GOD HELP ME (sediments)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Clastic
Formed by erosion of pre-existing rocks (ex. quartz arenite)
Orthochemical
Inorganic precipitates (ex. halite)
Allochemical
Biological precipitates (ex. limestone)
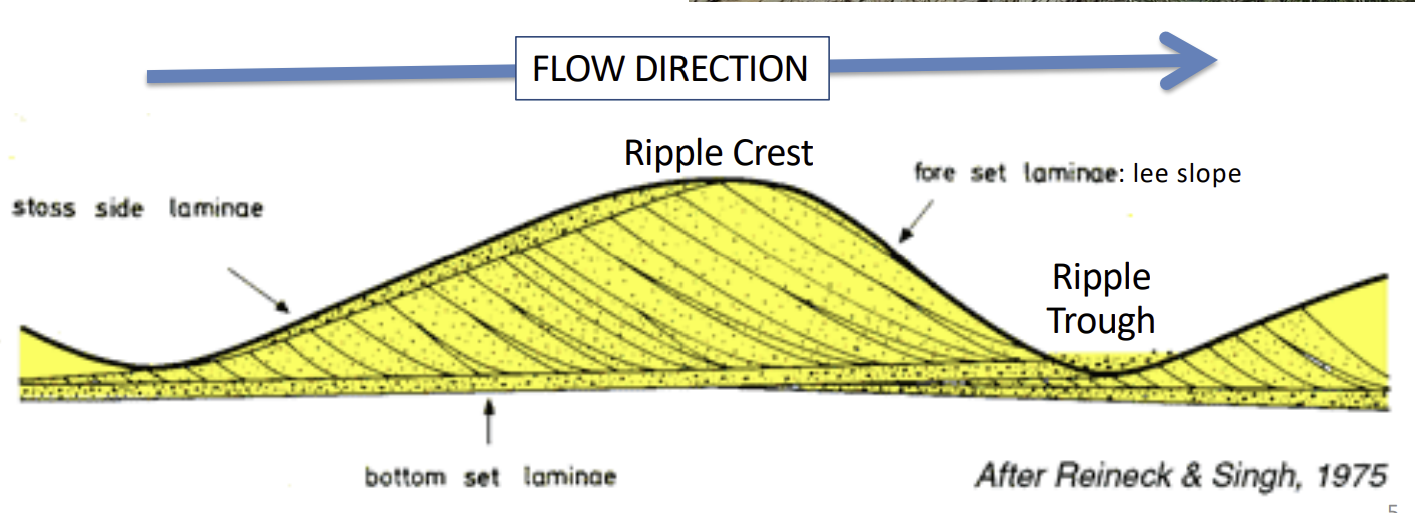
Unidirectional Ripples
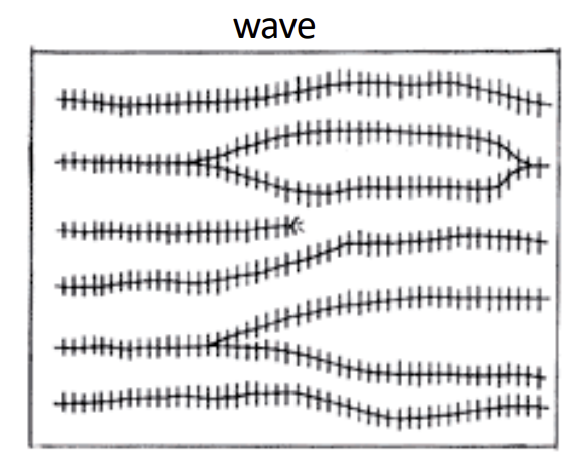
Wave Ripples
Beach
Graded Bedding
Evidence of waning current
Older to younger, larger to smaller grains
Buoma Sequence
Bounded by erosional sedimentary structures at their top and base, evidence of waning current (fines upwards)
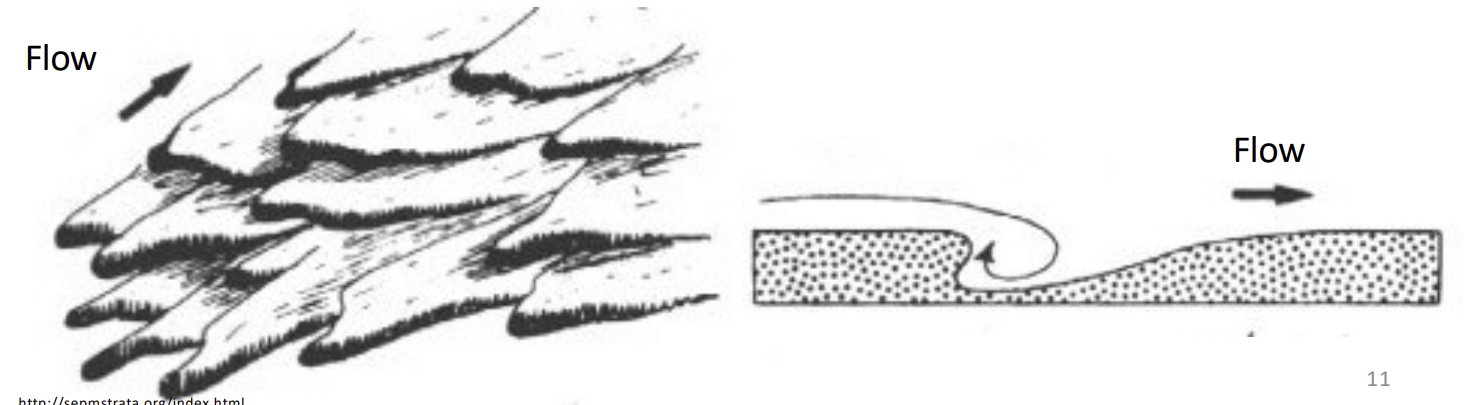
Flute Marks
Current flow
Convolute Bedding
where semi-consolidated sediment starts to slump
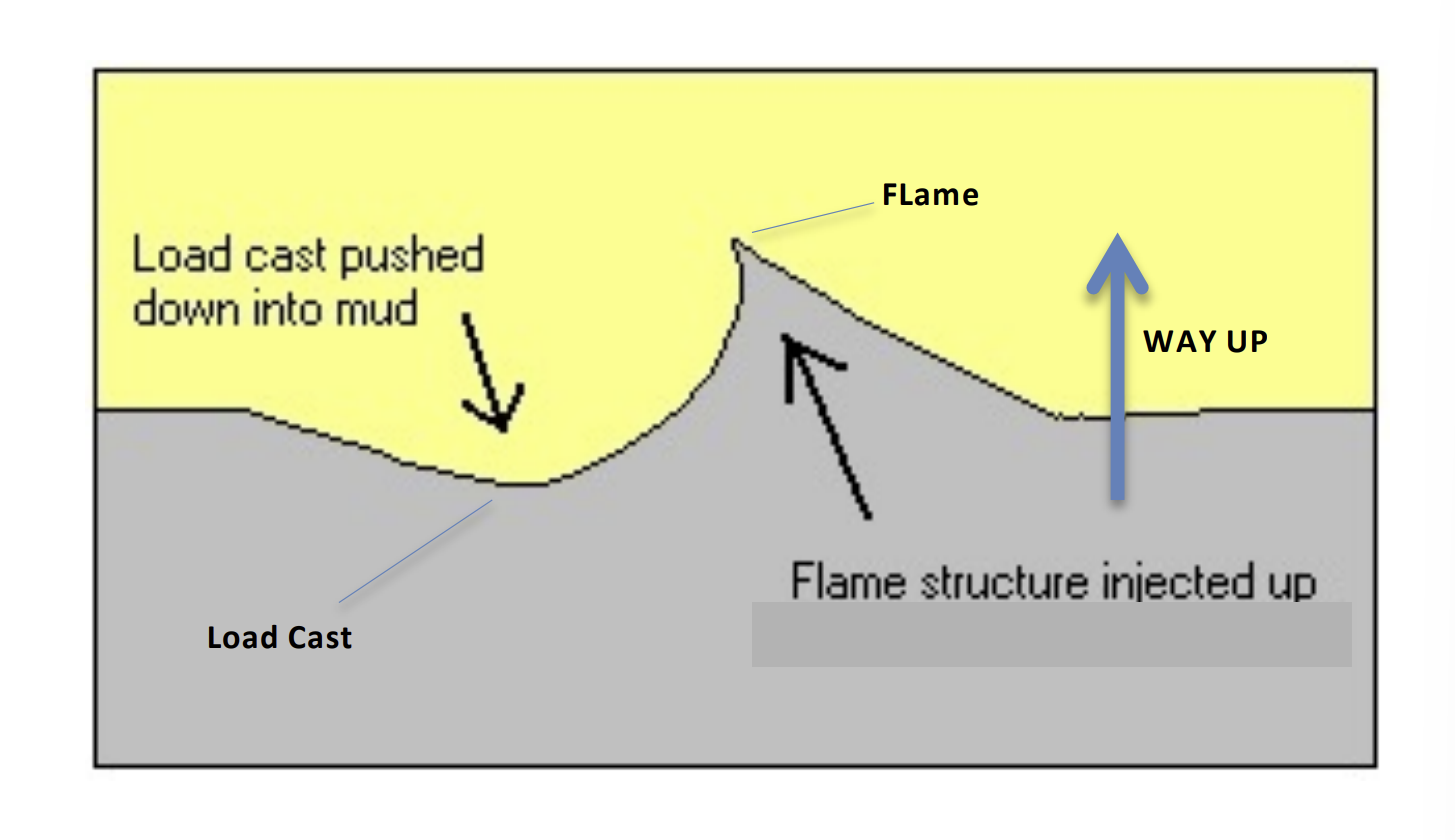
Flame Structures
any environment with water saturated sediment
Mudcracks
Drying lakes
Trace Fossils
Signs of biological activity, not actual remains of organisms
Stromatolites
formed in shallow waters
from biofilm of cyanobacteria photosynthesis
Most mature minerals (most stable at surface P/T)
Quartz, Zircon, Muscovite
Least mature minerals (least stable at surface P/T)
Pyroxene and olivine
Textural Maturity Signs
small grain size
more sorting
rounder
Conglomerate Depositional Environments
Beach
Fluvial
Alluvial Fans
Glacial
Where to find very mature
Eolian dunes
Beaches
Black Shale
anoxic, quiet, high organics
associated with pyrite from H2S production
Red Mudrock
Presence of hematite
Marine Mudstones
Grey, bioturbated
Near Shore Mudstones
Dark grey, identified by floral + fossils
Hemipelagic mudrocks
Dark grey but can be a variety of colours
Pelagic fossils
Glacial Mudstones
Contain varves
Calcite Seas
low-Mg Calcite
warm water
high seafloor spreading rates via removal of Mg from cycling through crust
Aragonite Seas
high-Mg Calcite
Aragonite
cool water
Ideal Precipitation Factors of Calcium Carbonate
Biological activity
Low pressure
High temperature
High water agitation
Less CO2 in water
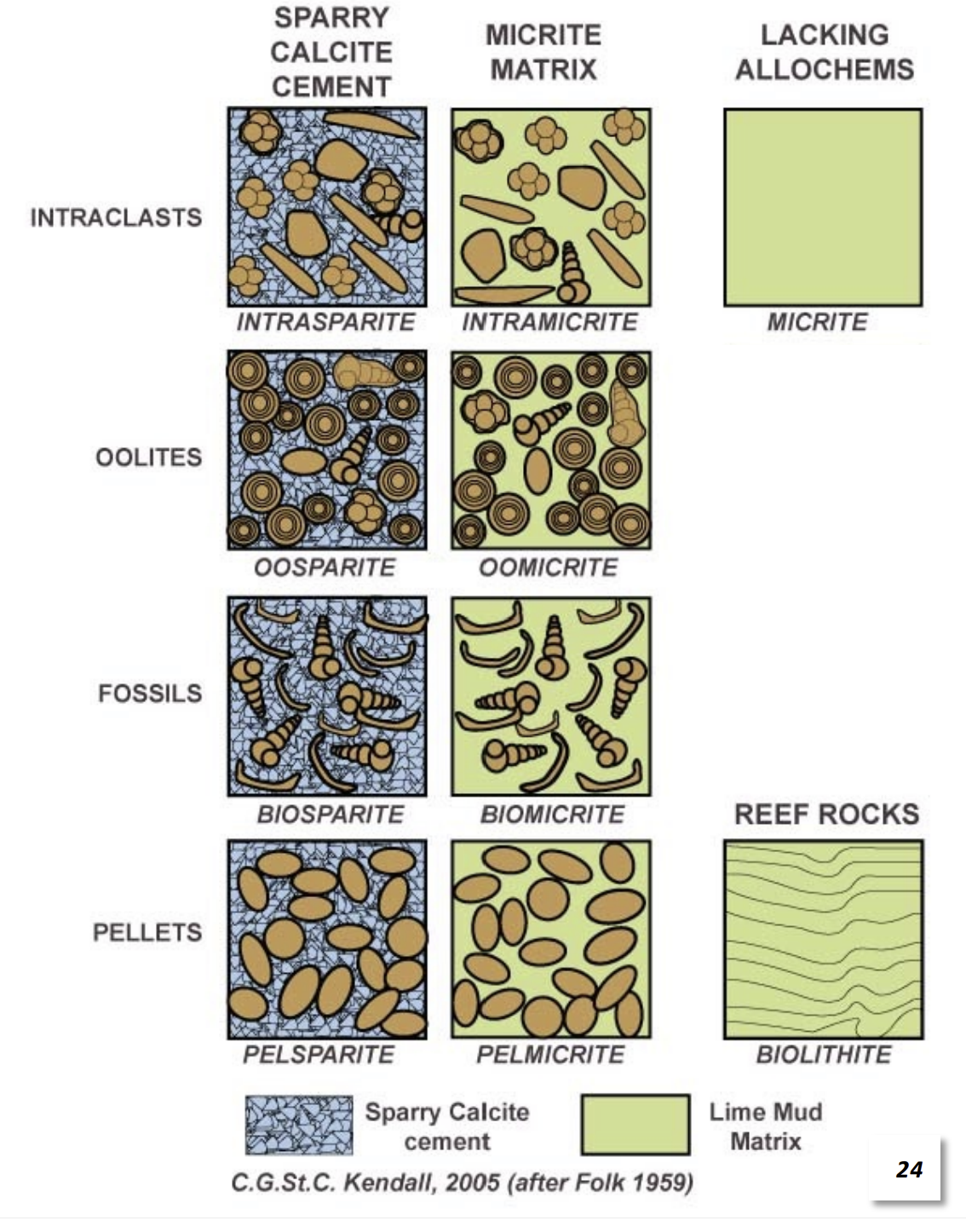
Ooids
Non-skeletal
Inorganically precipitated from excess calcium Carbonate
Concentrically layered
Oncoids
Organically precipitated concentrically around a nucleus
From cyanobacteria photosynthesis (in warm water photic zone)
Folk Scheme
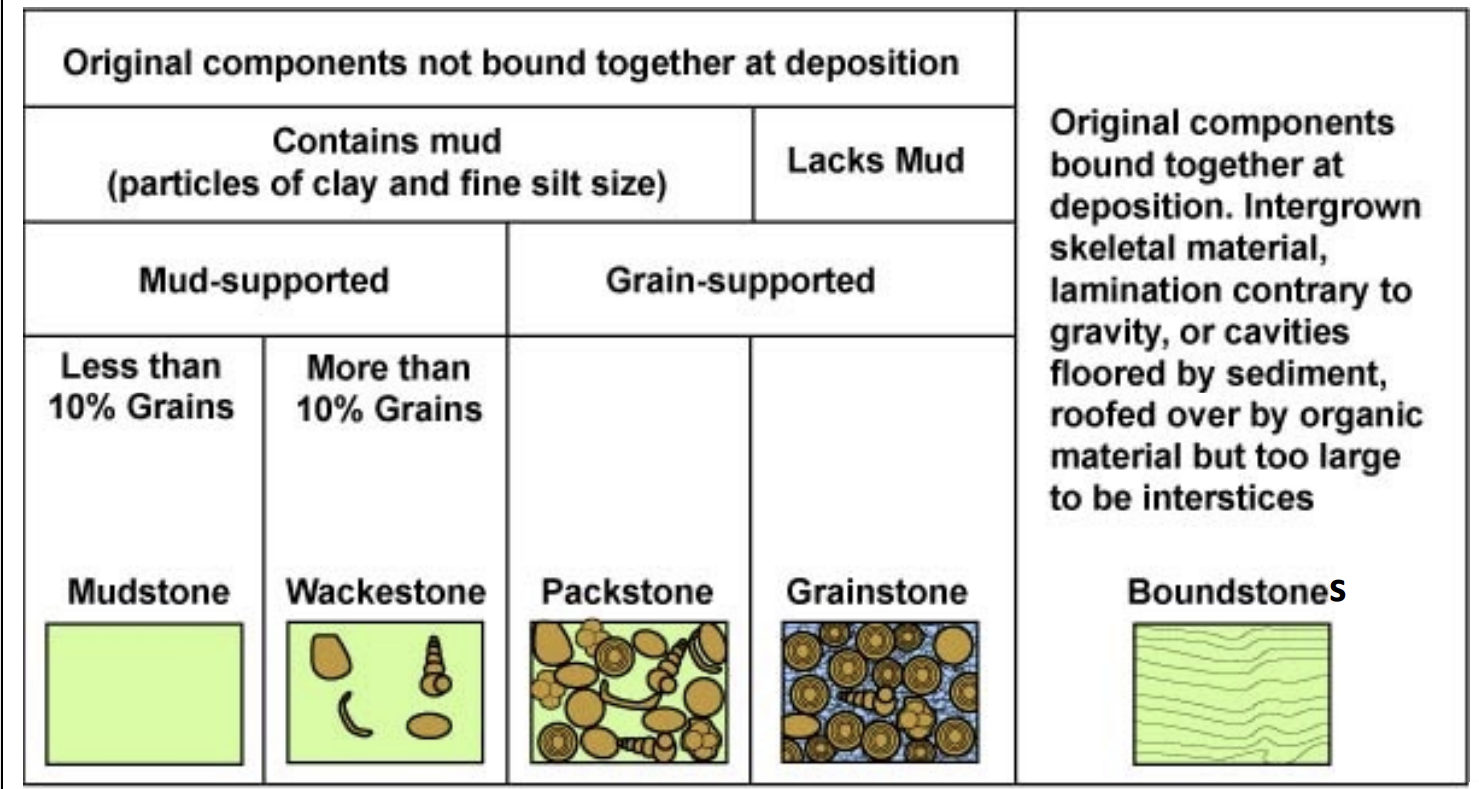
Dunham Classification
Near Shore Environment
pelmicrites with fenestrae
stromatolites with bioturbation
Reef System
Biolithes/Boundstones
Talus in the fore reef
Carbonate Compensation Depth
Depth below which calcium carbonate cannot accumulate, unless under a layer of clay or siliceous ooze
Starved Basins
pelagic sedimentation
turbidites
Processes in the Vadose Zone
Clay infiltration of pore waters
Unstable components (pyroxene, amphiboles, plagioclase) degrade
Growth of authigenic minerals like illite and kaolinite
Reddening of sediments due to hematite infiltration
Processes in the Phreatic Zone
Continued alternation and dissolution of grains
Pressure dissolution of minerals at grain contacts
Growth of cements: silica as quartz overgrowth, calcite cement
Mudstone Zone 1
0-0.5m
red-brown clays
oxic zone
bioturbation
Mudstone Zone 2
0.5-10m
zone of bacterial sulfate (SO42-) → may form H2S which reacts with Fe3+ to produce pyrite
BLACK PYRITIC SHALES
Mudstone Zone 3
10m - 1km
SULFUR REDUCTION STOPS
zone of organic fermentation
expulsion of pore water, increased density
SIDERITIC MUDSTONES
Mudstones Zone 4
1-2.5km
decarboxylation breaks down organic matter further
sideritic mudstones
Mudstones Zone 5
2.5-7km
Hydrocarbon Diagenesis
Remaining organic matter generates petroleum!!
Expulsion of water moves petroleum into reservoir
Mudstone Zone 6
>7km
Metamorphic zone transition
Illite → Muscovite at 300C
Kaolinite → Chlorite at 200C
Carbonate Diagenesis
Cementation: affected by Mg:Ca ratio and carbonate supply
Neomorphism
Dissolution: slightly acidic groundwater creates drainage system
Compaction: chemical compaction at deep burial causes pressure solution
Dolomitization
Carbonate Meteoric Zone
Upper Vadose: acidic rainwater dissolves high-Mg calcite and aragonite
Lower Vadose: recrystallization of unstable minerals + precipitation of meniscus cements + high-Mg to low-Mg
Carbonate Phreatic Zone
precipitation of low-Mg cements
initially isopachous (fine) cements to coarser blades
syntaxial overgrowths
Carbonate Marine Diagenesis
micritization
formation of hardgrounds
pendant cements
isopachous fibrous cements, but high-Mg calcite and aragonite!!
Deep Burial Carbonate Diagenesis
larger crystal size + more iron
Ferroan calcite = deep burial in ANOXIC conditions
Evaporite - Brine Dolomitization
evaporation of sea water causes precipitation of gypsum
Mg-rich brine sinks and causes dolomitization
Evaporative Pumping Dolomitization
Intense evaporation draws saline water through limestone
Causes an increase in Mg → dolomitization
Groundwater Mixing Dolomitization
freshwater mixed with 30% marine water suitable for dolomitization
Sea Water Model Dolomitization
Sea water flushed into sediment pores
Replenishing influx of fresh sea water puts calcite in contact with Mg
high tides
Sabkha
Supratidal environments on arid coastlines where saline fluid flows through sediment pores via evaporative pumping
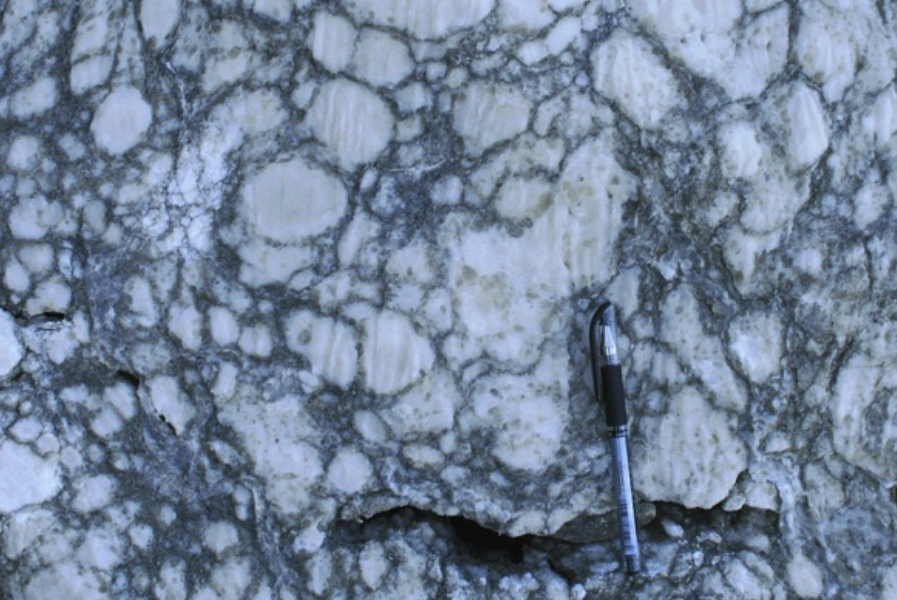

Chicken wire gypsum
50% / 84% / 90% / 96% marine water evaporated precipitates
50%: carbonates
84%: gypsum
90%: halite
96%: sylvite
Brine Reflux Model
repeated influx of sea water of evaporating basin allows evaporite thickening
brines formed sink / move below
Evaporite Facies
K + Mg Salts in Sabkha
Halite
Halite (during higher salinity) and Anhydrite (during lower salinity)
Anhydrite
Carbonates
Organic rich sediments (where anoxic organic rich shale forms)
Salt Lake vs Bitter Lake
Salt Lake: Halite
Bitter: Sodium Carbonate and Sulfates
Banded Iron Formation Process
Archean waters full of Fe2+ of SiO2 → chert continuously precipitated
Green sulfur photosynthesis results in oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+
Increase in stromatolites/cyanobacteria causes excess in oxygen, oxygenated waters drives green sulfur bacteria deeper until photosynthesis is impossible (2.4 Ga)
Post GOE - sulfidic ocean forms from hydrogen sulfide produced on land washing into oceans and generates in pyrite in oceans instead of iron minerals (occurred around 1.84 Ga)
Hyaloclastites
When volcanic eruptions interact with water
Eustatic (Global) Sea Level Change
glacial control on sea
spreading ridge volume (faster the spread, more sea level rise)
Local Sea Level Change
crustal deformation
convergence causes relative sea level fall
isostatic changes (crustal decompression)