ATI Health Education
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Cognitive Learning Theory
This theory looks at an individual’s thought process.
Behavioral Learning Theory
This theory suggests that learning is influenced mostly by external forces.
Social Learning Theory
This theory asserts that learning happens by observing others.
Experiential Learning Theory
This theory tells us that learning comes from experiences.
Transformative Learning Theory
This theory suggests that learners can change the way they think once they have new information.
Humanistic Learning Theory
This theory describes learning as a holistic process.
Three domains of learning
cognitive (thinking), affective(feeling), and psychomotor (what ppl do)
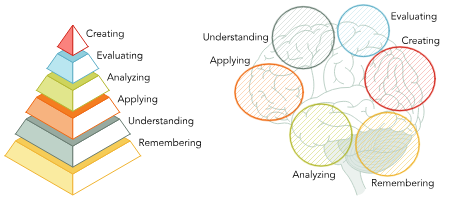
Cognitive Domain
Focuses on how an individual thinks and the development of knowledge and intellectual skill.(Bloom’s Taxonomy)
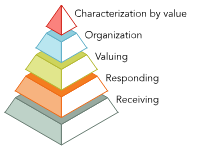
Affective Domain
Involves a learner’s feelings, beliefs, attitudes, and values. Built off of the concept that new information must affect the way people feel in order to provoke change.
Psychomotor Domain
The ability to perform a skill that was learned and involves fine and gross motor skills, as well as autonomic responses and reflexes.
Health Belief Model
A conceptual framework that has been used widely for decades to determine an individual’s motivation to make health-related changes.
Three categories of the health belief model
individual perceptions, modifying factors, and likelihood to take action
Health Promotion Model
A model used to determine factors that influence individuals' health behavior.
Three categories of the health promotional model
individual characteristics, behavior-specific cognitions and affect, and behavioral outcome.
Main difference between the health belief model and health promotional model.
HBM doesn’t consider an individual’s self-efficacy while the HPM does
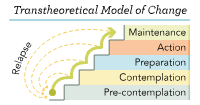
Transtheoretical Model of Change
Culture Care Theory (CCT)
A theory of nursing that is used to provide culturally congruent care.
Health literacy
An individual’s ability to obtain, understand, and make health related decisions for themselves
Personal health literacy
An individual’s ability to obtain, understand, and make health-related decisions for themselves and others.
Organizational literacy
An organization’s ability to enable individuals to obtain, understand, and make health-related decisions for themselves.
Objectives of Healthy People 2030
"Increase the proportion of adults whose health care provider checked their understanding of health-related information."
"Decrease the proportion of adults who report poor communication with their health care provider."
"Increase the proportion of adults whose health care providers involved them in decisions as much as they [adults] wanted."
"Increase the proportion of people who say their online medical record is easy to understand."
"Increase the proportion of adults with limited English proficiency who say their providers explain things clearly."
"Increase the health literacy of the U.S. population.”
Health literacy universal precautions
A practice that assumes that all clients, regardless of education level or language spoken, may have difficulty understanding health information and services.
Community engagement
Working collaboratively with community members rather than “working for” them.N
Needs assessment
Identifying what the audience is interested in learning about, their readiness to learn, and barriers that may impede learning efforts.
Teach-back method
Involves the learner explaining in their own words and/or demonstrating the skill that they have learned; most effective as a short-term evaluation method.