Rad Bio: Unit 1 Exam
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 05/20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Radiation Biology
The study of the effects of ionizing radiation on biological tissue
At what level of organization does radiation interact at?
Atomic
When do early effects of radiation occur?
Within minutes or days
Early effects of radiation
Radiation sickness, GI or CNS syndome, hematologic syndrome
When does late effects of radiation occur?
Within months or years
Late effects of radiation
Cancers, skin damage, cataracts
Fetal effects of radiation
Prenatal death, neonatal death, congenital malformation, childhood malformation, diminished growth and development
What is exposure measured in?
Coulomb/kG
What is air kerma and absorbed dose measured in?
Gy
Air Kerma
Kinetic energy released in matter
Absorbed Dose
Amount of energy (radiation) absorbed per unit mass (patient tissue) of an irradiated object
What is equivalent and effective dose measured in?
Sv
Equivalent dose
Measures biologic harm; average absorbed dose in human tissue or organs by different types of radiation
Effective Dose
Defined as the sum of the tissue-equivalent doses weighted by the ICRP organ (tissue) weighting factors (Wt); best measure of radiologic harm
Occupational cumulative dose limit
Age x 10 mSv
Occupational annual dose limit
50 mSv
Occupational eye dose limit
150 mSv
Occupational skin/extremity dose limit
500 mSv
Occupational 1 month fetus dose limit
0.5 mSv
Occupational fetus gestation dose limit
5 mSv
What NCRP report discusses dose limits?
116
Public annual frequent radiation dose limit
1 mSv
Public annual infrequent radiation dose limit
5 mSv
Public eye and skin/extremity dose limit
50 mSv
Nucleus
Center of atom composed of protons and neutrons
What is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom?
Binding energy
Energy shells
Orbit nucleus occupied by electrons
What orbital shell is closest to the nucleus?
K
What orbital shell has the highest binding energy?
Shell closest to the nucleus
What orbital shell would have more # of electrons?
Outer shells of an atom can hold more electrons, specifically the valence shells.
How do you determine the max # of electrons per shell?
2n2
Valence electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom
Octet Rule
Electrons in outermost shell can have no more than 8 electrons
Ionization
Adding or removing an orbital electron from an atom
Binding energy of carbon
.3 keV
Binding energy of barium
37 keV B
Binding energy of tungsten
70 keV
Molecules
Combination of atoms formed by ionic and covalent bonding
Ionic Bonding
Attraction, giving of an electron (two oppositely charged particles (ions))
What is an example of ionic bonding?
NaCl
Covalent Bonding
Sharing of electrons
What is an example of covalent bonding?
h2o
Atomic Number
Z number; number of protons
Atomic Mass Number
A number; number of protons + number of neutrons in nucleus
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number but different atomic mass numbers
What is an example of an isotope?
Barium (Z# 56, A# 138)
Radioisotopes
Combination of protons and neutrons that lead to an unstable nucleus
Coherent (classical) scattering
X-ray interacts with an atom and excites it, the photon scatters when it is released and does not change direction (same energy, same wavelength); occurs at very low energy levels (typically 10 kV)
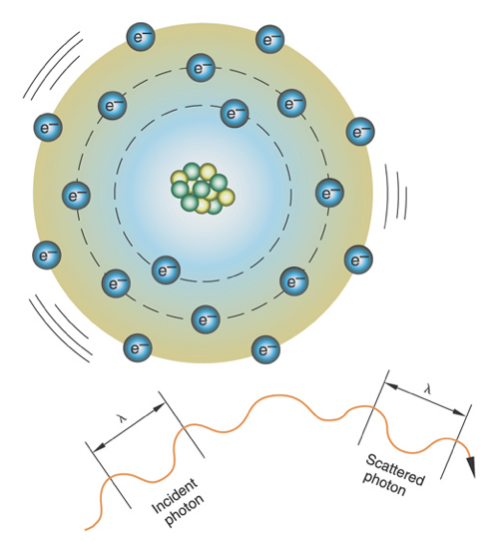
Coherent (classical) scattering
Compton scattering
Ionization of an outer shell electron; outer shell electron is ejected and the incoming x-ray photon scatters in a different direction; the scattered photon has less energy, longer wavelength and lower frequency
What interaction causes occupational exposure?
Compton scattering
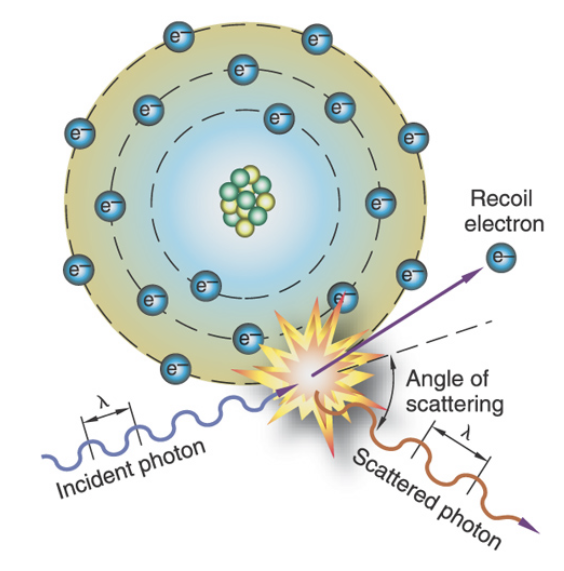
Compton scattering
Photoelectric absorption
X-ray photon absorbed; ionization of inner shell electron, electron is ejected causing an unstable atom because an inner shell electron is missing (inner shell vacancy is filled by outer shell electrons – characteristic cascade)
What interaction results in a major part of image production and contrast?
Photoelectric absorption
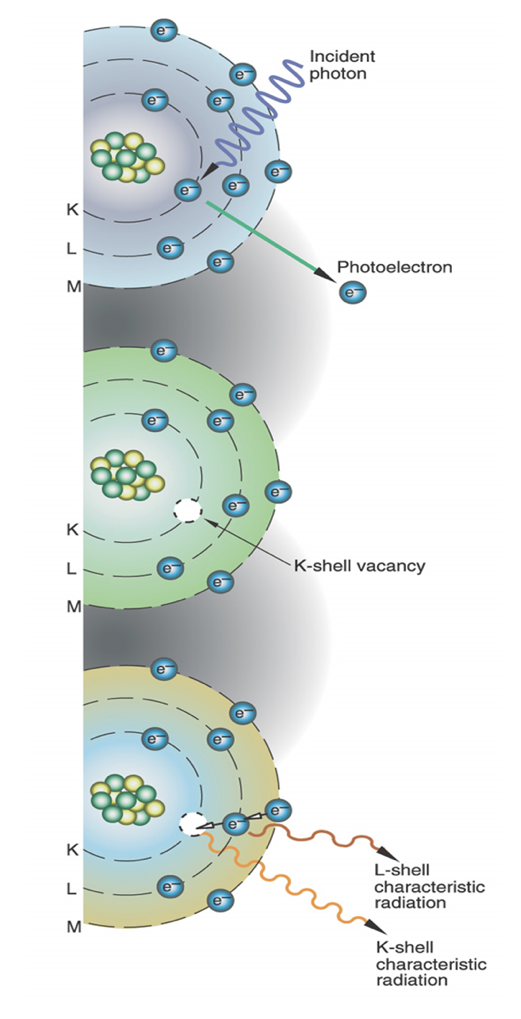
Photoelectric absorption
Pair production
X-ray or gamma ray has strong energy that may escape interaction with electrons coming close enough to nucleus and be influenced by its strong electric field; x-ray disappears and positron (+) and negatron (-) appear in its place
What energy level does pair production occur?
1.02 MeV
What imaging uses pair production?
PET scans
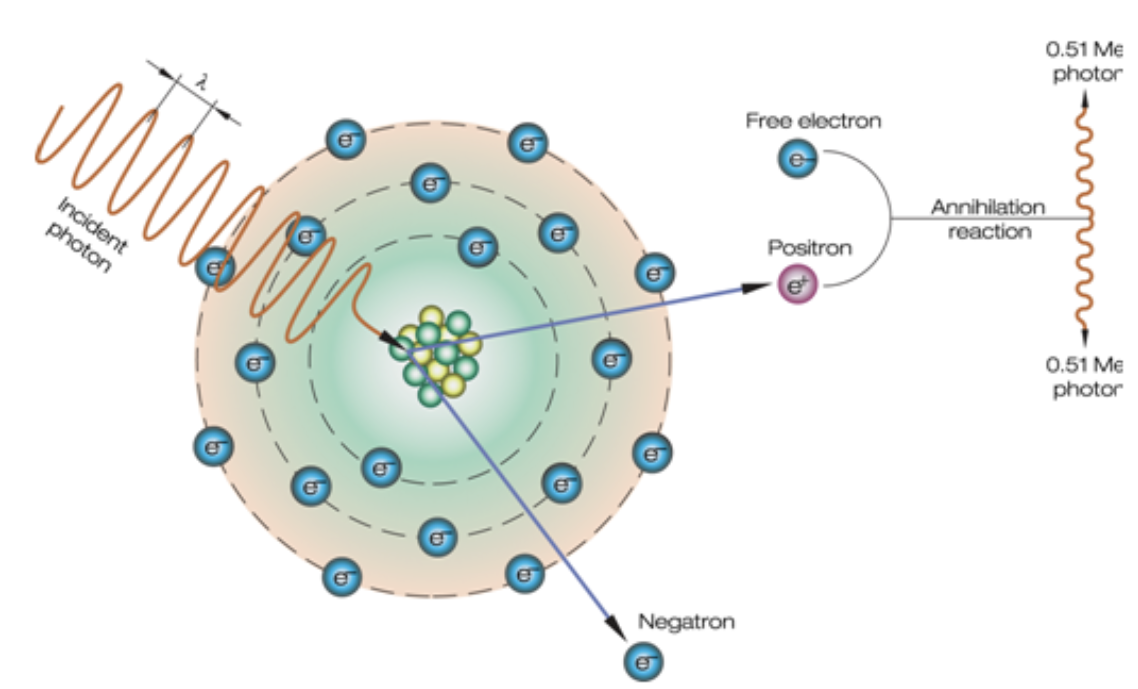
Pair production
What occurs when a positron unites with an electron?
2 gamma rays are created
What does C/kg measure?
Tube output
What is the unit for air kerma?
Gy
What is occupational exposure measured in?
Sievert
Cumulative occupational lifetime dose limit?
Age x 10 mSv
What particles make up an atom?
Protons, neutrons, electrons
Which orbital shell has the highest binding energy?
K shell
27Al has an atomic mass of 27. How many neutrons does it have?
14
60Co has an atomic mass of 60. How many neutrons does it have?
33
Isotopes of an element have the same number of what subatomic particle?
Protons
What interaction contributes most to image production?
Photoelectric
What new energy is created via pair production?
2 gamma rays of equal energy
What causes atoms to disintegrate radioactively?
Too many or too few neutrons
As the number of protons increases, does nuclear stability increase or decrease?
Decrease
If an atom is neutron rich, it would most likely decay by emitting what?
Neutrons into protons
If an atom is neutron poor, it would most likely decay by emitting what?
Protons into neutrons
The heaviest elements decay by emitting what?
Alpha particles
What occurs to create a beta particle?
Neutron → proton; Z number increases by 1 and A number stays the same, new element is formed
What occurs to create a positron?
Proton → neutron; Z number decreases by 1 and A number stays the same, new element is formed
What occurs to create an alpha particle?
2 protons & 2 neutrons emitted; Z number decreases by 2 and A number decreases by 4, new element is formed
Does the element change with solely gamma emission?
No
Particulate radiation
Alpha and beta particles
What radiation gives a shallow dose?
Particulate radiation
What radiation gives a whole body dose?
Electromagnetic
Electromagnetic radiation
X-rays and gamma rays
What is the travel range of particulate radiation?
Short
What is the travel range of electromagnetic radiation?
Unlimited
Half-value layer
The time it takes for radiation to reduce 50% of its original exposure
How many half lives are required before the quantity of any radioactive material has decayed to less than one?
6
What particulate radiation is the most damaging to local/internal tissue?
Alpha particles
Radioactivity
The emission of particles and energy from an unstable nucleus in order to become stable
Radioactive decay/disintegration
Naturally occurring process whereby unstable nucleus relieves instability by spontaneously emitting particles and energy transforming into another atom
Radionuclides
Nuclei that are radioactive
Radioisotopes
(atoms containing radioactive nuclei) radioactive atoms with same number of protons, changed into different atoms by disintegration of the nucleus accompanied by emission of ionizing radiation
What is the greatest source of occupational exposure for a nuclear medicine technologist?
The patient
Avg effective dose per capita (excluding radiation therapy) in 2006 was ___________
6.2 mSv
After nuclear medicine/radiation therapy, how far away should the patient stay from other people?
1m