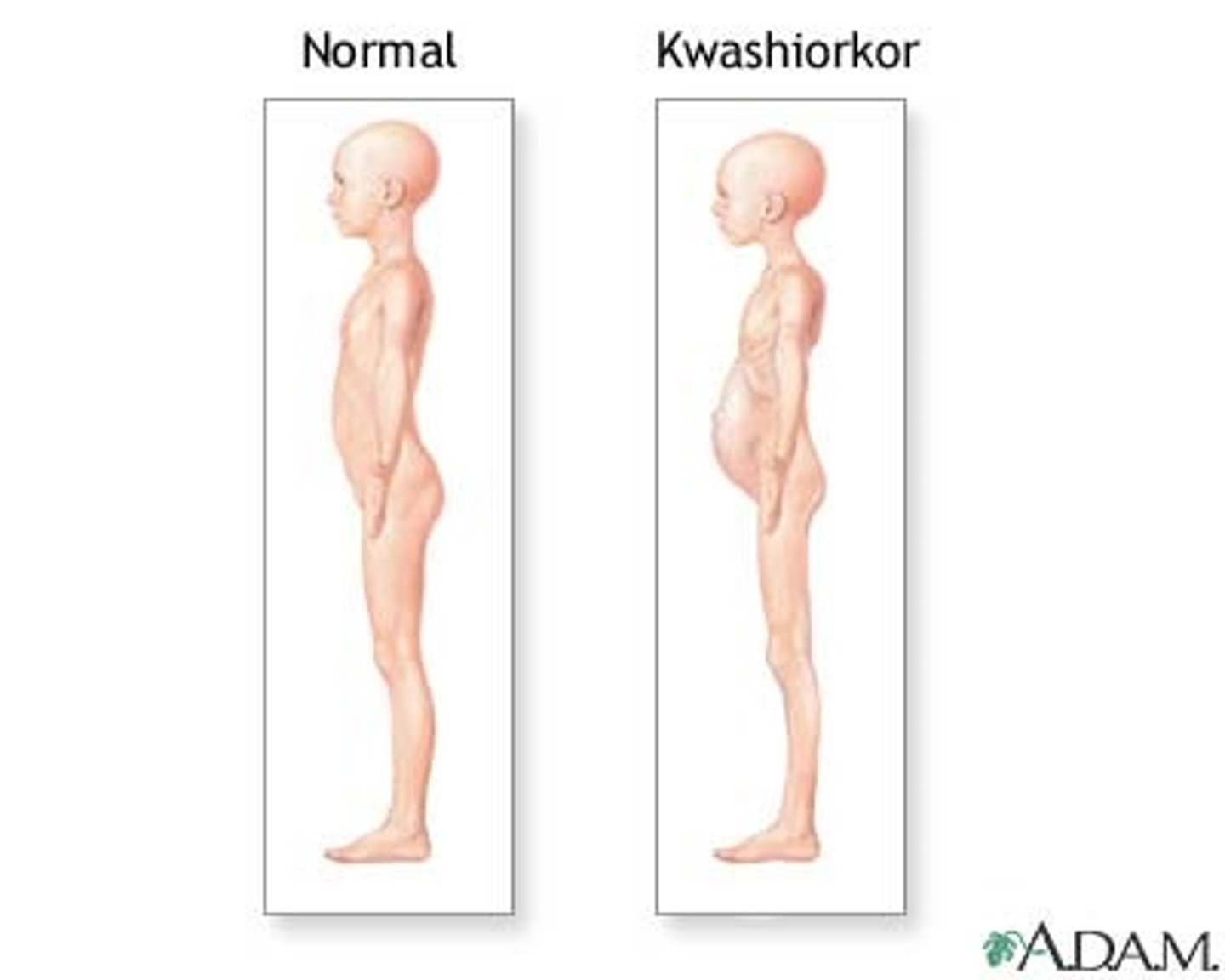
What is kwashiorkor?
Disease resulting from loss of appetite and swelling of abdomen due to lack of protein
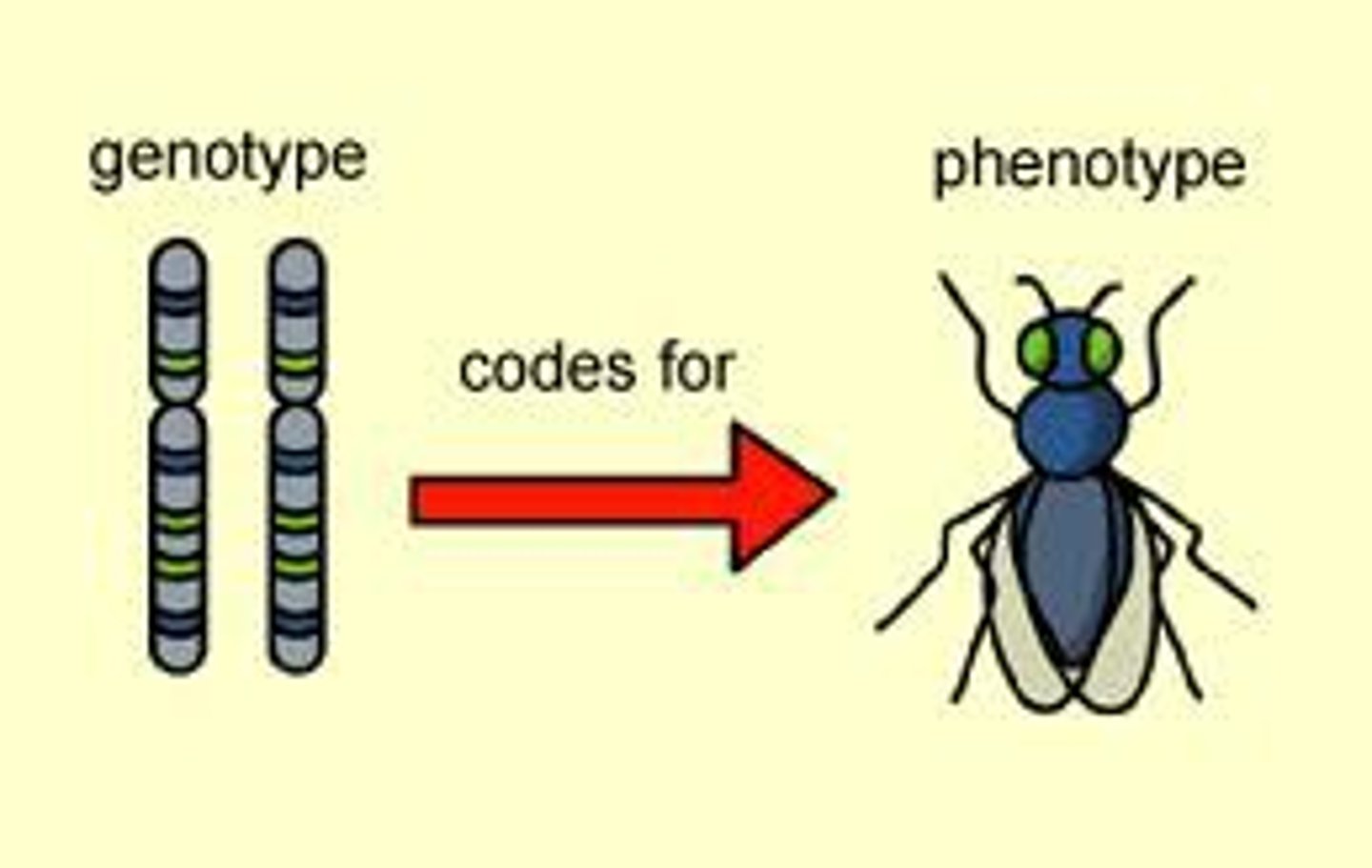
What does genotype refer to?
Sum total of all inherited genes

What does phenotype refer to?
Features that are actually expressed
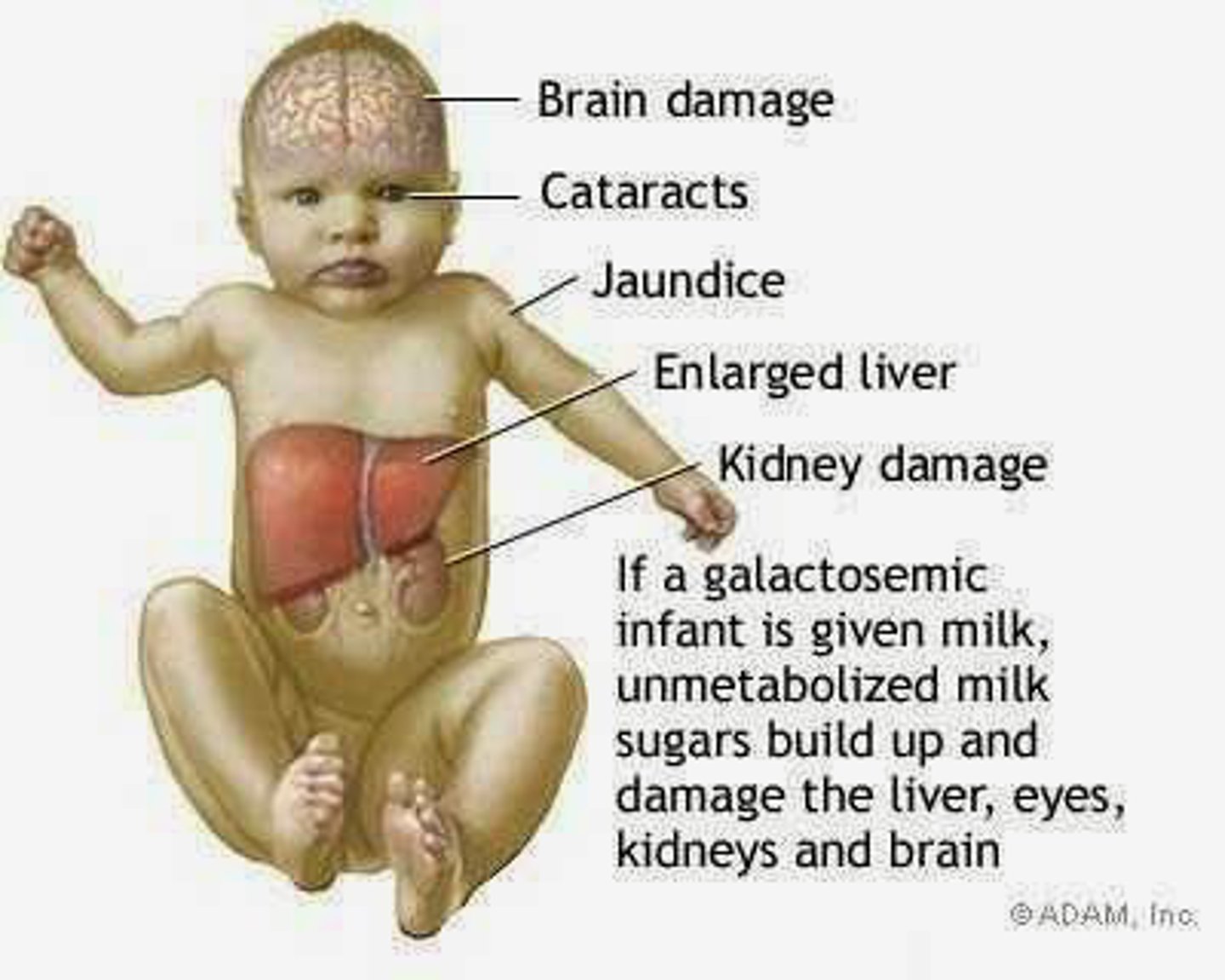
What is Phenylketonuria (PKU)?
Metabolic disorder where individual cannot metabolize phenylalanine
What is Tay-Sachs?
Enzyme deficiency resulting in lipid accumulation in brain nerve cells
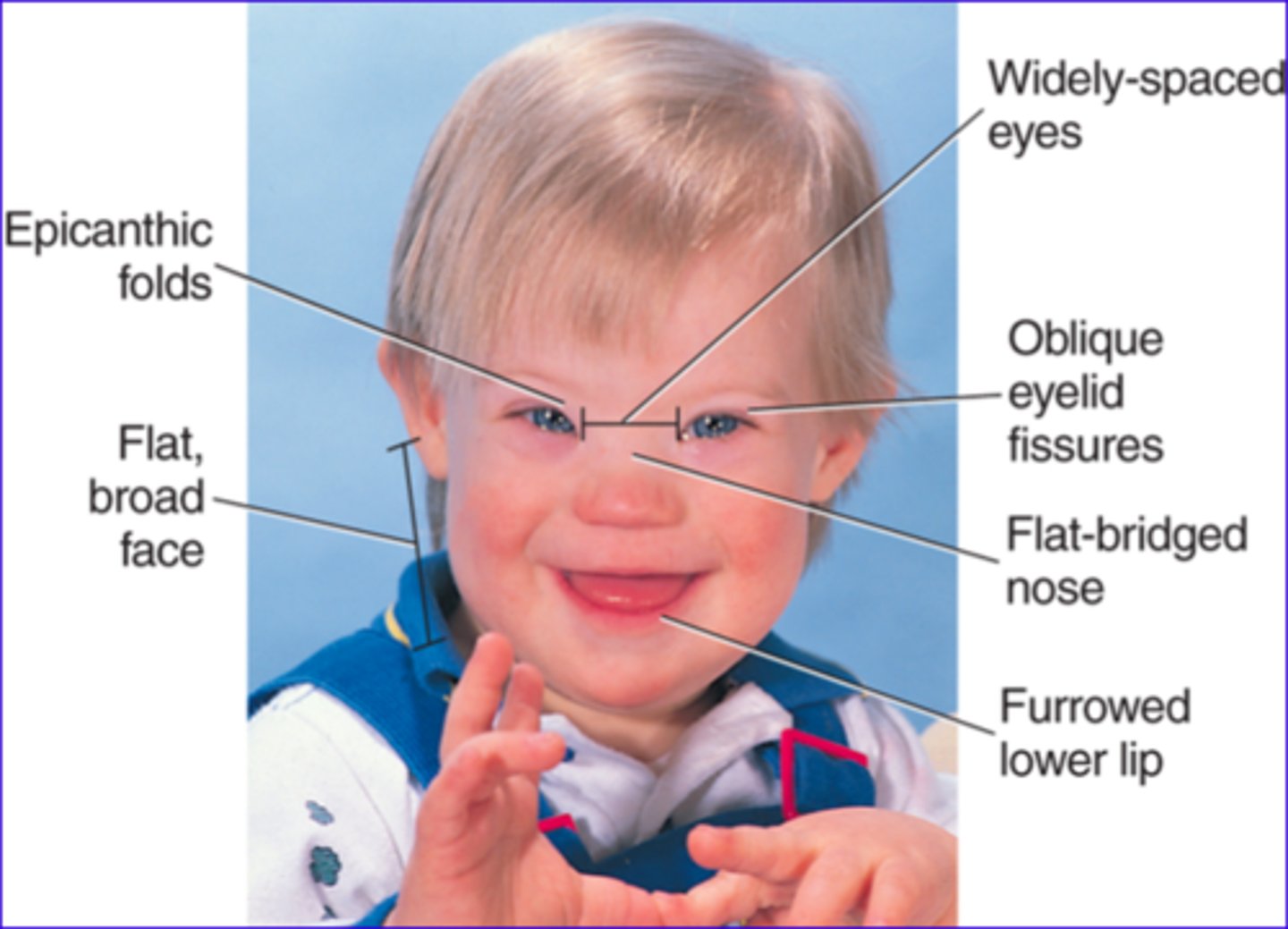
What is Down Syndrome?
Condition where there are three 21st chromosomes, leading to intellectual disability and physical features
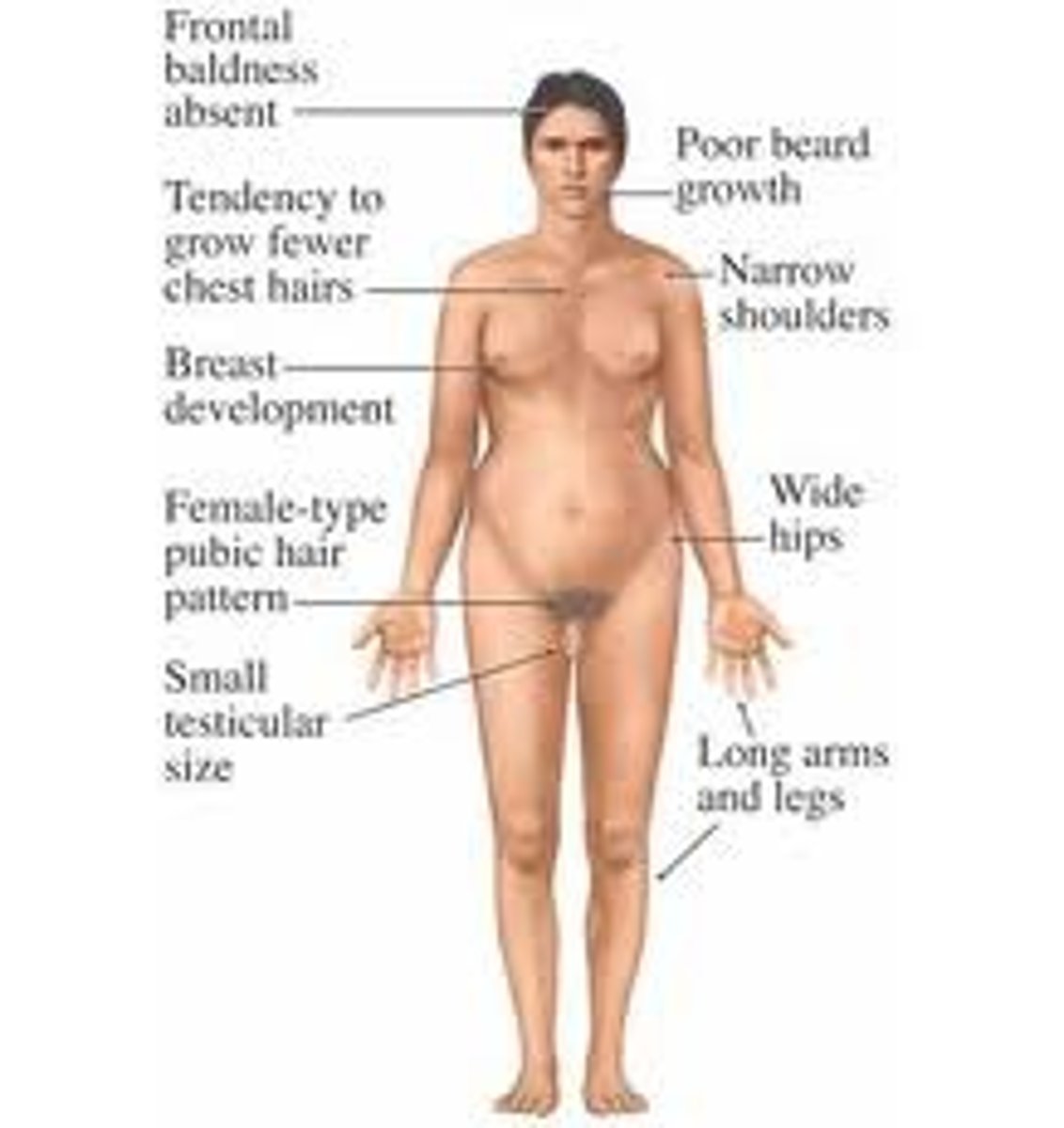
What is Klinefelter Syndrome?
Condition where an extra X chromosome is present in cells of a male, leading to small testes, breast development, infertility, and low testosterone levels
What is a teratogen?
Environmental factors that can contribute to birth defects
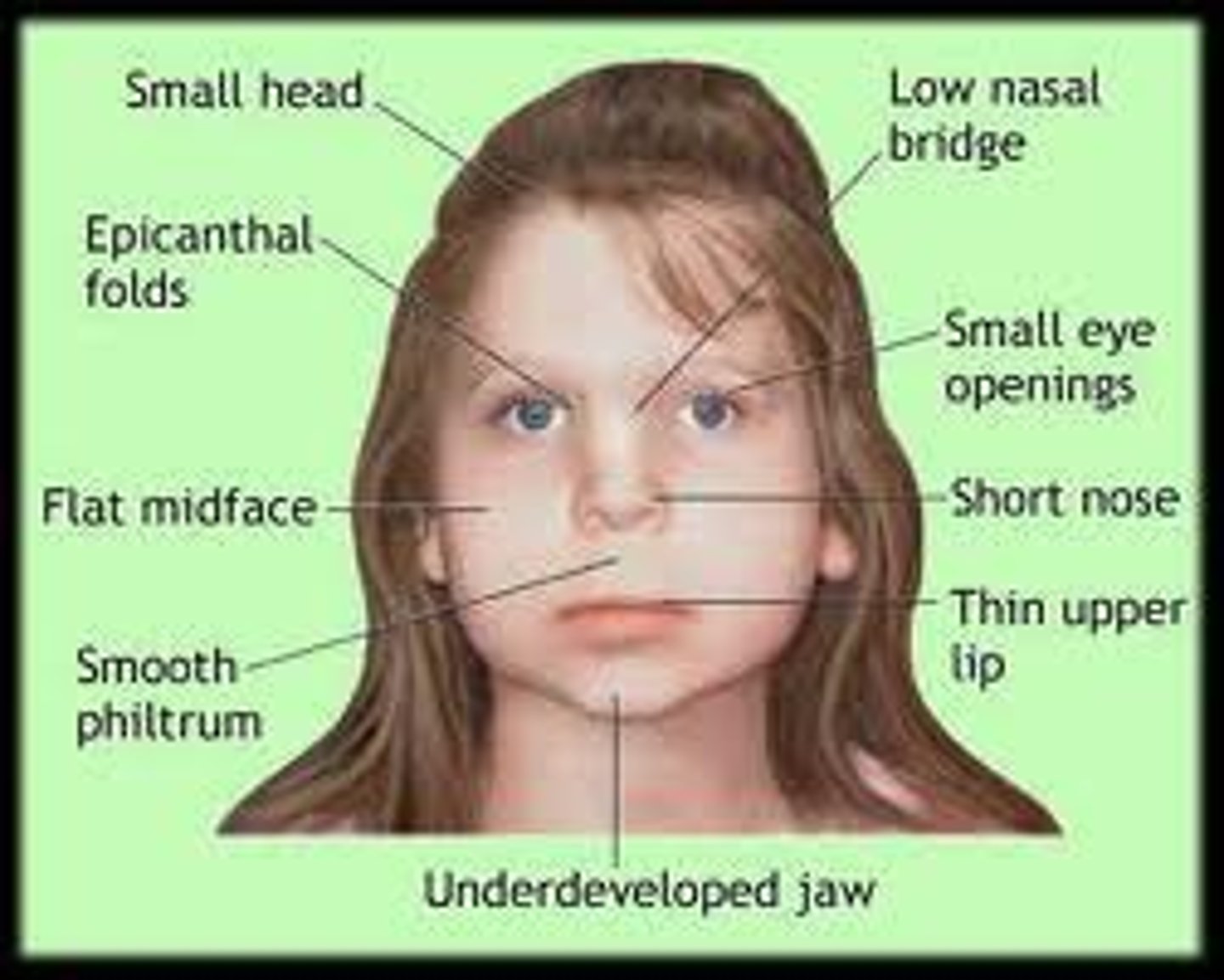
Describe the effects of alcohol on a developing embryo or fetus.
Flattened noses, small eye holes, small heads, poor judgment, poor impulse control, higher rates of ADHD, learning issues, and lower IQ scores
What are the potential effects of nicotine exposure during pregnancy?
low birth weight, ectopic pregnancy, placenta previa, placental abruption, preterm delivery, stillbirth, fetal growth restriction, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), birth defects, learning disabilities, and early puberty in girls.
What are the potential effects of rubella during pregnancy?
damage can occur in the eyes, ears, heart, or brain. Deafness.
What is synaptogenesis?
formation of connections between neurons.
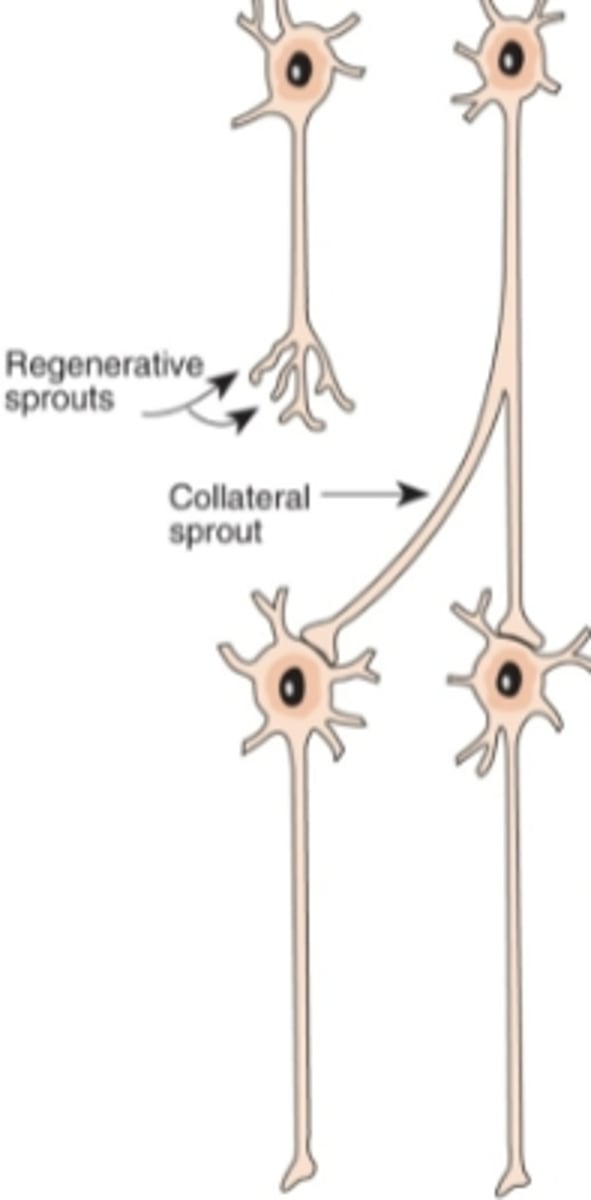
What is synaptic blooming?
period of rapid neural growth.
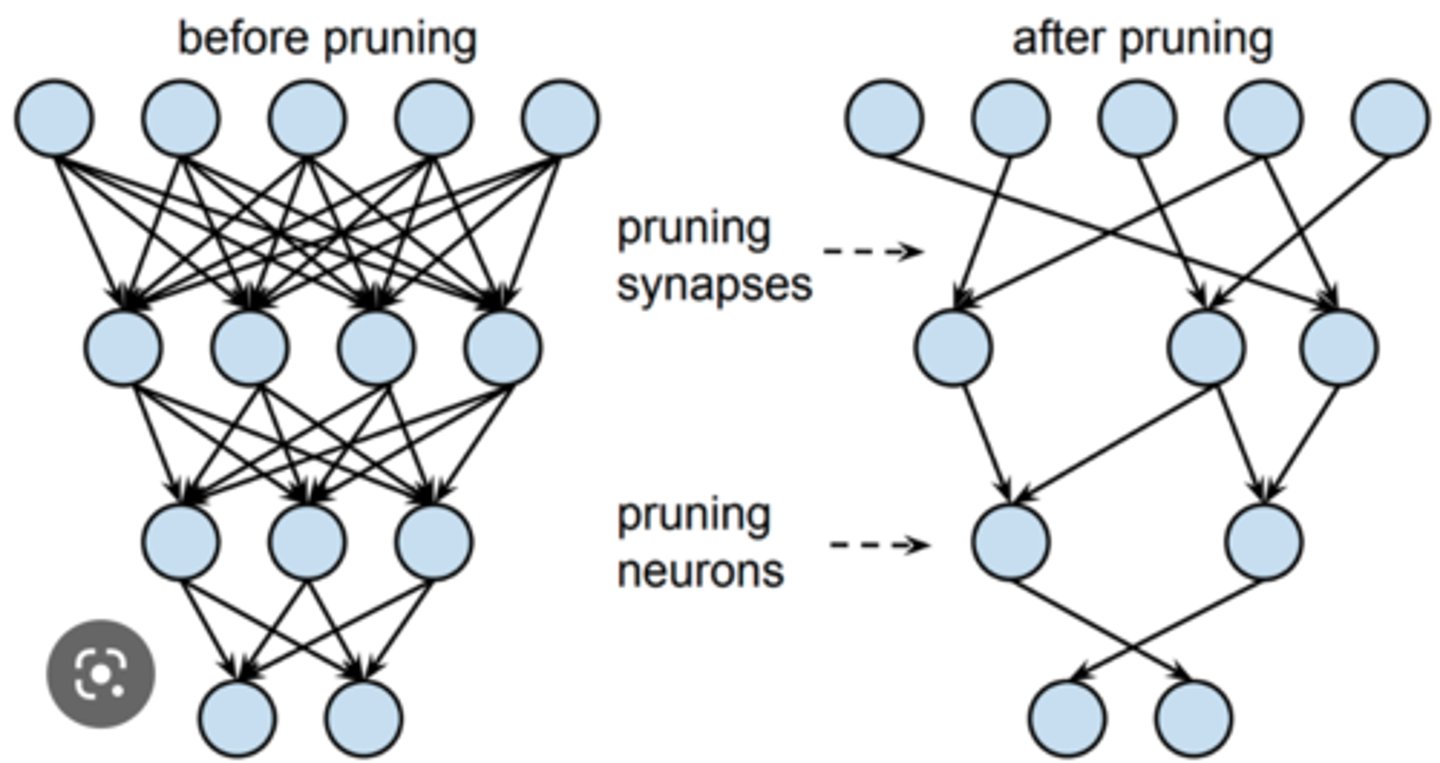
What is synaptic pruning?
reduction of neural connections, making those used much stronger.
What is lateralization?
process in which different functions become localized primarily on one side of the brain.
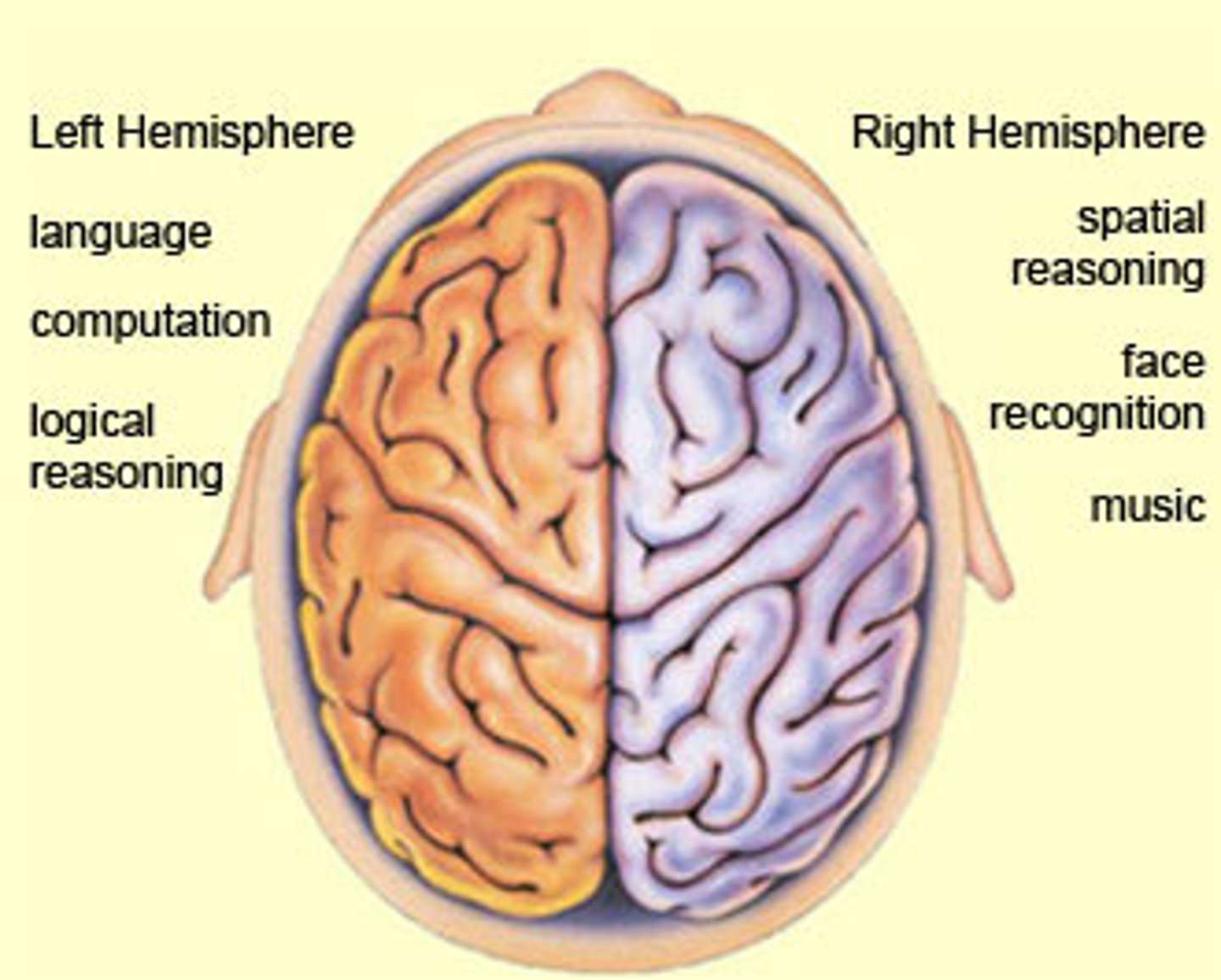
Give an example of lateralization.
In most adults, the left hemisphere is more active than the right during language production, while the reverse pattern is observed during tasks involving visuospatial abilities.
What is neuroplasticity?
the brain's ability to change, both physically and chemically, to enhance its adaptability to environmental change and compensate for injury.
What are benefits of neuroplasticity?
Enhanced adaptability to environmental change and compensation for injury.
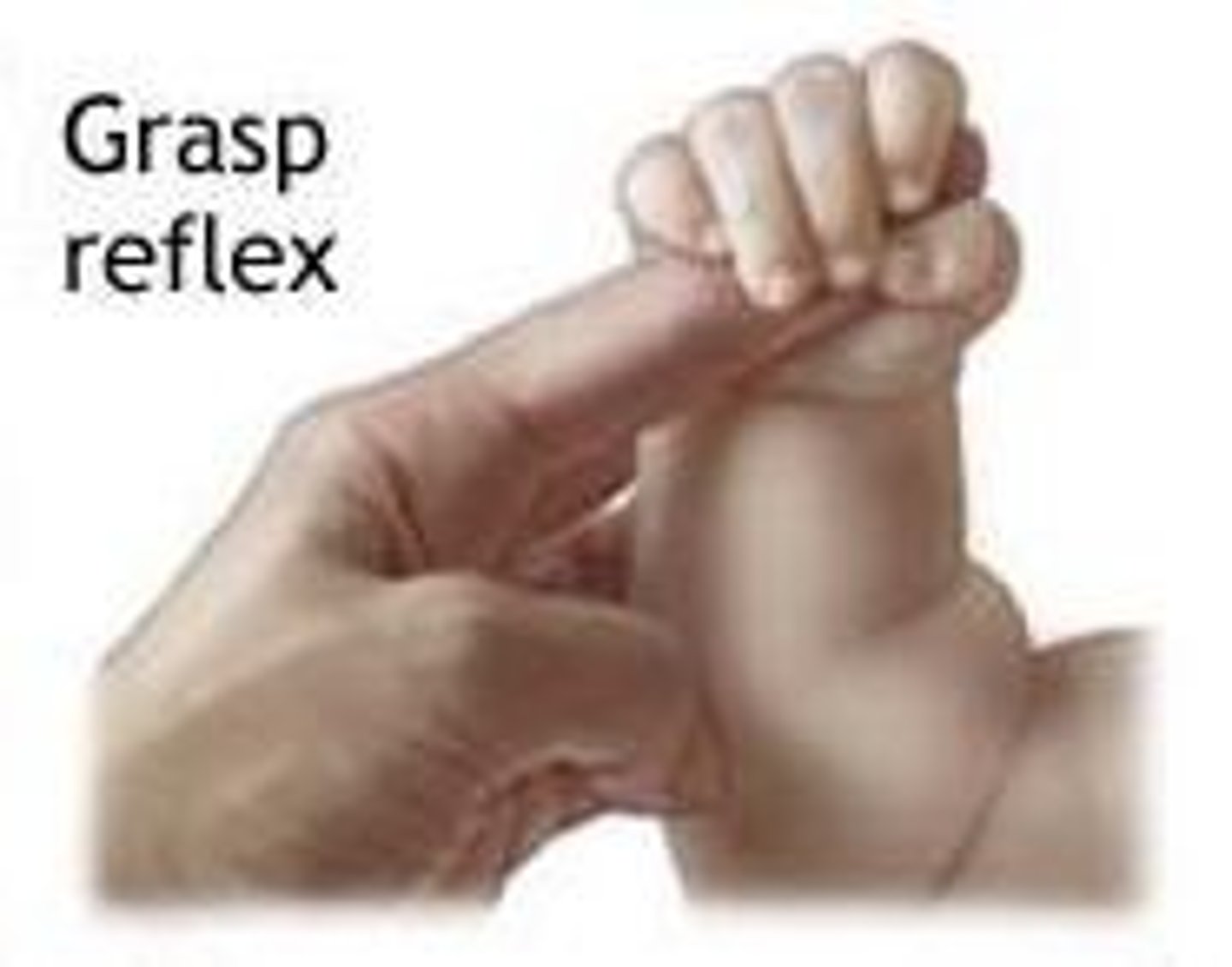
What is the palmer grasp?
Whole hand grasping of an object and newborn reflex.
What is pincer grasp?
Using forefinger and thumb to grasp objects. Around 9 months of age.
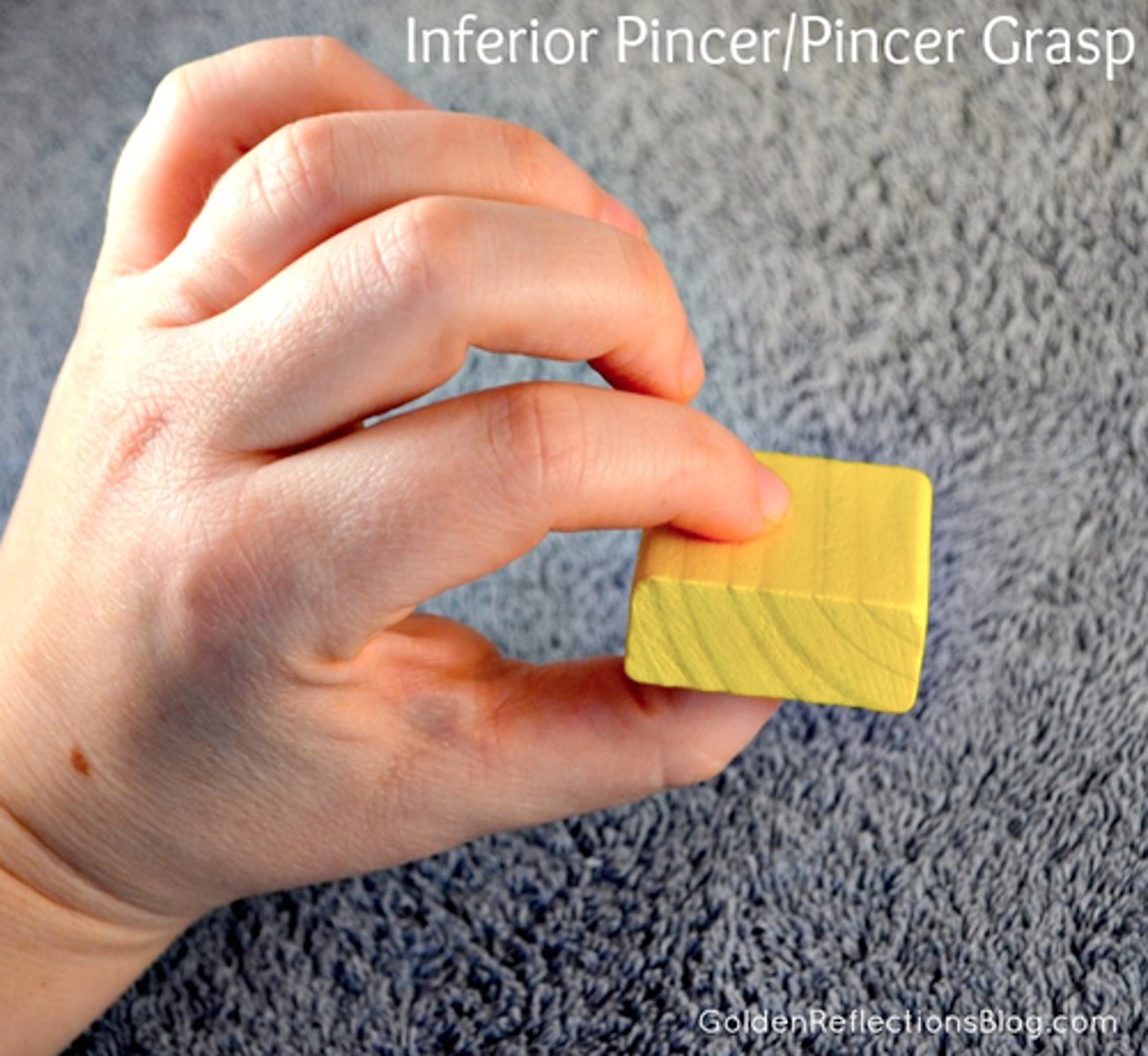

Give an example of pincer grasp.
Self-feeding or holding a pencil.

What is object permanence?
Understanding that something still exists even if out of sight.

What are gross motor skills?
Development of large muscles for activities like walking, running, etc.
What are fine motor skills?
Ability to make movements using small muscles in hands.

How many stages of cognitive development did Jean Piaget propose?
Four stages.

What is the preoperational stage?
Stage where children use symbols and engage in pretend play.

What is the Intuitive Thought Substage?
Stage with greater dependence on intuitive thinking.

What is scaffolding?
Temporary support given by parents or teachers to a child.

What are declarative memories?
Memories for facts or events that can be consciously recollected.

What are some examples of declarative memories?
Remembering historical facts, recalling a specific event, etc.
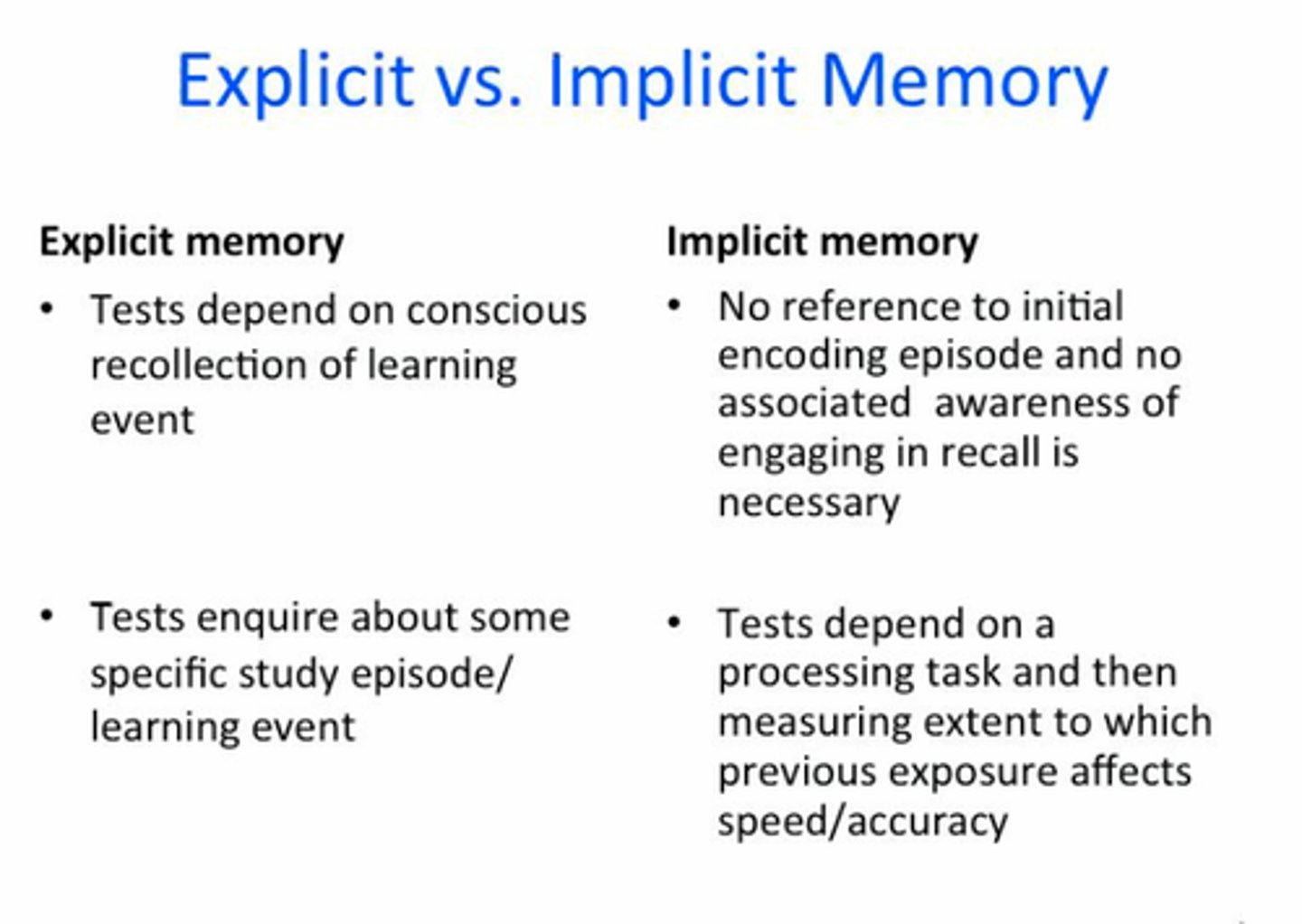
What are non-declarative memories?
Automated skills that don't require conscious recollection.
What are semantic memories?
Memories for facts and knowledge not tied to a timeline.

What are episodic memories?
Memories tied to specific events in time.

What is behavioral genetics?
Study of genetic and environmental contributions to behavior.

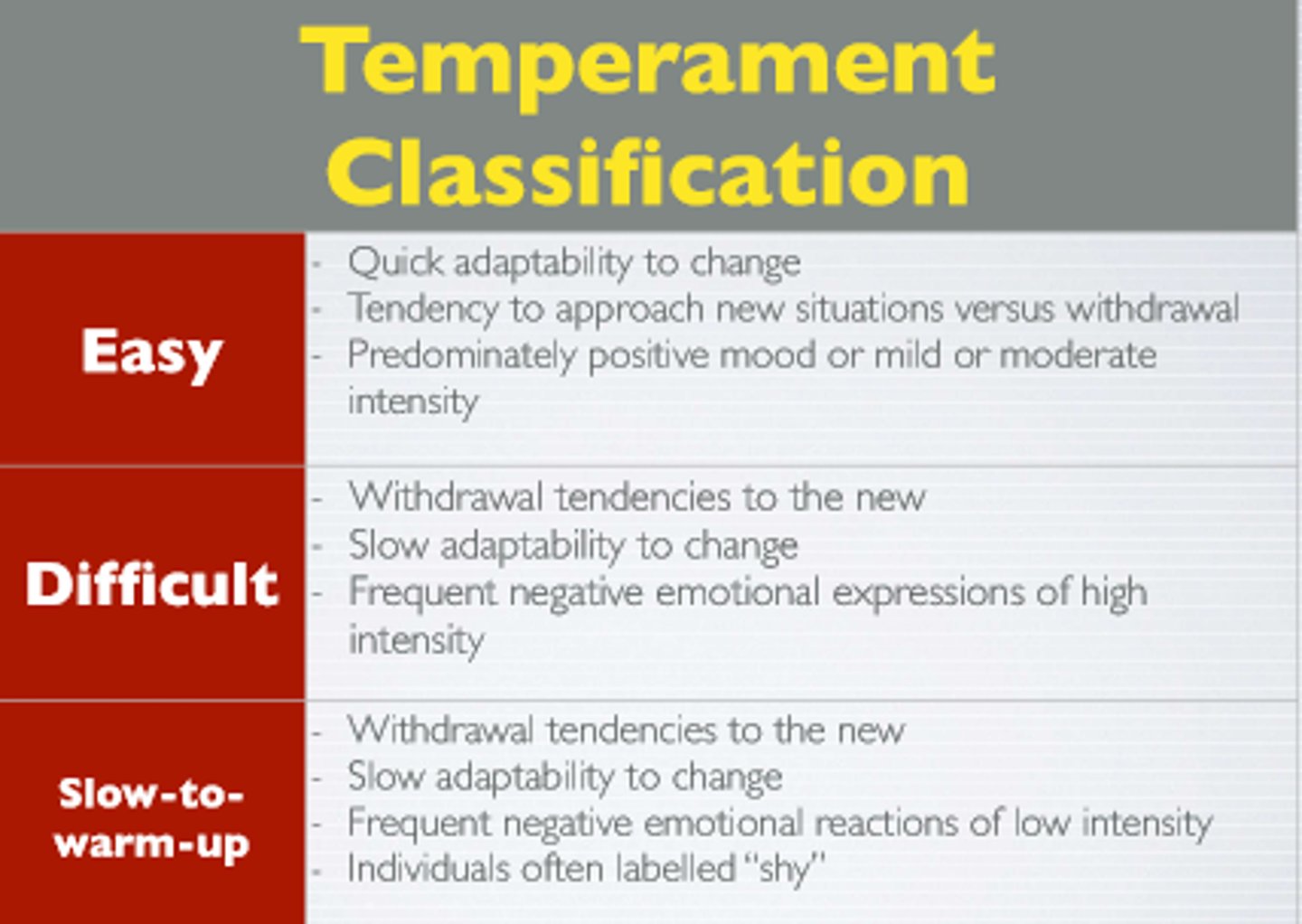
What is temperament?
Innate characteristics of an infant noticed soon after birth.
What is collectivistic culture?
Culture emphasizing conformity to family and cultural values.
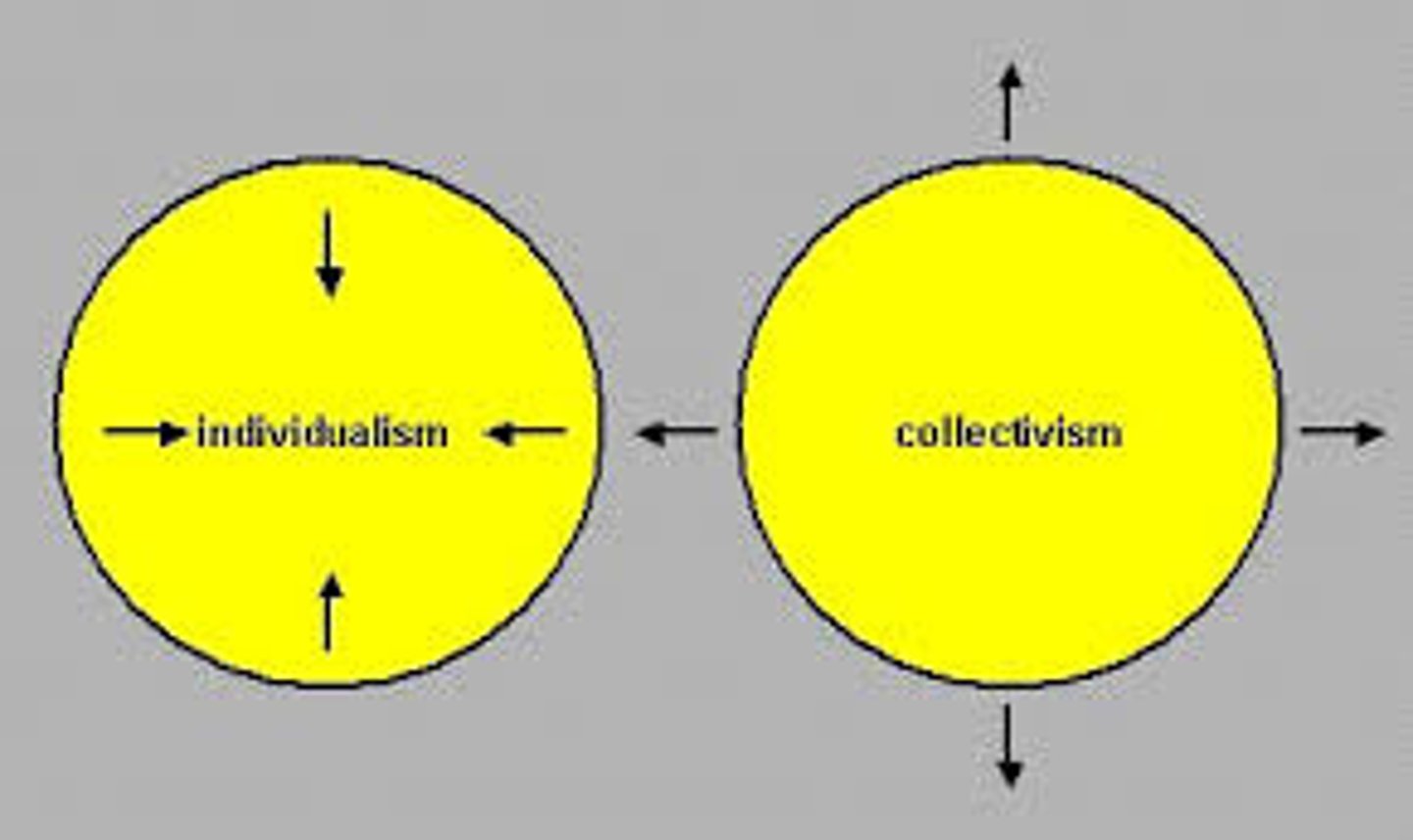
What is individualistic culture?
Culture emphasizing autonomy and social skills over conformity. Encouraging children to think for themselves and assert their own opinion.

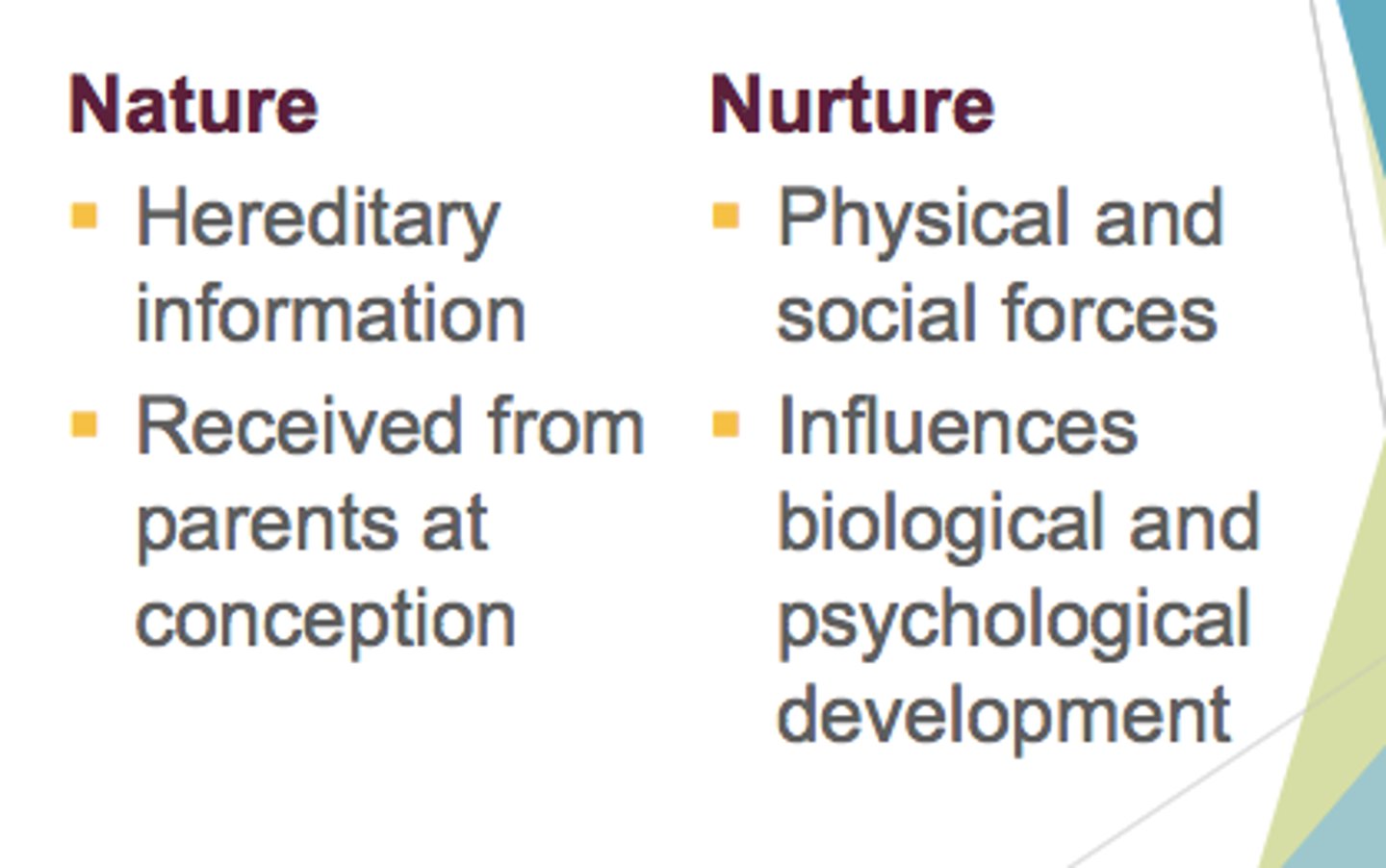
What is the nature/nurture debate?
Debate about the interplay between genetic and environmental contributions to behavior.
What is self-concept?
Your self-description according to various categories.
What is self-esteem?
An evaluative judgment about who you are.
What is Social Learning Theory?
Learning through observation, modeling, reinforcement, and punishment.

What is Gender Schema Theory?
Own conceptions of the attributes associated with sex.

What is Developmental Intergroup Theory?
Stereotypes are strong due to cultural emphasis on gender.

What is parallel play?
Children play alongside each other, using similar toys, but do not directly interact with each other.

What is associative play?
Children interact with each other and share toys, but not working toward a common goal.
What is cooperative play?
Children interact to achieve a common goal, taking on different tasks.

What is authoritative parenting?
Expressing warmth, listening to child's point of view, and providing opportunities for independence.

What is authoritarian parenting?
Using rigid rules with firm consequences and exhibiting control over child's decisions and behavior.

How do parenting styles differ in individualistic vs collectivistic cultures?
Individualistic cultures favor independence, self-reliance, and responsibility, while collectivistic cultures favor obedience and compliance.
What are primary emotions?
Emotions that first appear in infants, including happiness, anger, and fear.
What are secondary emotions?
Emotions that appear as children develop a self-concept and require social instruction, including doubt, envy, fear, and guilt.
What is a secure attachment style?
Allows a child to explore freely while the caregiver is present, may engage with a stranger.

What is an ambivalent attachment style?
Makes a child wary of new situations or strangers, stays close or clings to the caregiver.

What is an avoidant attachment style?
Child avoids or ignores the caregiver, shows little emotion when the caregiver departs or returns.
What is intersectionality?
Study of relationships between different forms of discrimination.
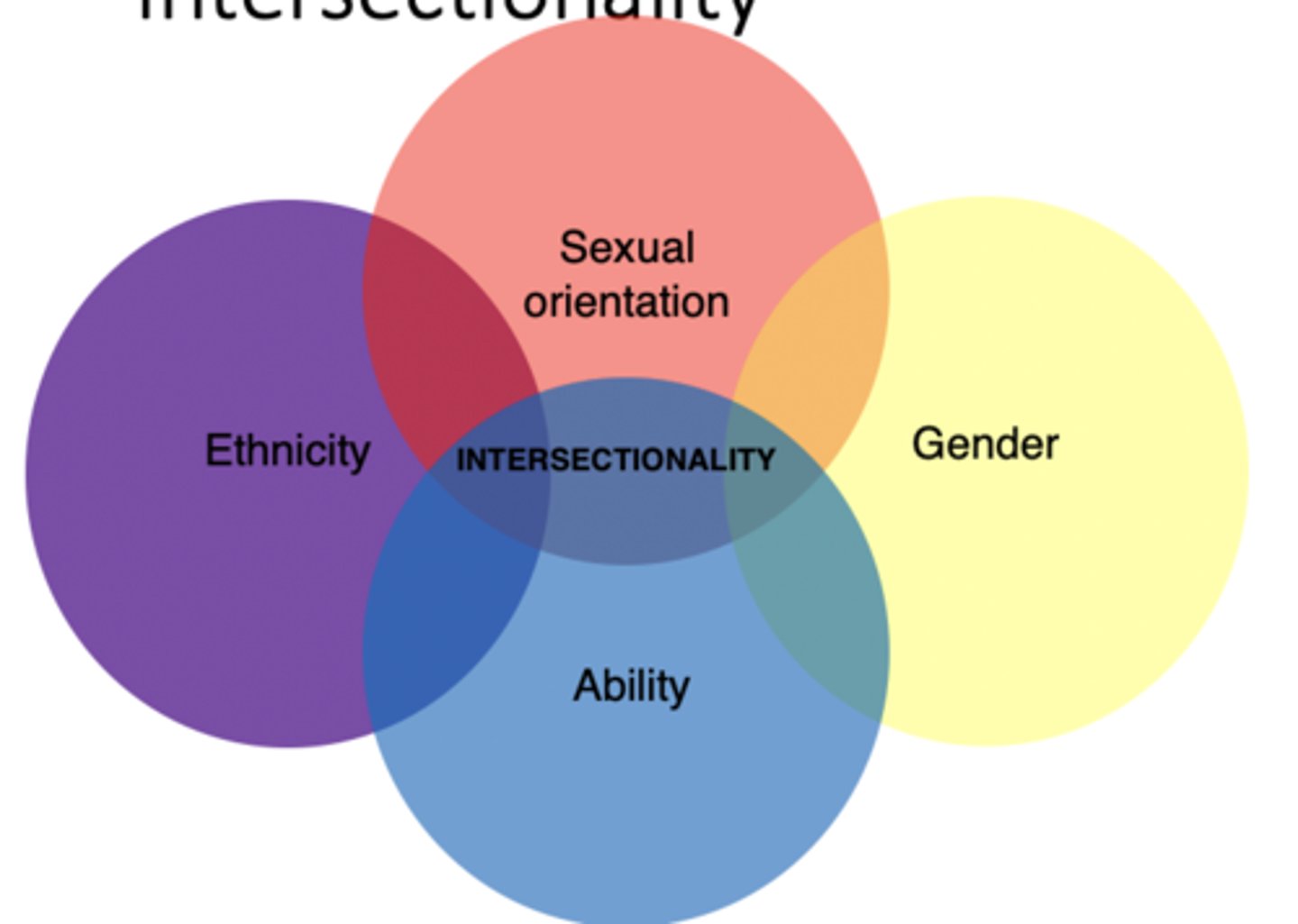
What does intersectionality theory suggest?
Various categories like race, gender, or class may interact to contribute to social inequality.