Important People in Psychology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:18 AM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
Mary Whiton Calkins
* first female president of the American Psychological Association
* memory, dreams and the self
* memory, dreams and the self

2
New cards
Charles Darwin
* functionalism
* evolutionary theory + natural selection theory
* huge influence → how psychologists viewed the mind
* evolutionary theory + natural selection theory
* huge influence → how psychologists viewed the mind
3
New cards
Dorothea Dix
* advocated for humane treatment of the mentally ill
* created first generation of american mental asylums
* created first generation of american mental asylums

4
New cards
G. Stanley Hall
* first president of the APA
* **developmental** and **evolutionary** theory
* created:
* “genetic psychology” concept
* Theory of Adolescence (beginning of new life / storm and stress)
* **developmental** and **evolutionary** theory
* created:
* “genetic psychology” concept
* Theory of Adolescence (beginning of new life / storm and stress)

5
New cards
William James
* functionalism - mental states are identified by what they do rather than by what they are made of
* “stream of consciousness” = consciousness is best described as an uninterrupted stream
* trained Mary Whiton Calkins
* “stream of consciousness” = consciousness is best described as an uninterrupted stream
* trained Mary Whiton Calkins
6
New cards
Margaret Floy Washburn
* motor theory of consciousness
* animal behavior
* second female president of APA
* animal behavior
* second female president of APA

7
New cards
motor theory of consciousness
Margaret Floy Washburn’s theory
“thought or consciousness could be seen in bodily movements. consciousness is the result of sensation and motion”
“thought or consciousness could be seen in bodily movements. consciousness is the result of sensation and motion”
8
New cards
Wilhelm Wundt
* founded modern experimental psychology
* method of introspection = systematic examination of subjective mental experiences through self-reporting thoughts
* method of introspection = systematic examination of subjective mental experiences through self-reporting thoughts

9
New cards
method of introspection
Wilhelm Wundt’s theory
= systematic examination of subjective mental experiences through self-reporting thoughts
= systematic examination of subjective mental experiences through self-reporting thoughts
10
New cards
Milgram
famous experiment → human tendency to obey commands issued by an authority figure

11
New cards
Zimbardo
famous experiment → people will readily conform to the social roles they are expected to play

12
New cards
Phineas Gage
Unit: Biopsychology
* accident helped teach us that different parts of the brain play a role in different functions
* frontal lobe damage
* → what the frontal cortex does with regard to personality
* accident helped teach us that different parts of the brain play a role in different functions
* frontal lobe damage
* → what the frontal cortex does with regard to personality

13
New cards
Broca
Unit: Biopsychology
discovery of the speech **production** center of the brain
discovery of the speech **production** center of the brain

14
New cards
Wernicke
Unit: Biopsychology
discovery of the speech **comprehension** center of the brain
discovery of the speech **comprehension** center of the brain

15
New cards
Sperry
Unit: Biopsychology
* split-brain research
* split-brain research

16
New cards
Gazzaniga
Unit: Biopsychology
* extended Sperry’s split-brain research on cats to people
* “two halves of the brain experience the world quite differently”
* extended Sperry’s split-brain research on cats to people
* “two halves of the brain experience the world quite differently”

17
New cards
Hobson and McCarley
Unit: Biopsychology
* activation-synthesis dream theory = dreams occur when the mind tries to make sense of the activity in the brain which is taking place whilst someone sleeps
* activation-synthesis dream theory = dreams occur when the mind tries to make sense of the activity in the brain which is taking place whilst someone sleeps

18
New cards
Hilgard
Unit: Biopsychology
neodissociationist theory of hypnosis
neodissociationist theory of hypnosis

19
New cards
Freud
* founder of psychoanalysis
* conscious and unconscious;
* the id, ego, and superego;
* dream interpretation;
* psychosexual development
* conscious and unconscious;
* the id, ego, and superego;
* dream interpretation;
* psychosexual development

20
New cards
Fechner
Unit: Sensation and Perception
* a founder of psychophysics
* transforming psychology into a quantitative science,
* the Weber-Fechner Law = subjective sensation is proportional to the logarithm of the stimulus intensity
* a founder of psychophysics
* transforming psychology into a quantitative science,
* the Weber-Fechner Law = subjective sensation is proportional to the logarithm of the stimulus intensity
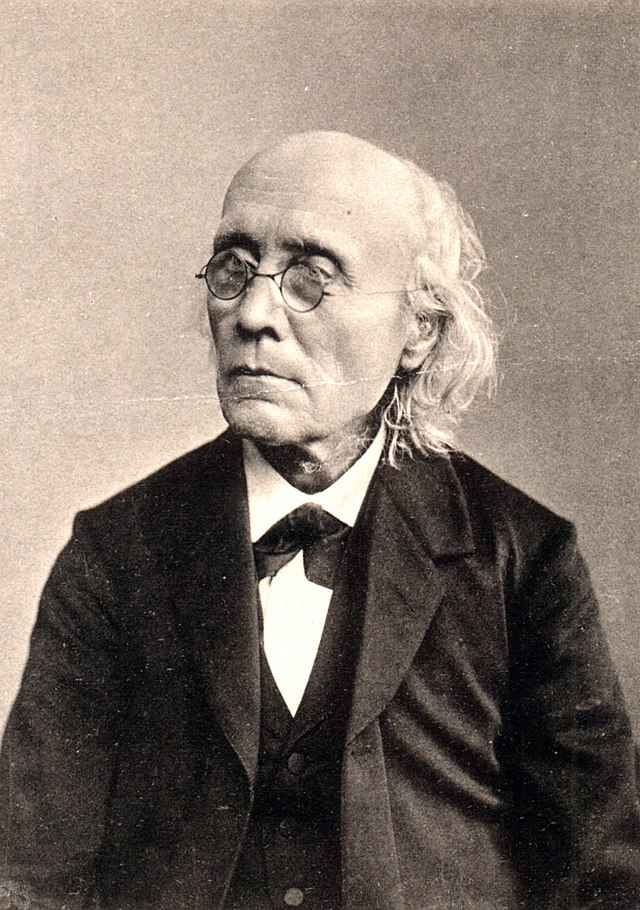

21
New cards
Weber
Unit: Sensation and Perception
* a founder of psychophysics
* just-noticeable difference
* a founder of psychophysics
* just-noticeable difference

22
New cards
Hubel and Wiesel
Unit: Sensation and Perception
* “ocular dominance” = some neurons were only responsive to information that came from a single eye
* “ocular dominance” = some neurons were only responsive to information that came from a single eye

23
New cards
Pavlov
Unit: Learning
* classical conditioning
* classical conditioning
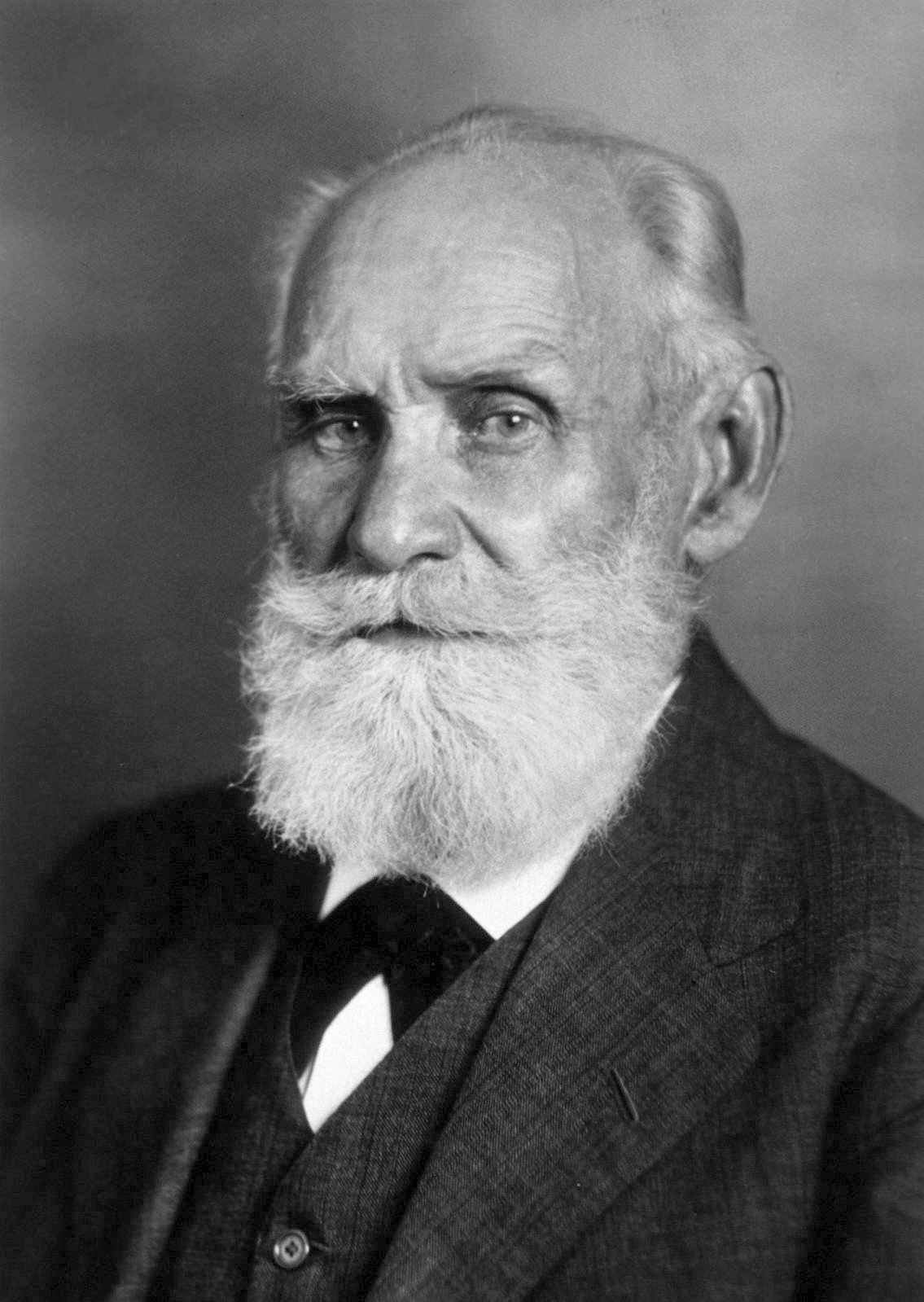

24
New cards
Tolman
Unit: Learning
* cognitive behaviorism,
* cognitive maps + the theory of latent learning
* famous rat maze experiment
* cognitive behaviorism,
* cognitive maps + the theory of latent learning
* famous rat maze experiment
25
New cards
Thorndike
Unit: Learning
* first to apply psychological principles to the area of learning
* concept of reinforcement
* operant conditioning
* first to apply psychological principles to the area of learning
* concept of reinforcement
* operant conditioning

26
New cards
B. F. Skinner
Unit: Learning
* argued that the goal of a science of psychology was to predict and control an
* organism's behavior from its current stimulus situation and its history of reinforcement
* argued that the goal of a science of psychology was to predict and control an
* organism's behavior from its current stimulus situation and its history of reinforcement
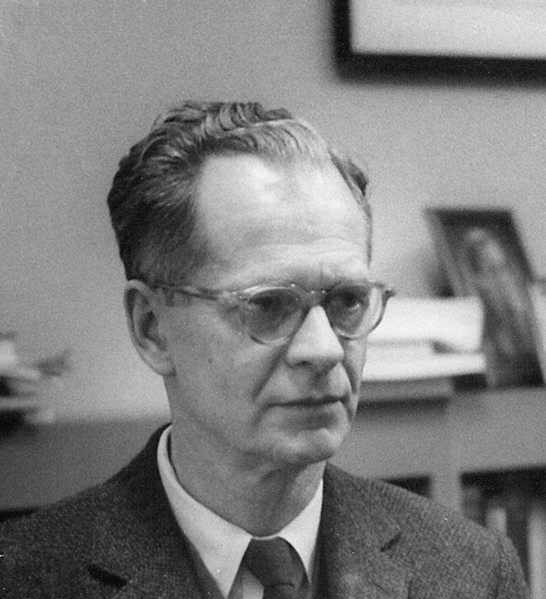

27
New cards
John Watson
Unit: Learning
* Popularized Behaviorism
* famous experiment → classical conditioning on child
* Popularized Behaviorism
* famous experiment → classical conditioning on child
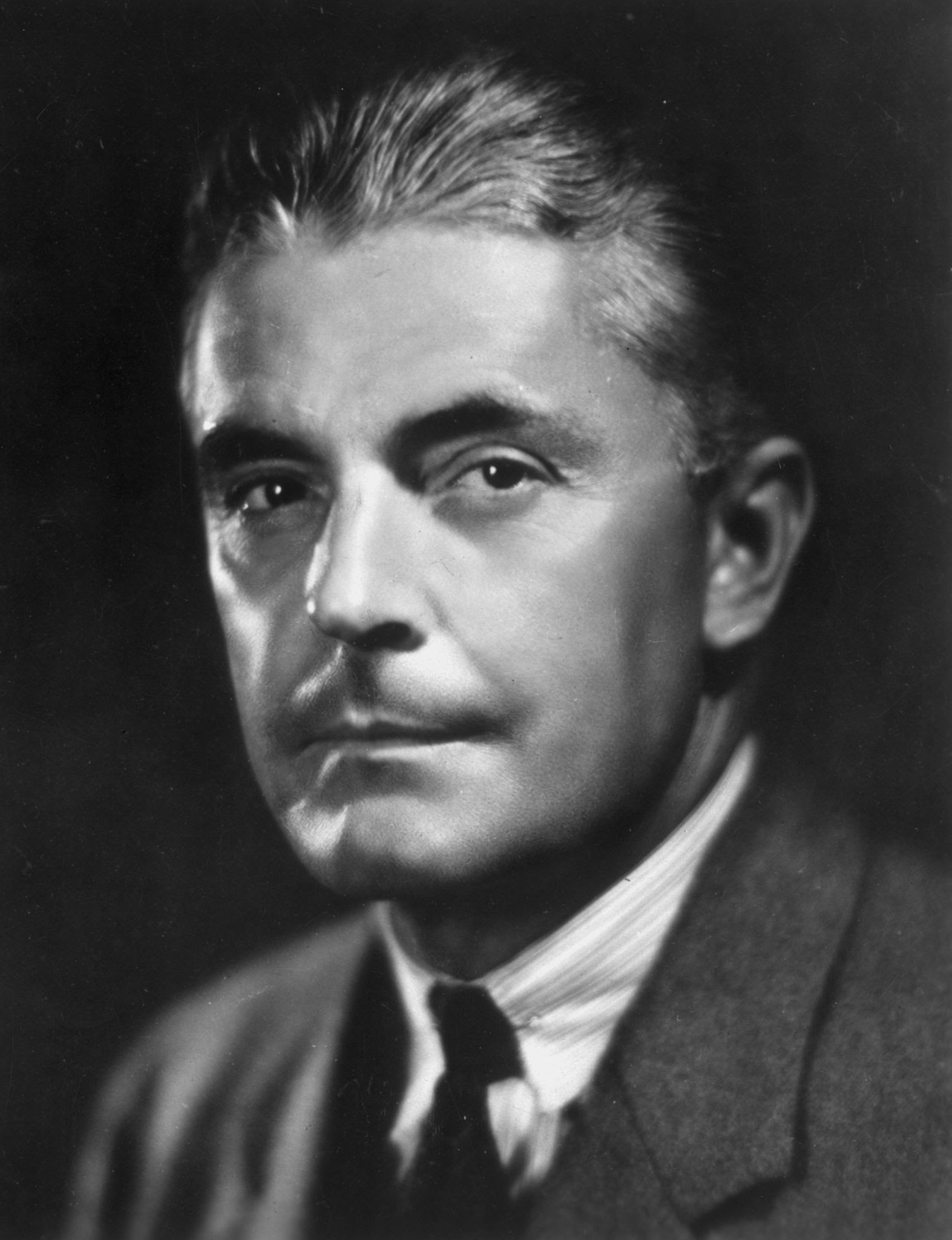

28
New cards
Bandura
Unit: Learning
* social learning theory
* self-efficacy
* social learning theory
* self-efficacy

29
New cards
Seligman
Unit: Learning
* learned helplessness
* learned helplessness

30
New cards
Wolfgang Köhler
Unit: Learning
* **insight learning** = sudden understanding of the relation between a problem and a solution
* monkeys
* **insight learning** = sudden understanding of the relation between a problem and a solution
* monkeys

31
New cards
Rescorla
Unit: Learning
* **associative learning** = emphasized the associations between unconditioned and conditioned stimuli
* **associative learning** = emphasized the associations between unconditioned and conditioned stimuli

32
New cards
Garcia
Unit: Learning
* taste aversion
* taste aversion

33
New cards
Premack
Unit: Learning
\
famous **principle** → “%%more probable behaviors (rewards)%% __will reinforce__ ==less probable behaviors==” → increases the likelihood of compliance through **positive reinforcement**
ex. First ==clean your room==, then you can %%play video games%%.
ex. Get your ==homework done==, then you can %%watch TV%%.
ex. If you ==eat your vegetables==, you can have %%ice cream%%
\
famous **principle** → “%%more probable behaviors (rewards)%% __will reinforce__ ==less probable behaviors==” → increases the likelihood of compliance through **positive reinforcement**
ex. First ==clean your room==, then you can %%play video games%%.
ex. Get your ==homework done==, then you can %%watch TV%%.
ex. If you ==eat your vegetables==, you can have %%ice cream%%

34
New cards
Ebbinghaus
Unit: Cognition
forgetting curve
forgetting curve

35
New cards
George Miller
Unit: Cognition
\
short-term memory can hold between 5 and 9 pieces of information (7±2)
\
short-term memory can hold between 5 and 9 pieces of information (7±2)

36
New cards
Loftus
Unit: Cognition
\
one of the nation's leading experts on memory
* misinformation effect
* false memory
* eyewitness testimony (EWT) is fragile and can easily be distorted
→ Facts, ideas, suggestions and other post-event information can modify our memories
\
one of the nation's leading experts on memory
* misinformation effect
* false memory
* eyewitness testimony (EWT) is fragile and can easily be distorted
→ Facts, ideas, suggestions and other post-event information can modify our memories

37
New cards
Daniel Schachter
Unit: Cognition
\
7 sins of memory
\
7 sins of memory

38
New cards
Kahneman and Tversky
Unit: Cognition
\
* cognitive biases (caused by fast but fallible cognitive strategies = heuristics)
* loss aversion = losses have a greater emotional impact than a gain of the same amount
\
* cognitive biases (caused by fast but fallible cognitive strategies = heuristics)
* loss aversion = losses have a greater emotional impact than a gain of the same amount

39
New cards
Chomsky
Unit: Cognition
\
* universal grammar = all languages hold similar structures and rules
\
* universal grammar = all languages hold similar structures and rules

40
New cards
Genie
Unit: Cognition
\
victim of severe abuse, neglect, and social isolation
* helped study linguistics and abnormal child psychology
\
victim of severe abuse, neglect, and social isolation
* helped study linguistics and abnormal child psychology

41
New cards
Erikson
Unit: Development
8 stages of psycho==**social**== development
(each having a crisis to overcome)
* neo-freudian: believed people had to resolve major conflicts (based on SOCIAL interactions, not sexual pleasures, like Freud) before advancing to next developmental stage
8 stages of psycho==**social**== development
(each having a crisis to overcome)
* neo-freudian: believed people had to resolve major conflicts (based on SOCIAL interactions, not sexual pleasures, like Freud) before advancing to next developmental stage

42
New cards
Harlow
Unit: Development
\
maternal-separation, dependency needs, and social isolation experiments on rhesus monkeys
\
maternal-separation, dependency needs, and social isolation experiments on rhesus monkeys

43
New cards
Piaget
Unit: Development
\
4 stages of @@**cognitive**@@ development
\
4 stages of @@**cognitive**@@ development

44
New cards
Vygotsky
Unit: Development
\
Cognitive Development:
* parental instruction + environmental factors → development
* **parents** provide scaffolding for children’s cognitive development
\
**Zone of Proximal Development** = distance between where learner is vs. where learner *could be*
\
Cognitive Development:
* parental instruction + environmental factors → development
* **parents** provide scaffolding for children’s cognitive development
\
**Zone of Proximal Development** = distance between where learner is vs. where learner *could be*

45
New cards
Kohlberg
Unit: Development
\
6 stages of @@**moral**@@ development
\
6 stages of @@**moral**@@ development

46
New cards
Gilligan
Unit: Development
\
* development of women's morality and sense of self
* men prioritize justice when making moral decisions, women prioritize a care orientation
\
* development of women's morality and sense of self
* men prioritize justice when making moral decisions, women prioritize a care orientation

47
New cards
Ainsworth
Unit: Development
\
* theory of attachment
* 4 attachment styles
* “Strange Situation” experiment
\
* theory of attachment
* 4 attachment styles
* “Strange Situation” experiment

48
New cards
Baumrind
Unit: Development
\
styles of parenting: authoritarian, authoritative and permissive
\
styles of parenting: authoritarian, authoritative and permissive

49
New cards
Lorenz
Unit: Development
\
* founding fathers of the field of ethology, the study of animal behavior
* **imprinting**
\
* founding fathers of the field of ethology, the study of animal behavior
* **imprinting**

50
New cards
Kübler-Ross
Unit: Development
\
five stages of grief
\
five stages of grief

51
New cards
Maslow
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
\
hierarchy of needs
\
hierarchy of needs

52
New cards
Ekman
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
study of **emotions** in relation to **facial expressions**
study of **emotions** in relation to **facial expressions**

53
New cards
Selye
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
“general adaptation syndrome,” which could lead to
1. shock,
2. alarm
3. and eventually exhaustion
“general adaptation syndrome,” which could lead to
1. shock,
2. alarm
3. and eventually exhaustion

54
New cards
Schachter and Singer
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
\
two factor theory of emotion
\
two factor theory of emotion

55
New cards
Lazarus
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
\
model of stress and coping
* stress depends on the person's cognitive appraisal of the stressful event, and the subsequent type of behavioral coping strategy used.
\
model of stress and coping
* stress depends on the person's cognitive appraisal of the stressful event, and the subsequent type of behavioral coping strategy used.

56
New cards
Lewin
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
\
* founder of modern social psychology
* expanding on gestalt theories and applying them to human behavior
* experiential learning = learning from experience
* Field Theory = behavior is the result of the individual and the environment
\
* founder of modern social psychology
* expanding on gestalt theories and applying them to human behavior
* experiential learning = learning from experience
* Field Theory = behavior is the result of the individual and the environment

57
New cards
LeDoux
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
\
first to discover that it is the **amygdala** that produces a **behavioral response when we feel a threat**
\
first to discover that it is the **amygdala** that produces a **behavioral response when we feel a threat**

58
New cards
Mischel
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
\
* personality theory and social **psychology**
* behavior is not simply the result of his or her traits, but fundamentally dependent on situational cues
* marshmallow test
\
* personality theory and social **psychology**
* behavior is not simply the result of his or her traits, but fundamentally dependent on situational cues
* marshmallow test

59
New cards
Kinsey
Unit: Motivation + Emotion
\
* Kinsey believed that sexuality is fluid and subject to change over time
* sexual behavior comprises __more than physical contact__. It also includes desire, arousal, attraction, and fantasy
\
* Kinsey believed that sexuality is fluid and subject to change over time
* sexual behavior comprises __more than physical contact__. It also includes desire, arousal, attraction, and fantasy

60
New cards
Binet
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
invented the first practical IQ test
\
invented the first practical IQ test

61
New cards
Terman
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
* Further development and refinement of the Binet-Simon IQ test
\
* Further development and refinement of the Binet-Simon IQ test

62
New cards
Galton
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
* negative contributions to psychology:
* believed that intelligence and most other physical and mental characteristics of humans were inherited and biologically based
* operationalized intelligence as **reaction time**
\
* negative contributions to psychology:
* believed that intelligence and most other physical and mental characteristics of humans were inherited and biologically based
* operationalized intelligence as **reaction time**

63
New cards
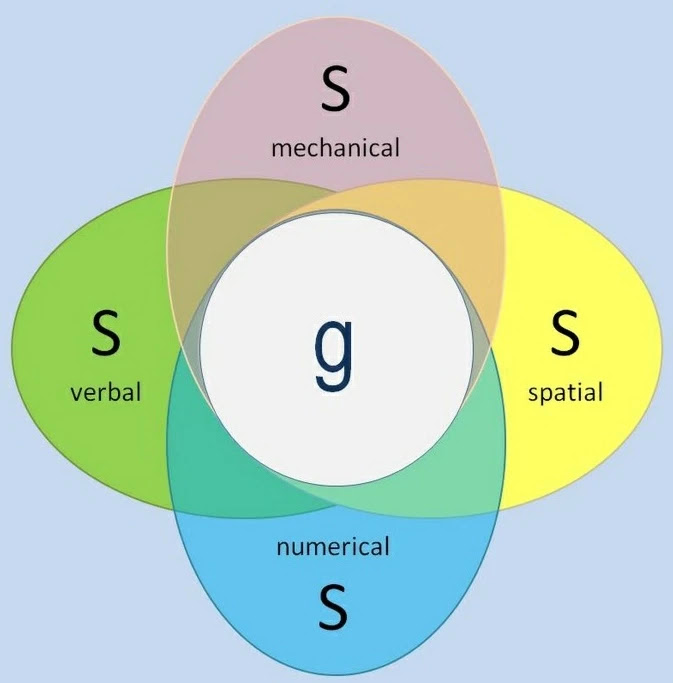
Spearman
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
two-factor theory proposes that intelligence has two components: general intelligence ("g") and specific ability ("s").
\
two-factor theory proposes that intelligence has two components: general intelligence ("g") and specific ability ("s").

64
New cards
Wechsler
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
\
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)

65
New cards
Cattell
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
* fluid versus crystallized intelligence
* 16-factor personality model
\
* fluid versus crystallized intelligence
* 16-factor personality model

66
New cards
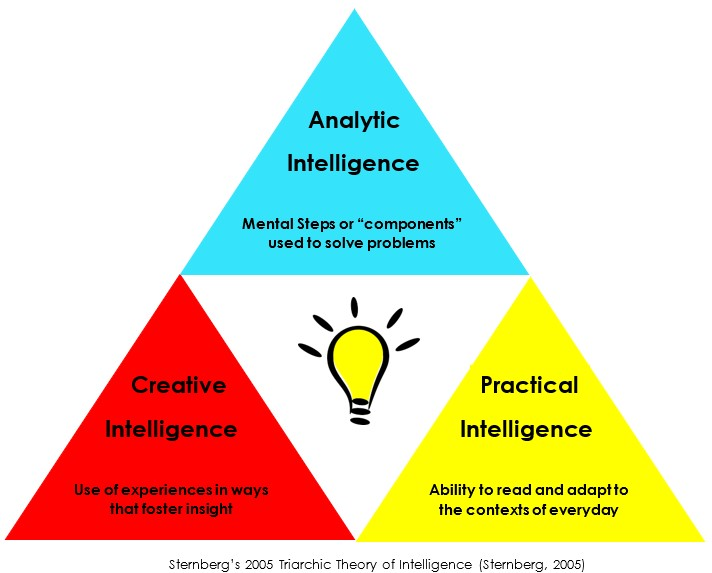
Sternberg
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
triarchic theory of intelligence
\
triarchic theory of intelligence

67
New cards
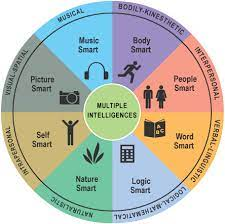
Gardner
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
theory of multiple intelligences
\
theory of multiple intelligences

68
New cards
Flynn
Unit: Intelligence + Testing
\
The Flynn effect
\
The Flynn effect

69
New cards
Alfred Adler
Unit: Personality
\
Neo-Freudian
* **Inferiority Complex** = **unconscious** feelings of inadequacy
* **Compensation** = attempts to make up for deficiencies (real or imagined)
\
Neo-Freudian
* **Inferiority Complex** = **unconscious** feelings of inadequacy
* **Compensation** = attempts to make up for deficiencies (real or imagined)
70
New cards
Jung (YOONG)
Unit: Personality
\
Neo-Freudian
* **collective unconscious** = instinctive memories common to all humans like genetic code
* **archetypes** = ancient images that appear in art/literature
* **animus vs. anima** = masculine vs. feminine aspects of personality
* introversion vs. extraversion
\
Neo-Freudian
* **collective unconscious** = instinctive memories common to all humans like genetic code
* **archetypes** = ancient images that appear in art/literature
* **animus vs. anima** = masculine vs. feminine aspects of personality
* introversion vs. extraversion

71
New cards
Horney
Unit: Personality
\
Neo-Freudian
* founder of __**feminine psychiatry**__
* __**gender power**__ __**imbalances**__ affect
* → mental health
* → development of psychological theories
\
**Basic Anxiety** **=** sense of uncertainty and isolation
3 coping behaviors:
* toward others
* against others
* away from others
\
Neo-Freudian
* founder of __**feminine psychiatry**__
* __**gender power**__ __**imbalances**__ affect
* → mental health
* → development of psychological theories
\
**Basic Anxiety** **=** sense of uncertainty and isolation
3 coping behaviors:
* toward others
* against others
* away from others

72
New cards
Allport
Unit: Personality
\
three-tiered hierarchy of personality traits, consisting of:
* Cardinal traits: Rare, but strongly deterministic of behavior.
* Central traits: Present to varying degrees in all people
* **Secondary traits**: These are traits that are only present under certain conditions and circumstances
\
three-tiered hierarchy of personality traits, consisting of:
* Cardinal traits: Rare, but strongly deterministic of behavior.
* Central traits: Present to varying degrees in all people
* **Secondary traits**: These are traits that are only present under certain conditions and circumstances

73
New cards
Eysenck
Unit: Personality
= believed personality comes from genetics
* 3 scales
* introversion vs extroversion
* stability vs neuroticism
* self-control vs psychoticism
developed the concept of neuroticism, arguing that it was a **biological** form of emotional instability
= believed personality comes from genetics
* 3 scales
* introversion vs extroversion
* stability vs neuroticism
* self-control vs psychoticism
developed the concept of neuroticism, arguing that it was a **biological** form of emotional instability
74
New cards
Costa and McCrae
Unit: Personality
\
NEO Personality Inventory (or NEO-PI) to measure neuroticism, extraversion, and openness
\
NEO Personality Inventory (or NEO-PI) to measure neuroticism, extraversion, and openness
75
New cards
Rogers
Unit: Personality
\
* founders of humanistic psychology.
* client-centered approach to psychotherapy
* unconditional positive regard
\
* founders of humanistic psychology.
* client-centered approach to psychotherapy
* unconditional positive regard
76
New cards
Rosenhan
Unit: Clinical Psychology
\
famous experiment → determine the validity of psychiatric diagnosis
\
1973 study aimed to investigate the reliability of staff in psychiatric hospitals to identify the sane from the insane
\
famous experiment → determine the validity of psychiatric diagnosis
\
1973 study aimed to investigate the reliability of staff in psychiatric hospitals to identify the sane from the insane
77
New cards
Szasz
Unit: Clinical Psychology
\
“The Myth of Mental Illness” questioned the legitimacy of clinical psychology field
believes that **the concept of mental illness is not only logically absurd but has harmful consequences**
\
“The Myth of Mental Illness” questioned the legitimacy of clinical psychology field
believes that **the concept of mental illness is not only logically absurd but has harmful consequences**
78
New cards
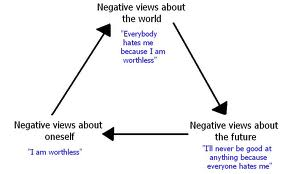
Aaron Beck
Unit: Clinical Psychology
\
believed that depression-prone individuals develop a negative self-schema
* cognitive triad
\
believed that depression-prone individuals develop a negative self-schema
* cognitive triad
79
New cards
Albert Ellis
Unit: Clinical Psychology
\
rational emotive behavior therapy = cognitive theory developed for confronting and changing irrational beliefs and behaviors
\
rational emotive behavior therapy = cognitive theory developed for confronting and changing irrational beliefs and behaviors
80
New cards
Wolpe
Unit: Clinical Psychology
\
* systematic desensitization
developed the Subjective Units of Disturbance Scale (SUDS) for assessing the level of subjective discomfort or **psychological** pain
\
* systematic desensitization
developed the Subjective Units of Disturbance Scale (SUDS) for assessing the level of subjective discomfort or **psychological** pain
81
New cards
Linehan
Unit: Clinical Psychology
\
* creator of dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), a type of psychotherapy that combines cognitive restructuring with acceptance, mindfulness, and shaping
\
* creator of dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), a type of psychotherapy that combines cognitive restructuring with acceptance, mindfulness, and shaping
82
New cards
Asch
Unit: Social Psychology
\
conformity line experiment
\
conformity line experiment
83
New cards
Festinger
Unit: Social Psychology
\
research concerned how **people resolve conflict** (group dynamics), ambiguity (social comparison), and inconsistency (cognitive dissonance)
\
research concerned how **people resolve conflict** (group dynamics), ambiguity (social comparison), and inconsistency (cognitive dissonance)