Labeling Animal and Plant Cell
1/19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
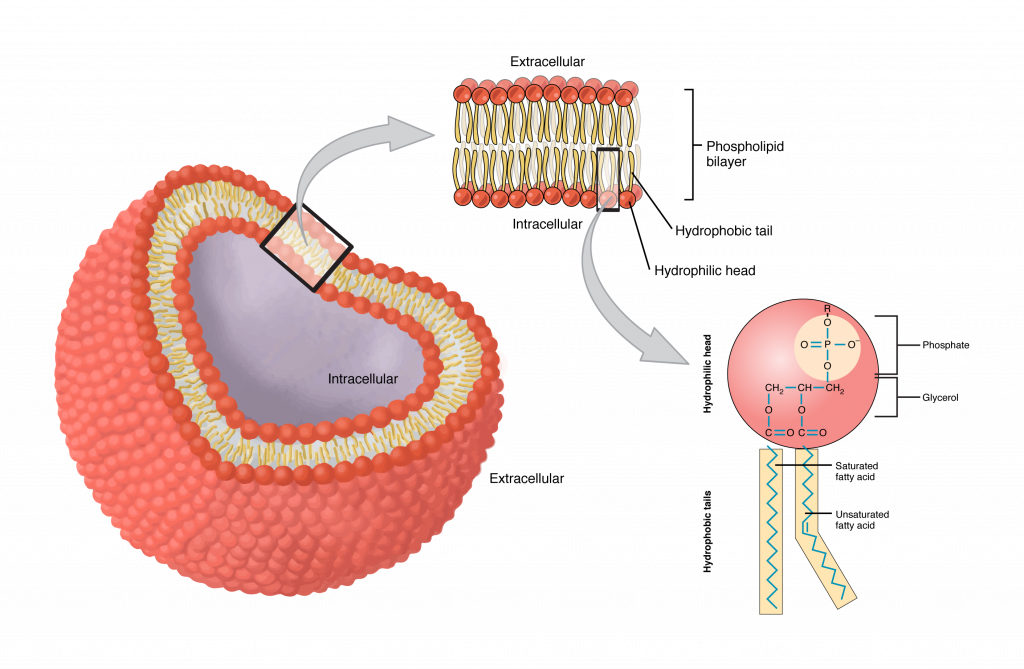
Cell Membrane
(both) Surrounds the outside of cell (made of two layers — phospholipid bilayer)
Controls what goes in and out of the cell
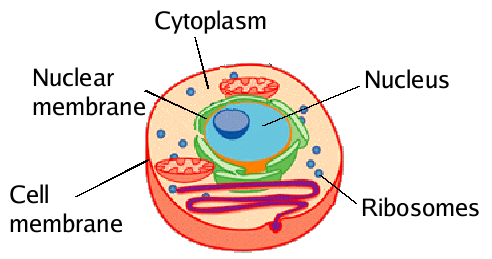
Ribosomes
(both) Made of Proteins and rRNA
Located on Rough ER and floating in cystoplasm
Makes Proteins
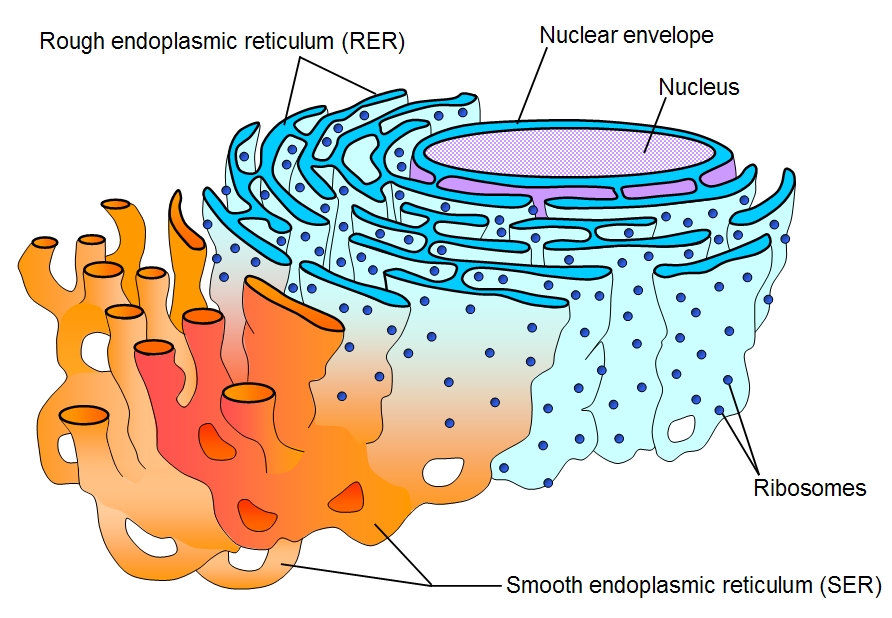
Smooth ER
(both) No ribosomes on surface; attached to Rough ER
Makes lipids (membrane)
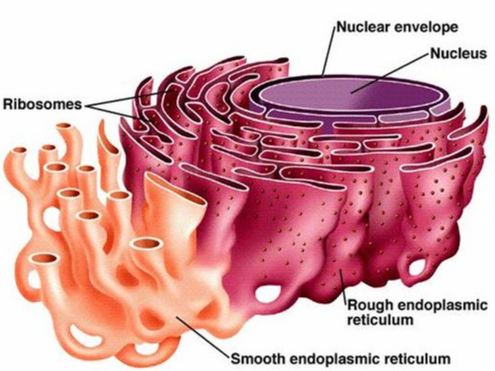
Rough ER
(both) Has ribosomes on surface; hugs nucleus
Makes proteins; packages proteins for secretion (discharge)
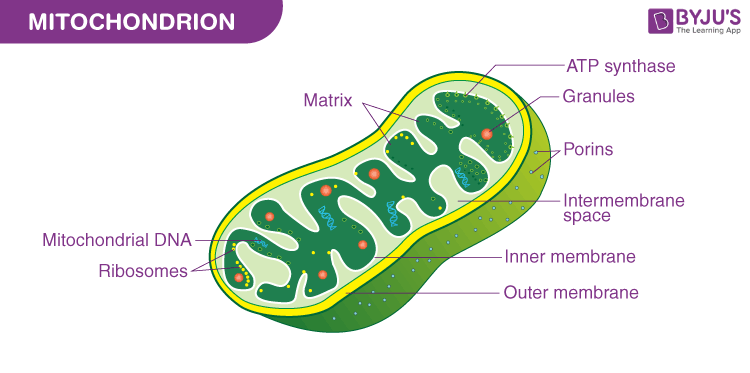
Mitocondria
(both) Two parts: inner membrane and matrix (fluid part)
Where cellular respiration (breaking down food to release energy as ATP (source of energy for cells)) happens
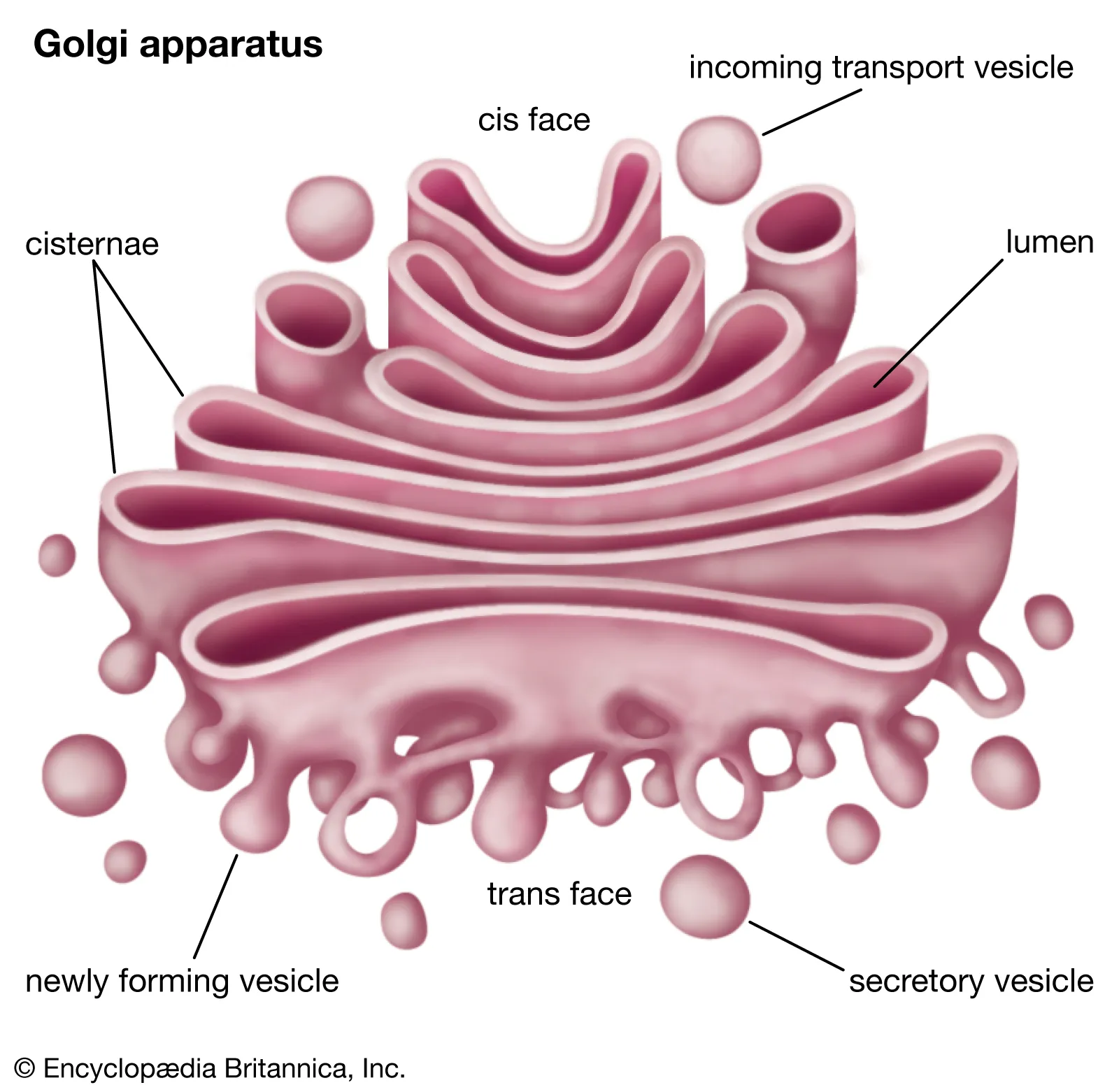
Golgi Apparatus
(both) folded membrane
Gets vesicles (carts for transporting pro. around cell) of protein from the ER; processes, sorts, and ships proteins where needed
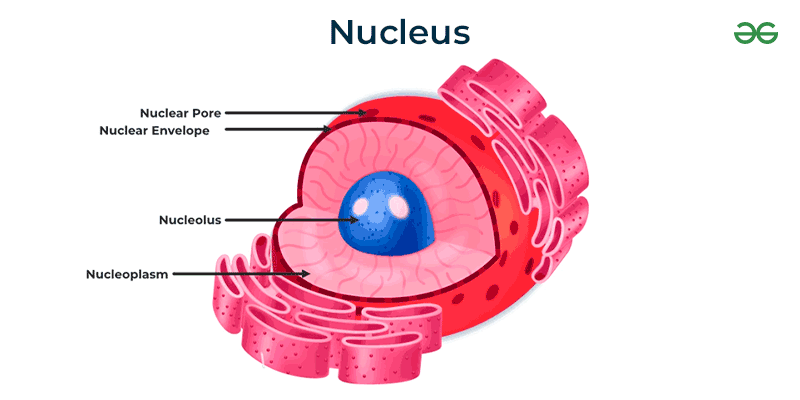
Nucleus
(both) Contains Genetic material (DNA); surrounded by a nuclear envelope/membrane with pores that control what goes in and out
Protects the DNA that controls the activities of the cell
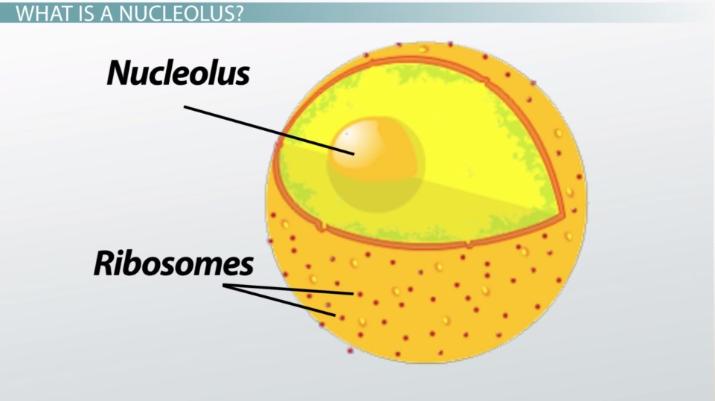
Nucleolus
(both) Inside of the nucleus
Makes rRna which makes up ribosomes
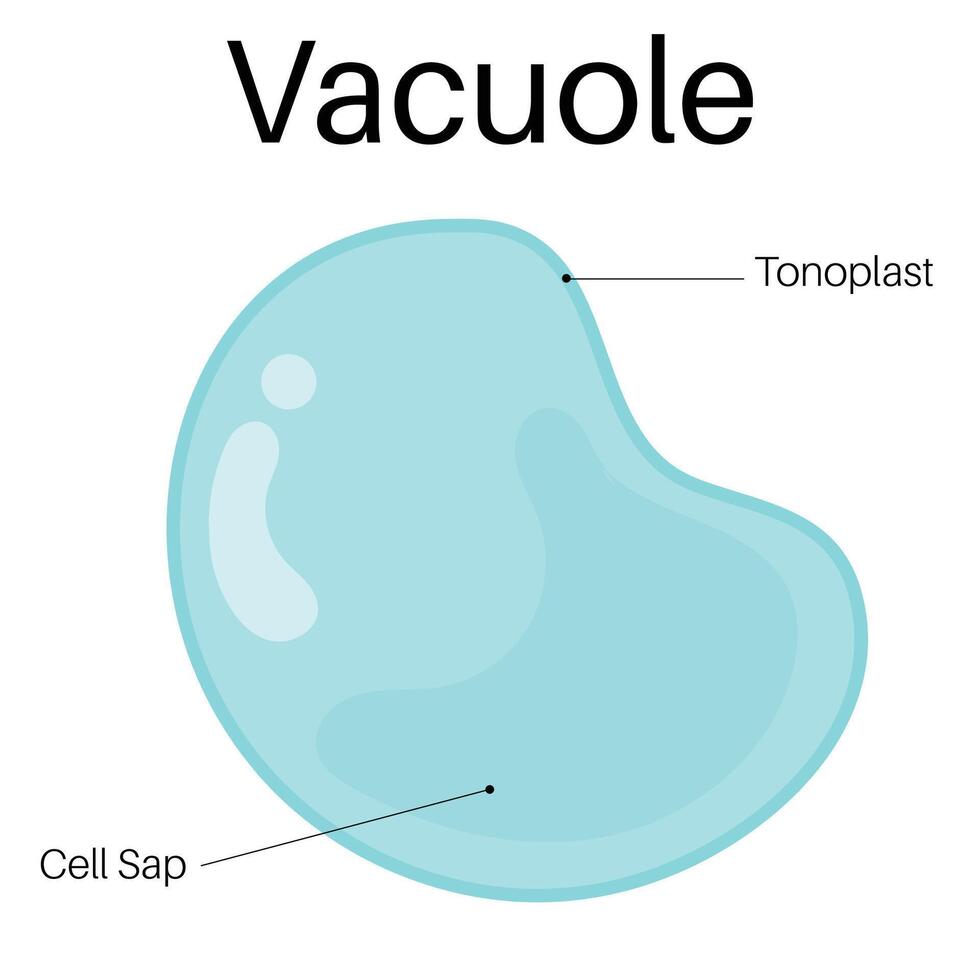
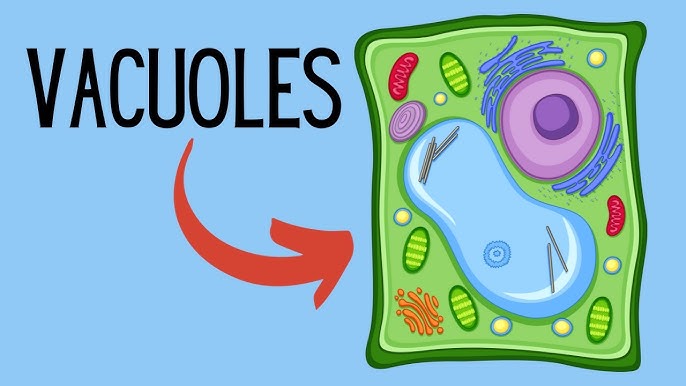
Vacuole
(animal) small and numerous
Storage (water, nutrients, waste, etc)
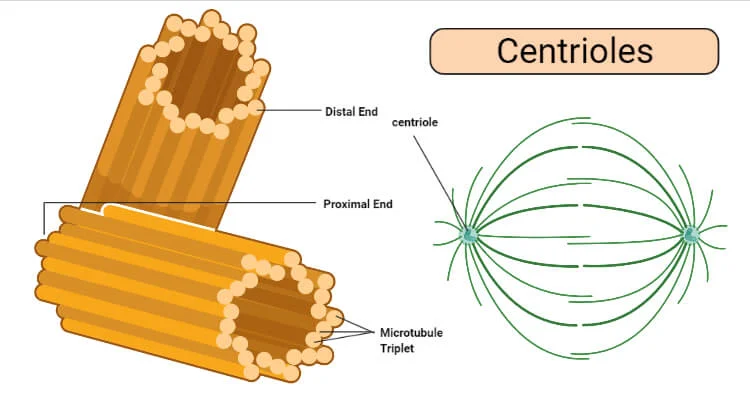
Centrioles/Centrosomes
(animal) Made of microtubles **centrosome: 2 centrioles together**
Appear during cell division; help cells divide by pulling chromosomes apart
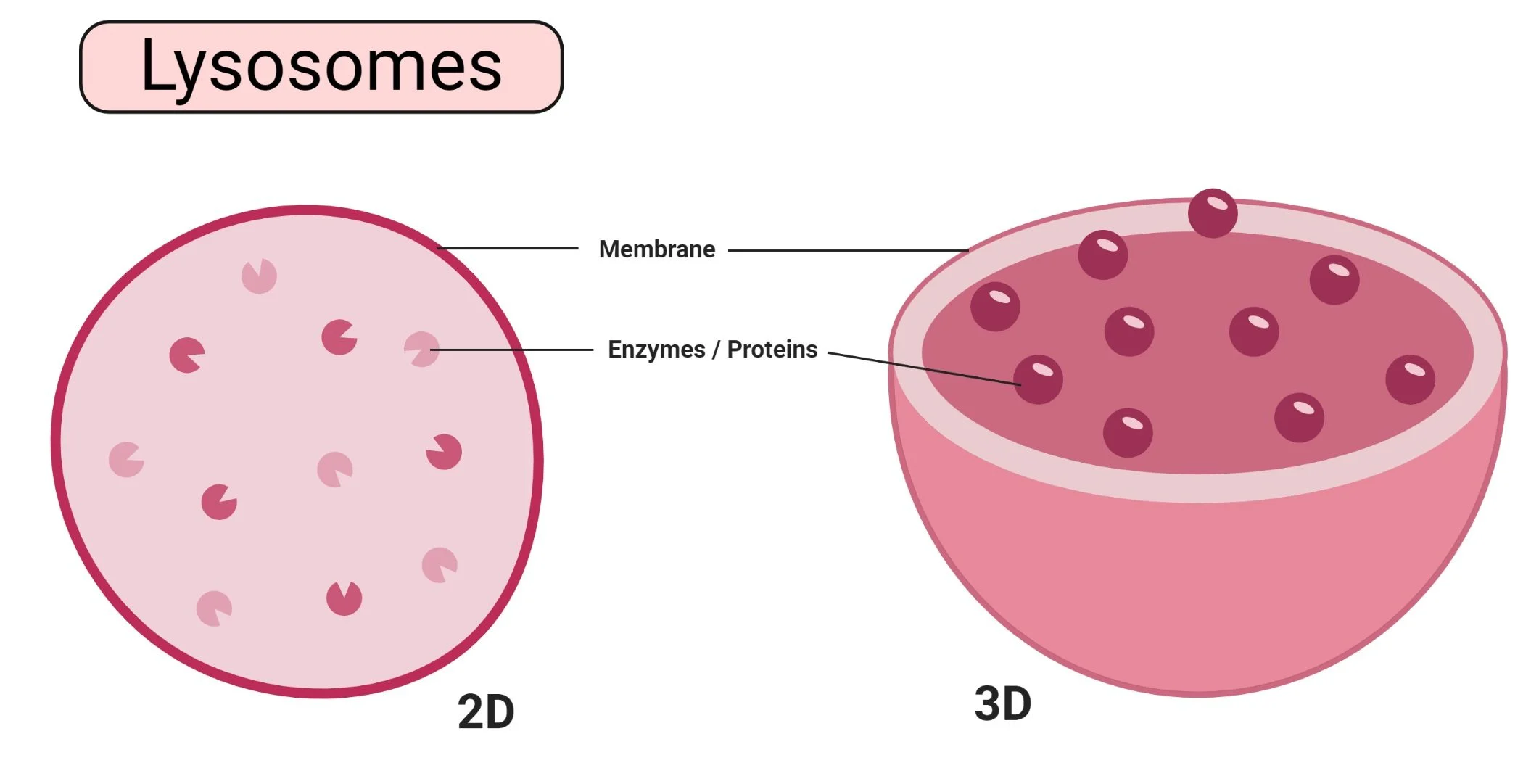
Lysosomes
(animal) contains enzymes
Break down dead stuff (food, bacteria, old parts of cell, etc); can do programmed cell death (apoptosis)
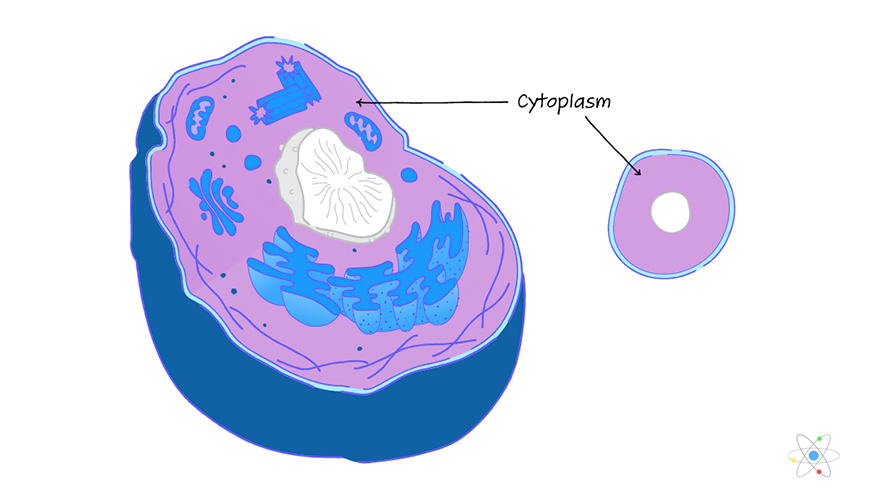
Cytoplasm
(both) Jelly-like substance; mainly made up of water
Holds everything in place
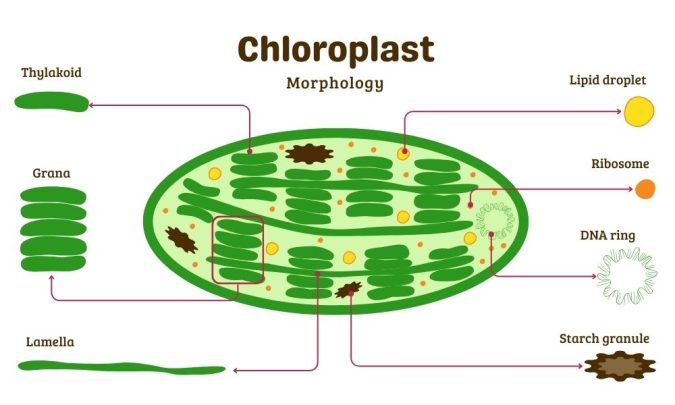
Chloroplast
(plant) Two parts: grana (stacks) and stroma (fluid)
Where photosynthesis happens; converts energy from the sun (energy into sugar)
Central Vacuole
(plant) 1 massive central structure
Storage centerc
Cell Wall
(plant) Made of cellulose (in plants), chitin (in fungi), and peptiodoglycan (in bacteria)
Protect and maintain shape of cell
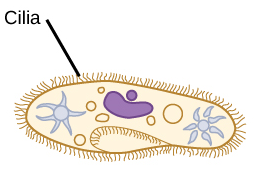
Cilia
(animal + bacteria) shorter, more numerous, like tiny oars
move fluid across cell’s surface
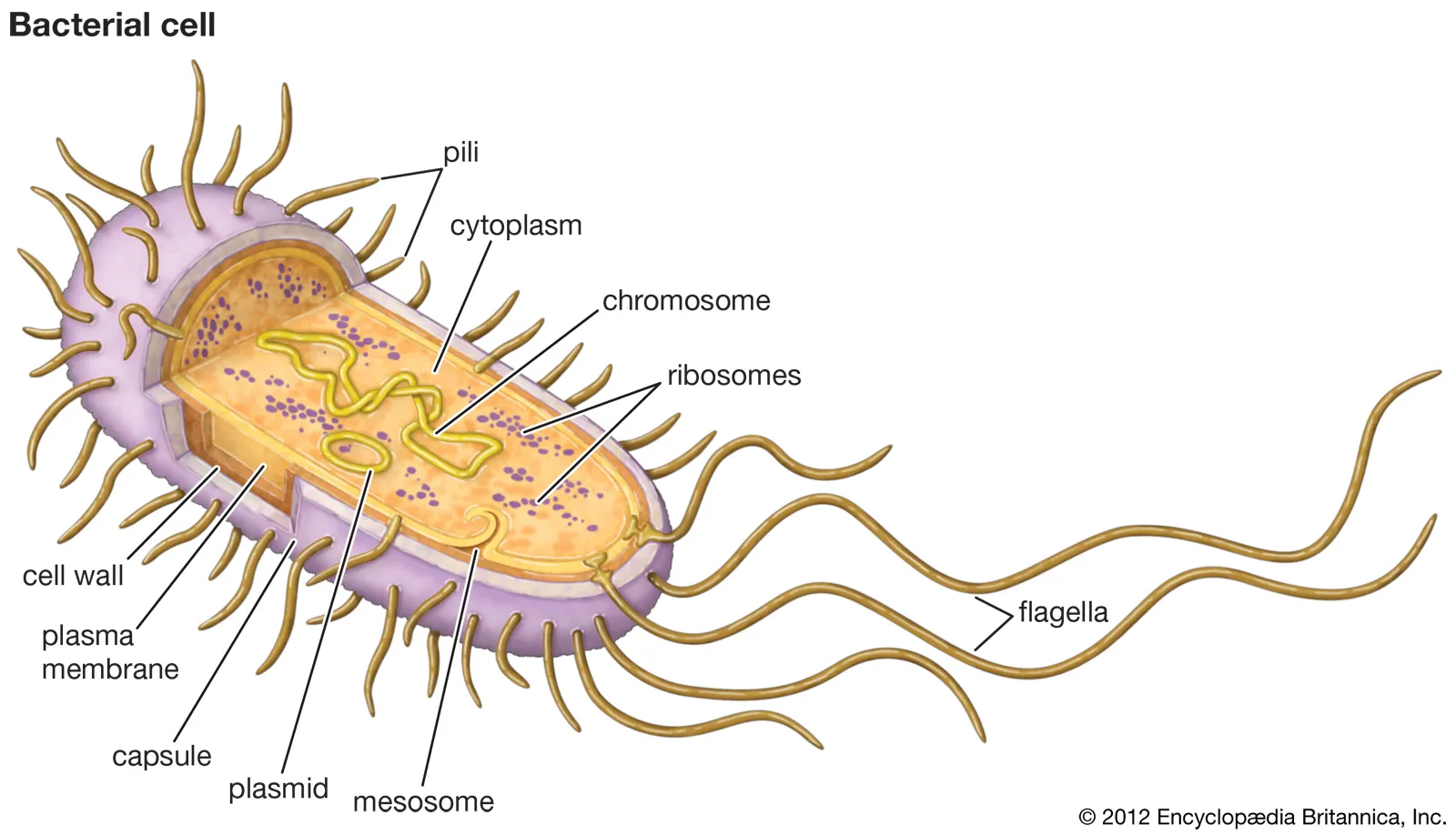
Flagella
(animal + bacteria) longer, fewer, acts like a whip to move cell
move entire cell through extracellular fluid
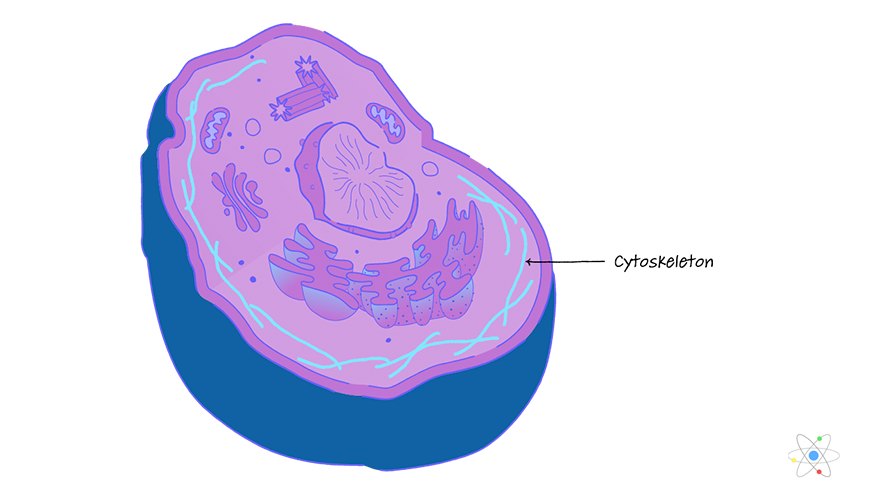
Cytoskeleton
(both) thread-like fibers; made of proteins, usually not pictured in a cell diagram
Give the cell shape; can also move organelles around; provide structural support for animal cells
Prokaryote
Binary fission; no nucleus; no membrane bound organelles; unicellular (EX: bacteria)
Eukaryote
Mitosis; Uni or Multicellular; membrane bound organelles; nucleus (EX: animals, plants, fungi)