Biology IGCSE - Transport in Plants
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
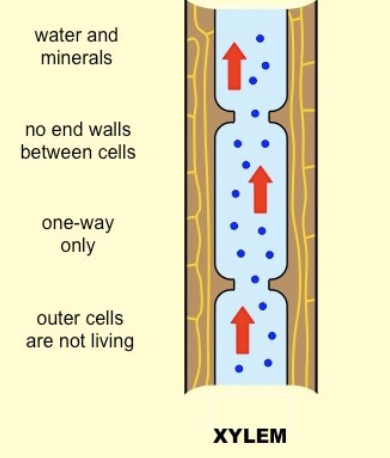
Xylem
transport water and dissolved minerals from the root up to leaves → helps supporting stem
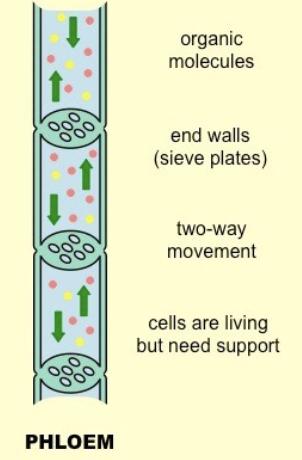
Phloem
transport food nutrients (sucrose and amino acids) from the leaves and to leaves (source to sink) → called translocation
Differences between xylem and phloem
Xylem | Phloem |
|
|
Vascular bundles
Group of xylem and phloem vessels found closely together
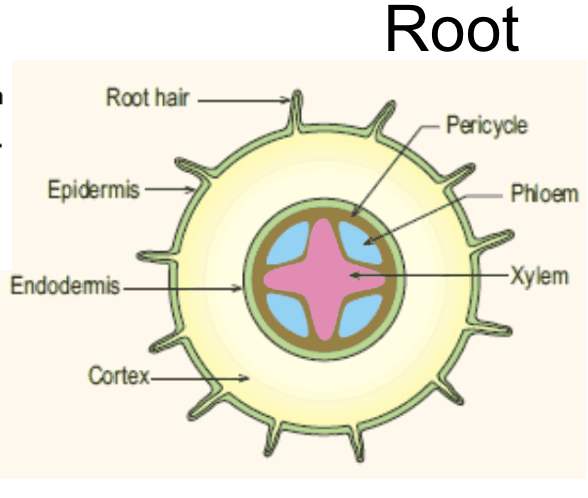
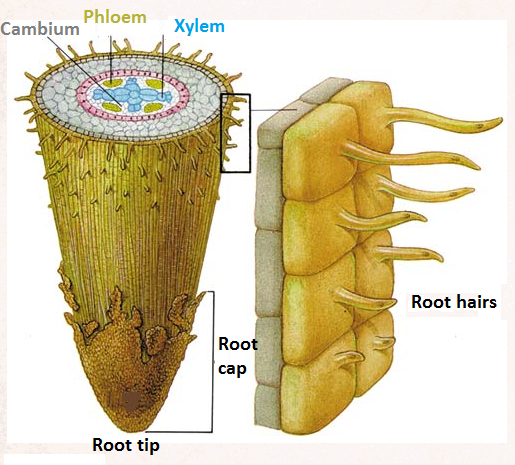
Position of xylem and phloem in roots
Position of xylem and phloem in stems
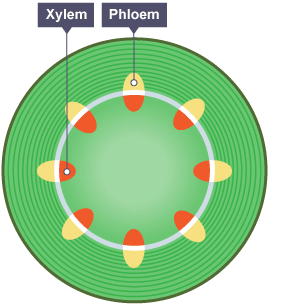
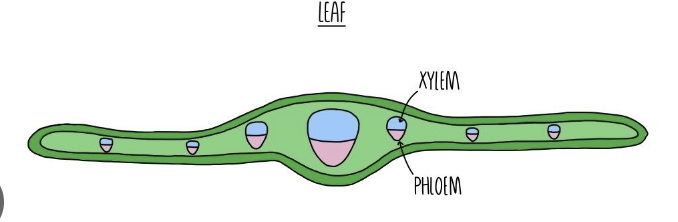
Position of xylem and phloem in leaves
Root hair cell diagram
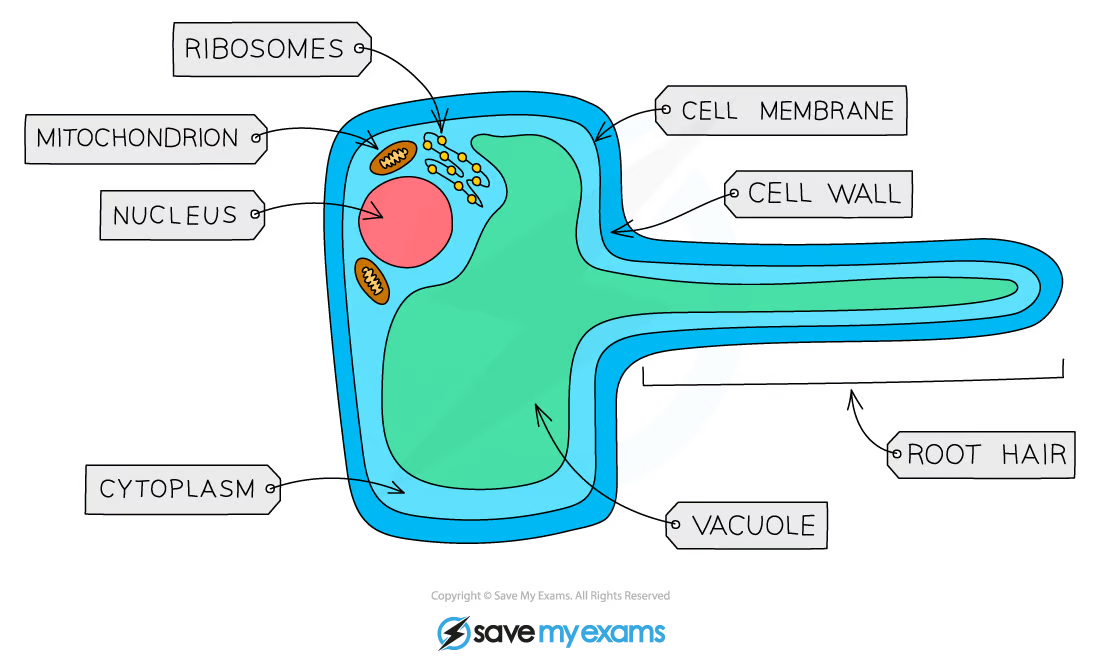
Root hair cell functions
Roots are covered in many root hair cells that have root hairs to increase surface area
Root hair cells contain lots of mitochondria to provide energy for active transport
The cell membranes of root hair cells have lots of carrier proteins for active transport
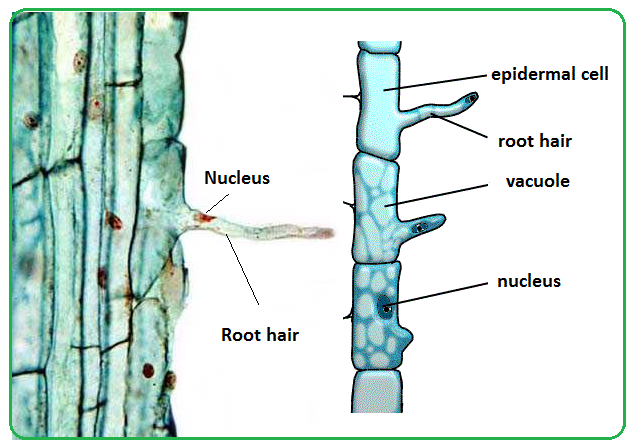
Root hair cell adaptations
large surface area
thin/permeable
Surface areas of root hair cells
large surface area of root hairs increases the uptake of water and mineral ions
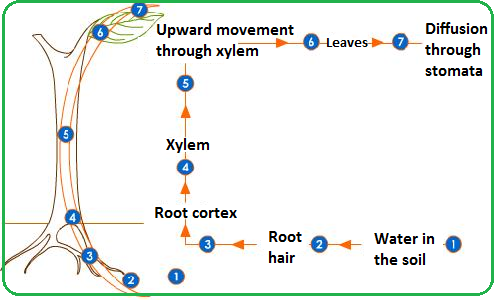
Pathway taken by water through root, stem and leaf as: root hair cells, root cortex cells, xylem, mesophyll cells
Transpiration
the loss of water vapour from plant leaves by evaporation of water at the surfaces of the mesophyll cells followed by diffusion of water vapour through the stomata.
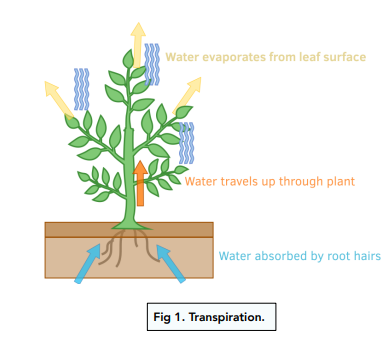
How water and minerals ions are moved from the roots to the leaves in the plants via transpiration
Water will travel down its concentration gradient, towards the root cortex. Excessive water loss in the leaves cause it to have lower water potential compared to the root cortex. As a result, water and mineral ions will move down its concentration gradient to the xylem. Finally, it will reach the leaves to compensate the water loss due to transpiration. This creates a transpiration stream from the xylem to the leaves.
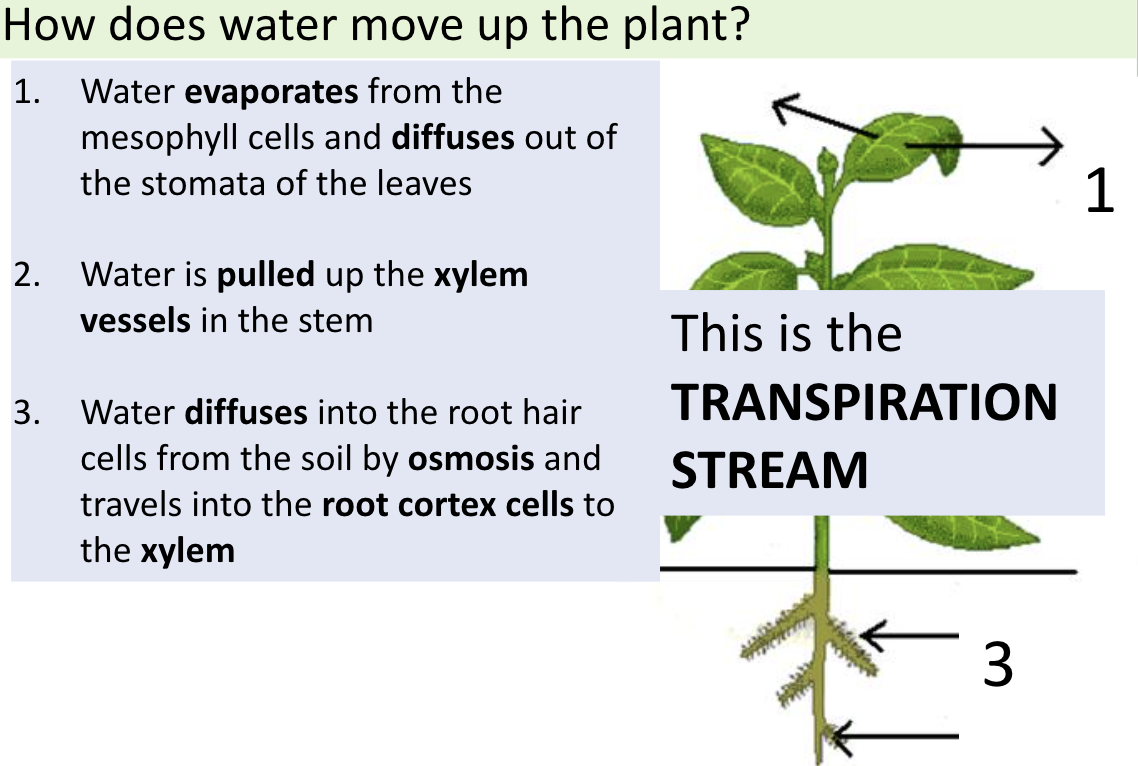
Step 1 of transpiration
Water evaporates from the mesophyll cells (spongy + palisade) and diffuses out of the stomata of the leaves
Step 2 of transpiration
Water is pulled up the xylem vessels in the stem
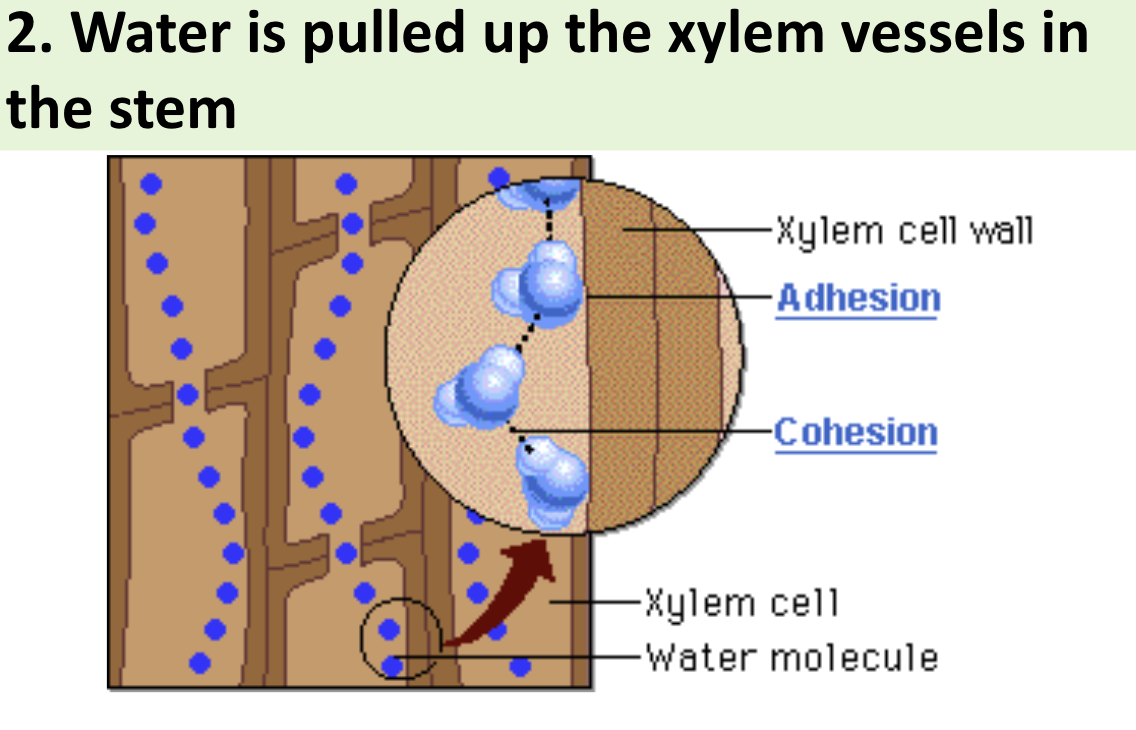
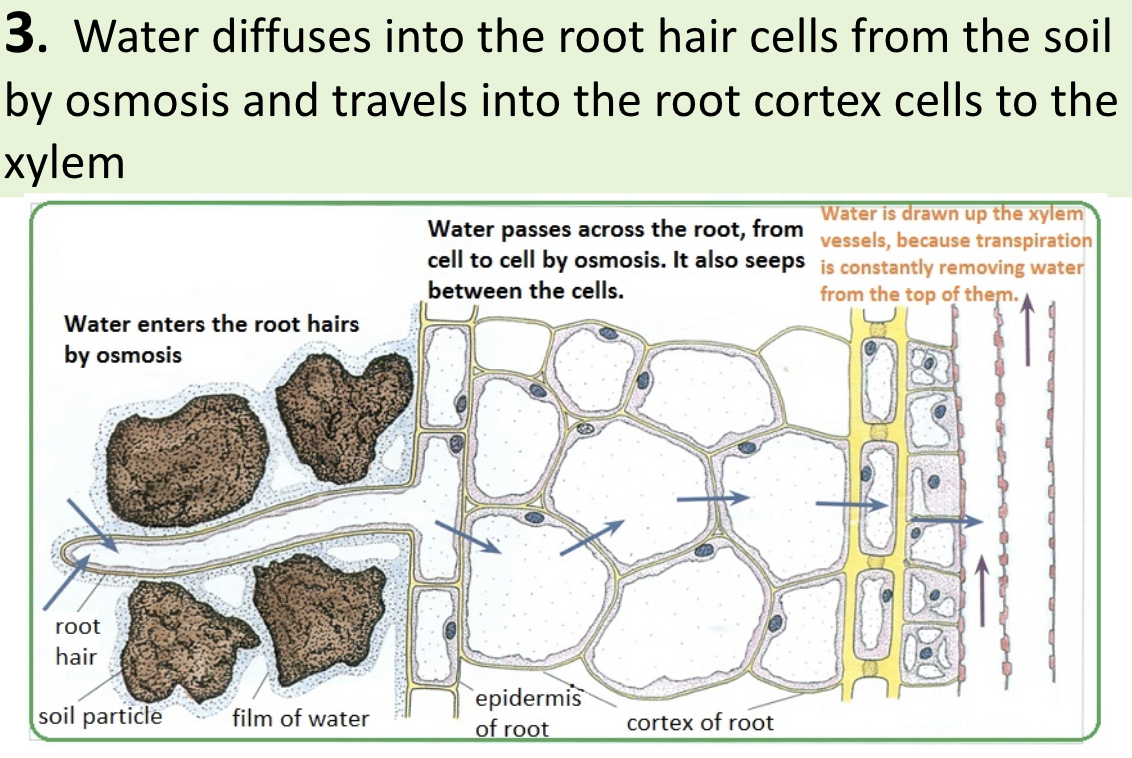
Step 3 of transpiration
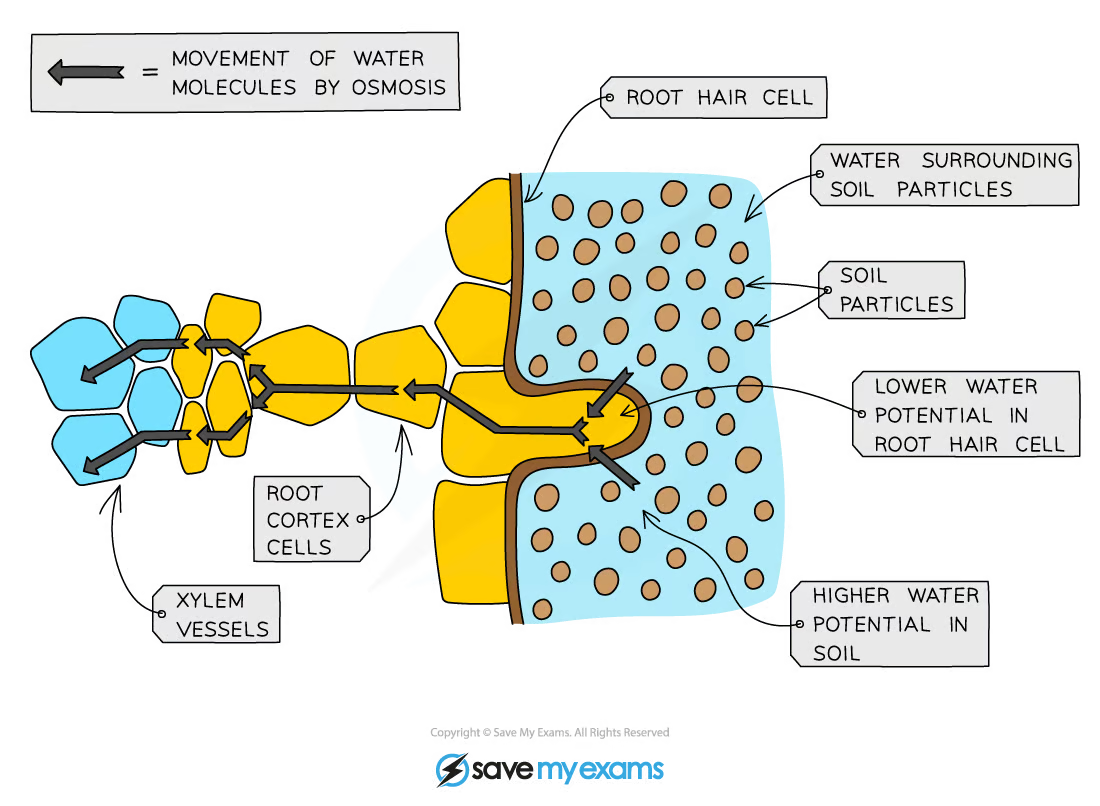
Water diffuses into the root hair cells from the soil by osmosis & travels into the root cortex cells to the xylem
high concentration of minerals → low water potential → water more attracted to diffuse via osmosis
How water vapour occurs
water evaporates from the surfaces of the mesophyll cells into the air spaces and then diffuses out of the leaves through the stomata as water vapour
Describe the effects of variation of temperature and wind speed on transpiration rate
High temperature → increase transpiration rate
Low temperature → decrease transpiration rate
greater the wind speed → increased transpiration rate
larger leaf surface → increase transpiration rate
Explain the effects on the rate of transpiration because of temperature
increased temperature → kinetic energy of water molecules increase → move and evaporate (stomata are open) more quickly → rate of transpiration increase
Explain the effects on the rate of transpiration because of wind speed
increased wind speed → removes layers of humid air surrounding leaf → the water released is carried away faster → increase concentration gradient for water vapour diffusion → increase rate of transpiration
Explain the effects on the rate of transpiration because of humidity
increased humidity → more amount of water in the air → harder for more water to evaporate → decreases concentration gradient for water vapour diffusion from leaf to air → decreased rate of transpiration
What conditions will increase the rate of transpiration
warm (sunny)
dry (decrease humidity, less water potential outside leaf)
windy
sunny
Explain how and why wilting occurs
stomata open → leads to lots of water loss → loss of water not compensated → stomata become flaccid → wilting
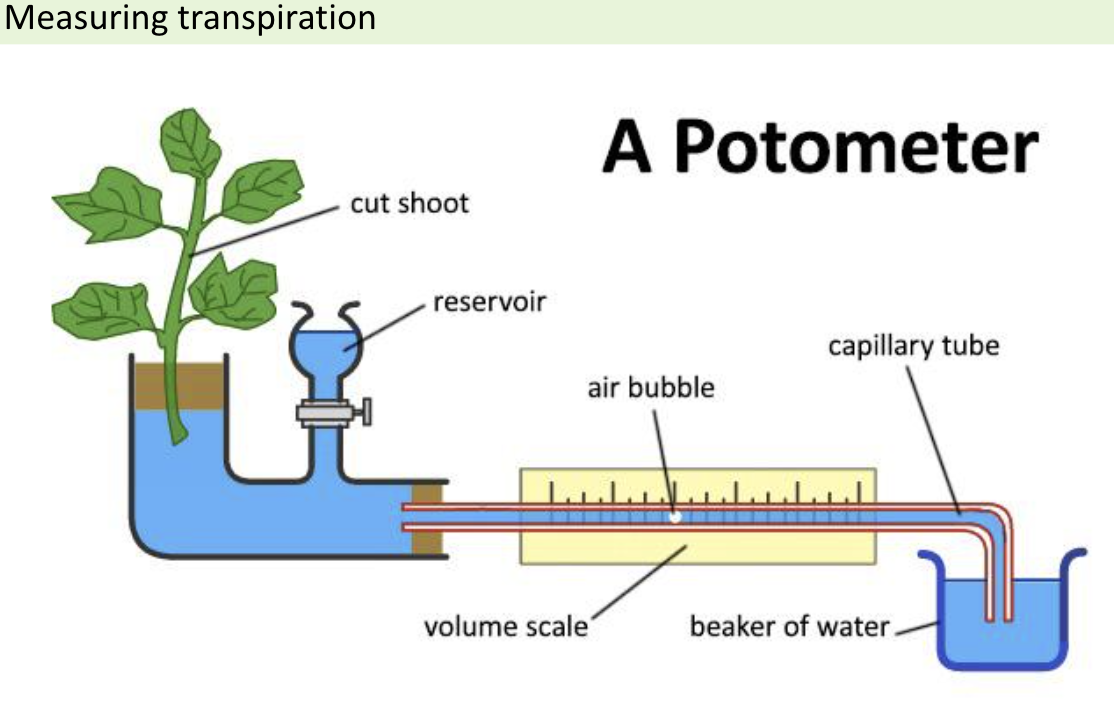
How to measure rate of transpiration
Potometer
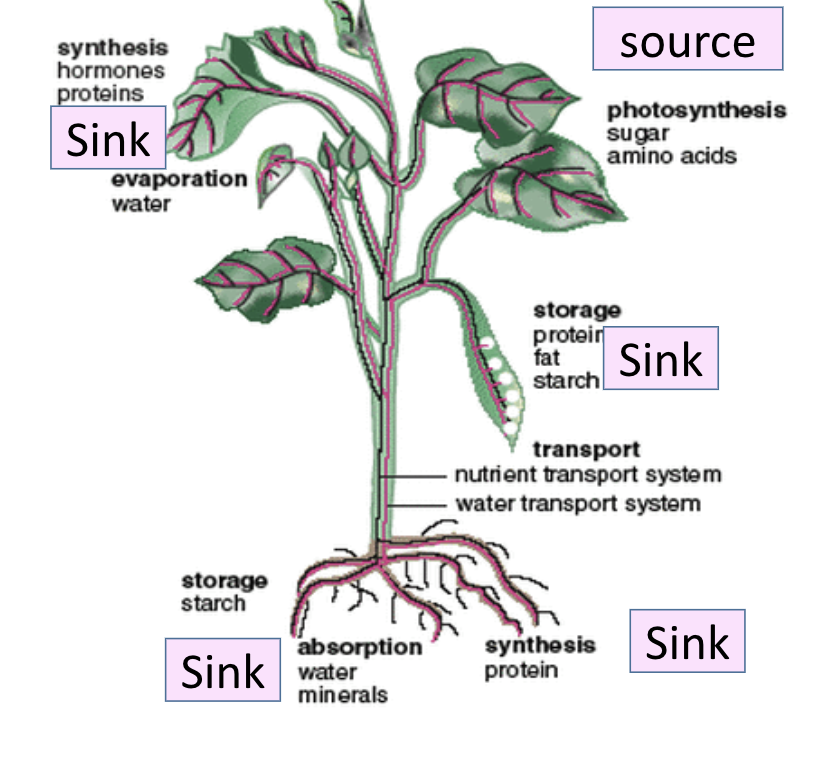
Translocation
the movement of sucrose and amino acids in phloem from sources to sinks
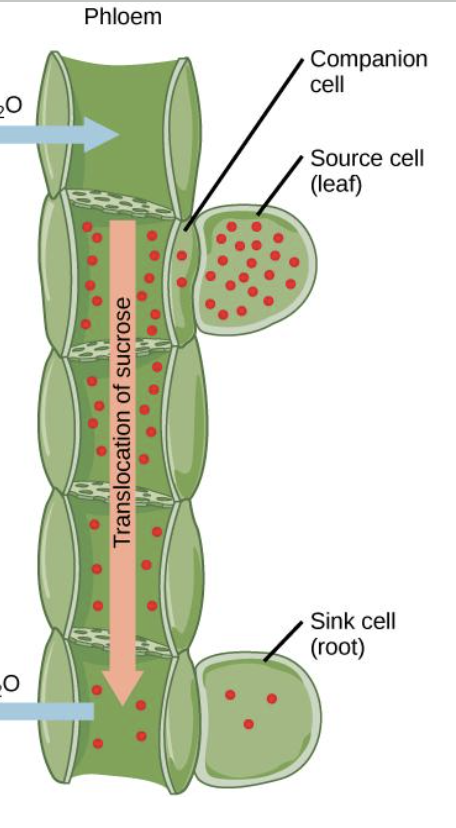
Sources
A part of the plant that release sucrose or amino acids (PRODUCTION)
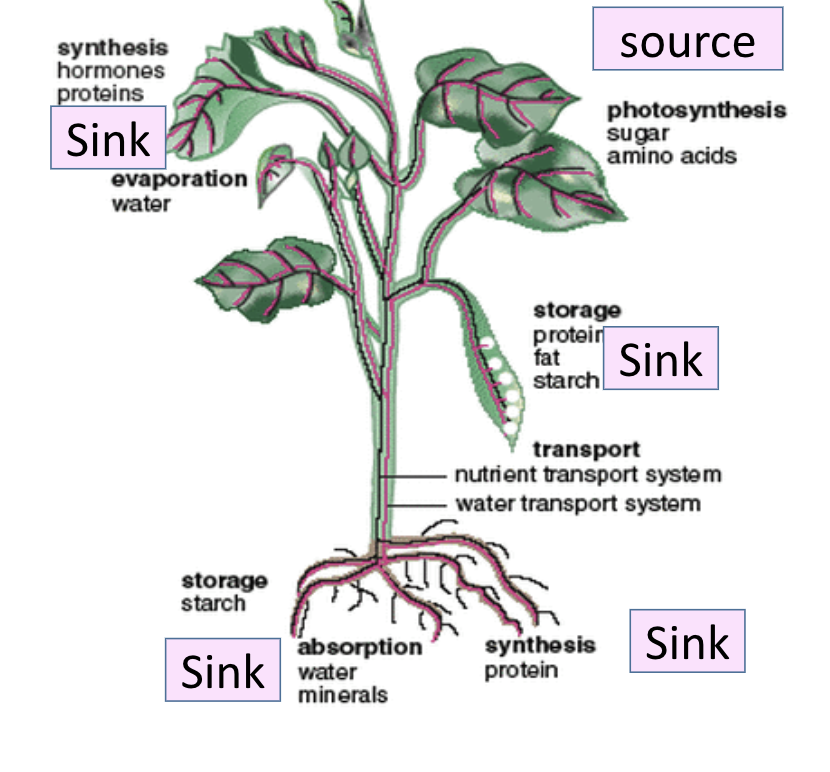
Sink
A part of the plant that use or store sucrose or amino acids (USAGE AND STORAGE)