Generations of Computing and Key Contributors
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the four generations of computing classified by?
The salient technology of the era.
What is Generation Zero in the history of computing?
Mechanical Calculating Machines (1642 - 1945).
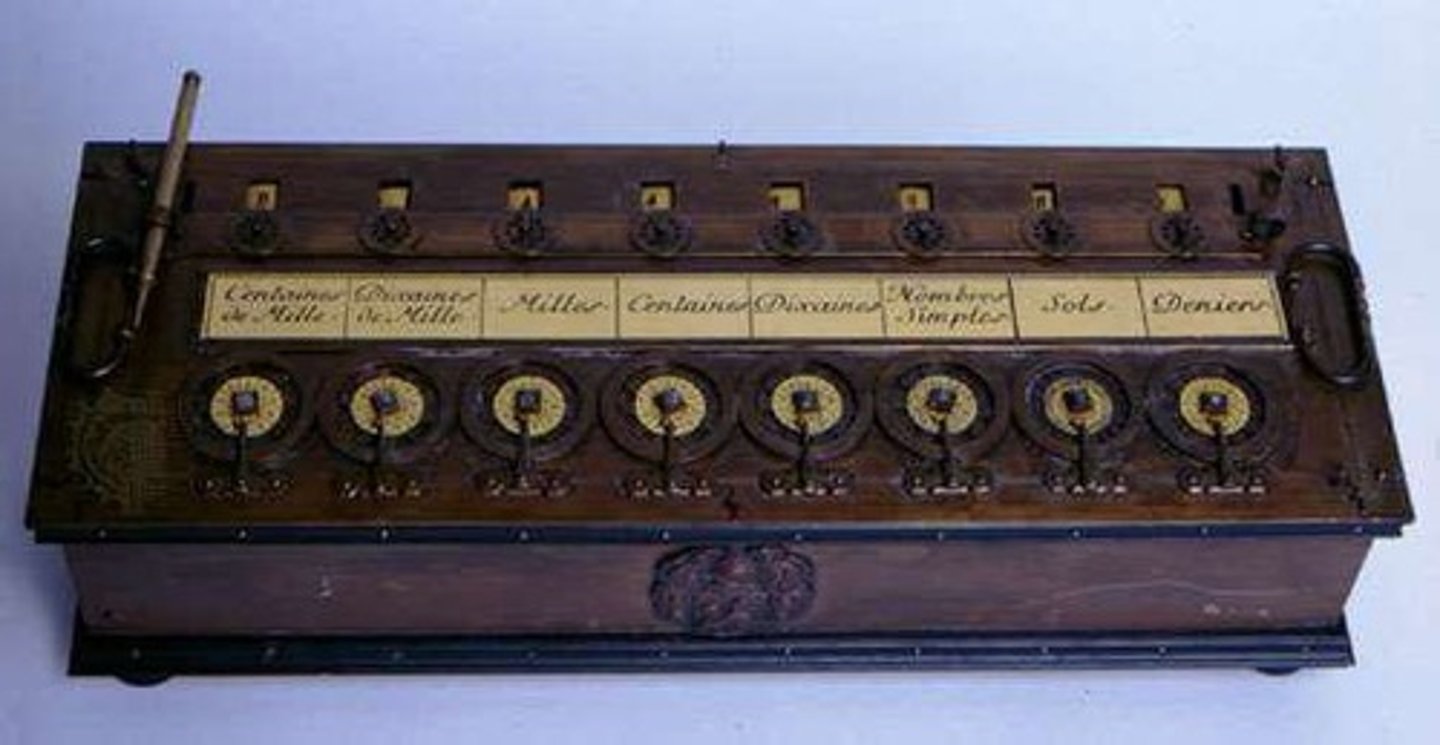

Who invented the Calculating Clock?
Wilhelm Schickard.
What was the Pascaline and who created it?
A mechanical calculator that could add and subtract, created by Blaise Pascal.
What is the Difference Engine and who designed it?
A mechanical calculating machine designed by Charles Babbage.
What was the purpose of the punched card tabulating machines developed by Herman Hollerith?
They were used for computer input, especially for the Census.
Who is considered the first computer programmer?
Ada Lovelace.

What significant computer was developed between 1945 and 1953?
The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), the first general-purpose computer.
What is the significance of the Atanasoff Berry Computer (ABC)?
It solved systems of linear equations and was developed by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry.
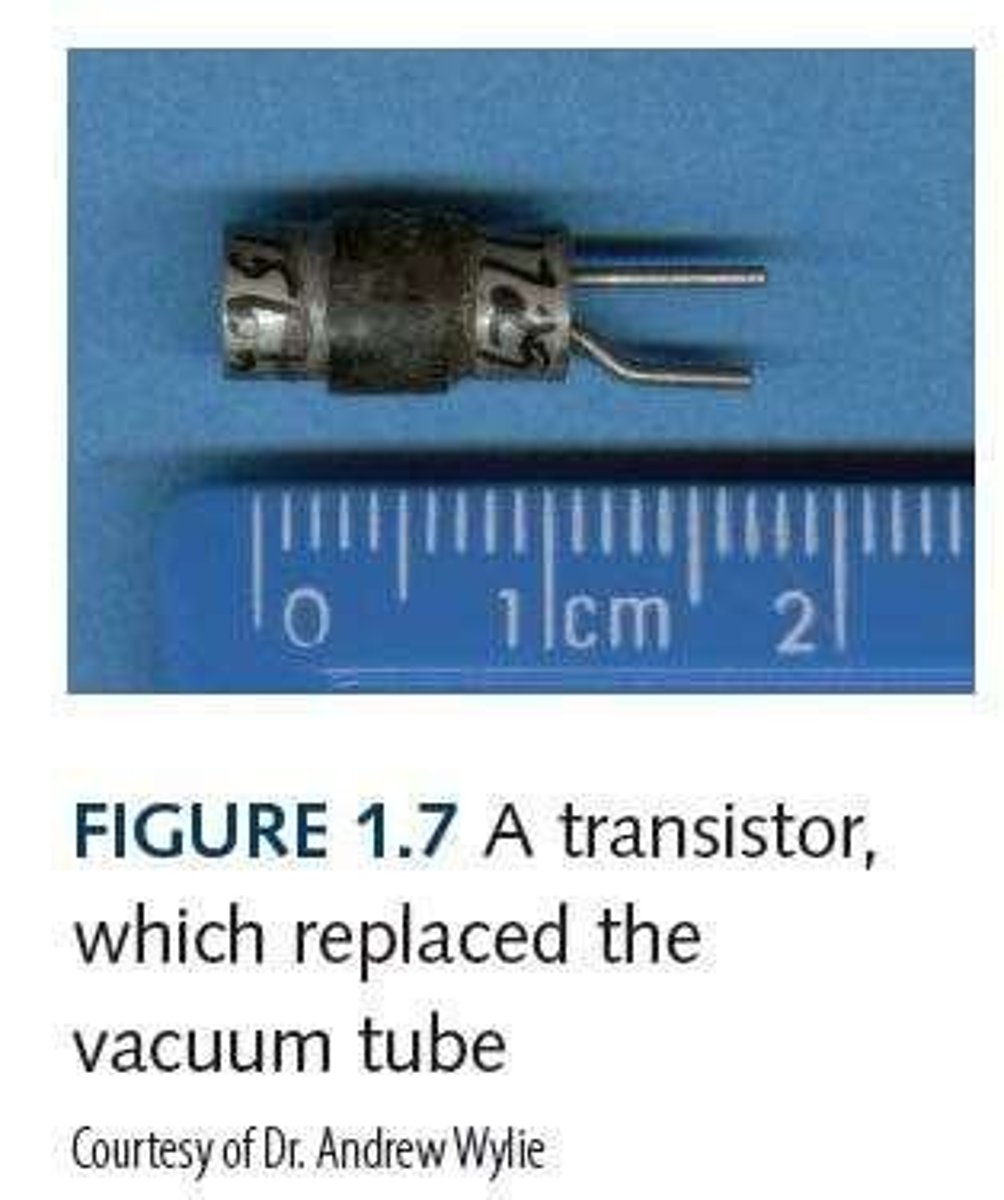
What replaced vacuum tubes in the second generation of computers?
Transistors.
What are magnetic cores and how did they change data storage?
They replaced magnetic drums, allowing information to be available instantly.
What characterizes the third generation of computers?
The use of integrated circuits, which replaced circuit boards and made computers smaller, cheaper, and faster.
What was the IBM 360 and its significance?
A dominant mainframe computer in the third generation that exemplified the era's technology.
What does VLSI stand for and what is its importance?
Very Large Scale Integration, which enabled the creation of microprocessors.
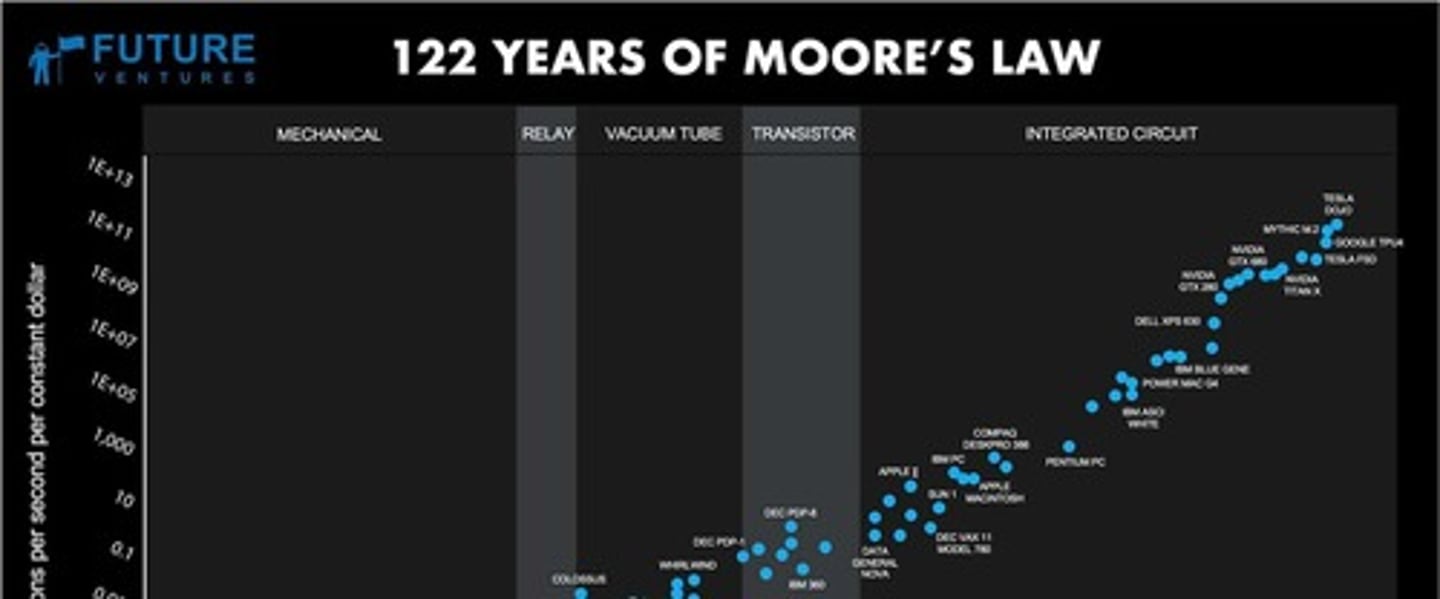
What is Moore's Law?
The observation that the density of transistors in an integrated circuit will double approximately every two years.
What is Rock's Law?
The assertion that the cost of capital equipment to build semiconductors will double every four years.
How does Moore's Law relate to Rock's Law?
For Moore's Law to hold, Rock's Law must fall, or vice versa.
What was the first microprocessor and when was it created?
The 4-bit Intel 4004.
What was the impact of the IBM 7094 in computing history?
It was a significant scientific computer in the second generation.
What technological advancement allowed personal computers to emerge?
The development of very large scale integrated circuits (VLSI).
What role did Ada Lovelace play in computing history?
She is recognized as the first computer programmer.
What was the significance of the Cray-1 supercomputer?
It was a notable example of a supercomputer in the third generation.
What are some examples of companies that emerged with the personal computer market?
Apple, Sun, Dell.
What is the relationship between the cost of chip plants and Rock's Law?
The cost of constructing chip plants has increased significantly, illustrating Rock's Law.
What does the term 'Turing completeness' refer to?
A concept developed by Alan Turing that defines a system capable of performing any computation.
What is the importance of stored-program computers?
They allow computers to store instructions in memory, enabling more complex operations.
What is a terminal in computing?
An input/output device with a keyboard and screen.