International trade and exchange rates
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Define absolute advantage.
ability to produce more of a good or service than another with the same resources, because it can be produced at a lower cost.
Define comparative advantage and state its assumptions.
one country has a lower opportunity cost for producing a good than another country.
no transport costs, goods are homogenous and no trade barriers
Benefits of trade
Choice
Economies of scale meaning more products can be made for cheaper cost
Specialisation
Economic growth through imports and exports
Draw a trade diagram showing its benefits and losses for apples in south korea market and the USA market when USA has a comparative advantage in apples.
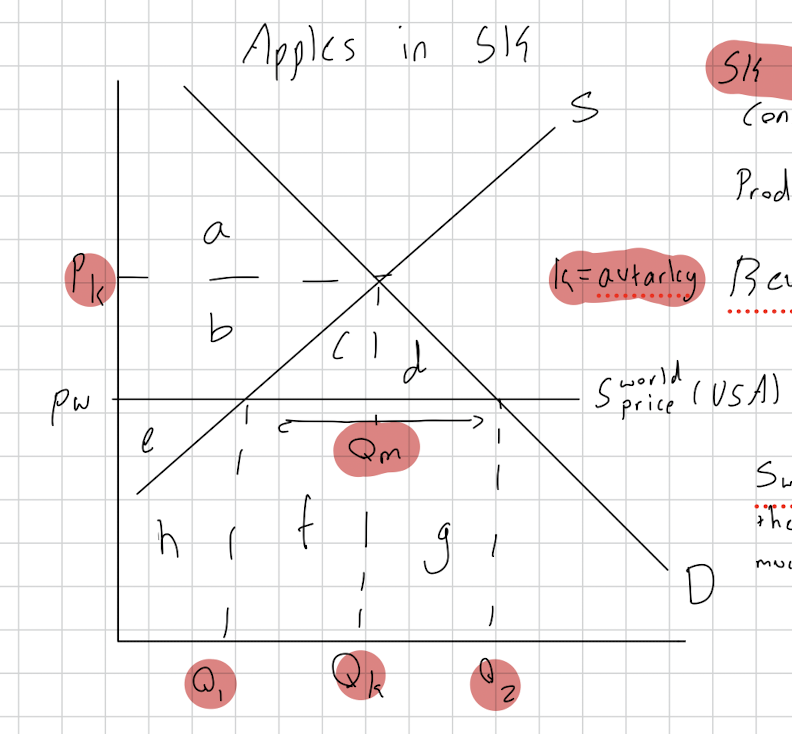
USA has a comparative advantage in apples compared to South Korea.
Benefits: Price is lower at S world
Gives a consumer surplus gain of b+c+d
Government revenue of f + g
Total net welfare gain of c+d
Increases global efficiency cus CA country is producing
In the long run its good cus resource are allocated properly
Losses:
Producers lose area b
Causes structural unemployment in country in apple industry
Loss of domestic industry
For the USA market with exports
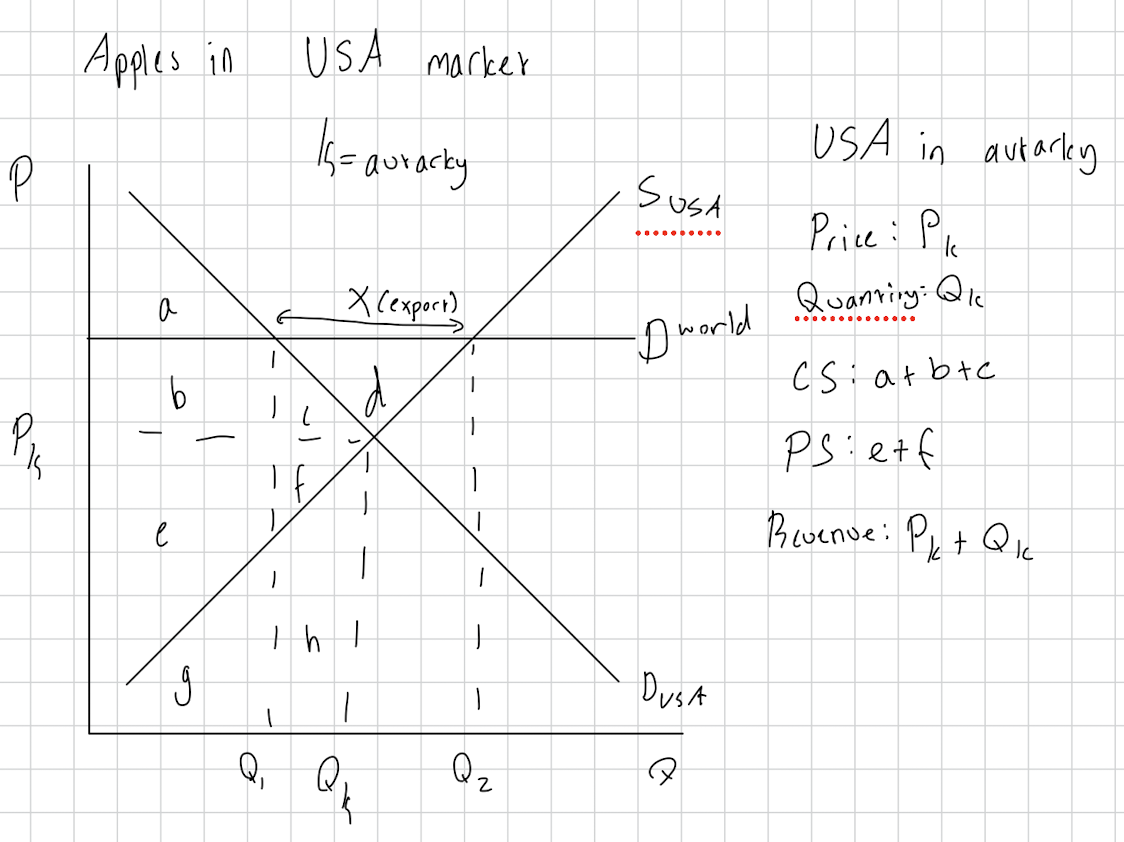
Gains: Producer surplus gain of b+c+d
Net welfare gain of d
Job creation and boosts apple industry in USA
Losses: Consumer surplus loss of b + c in the USA market, as prices rise for domestic consumers due to exports.
Higher prices for consumers
Production harms the environment
Definition of tariff and RWE of tariff
A tax on imports in a domestic country inflicted on foreign imports.
USA 25% tariff on steel 2025
Draw a tariff diagram including the definition, why its done, what the effect is and what the welfare effects are.
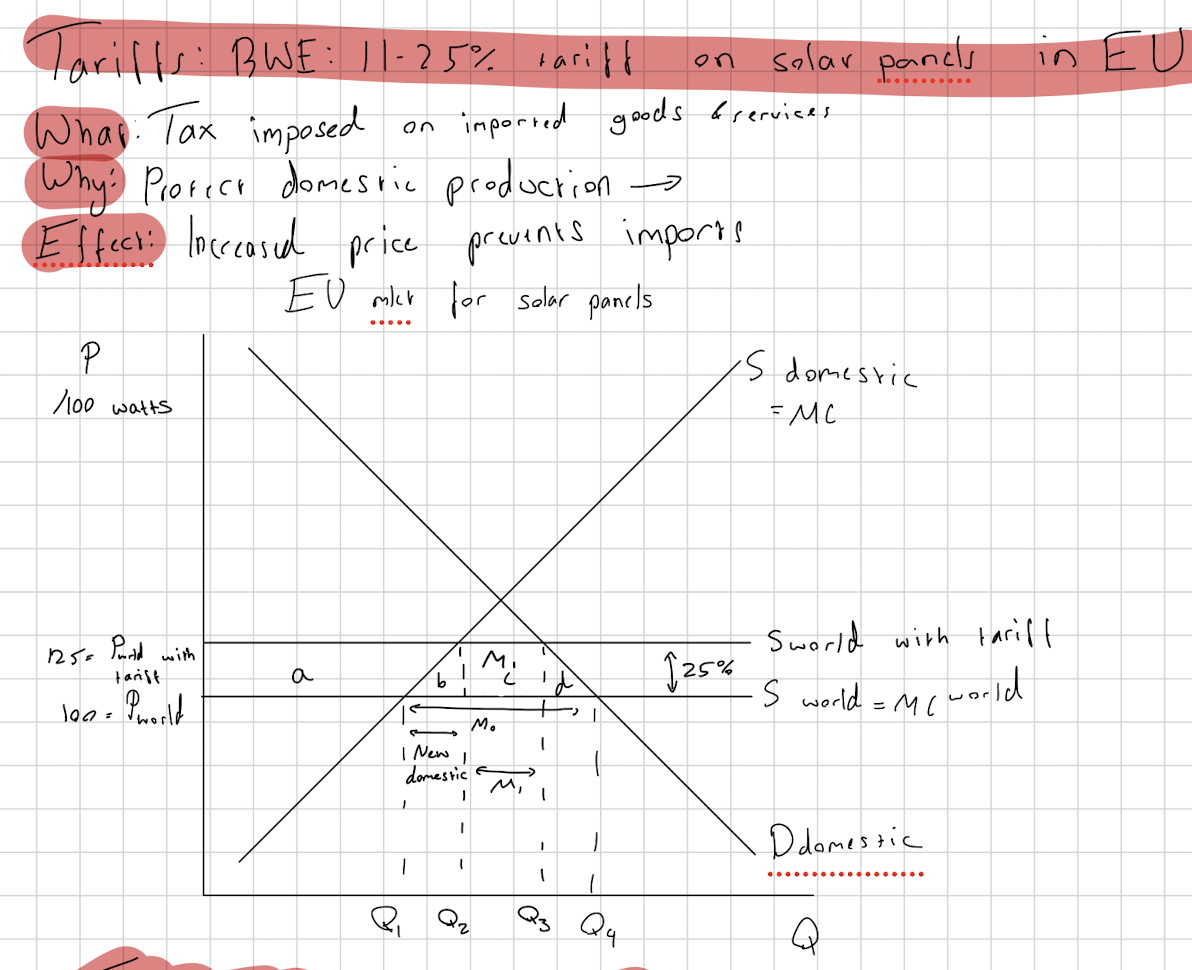
CS: loss of all
PS: gain a
Gov: gain c
NWL: loss b+c
Why are tariffs inefficient for PE and AE
NWL
area b is lost due to prod inefficient
area d is lost due to allocative inefficient
Advantages of tariffs? Disadvantages of tariff
Pros:
Reduces UnE in domestic country.
Domestic producers gain due to less foreign comp.
Government gains tax revenue.
Improved national security
Cons:
consumers pay more
Inequitable since area a is taken from cons and given to prod
Increased inflation
Less global competition and thus less innovation
Trade wars
Net welfare loss
Quota definition, effect and RWE
Definition: Physical limit of imported goods
Effect: supports domestic jobs by limiting imports to promote purchasing of domestic goods
RWE: EU made 56’000 tonne limit of imported olive in 2023
Draw a quota diagram, say the welfare gains, and say a quotes advantages and disadvantages.
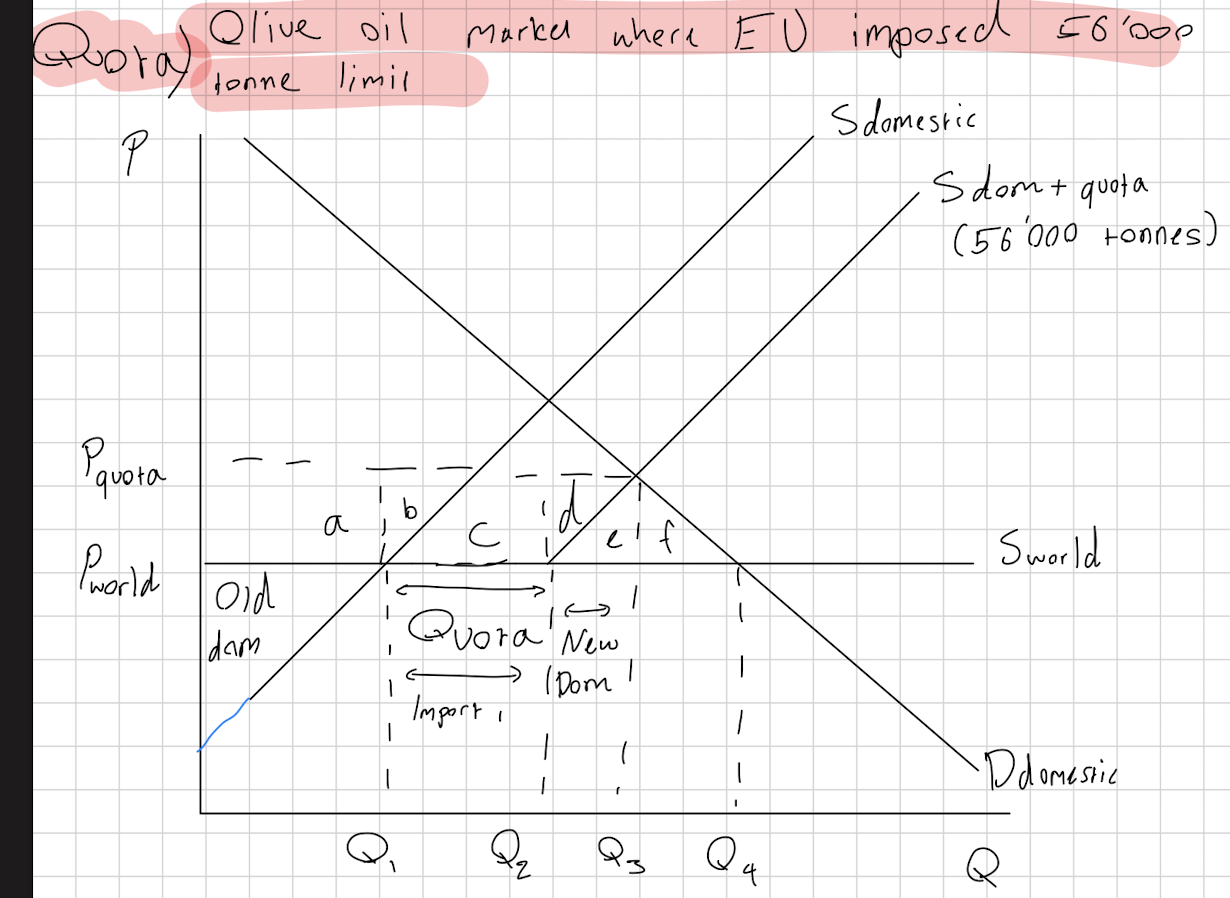
CS: lose all
PS: gain a+d
Govt: -
Foreign prod: gain b+c
NWL: loss of e+f
Advantages:
Supports domestic producers and industry through producer surplus gain
Infant industry argument
Protects employment of producers domestically
Foreign producer surplus gain
Reduces trade deficits by importing less and exporting more
Disadvantages:
Higher consumer price and consumer surplus loss which is inequitable
Reduced efficiency through NWL
Trade wars
No government surplus
Higher prices so inflation
Reduces consumer choice
What is a voluntary export restraint. Give eg
to avoid a tariff, foreign producers may accept a VER quota instead since quota are better for foreign producers than tariffs.
Korea accepting VER from USA to avoid a tariff
Define trade subsidies. RWE?
Draw the diagram.
What are the welfare effects?
What are pros and cons?
A payment to domestic producers to help compete against foreign producers.
Microchips act in 2024 is 106 billion $ subsidy to USA microchip producers.
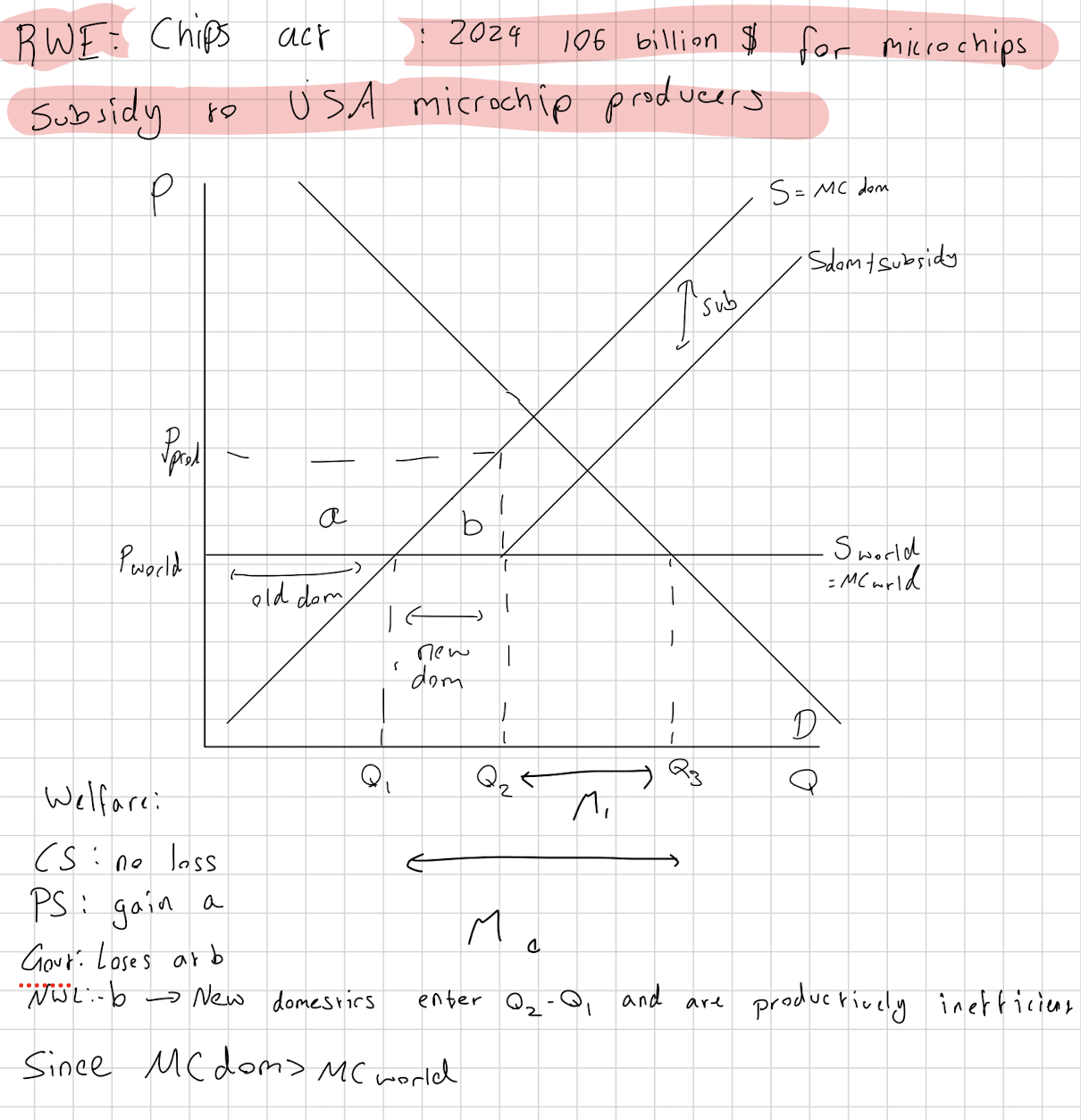
Advantages:
Producers gain through surplus
Domestic jobs protected
Boosts economies of scale
Current account deficit corrected
Disadvantages: Government opportunity cost
Expensive
May be wasted
Retaliation
Define dumping and state why it happens. RWE?
Explain how an anti dumping tariff works.
The sale of goods in a foreign market at a price less than what it costs to produce.
Countries may seek a market to sell.
Destroying a foreign market to outcompete domestic producers so they gain monopolistic power and can increase prices.
RWE: Chinese manufacturers selling for 30% less cost in USA market.
An anti dumping tariff is a tariff imposed on imported goods that are priced below fair market value, aimed at protecting domestic industries from unfair competition.
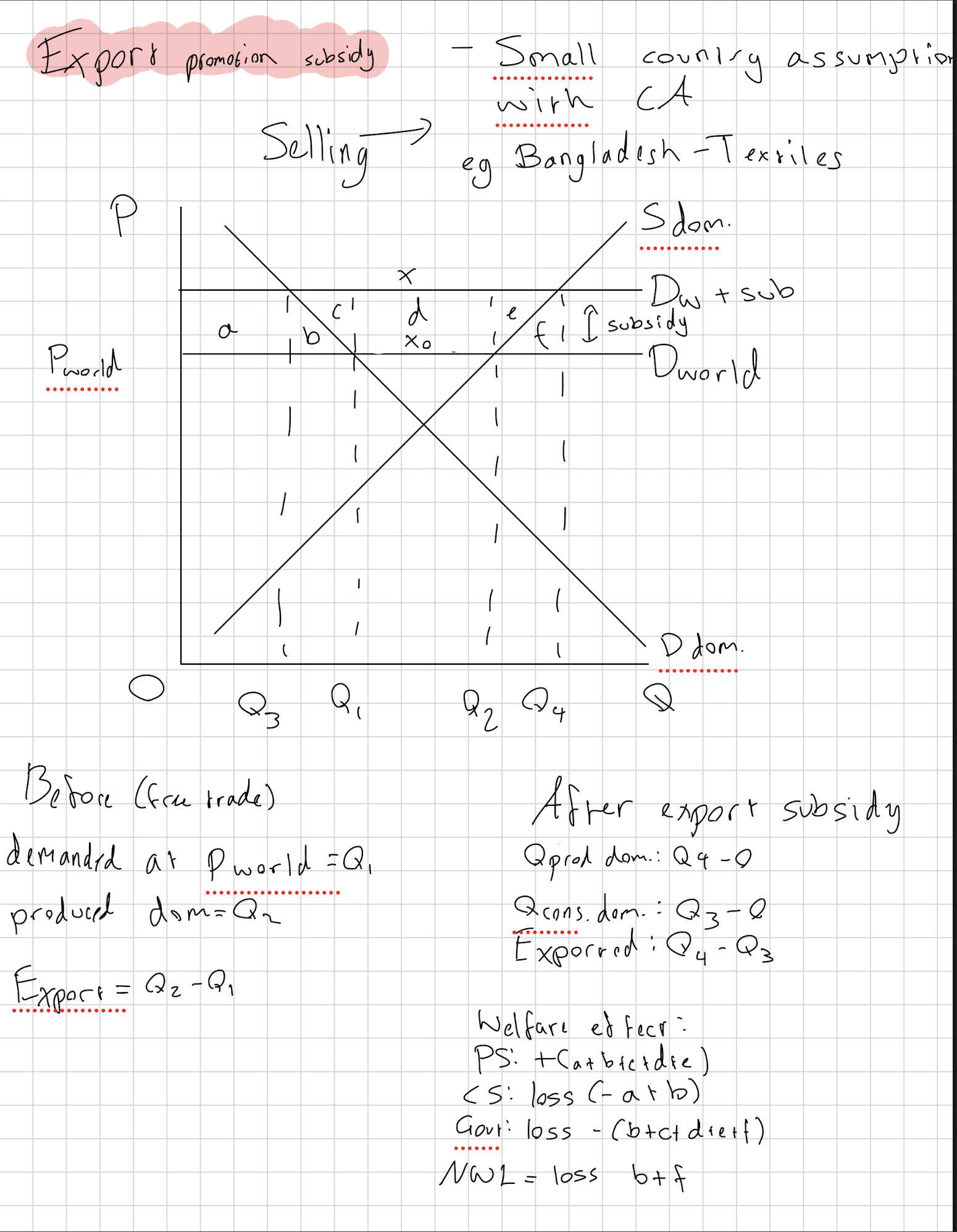
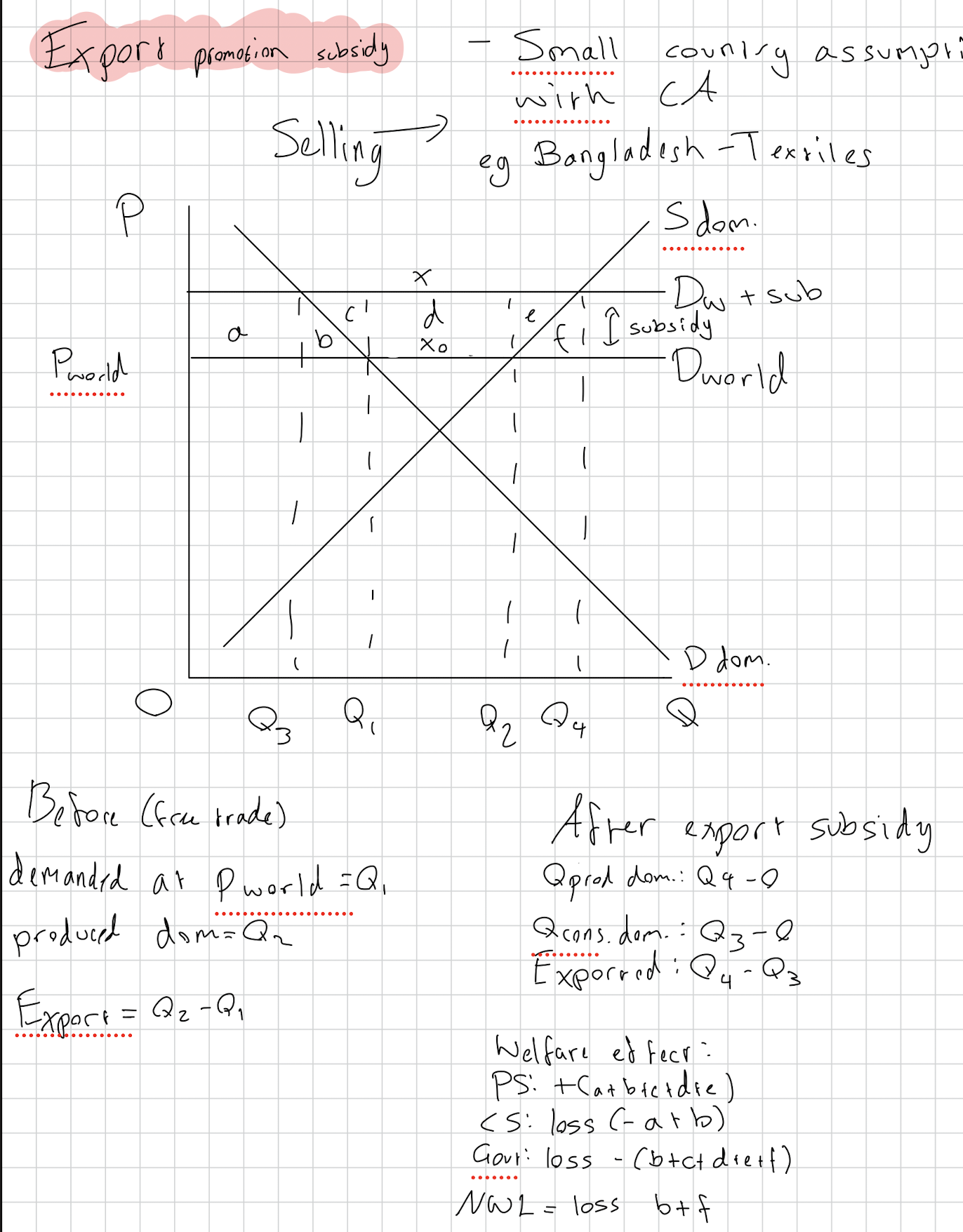
Draw an export promotion subsidy, stating the welfare effects.
What are administrative barriers?
Give 2 examples of administrative barriers.
They are trade barriers more subtle than tariffs or quotas
Examples:
Health regulations on products decreases their imports
Import product specification which only allows imports if they meet the requirements
Pros of protectionism. Cons of it.
Pros:
Infant industry argument —> new small firms can improve their economies of scale to produce cheaper. LIC benefit
Government revenue
National security
Protect domestic suppliers.
Dumping regulation
Job balance
Reduces trade deficit
Cons:
Allocative inefficient due to production moving from efficient
Consumers lose thus inequitable
Higher prices leads to inflation
Retaliation causing trade wars
No consumer choice
Corruption through bribes to stop tariffs etc
Define exchange rates. Give one example of an ER.
value of one currency expressed in terms of another currency.
£1=1.52 CHF
Define a floating ER
When the value of an ER is determined by supply and demand.
Define appreciation.
What causes appreciation
Draw an appreciation diagram.
Pros and cons of it.
increase in value of one floating ER against another one.
Increase in demand for a currency or a decrease in supply.
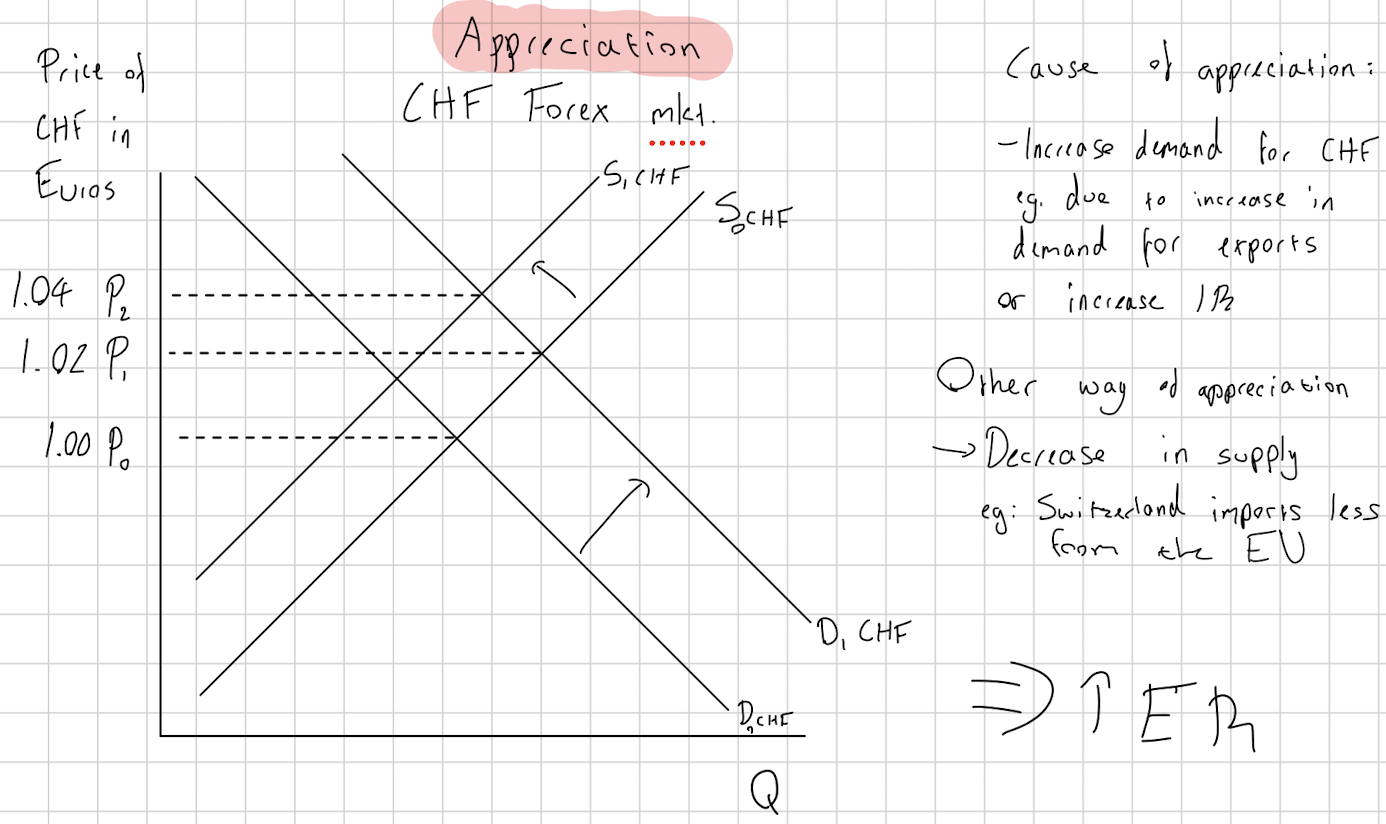
Exports more expensive and imports cheaper
Decrease in Aggregate Demand
Pros:
increased standard of living since imports are cheaper since consuemrs have higher purchasing power
Incentive to innovate in response to competition since imports are cheaper and more foreign products will be bought
Cheaper to pay off foreign loans
Lower costs of imports
Cons:
Less AD due to less net exports as they’re more expensive means less output thus increased UnE
Deflation since a recessionary gap caused by AD down
Pressure on domestic producers which struggle to compete with cheap imports
less FDI since it becomes more expensive
Define depreciation.
What causes depreciation?
Draw diagram
Talk about the effect on exports and imports
What are the advantages and disadvantages of depreciation?
Decrease in value of a currency
Decrease in demand and increase in supply.
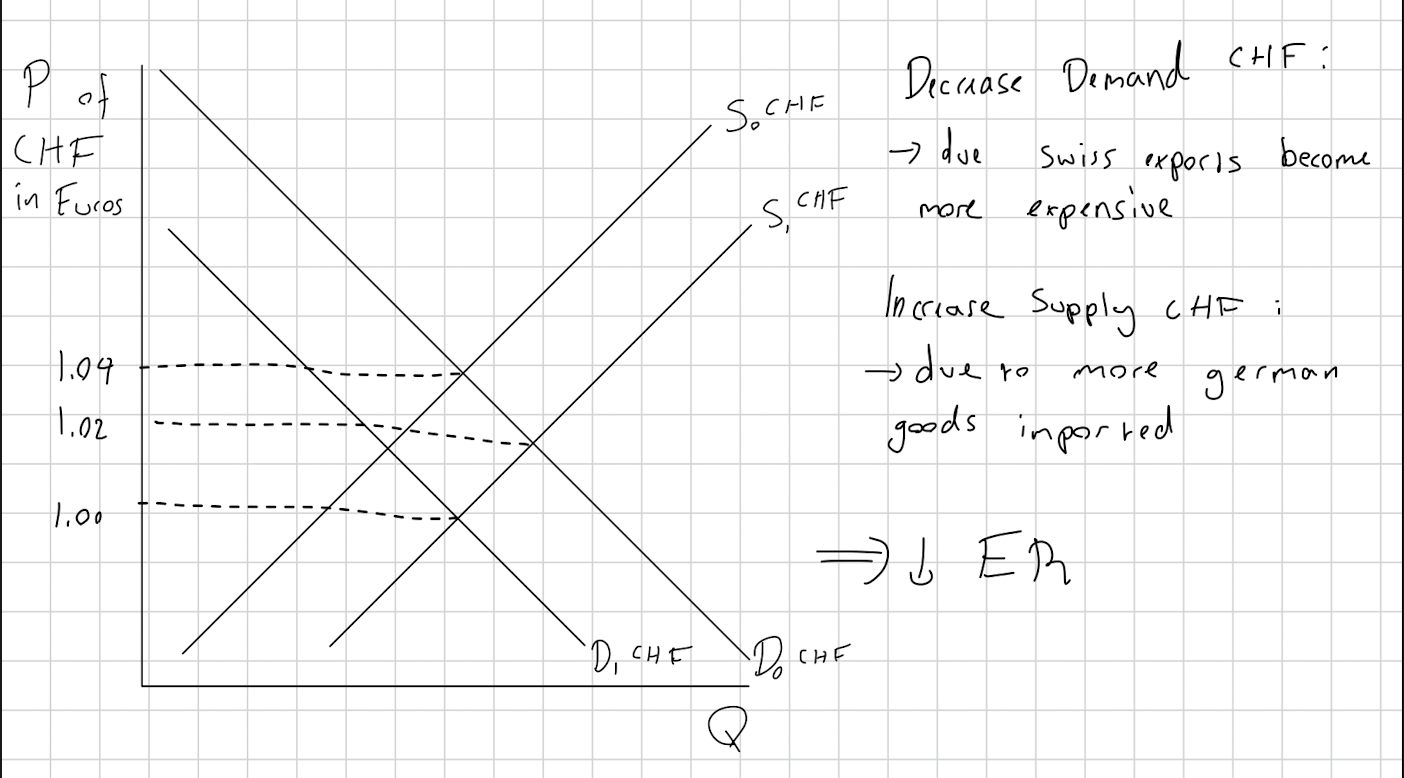
Exports are cheaper and imports and more expensive.
It leads to an increase in Aggregate Demand cus of more net exports
Pros:
Increase in output due to more AD since net exports increases, which decreases UnE
Decrease in current account deficit since less imports and more exports
Increase in competition since domestic firms need to compete harder to keep up with increased demand for exports but also since imports are more expensive locals buy domestic products, creating competition between local firms. This leads to more FDI leading to increased LRAS-
Increased foreign exchange since more exports bring in foreign currency
Cons:
Inflation due to AD shifting right and because firms charge higher prices due to increased production costs
Increased imports costs which decreases economic well being
Makes foreign currency debt more expensive to pay off because its more expensive relatively
Overall it is good
What is the effect of appreciation or depreciation on economic growth, inflation, unemployment, and living standards.
Economic growth: Increase in AD due to depreciation can improve economic growth. Appreciation does opposite.
Inflation: Depreciation increases AD which causes demand pull inflation.
Cost push inflation due to depreciation causing higher prices of imported goods causing shift in SRAS
Unemployment: depreciation leads to an increase in exports which increases employment to produce them. Also an increase in AD increase output.
Living standards: depreciation makes imports more expensive which makes living standards worse. However, more exports will make them better due to less unemployment.
What are the factors / cause of exchange rate flucuations?
Things to shift demand or supply for a currency
Interest rates as they influence the flow of hot money between countries. If the UK increase IR then more countries will demand their currency through banks.
Inflation: if inflation is higher in UK than in other places, the demand for UK currency decreases causing depreciation
demand for g/s requires a currency —> increase in currency demand
demand for foreign direct investment —> introduces more currency supply.
demand for financial investments like buying shares with a currency
Speculation if ppl think currency goes up theyl’ll demand it
Define devaluation and say why would it be done.
Define revaluation and say why it would be done.
Devaluation: when the value of a fixed currency is decreased by the govt. To decrease its strength.
Revaluation: value of fixed currency increased by govt. To increase the currencies strength.
What is a fixed exchange rate system?
How does the Central Bank influence the exchange rate?
A fixed exchange rate, often called a pegged exchange rate, is a type of exchange rate regime in which a currency's value is fixed or pegged by a monetary authority against the value of another currency.
To appreciate it, the Central Bank buys it on the forex market to increase its demand.
To depreciate it, the Central Bank sells it on the forex market to increase its supply.
Draw a diagram to show how a fixed currency system prevents appreciation.
Draw one to show it preventing depreciation.

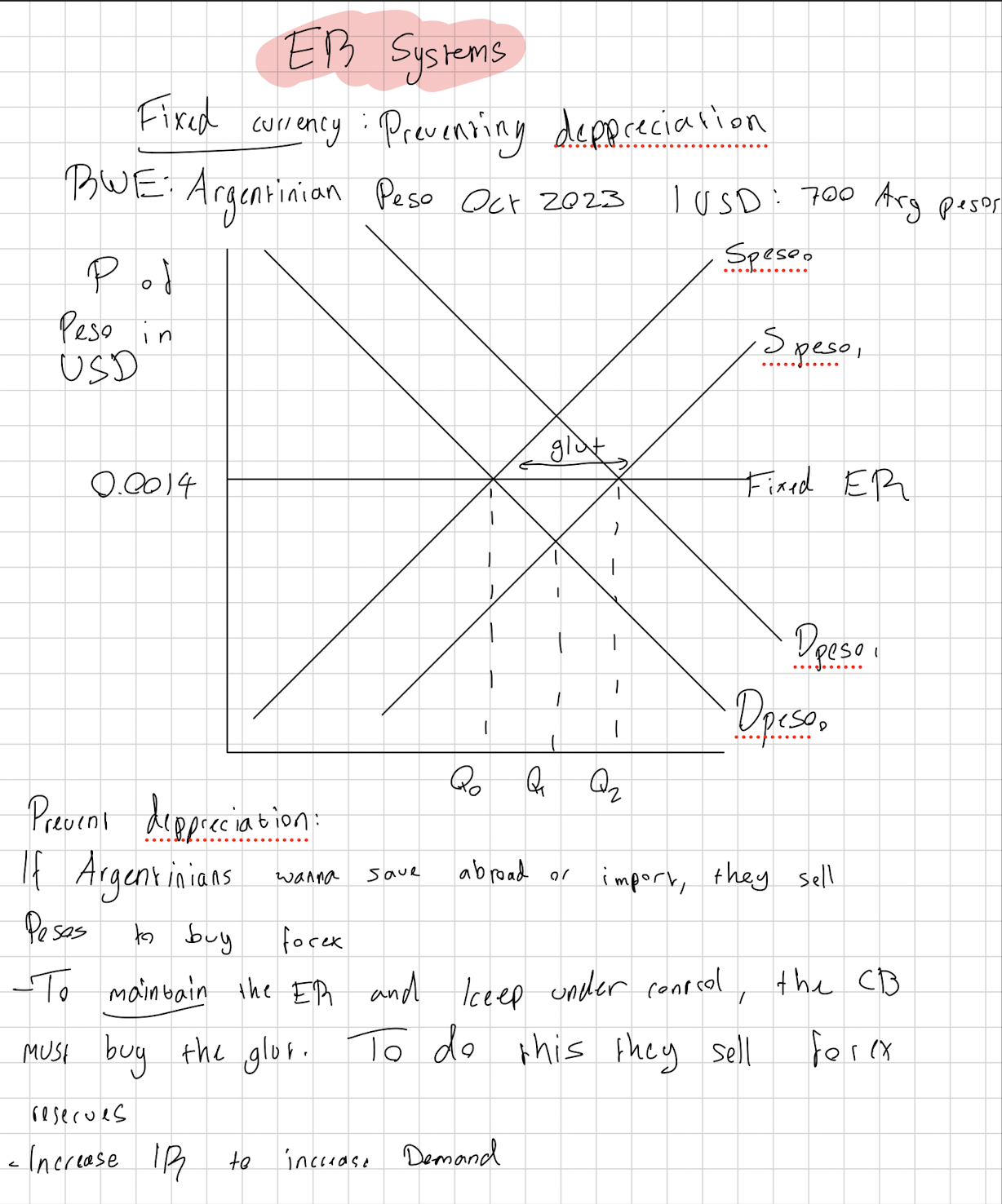
Pros and cons of fixed ER system?
Pros
Provides stability
Encourages trade
Encourages FDI since investors know it will be stable in the future
Controls inflation
Cons
Limited options to deal with external shocks as it does not have flexibility.
Monetary policy conflicts between supporting the ER system and the economy… if there is downward pressure and demand for currency needs to increase, increasing interest rates would help but would also harm the economy through decreased output. (AD decrease)
Requires huge liquid assets and using them to sustain the fixed ER has an opportunity cost for other stuff.
Risks speculation when people dont believe in the currencies fixed value.
What is a floating ER system.
What are the pros and cons?
A system where the value of a currency is determined by market forces like supply and demand without intervention
Pros:
domestic policy freedom eg monetary policy
Is flexible to external shocks
No currency reserves needed
Cons:
Uncertainty for investors
Risks import inflation due to currency decrease.
Volatility leads to economic fluctuations
What is a managed exchange rate? Give a RWE
Draw the diagram for when the currency is kept from going below price floor and above price ceiling.
How does the CB make sure the currency does not go below price floor or above price ceiling?
ER that floats in the forex market and can be intervened by the central bank if needed.
Danish Krona to Euro 0.13 EU: 1 DK
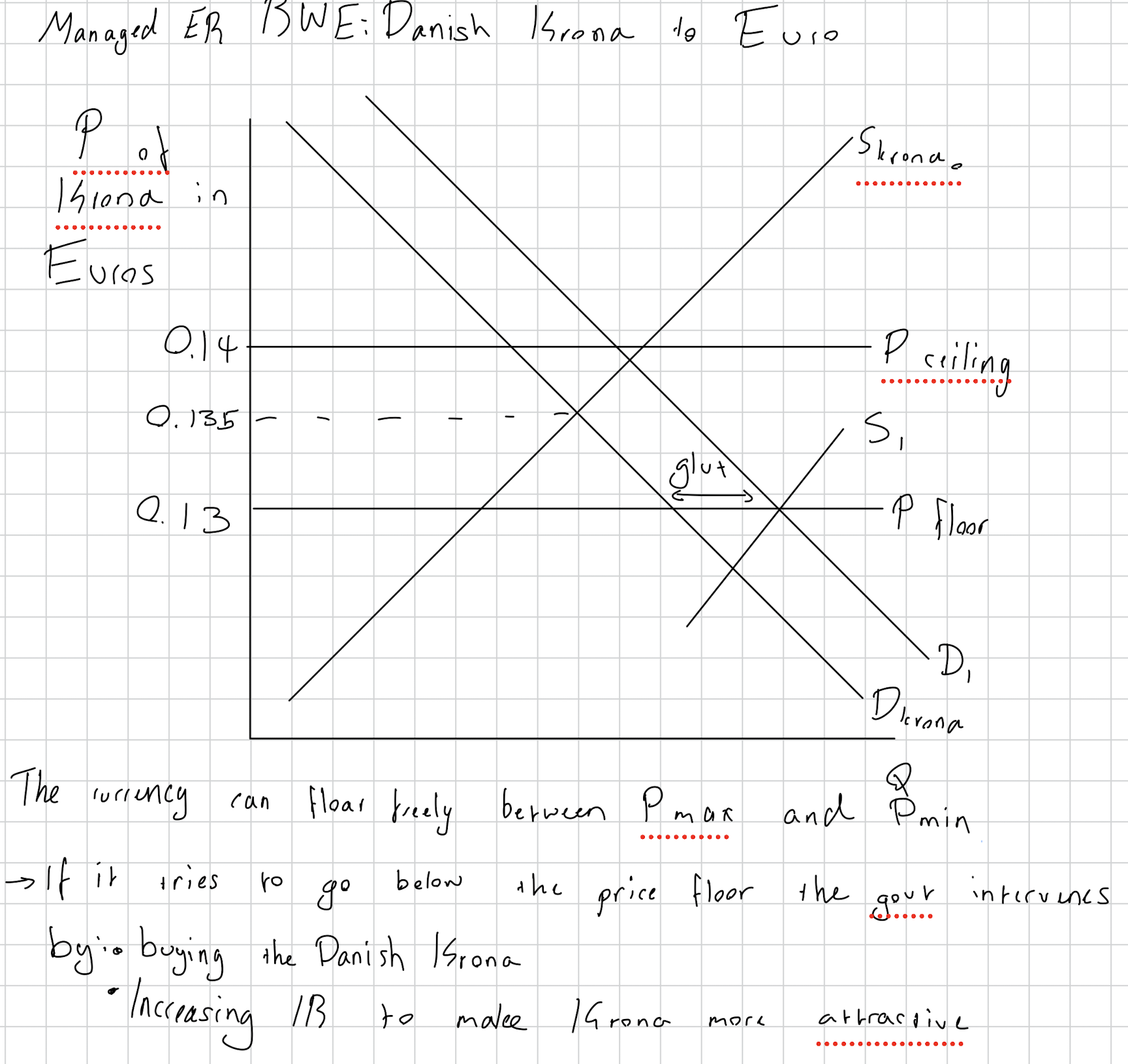
If there is too much supply of the currency, it risks falling below the price floor. Then, the CB buys the currency to increase demand for the currency.
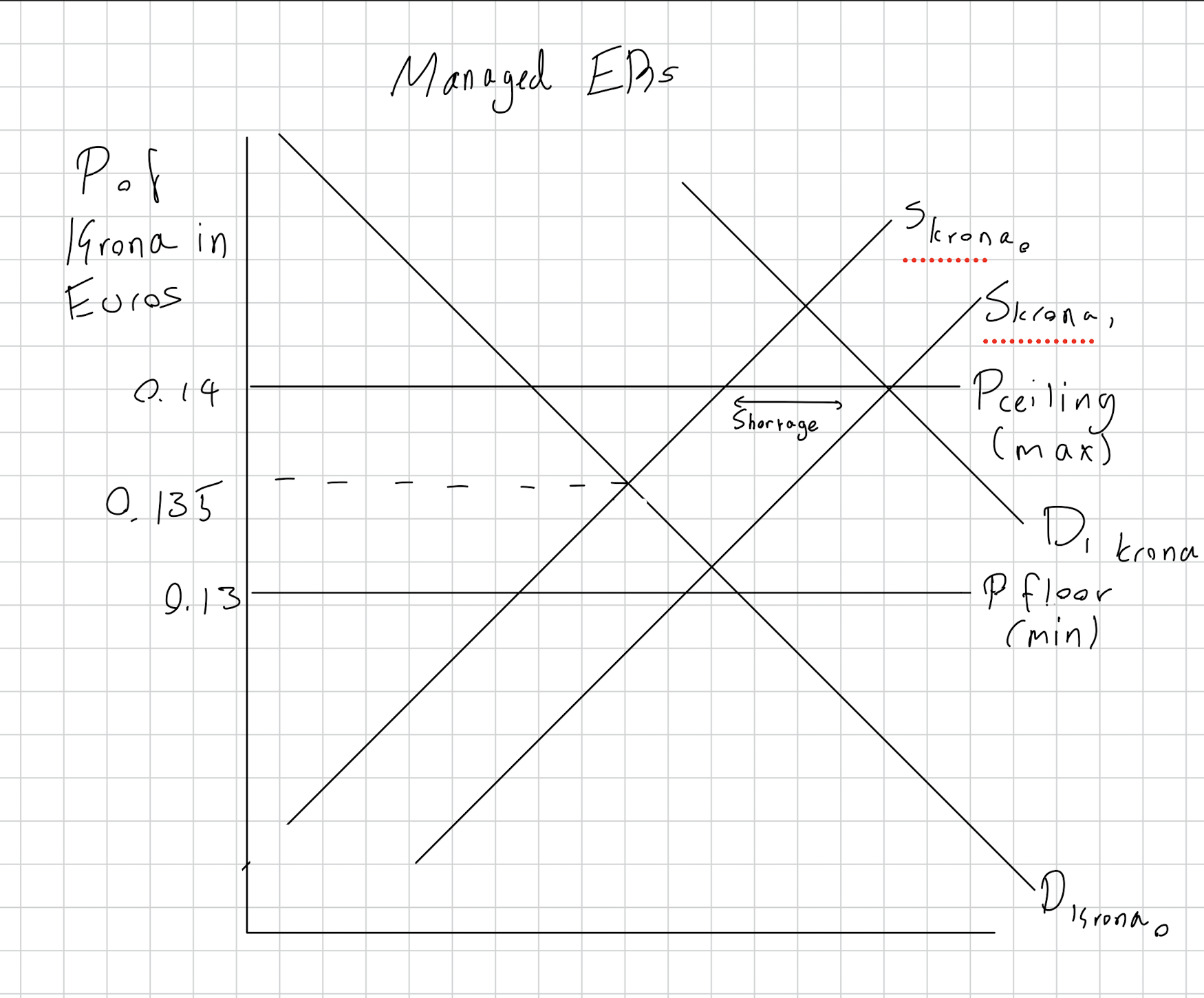
If there is too much demand for the currency, it might go above the price ceiling.
In response, the CB increases its supply by selling it.