RAD111 Unit 2
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Hyposthenic
slightly thinner than sthenic body habitus
Hypersthenic
Broad body habitus
special consideration to costophrenic angles
landscape IR
Asthenic
very long and slim body habitus
IR= portrait
Left bronchus
longer, more lateral, smaller in diameter
right bronchus
shorter, more vertical, wider in diameter
food particles more likely to enter
left lung
2 lobes; superior and inferior
right lung
slightly higher and 3 lobes; superior, middle, inferior
parietal pleura
lines inner surface of thoracic cavity
pulmonary pleura
covers lung surface
hilum
root area of the lung
bronchi, blood vessels, lymph vessels
nerves enter and leave
apex
round upper area above clavicle
extends up to T1
base
lower concave area of lung
rests on diaphragm
costophrenic angle
outermost lower corner of lung
mediastinum
medial portion of thoracic cavity between lungs
trachea
esophagus
thymus gland
heart and great vessels
vertebral pominens
C7
7-8 inches inferior
kVp range (chest)
110-125
SID (chest)
72in; less magnification
Degree of inspiration
10 ribs identifiable; on 2nd breath
Position (PA)
erect, chin raised, shoulders rolled forward, no rotation
align MSP with CR and midline of IR
CR directed to midline at level of T7
7-8 inches below vertebral prominens
top of IR = 1 1/2 - 2 inches above shoulder
Position (Lateral)
erect, left side against IR; arms raised over head, chin up
middle cell
coronal plane perpendicular to IR
sagittal plane parallel to IR
CR directed to midline at T7
lower IR/CR 1 inch from PA
Position (AP Supine)
supine
head end of bed = semierect
roll shoulders forward
CR angled 5 degrees caudally (perpendicular to sternum)
align center to IR to CR 1 ½ inch above shoulders
CR directed to midline of patient at T7
3-4 inches from jugular notch
fluid side
down
air side
up
Lateral Decubitus
back against IR, chin raised, arms above head, pillow, knees slightly flexed
radiolucent sponge under patients
on right side = Right
on left side = left
center patient = midsagittal plane & T7
top of IR = 1 inch above vertebral prominens
horizontal beam
AIR UP
FLUID DOWN
AP Lordotic Position
leaning shoulders/ neck onto bucky from about 1 foot away, back of hands on hips, roll shoulders forward
IR = lengthwise or crosswise
AP Lordotic
for visualizing area under clavicles
rules out califications and masses beneath clavicles
Semiaxial AP Lordotic
lordotic laying down (supine)
CR angled 15-20 degrees toward head
used if patient cannot stand
Ant. Oblique Position
45 degree rotation (LAO or RAO)
anterior shoulder against IR
opposite arm raised on bucky
chin raised straight ahead
Oblique
expands visual of side further from IR
Pneumothorax
collapsed lung
usually only a portion of lung collapses
air pushes on pleural space making it collapse
no lung markings
exposure remains the same
Pleural effusion
fluid in the pleural space
fluid is thick and stays in place
lateral decubitus
increase exposure
Emphysema
a condition in which the air sacs of the lungs are damaged and enlarged
labored breathing
lungs appear very radiolucent
decrease exposure
COPD
persistent obstruction of airways
difficult to empty lungs
asthma
identified by
hyperexpansion
bronchovascular markings
mild cases not visible on x ray
COPD
caused by
emphysema
chronic bronchitis
smoking (predominant cause)
Atelectasis
one or more areas of lung/lobes collapse or dont inflate
caused by obstruction of bronchus or puncture of an air passageway
increase exposure
Bronchiectasis
permanent abnormal dilation of 1 or more large bronchi
due to destruction of the elastic and muscular component of the bronchial wall
produces
mucus = chrronic cough
pus collection in dilated areas = densities
most common in lower lobes
viral or bacterial infection
Pulmonary edema
accumulation of fluid in the lungs due to obstruction of pulmonary circulation
increase exposure
Dyspnea
difficulty breathing
pneumonia
lung inflammation due to bacteria, fungus, or virus
different types depends on location and cause
cystic fibrosis
genetic disorder causing progressive "clogging" of bronchi and bronchioles by heavy mucus
could cause bronchiectasis
most common inherited disease
increase exposure (severe conditions)
hemothorax
blood in the space between pleural layers
thyroid cartilage
laryngeal prominence/ adams apple
level C5
carina
where right and left bronchi bifurcate
level T4-5
alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
Chest kVp (pediatric)
70-85
pulmonary emboli
sudden blockage of a lung artery
grid
used to reduce scatter radiation
bony thorax
protective framework
sternum
clavicles
scapulae
12 pairs of ribs
12 thoracic vertebrae
provides accurate & consistent positioning
easy to locate
used to center IR & get all anatomy
respiratory system
exchange of gaseous substances between air and blood
pharynx
trachea
bronchi
lungs
ribs attach
to the manubirum
pharynx
passageway for food, fluids and air
digestive and respiratory system
posterior between nose and mouth above larynx and esophagus below
esophagus
digestive system
connects pharynx with stomach
most posterior
larynx
voicebox
suspended from hyoid bone
anterior portion of neck
adams apple
hyoid
not apart of the larynx
trachae
windpipe
keeps airway open by preventing collapse during expiration
C6→T4-5
divides into right and left primary bronchi
thyroid gland
rich in blood supply
stores and releases hormones
lungs
composed of light spongy highly elastic substance called parenchyma
parenchyma
allows for expansion and contraction of the lungs
pleura
delicate double walled sac
thymus gland
largest in infants and shrinks over time
thyroid and parathyroid glands
NOT apart of the mediastinum
why is the right lung short than the left?
space is being occupied by the liver
sthenic
average in shape and internal organ location
why do we wait till 2nd full inspiration?
allows the lungs to aerate fulle
allows diaphragm to settle
inspiration
increases in 3 dimensions
vertical
transverse
AP
Pediatrics
erect whenever possible
lower kV (70-85)
less mAs
newborns and infants
AP supine and recumbent lateral with horizontal beam
pigg o stat
chest technical factors
kV ( 110-125)
grid
high mA
short exposure time
correct marker placement
portrait or landscape IR (14×17in) (34×43cm)
72 inch SID
assume heart is located in left thorax
why do we use a high kV?
to visualize finer lung markings (many shades of gray)
situs inversus
perfect mirror image of normal organ position
visceral inversion
geriatrics
less inhalation ability
shallow lung field
center CR higher
pathologic conditions more common
pneumonia & emphysema
adjust exposure factors
how to determine rotation of x ray images
symmetric appearance and location of sternoclavicular joints
distance of sternal end of the clavicles from center line of spine should be equal
whichever is closer to spine = direction of rotation
why do we do Left Lateral?
they are more accurate in showing the heart regionw
why are chest x rays done at 72 SID?
to reduce the magnification & distortion of the heart
True PA/ Lateral
No tilt or rotation
why is erect best for PA chest?
diaphragm allowed to move down further
air and fluid levels may be visualized
engoregment and hyperemia of pulmonary vessels may be prevented
lungs expand more
internal organs drop allowing lungs to fully aerate
bony land markings
vertebral prominens
jugular notch
jugular notch
CR 3-4 inches below
recumbent AP chest
less than 72 inches SID
increases divergence of x ray beam
IR = landscape
side to side collimation (lateral)
light field margins to outer skins margins on each side u
upper and lower collimation
adjust the upper border of the light field to vertebrae
upper collimation
1 ½ inches above vertebral prominens
lower collimation
1-2 inches below costophrenic angles
posterior ribs furthest from IR (lateral chest)
magnified and projected slightly
should only be ¼ to ½ inch or 1 cm
horizontal beam
demonstrates air fluid levels
PA evaluation criteria
entire lungs included
no rotation
scapulae removed from lungs
chin elevated
full inspiration
equal collimation top and bottom
no motion
exposure factors
marker
hilum region markings
heart
great vessels
bony thorax
Lateral chest evaluation criteria
entire lungs included
no rotation
chin and arms elevated
correct collimation
no motion
exposure factors
marker
hilar region should be in center of IR
why do you angle the CR during AP Chest exams?
to prevent the clavicles from obscuring apices
CR should be perpendicular to the long axis of the sternum
AP supine/ semi-erect
similar to PA
magnification from shortre SID = increased OID of heart
air fluid levels not well defined
Lateral Decubitis Evaluation Criteria
entire lungs included
no rotation
arms not superimposed over lungs
full inspiration
marker
no motion
exposure factors
AP Lordotic Part/CR position
center MSP to CR and centerline of IR
Center IR to CR
top of IR 3 inches above shoulders
CR perpendicular to IR
center to midsternum
3-4 inches below jugular notch
2 full inspirations
Anterior/ Posterior Oblique part & CR Position
center patient to CR and IR
top of IR about 1 inch above VP
CR perpendicualr at T7
2nd full inspiration
marker
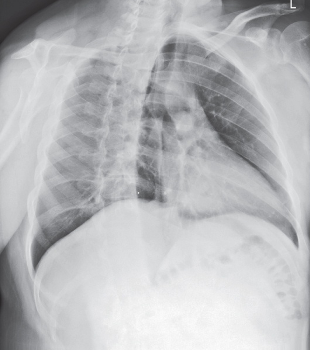
RAO
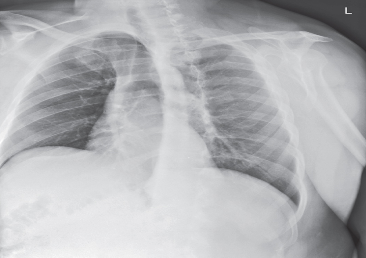
LAO