Linear Motion
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What are all the suvat equations?
v = u + at
s = ut + 1/2at²
s = 1/2(u+v)t
v²=u²+2as
s = displacement, m
u = initial velocity, ms^-1
v = final velocity, ms^-1
a = acceleration, ms^-2
t = time, s
What graph are all suvat equations derived from?
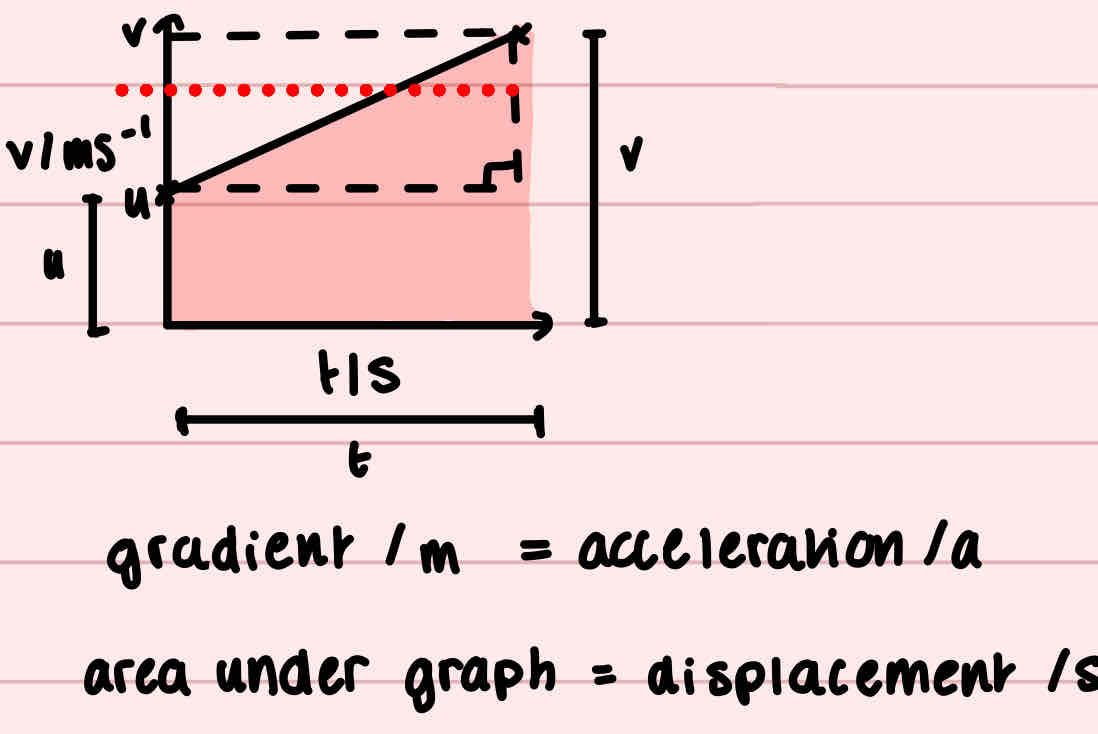
This velocity time graph
How is the equation without s derived?
Gradient
a = Δv / Δt = v - u / t, xt, +u
v = u + at
How is the equation without v derived?
Area under graph (rectangle and triangle)
Rectangle area = ut
Triangle area = ½ (v-u)t
v = u + at
s = ut + ½ at²
How is the equation without a derived?
Area under graph (trapezium)
½ (a+b)h
½ (u+v)t
How is the equation without t derived?
t = (v - u) / a
s = ½ (v+u) x (v - u) / a x2a
2as = (v+u)(v-u)
v² = u² +2as
What is the acceleration of freefall when an object is falling?
9.81ms^-2
What is the acceleration of freefall/g when an object is rising?
-9.81ms^-2
Describe how to determine the acceleration of freefall
We use a trapdoor and electromagnet/light gates, a steel ball bearing and a data logger.
1) A displacement between the trapdoor and electromagnet/light gates is measured with a metre ruler.
2) The steel ball bearing is dropped from rest. We record the time taken for the ball to travel the entire displacement measured on the data logger. This is repeated 3 times to calculate a mean time for this displacement. We repeat the entire process at regular decreasing displacement intervals.
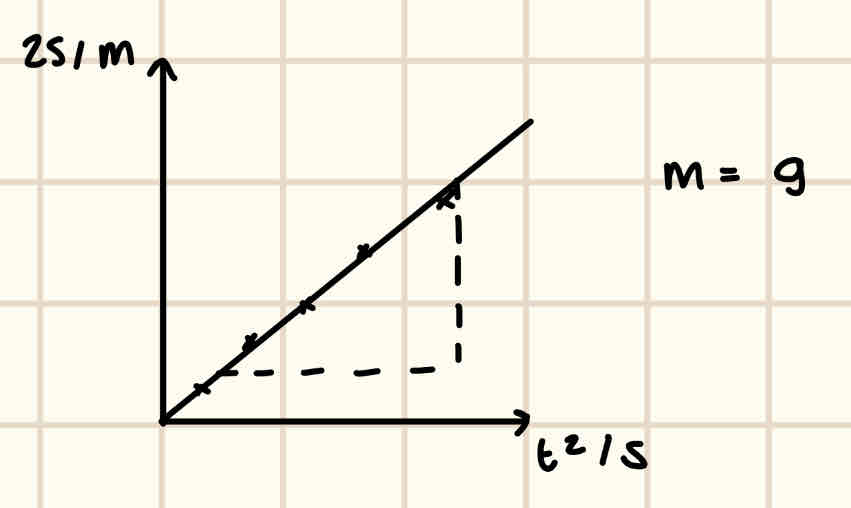
3) We rearrange s = ut + ½ at² to have it in the form y = mx + c where a = g since there’s no external forces acting on the bearing and u = 0 since it’s dropped from rest. We get, 2s = gt².
4) This is the graph:
We draw a line of best fit and the gradient of this line will equal g, m =g