Biol 204 Exam 1 lecture 1
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
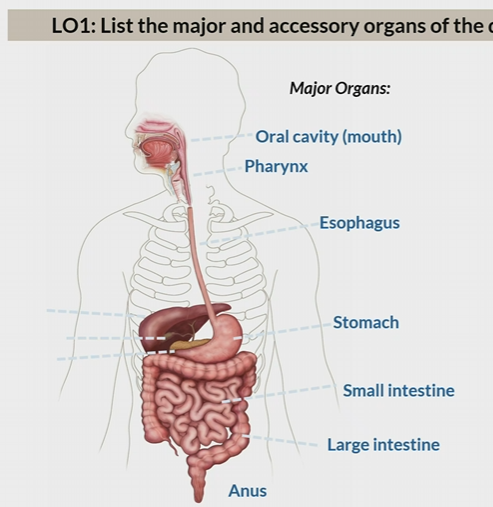
Major organs of the digestive system
Oral cavity
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
anus
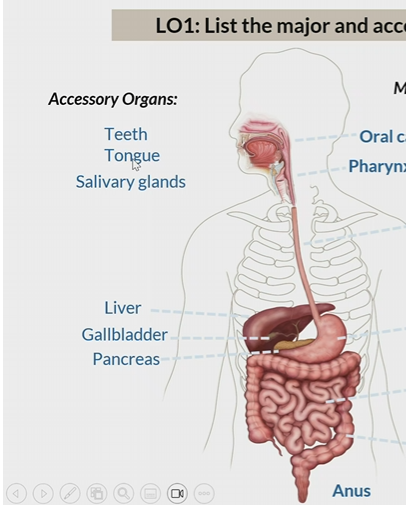
Acessory organs of digestive system
Teeth
tongue
salivary glands
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
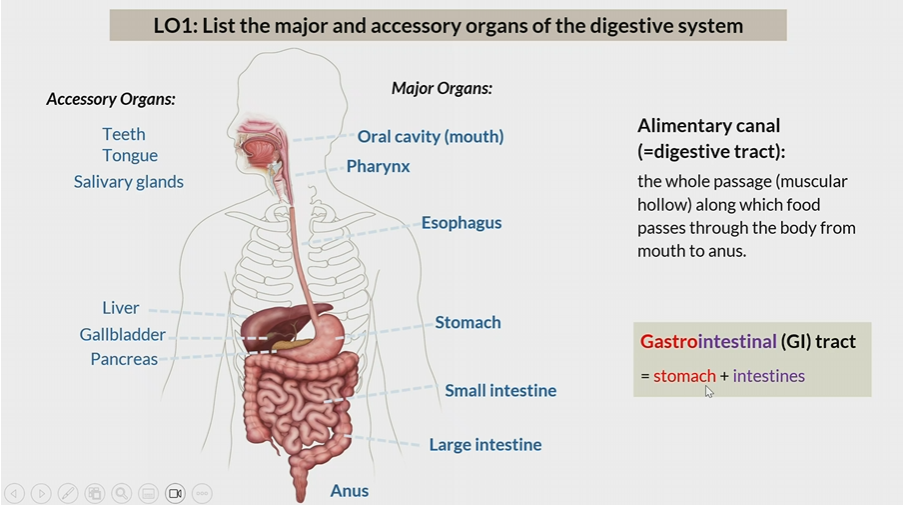
alimentary canal
same thing as digestive tract
whole passage from which food moves from mouth to anus
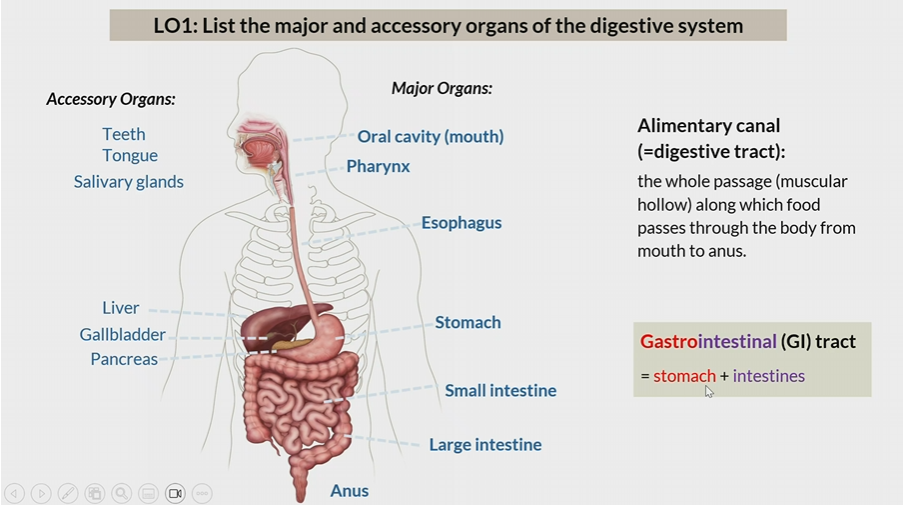
Gastrointestinal tracts
Stomach + intestines
ingestion
intake of food
propulsion
movement of bolus through swallowing or peristalsis
Mechanical digestion
physical breakdown of food (mastication / muscular contractions )
Chemical digestion
physical breakdown of food with enzymes/ acids
Absorption
uptake of nutrient molecules
(villi help intestine absorb important nutrients)
Compaction
absorbing water and consolidating the residue into feces
Defecation
elimination of feces
Physiological processes of the digestive system
ingestion
propulsion
mechanical digestion
chemical digestion
absorption
compaction
defactation
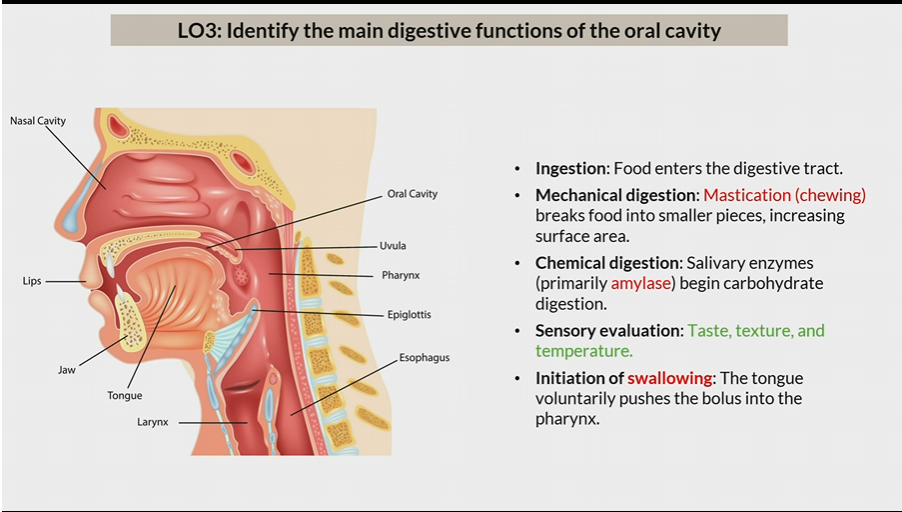
Digestive functions of oral cavity
ingestion: food enters the digestive tract
mechanical digestion: mastication
Chemical digestion: salivary enzymes
Sensory evaluation: Taste, texture, and temperature
Initiation of swallowing: Tongue pushes bolus into the pharynx
amylase
salivary enzyme that begin carb digestion
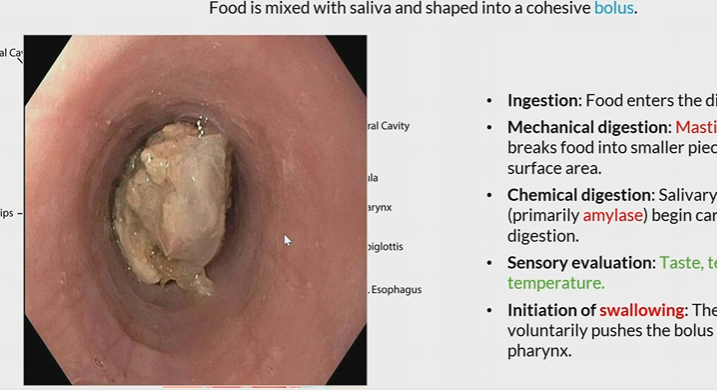
Bolus
food ball mixed with saliva
How much teeth are in each part of the Jaw
16
Incisor
blade shaped located in the front of the tooth, used for clipping or cutting
1 root
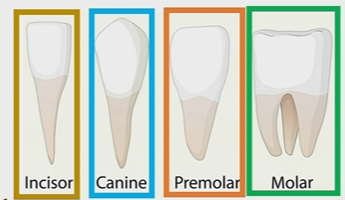
canine
Cuspids
pointed for puncturing and shredding
1 root
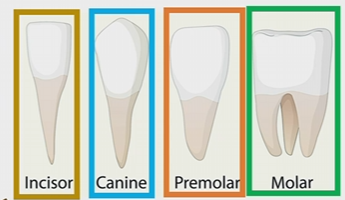
Premolar
1-2 roots
broad and lumpy for crushing shredding and grinding
molar
2-3 roots
broad and lumpy for crushing shredding and grinding
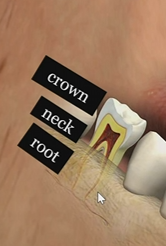
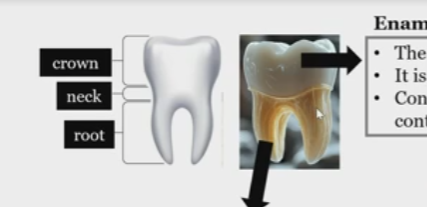
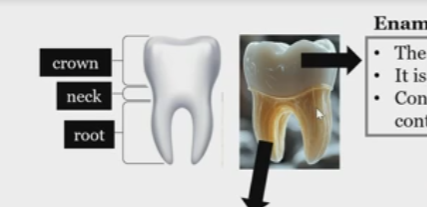
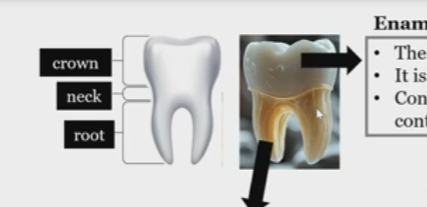
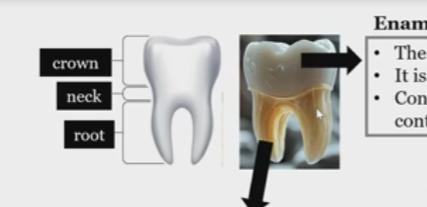
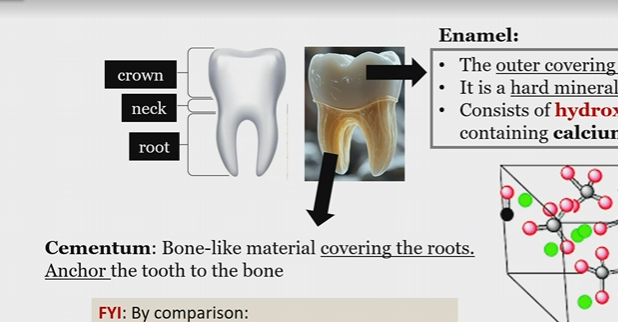
Crown
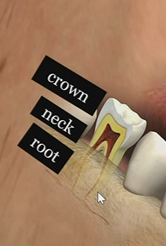
neck
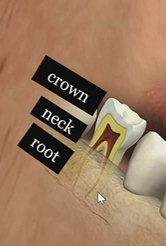
root
Root canal
passageway for blood vessels and nerves to the pulp cavity
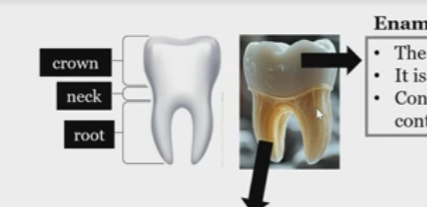
Enamel
hard coating of the crown, non living, made of hydroxyapatite crystals
hydroxyapatite crystals
make up enamel
contain calcium and phosphate
what are hydroxyapatite crystals made of
in enamel
calcium and phosphate
is the enamel living tissue?
false
cementum
Bone like material covering the roots that anchor the tooth to the bone
Dentin
yellowish tissue that makes up the bulk of teeth
offers strong support to enamel due to elasticity
% hydroxyapatite in dentin
70
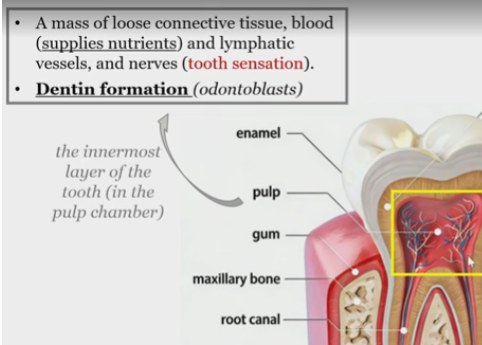
Pulp
mass of loose connective tissue,
blood
lymphatic vessels
and nerves
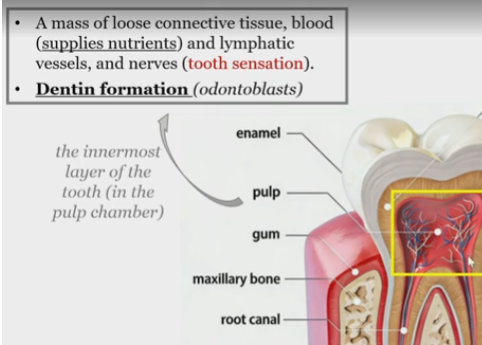
Pulp function
tooth sensation
dentin formation
Odontoblasts
cell bodies responsible for dentin formation
in pulp, odontoblast process into the dentin
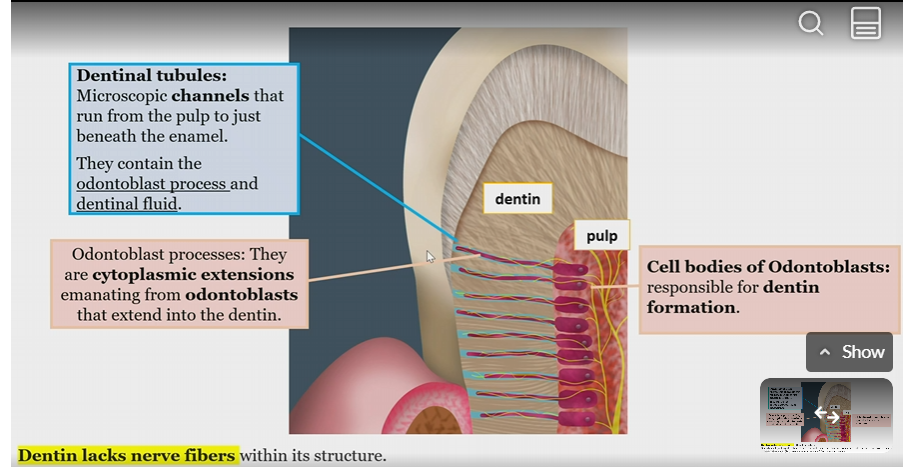
dentinal tubules
contain odontoblast process and dentinal fluid
channels that run from pulp to beneath the enamel
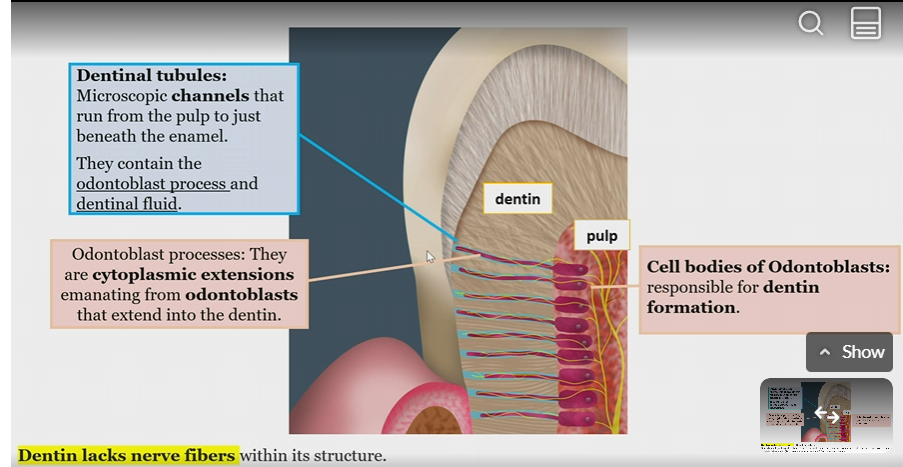
Odontoblast processes
cytoplasmic extensions emanating from odontoblasts extending into dentin
Does dentin have never fibers?
no
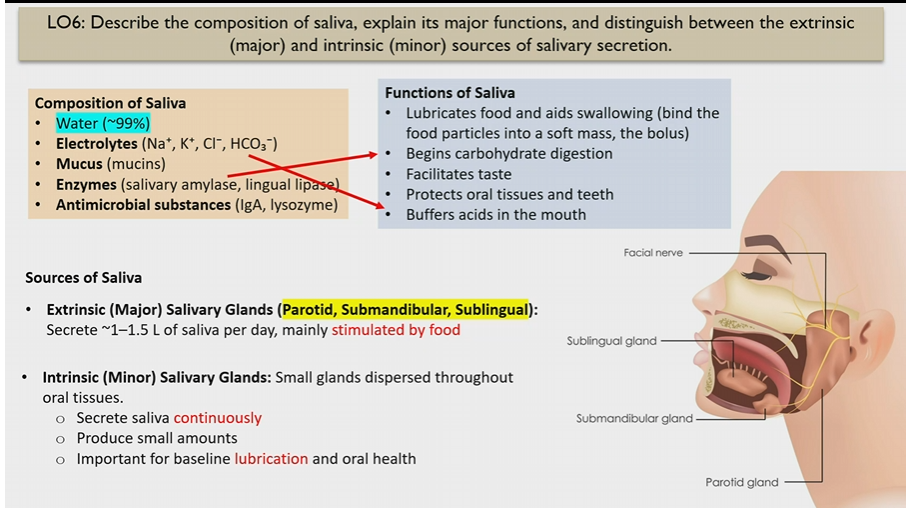
Extrinsic Salivary glands
Major glands
parotid, submandibular, sublingual
stimulated by food
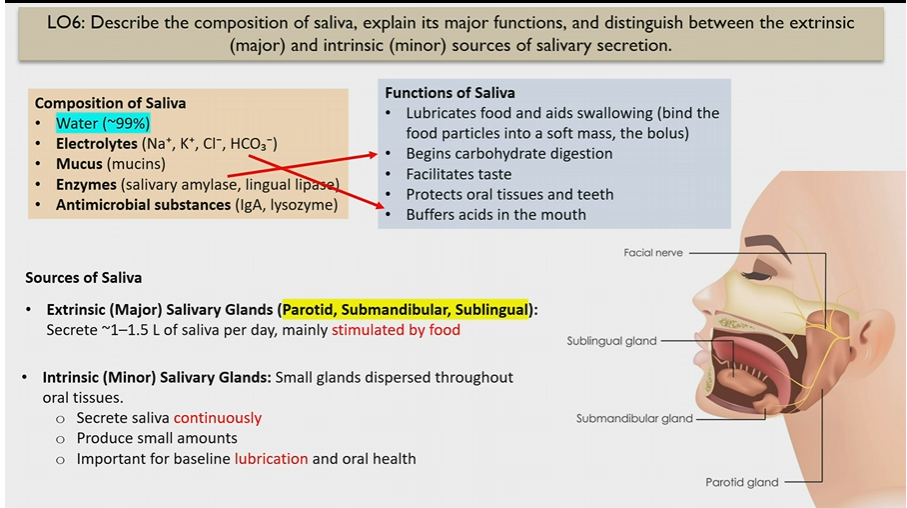
How much saliva do Extrinsic Salivary glands make
1-1.5 L of saliva, stimulated by food
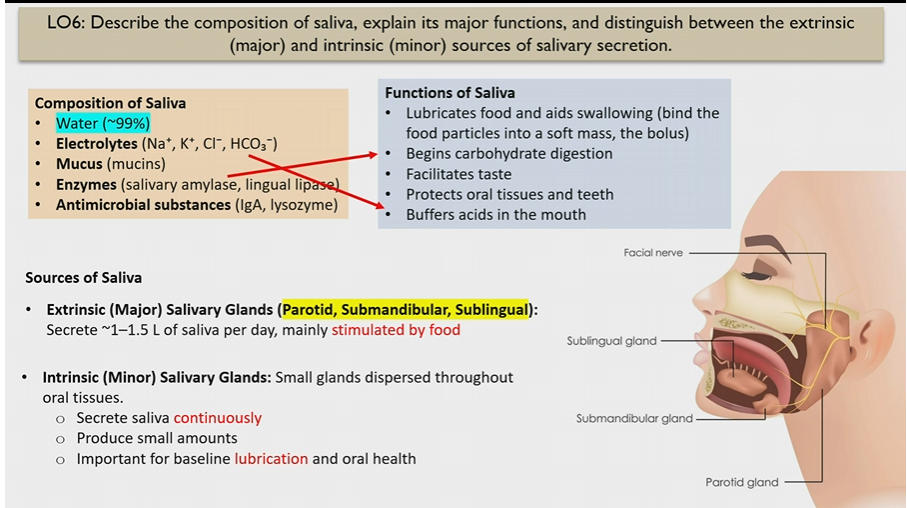
Intrinsic Salivary glands
small glands dispersed through oral tissues
secrete saliva continuously in small amounts
for lubrication and oral health
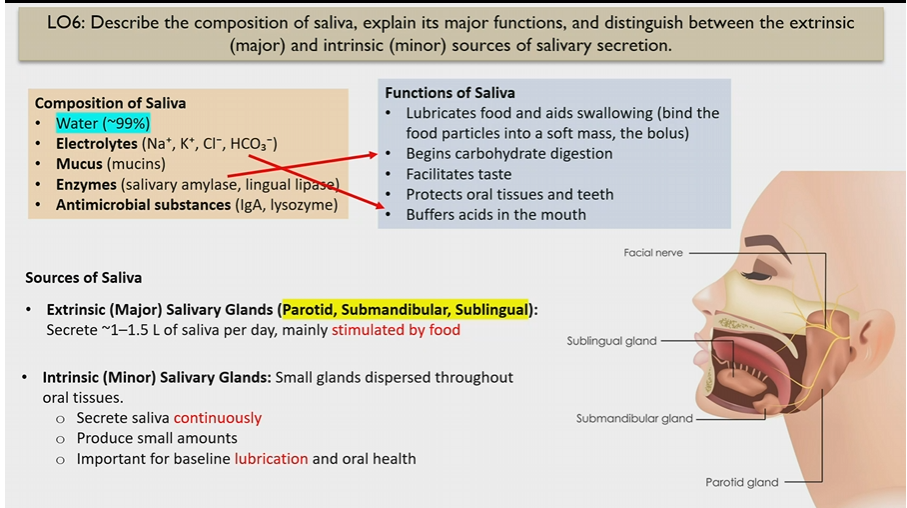
Composition of saliva
Water
electrolytes (buffer saliva)
mucus
enzymes (begin carb digestion)
antimicrobial substances
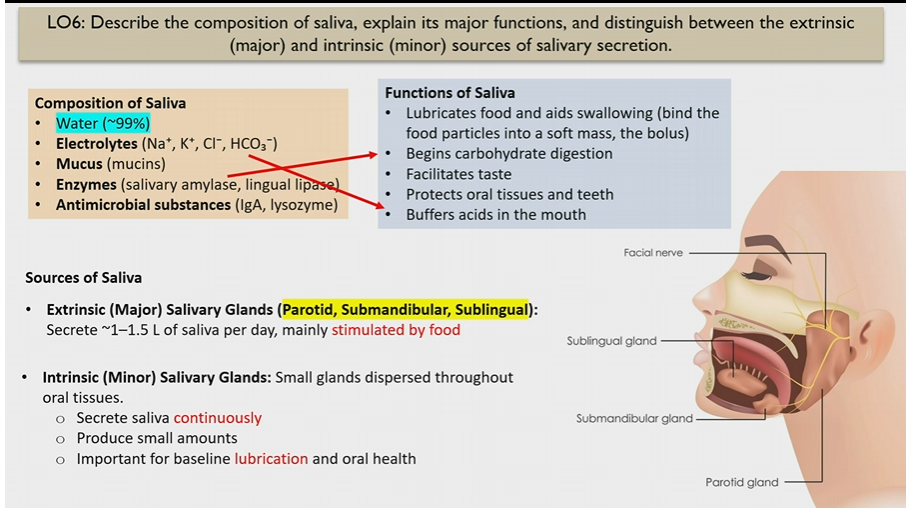
Functions of saliva
Lubricates food and helps to swallow
begins carb digestion
facilitates taste
protects oral tissues and teeth
buffers acids in moth
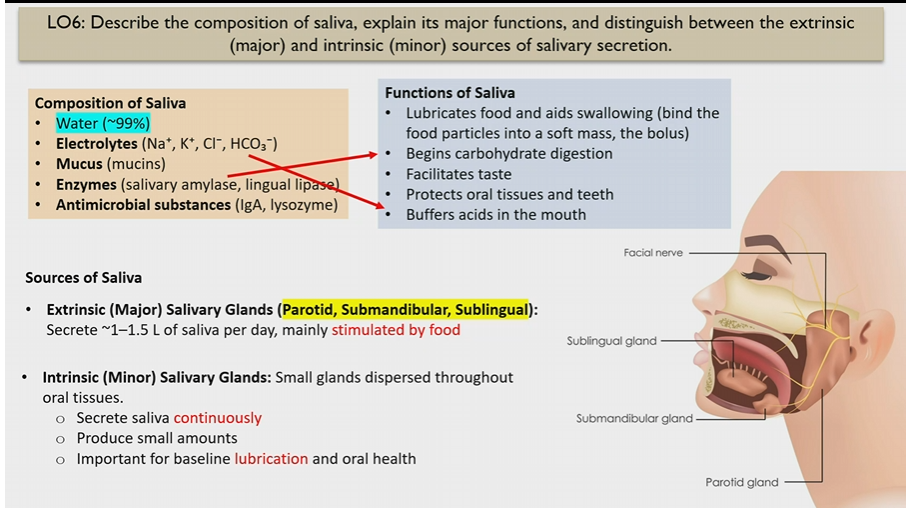
Electrolytes in saliva
Na+ K+ Cl- HCO3-
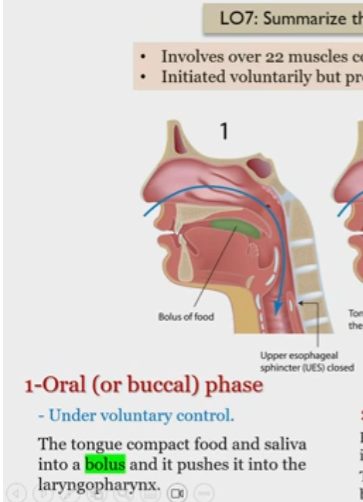
Deglutition
Mechanism of swallowing involving 22 muscles coordinated by the swallowing center
Proce
Deglutition phases
oral
pharyngeal
e
Oral Deglutition phase
Under voluntary control
tongue compacts food and saliva into a bolus, pushes it into laryngopharynx
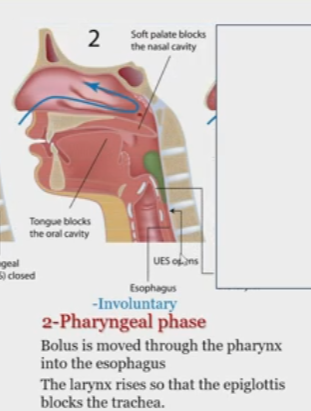
Pharyngeal Deglutition phase
Bolus moved through the pharynx into the esophagus
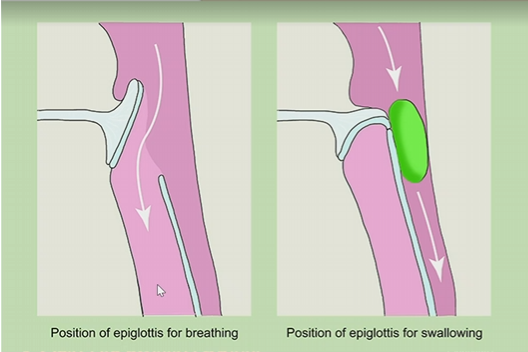
larynx rises so epiglottis blocks the trachea
Epiglottis during pharyngeal phase
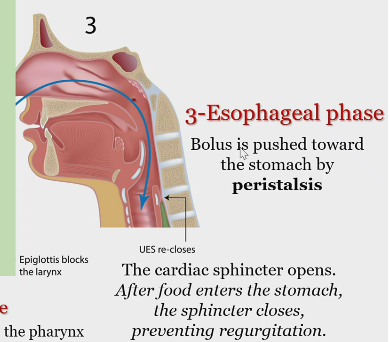
Esophageal phase
Bolus pushed down toward stomach by peristalsis
Cardiac sphincter opens after food enters the stomach, the sphincter closes, which prevents regurgitation.
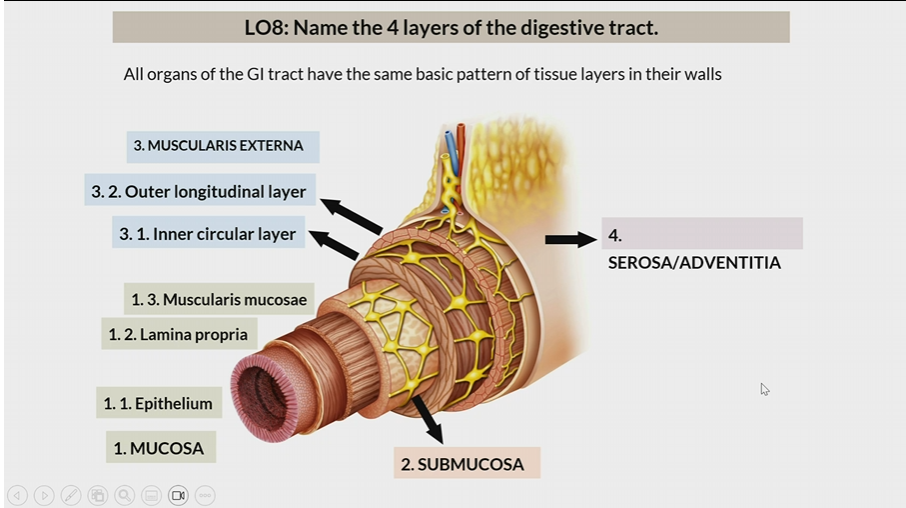
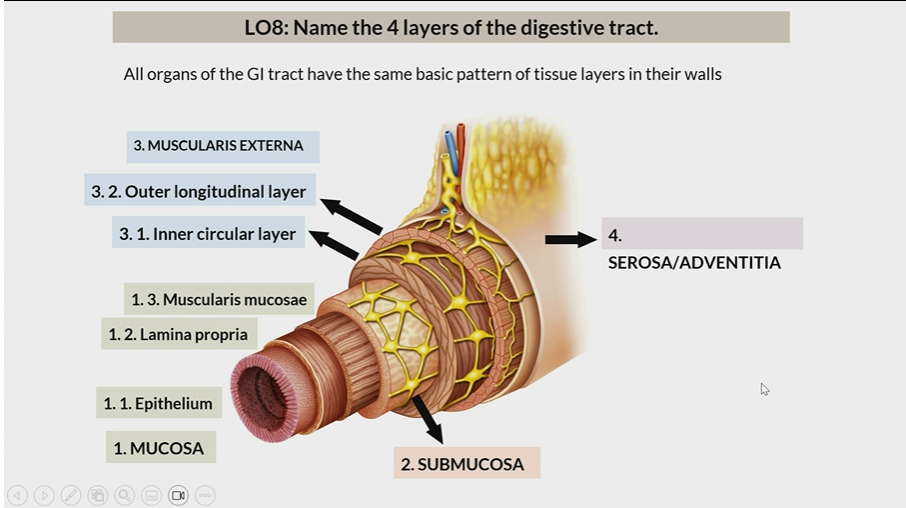
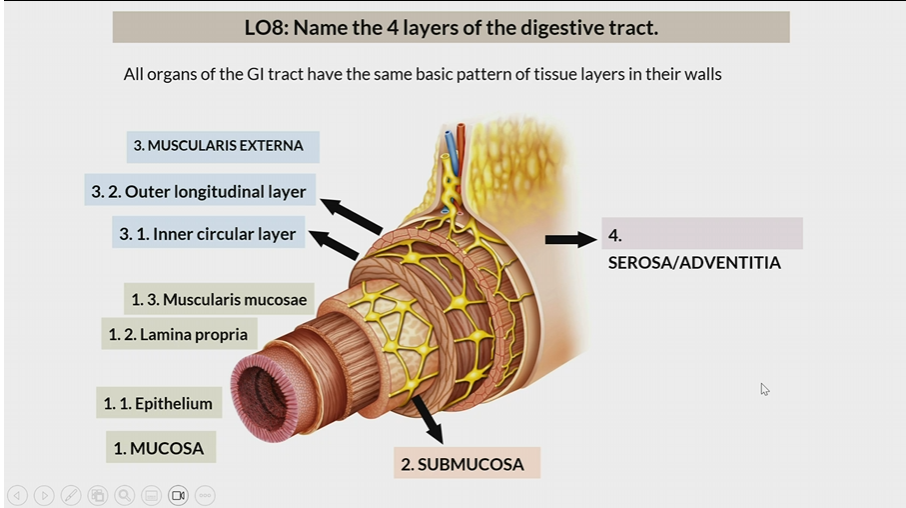
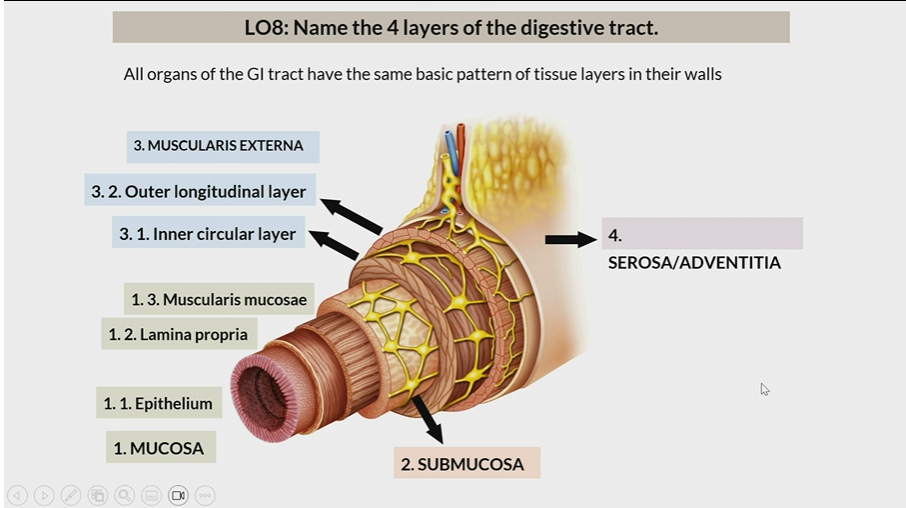
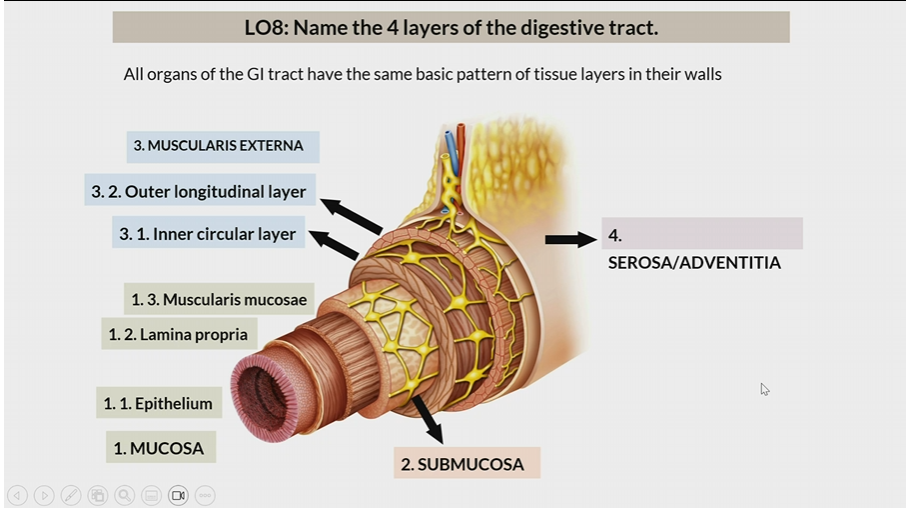
4 layers of digestive tract
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis Externa
Serosa/Adventitia
All organs have the same basic pattern of tissue layers in their walls
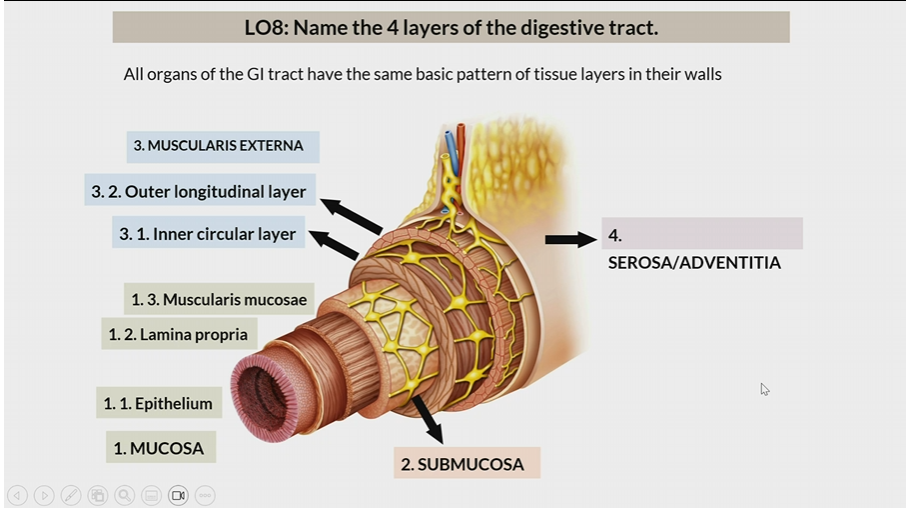
Mucosa
One of the 4 layers of the digestive tract
1st layer
Consists of
epithelium
lamina propia
muscularis mucosae
Submucosa
One of the 4 layers of the digestive tract
2nd layer
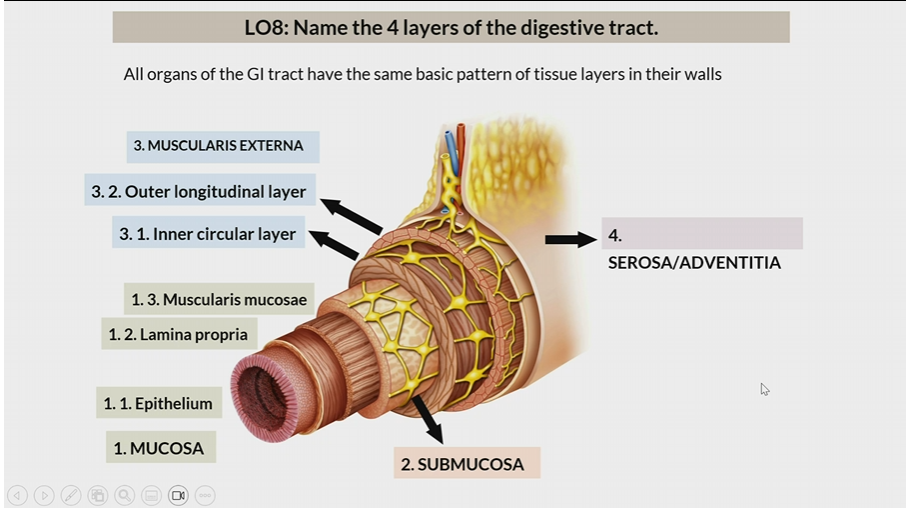
Muscularis Externa
One of the 4 layers of the digestive tract
3rd layer
inner circular later
outer longitudinal layer
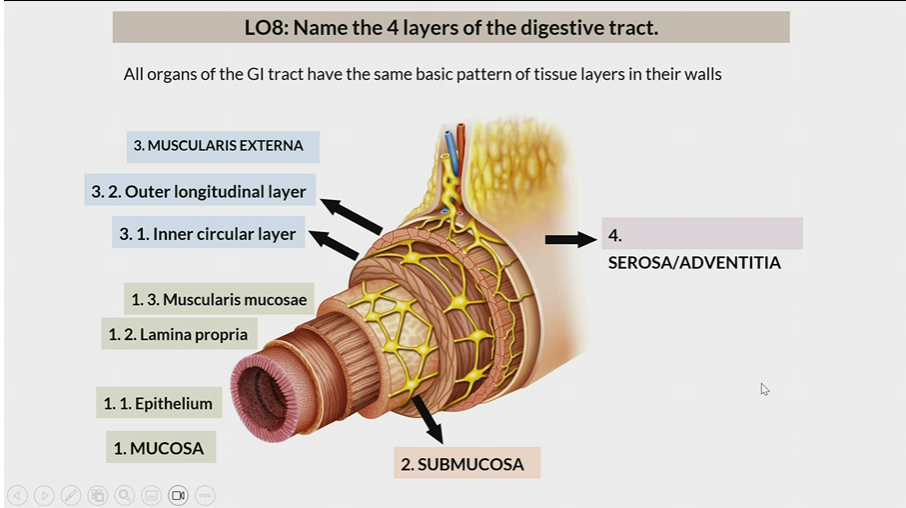
Serosa / Adventitia
One of the 4 layers of the digestive tract
4th later
Serosa : organs inside peritoneal cavity
Adventitia: organs outside the peritoneal cavity
epithelium
In mucosa, the 1st layer
lamina propia
In mucosa, the 2nd layer
muscularis mucosae
In mucosa, the 3rd layer
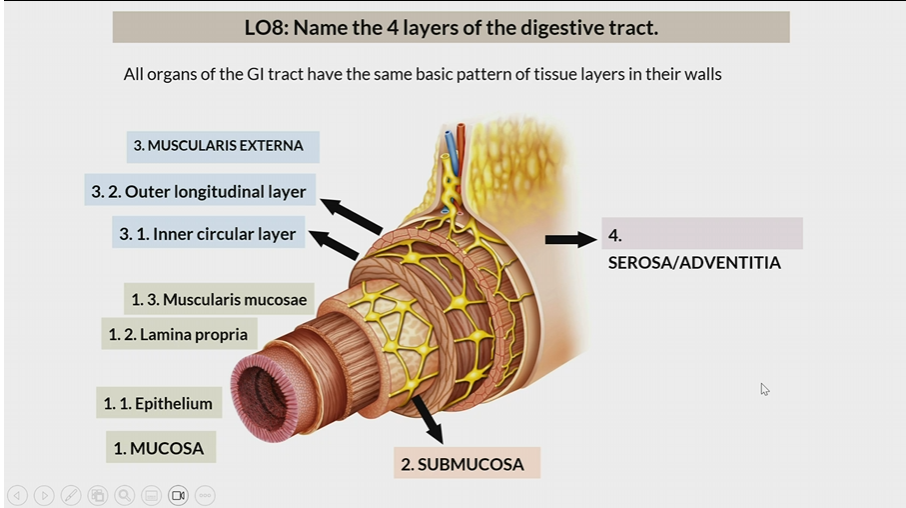
inner circular layer
In muscularis externa, the 1st layer
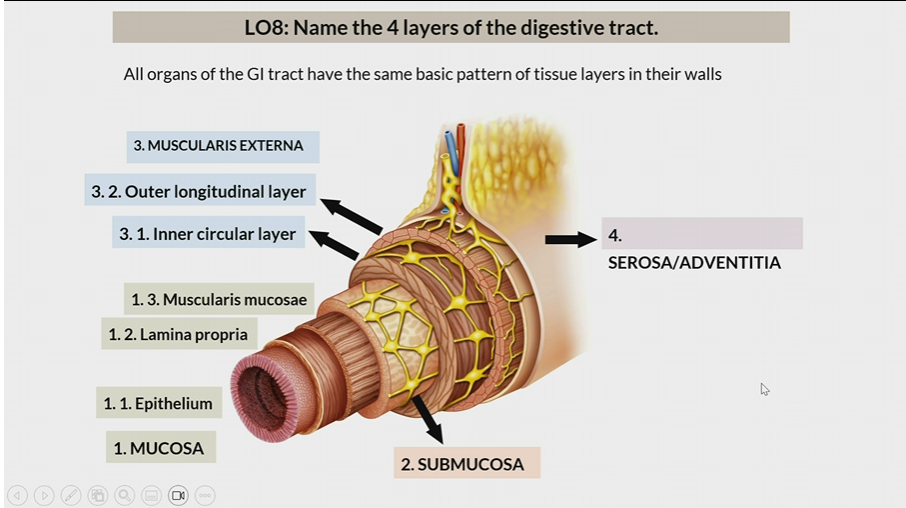
outer longitudinal layer
In muscularis externa, the 2nd layer
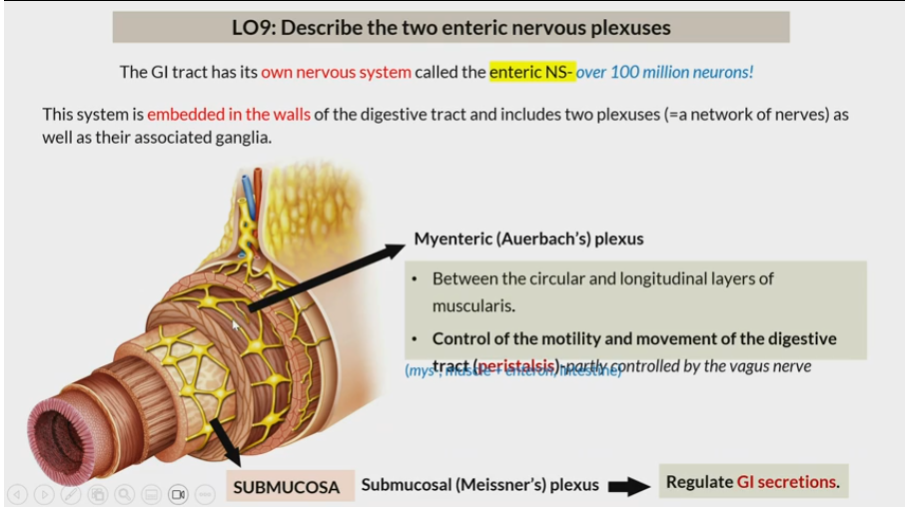
Enteric NS
NS of GI tract
embedded in walls of the digestive and includes two plexuses (network of nerves) as well as their associated ganglia
Myenteric (auerbach’s) plexus
Between circular and longitude layers of muscularis
Control of motility and movement of digestive tract (peristalsis)
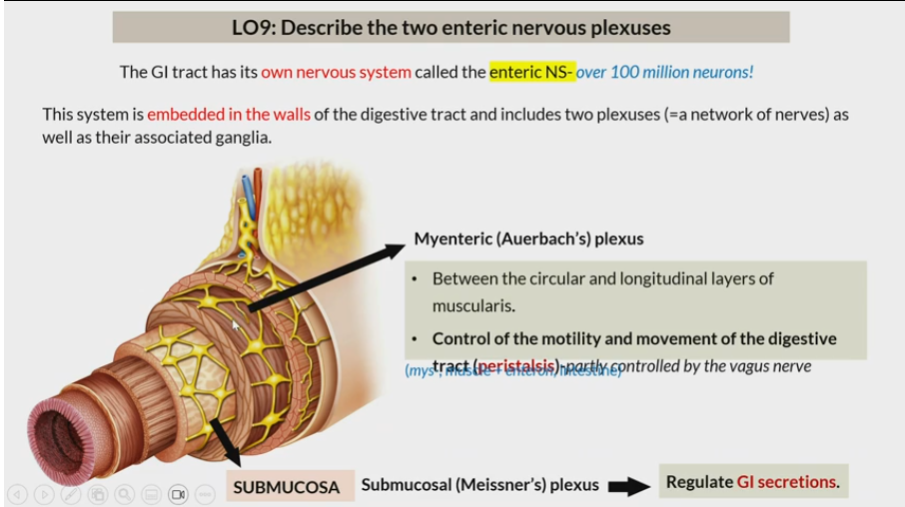
submucosal (Meissner’s) plexus
in submucosa
regulate GI secretions
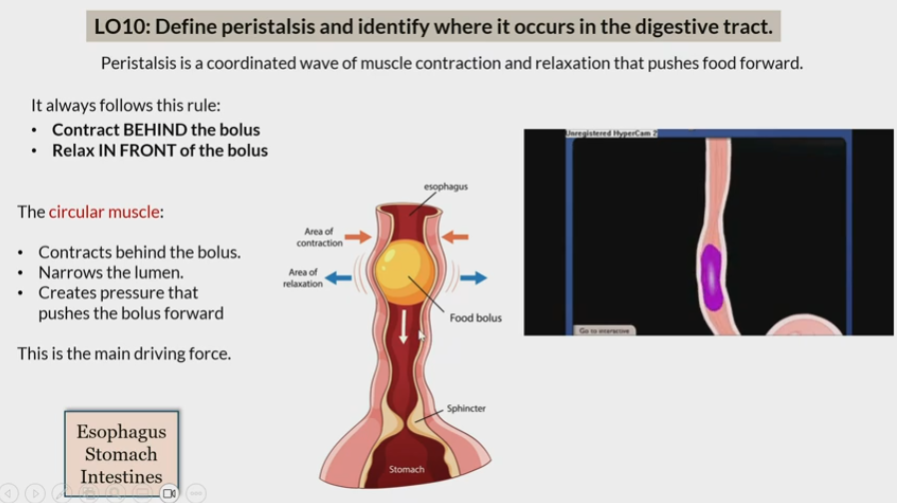
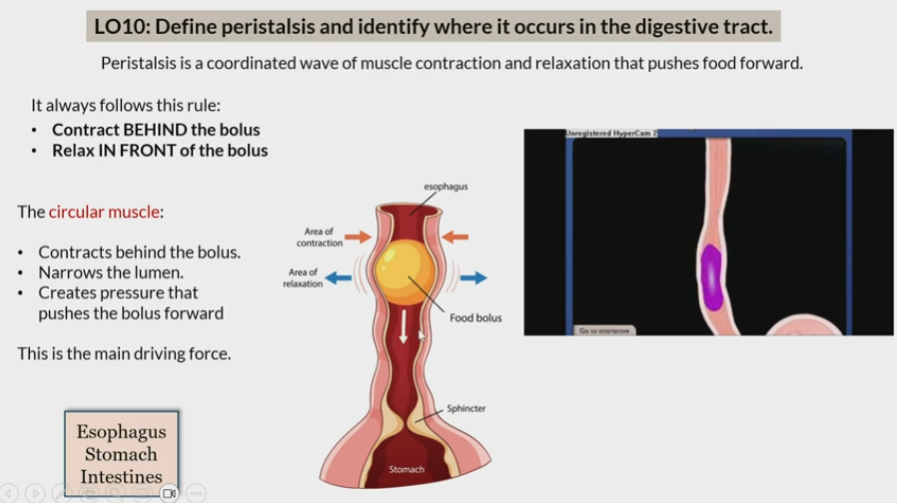
Peristalsis
Coordinated wave of muscle contraction and relaxation that pushes food forward
In esophagus
stomach
intestine
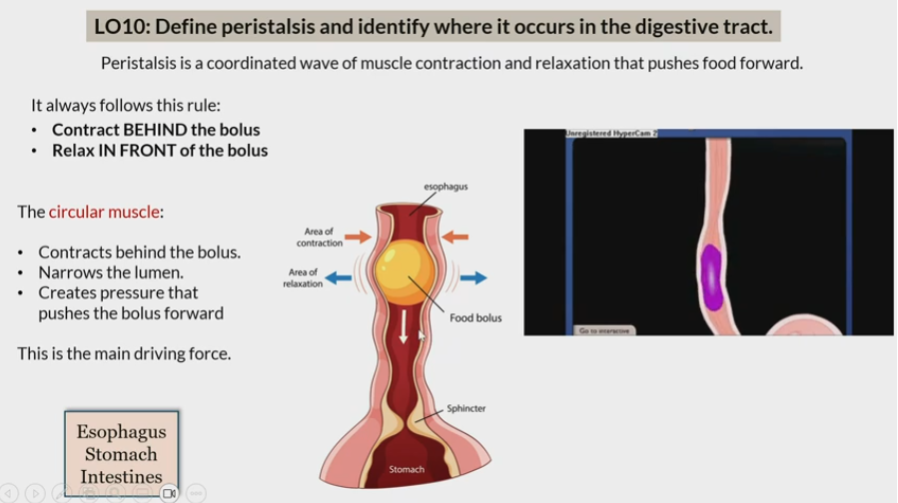
Rule of peristalsis
contract behind bolus
relax in front of bolus
Where does peristalsis happen
esophagus
stomach
intestine
long reflex
central loop
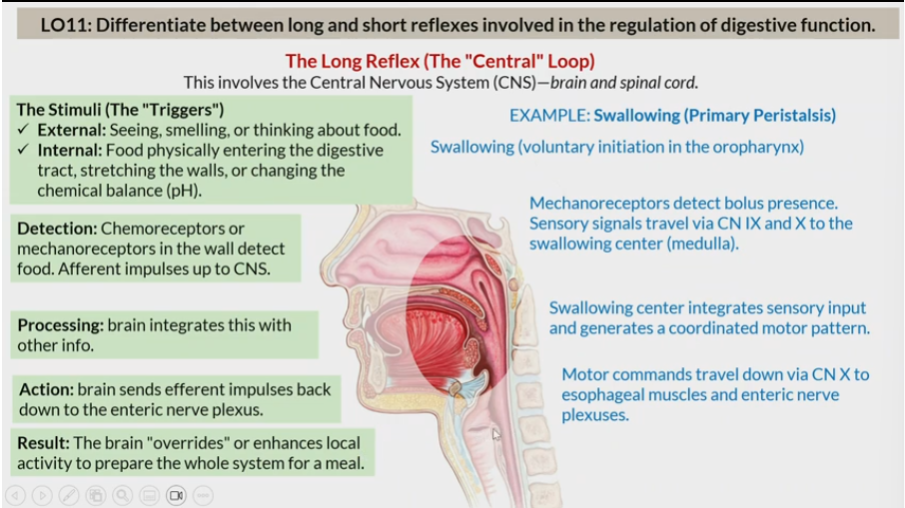
Short reflex
local loop
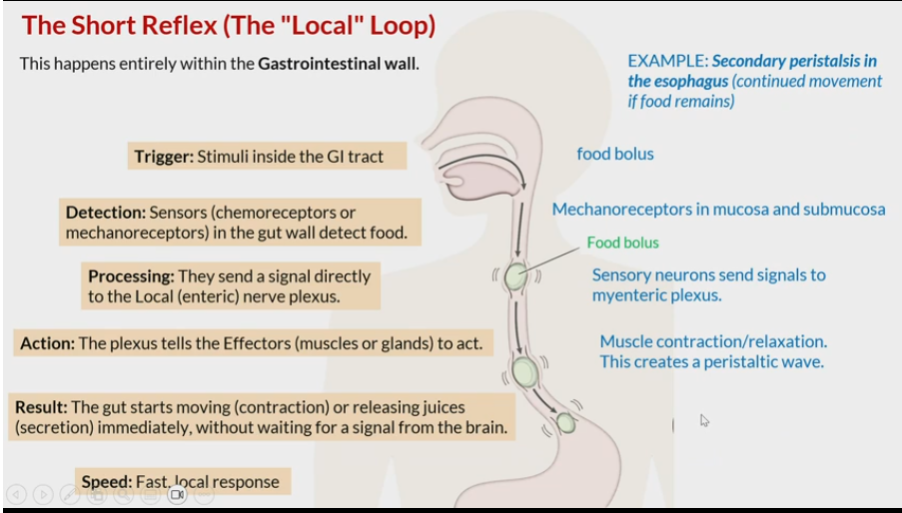
Saliva is composed of approximately 99%
water
electrolytes found in saliva
sodium, potassium, chloride, Bicarbonate
The glycoproteins responsible for the viscous quality of saliva are called
mucins
The enzyme that begins carbohydrate digestion in the mouth
salivary amylase
Saliva contains antimicrobial substances such as
immunoglobulin A, lysozymes
what is deglutition regulated by?
the medulla