Lecture 9 - (Freshwater Ecology) - Stream Communities: Biotic and Abiotic interactions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are main filters that affect community composition? that are scales of scales of influence
watershed / basin filters
valley / reach filters
channel unit filters
Microhabitat filters
What are mesohabitats of a river?
areas that are distinctive on the river bottom, still affected by differences in distribution because of biotic and abiotic factors
How does competition as a biotic factor affect species distribution?
occurs when individuals compete for resources which are in limited supply
very strong competition can lead to extinction in that area of a species
What is interspecific competition?
competition over limited resources between individuals of the same species
What is intraspecific competition
competition for limited resources within individuals of the same species
describe exploitation as a form of competition
where food or space is limited
What is interference as a form of competition?
aggressive interactions between competitor species / individuals - e.g species having limited algae to eat on a rock
resource partitioning can reduce competition
Give an example of a species showing evidence of competition
Baetis - a fugitive species - good coloniser but poor competitor
McAuliffee (1984) - reduced Glossoma (type of caddisfly) and saw the abundance of baetis increase = suggests competition between species
Give an example of a species using resource partitioning to reduce competition
Mississippi Stream - types of fish were separated out over a river, with only two types failing to separate
What species count as predators in freshwater
fish
invertebrates like stoneflies / dragonflies etc
what are prey tactics to reduce the risk of predation
reducing encounter rates - e.g low movement rates / reduced visability
reducing attack and capture rates - e/g armor / playing dead (thanatosis)
Give an example of a prey who has adapted to avoid predation
Water fleas in lakes
Thanotosis - playing dead
Morphological - e.g daphnia tail / helmet spines
Explain how the physical environment may limit opportunities for biotic interactions
‘the harsh benign’ - Peckarsky (1980)
a gradient from harsh to benign
Harsh = few competition / predation effects
Benign = environment allows for well developed competition / predation effects
How do harsh environments impact communities?
harsh environments experience disturbance e.g waves on rocky shores
disturbance = any discrete event in time that removes organisms and opens up space to be colonised by individuals of the same or different species e.g fires in woodlands
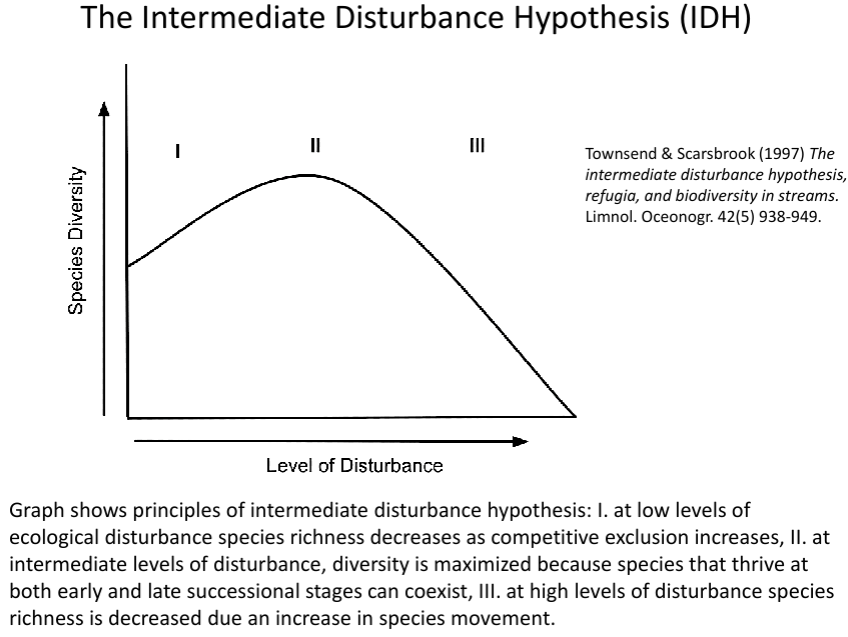
Describe the intermediate disturbance hypothesis (IDH)
a graph showing the relationship between disturbance and species diversity
at high levels of disturbance, only specialised, small numbers of animals can live there
What is the patch dynamics concept?
the idea that disturbance is continually opening up patches for colonisation and succession - fugitive species have recurrent opportunities for recolonisation
define fugitive species
species that is adapted to rapidly colonise new environments - normally found in unstable environments. De
Define competitive dominants
the degree to which a species is making up the biomass of an environment or have influence over other species in an area
what are reciprocal subsidies?
energy, organisms and nutrients that move between ecosystems
how are salmon life cycles linked to reciprocal subsidaries
salmon lay their eggs in freshwater before dying = their carcasses bring nutrients into freshwater and riparian vegetation
their carcasses input carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous into the system
their carcasses provide food - e.g for caddisflies
what is an example showing how aquatic invertebrates get eaten by terrestrial invertebrates
stoneflies can get eaten by terrestrial spiders
e.g aquatic species averaged 50% of the diet of dominant spiders