Chapter 22 enthalpy and entropy
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
The measure of disorder in a system.
The letter (S)
the more disorder the higher the entropy
what is entropy?
gas and solids
What has the highest and lowest entropy?
If the reaction is in the same state but more moles are made then entropy increases
How does the number of particles also affect entropy change?
higher entropy.
the reaction can be feasile even if it is enthalpically unfavourable (endothermic)
Will a reaction tend towards higher or lower entropy?
entropy of products - entropy of reactants
units: JK-1mol-1
formula and units for entropy change?
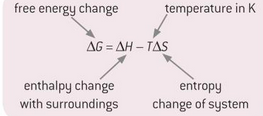
units of entropy must be divided by 1000
gibbs free energy formula
when it is negative it is feasible
How does Gibbs free energy tell us a reaction is feasible?
when Gibbs = 0 so Delta H = T delta S
how is the minimum temp for feasibility calculated?
activation energy may be too high or rate of reaction is too slow
Even if a reaction is feasible, why may a reaction not occur?
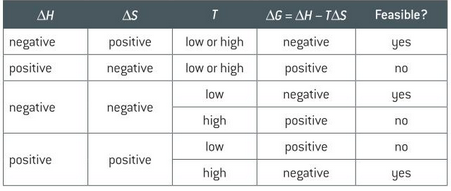
how does temperature affect delta G?
(table with different values for enthalpy and entropy)
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from it’s elements in their standard states under standard conditions.
definition enthalpy change of formation
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
measure of the strength of ionic bonding in a giant ionic lattice
exothermic (negative always)
definition of lattice enthalpy of formation
exo or endo?
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a gaseous 1+ ions are made from 1 mole of gaseous atoms
Na → Na+ + e-
defintion enthalpy change of ionisation
The smaller the ion, the stronger the electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions
The bigger the charge on an ion, the stronger the electrostatic attraction
what affects the ionic bonding?
the enthalpy change that happens when one mole of gaseous atoms are formed from elements in their standard states
always endothermic
definition enthalpy of atomisation
the enthalpy change when one electron is added to each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1- ions
exothermic
definition first electron affinity
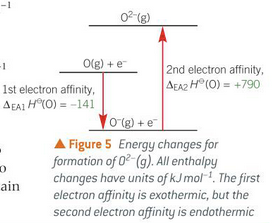
second are endothermic because a second electron is being gained by a negative ion
this repels electron away so energy must be put into it
What is the difference between second and first electron affinity?
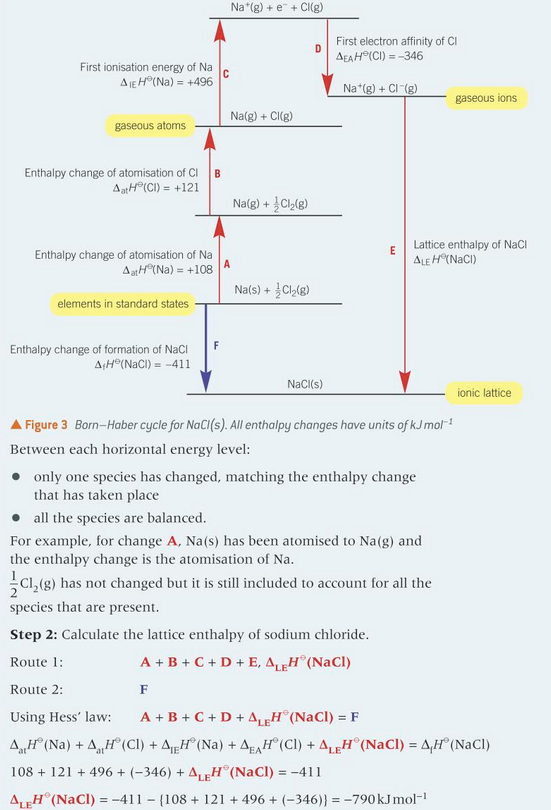
construct the born haber cycle of NaCl and find the lattice enthalpy
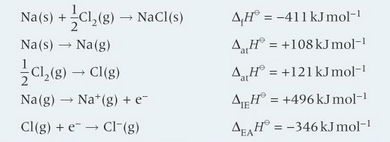
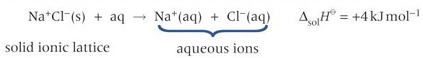
the enthalpy change when one mole of a solute dissolves in a solvent
definition: enthalpy change of solution
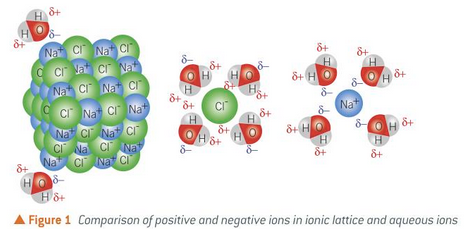
the ions separate and are surrounded by water molecules
the negative oxygen atom is attracted to the positive sodium ion
the positive hydrogen atoms are attracted to the negtaive chloride ion
what happens when an ionic substance is dissolved in water
ionic lattice is broken up forming separate gaseous ions (enthalpy of dissociation)
the separated gaseous ions interact with polar water molecule to form hydrated aqueous ions. This is enthalpy change of hydration
wha are the two types of energy involved in the dissolving process?
the enthalpy change when gaseous ions are dissolved in water to form one mole of aqueous ions.
definition enthalpy change of hydration?
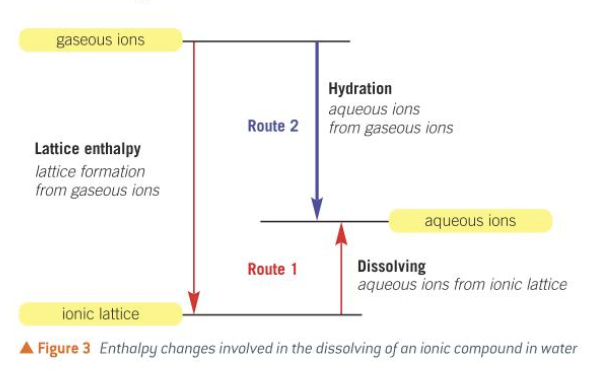
lattice enthalpy + enthalpy of solution = enthalpy of hydration
what is the cycle with lattice enthalpy, enthalpy of solution and enthalpy of hydration?
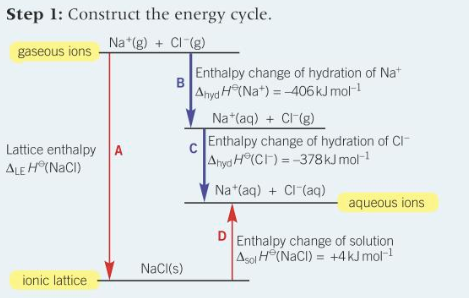
LE = -788
construct energy cycle for NaCl and find lattice enthalpy of NaCl
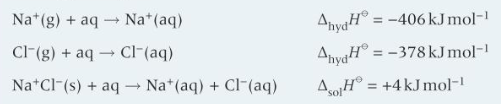
ionic size - as radius decreases, nuclear attraction increases so lattice enthalpy more negative, more energy needed to break
ionic charge - as charge increases, attraction increases and more energy needed, more negative LE, MP increases
opposite is true fo negative ions
factors affecting lattice enthalpy and hydration?
if the sum of the hydration enthalpies is greater than the lattice enthalpy, the enthalpy change of solution will be exothermic and will dissolve.
how do you predict solubility?