Unti 1 Lecture 4
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
How are genes regulated? study of heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes to the underlyding sequence
Epigenetics
How do genes evolve over time
Genome Evolution
What do gene sequences tell us about evolutionary relationships between species?
Molecular Phylogenetics
What are the functions of the genes in an organism?
Systems Biology and Bioinformatics
How do genes guide embryological development?
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
A computer algorithm and software package that allows researchers to quickly upload and compare sequences from species against online databases of samples from other species in hopes of finding homologous sequences.
BLAST
Determining the location of every gene on a chromosome, as well as the function of every gene.
Gene Mapping
Calculating the accumulation of sequence differences between diverse species following a sequence alignment.
Seqence Divergence
Collecting sequence samples from many different individuals from the same species to create a “consensus” sequence that identifies the genes that are shared by all individuals of that species.
Reference Sequences
Collecting and compiling information from reference sequences to create a complete sequence of all the nucleotides, in order, found on every chromosome of a species.
Whole Genome Sequencing
Genetically modifying a sequence of DNA to include a mutation that inactivates a gene in a model organism so researchers can see what effect that broken gene has on the phenotype of the organism.
-study loss/change of protein function
analyze the role of non-coding regions
investigate mutations that cause disease
Gene Knock-Outs
Arranging sequence data from multiple different species to find where sequences overlap and where homologs are present, as well as where changes to the sequences have accumulated.
Seqence Alignment
Studying genomes allows for the comparison of diverse taxa even if they do not share any morphological similarities
True
Genes mutate at the same frequency over time, and this stable rate of mutation across all species can be used to calibrate molecular clocks
False
Molecular phylogenies are the most accurate type of phylogeny and do not require revisions
False
Most mutations are selectively deleterious and lead to hybrid breakdown over time
False
Mutations are caused by environmental factors such as natural selection and gene flow
False
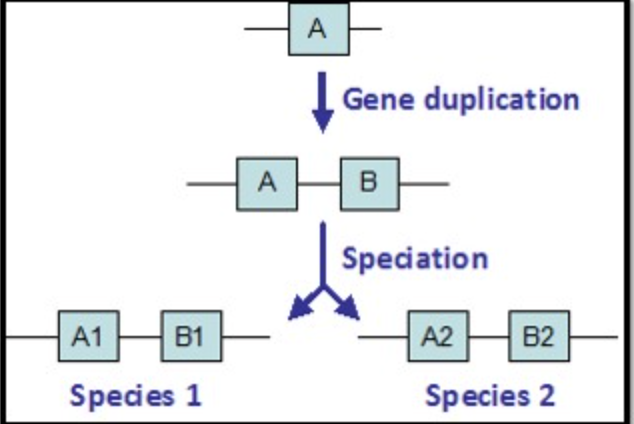
Gene A and Gene B arose due to a gene mutation within a single species. The functions of the two genes differ. These two genes are:
Paralogous
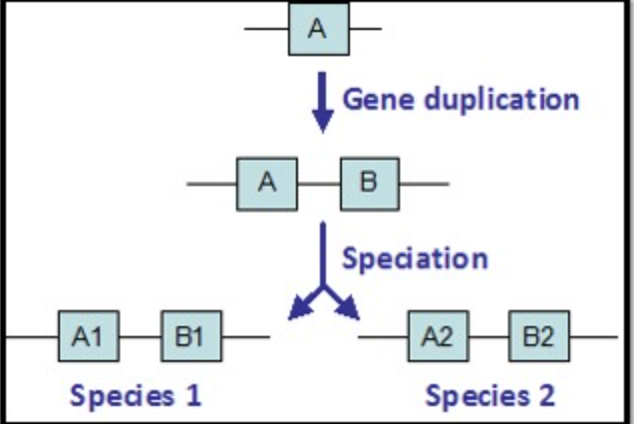
Genes A1, A2, B1, and B2 indicate common ancestry. These 4 genes are all:
Homologous
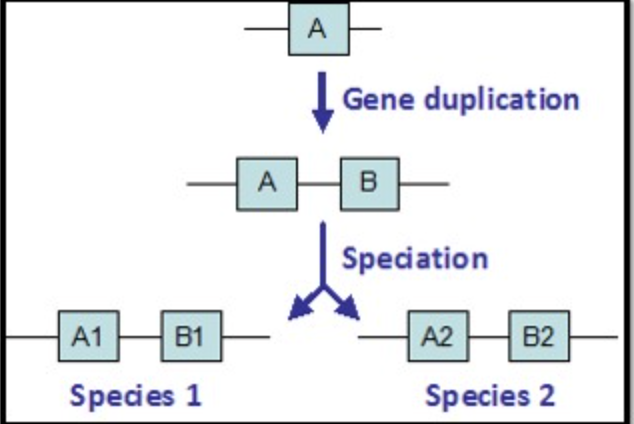
Gene A1 in species 1 is identical to Gene A2 in species 2. They encode for nearly identical proteins and are evidence of common ancestry. These two genes are:
Orthologous
Genome
genetic materal of an organism
Bioinformatics
computer-sciecnce based field
science of collecting and analyzing complex biological data ex. genetic codes
Sytems biolofy
aims to model the behavior of entire biological systems based on the study of the ststems paths
-omics fields careate cataloigues of genes and their products
Point mutations
alter a single gene
Homologous genes
show common ancestry and result from divergent evolution
Orthologous
genes that are present in different species
Paralogous genes
genes that result from duplication of a gene within a singe species, resulting in the potential for different gene functions
present in different species
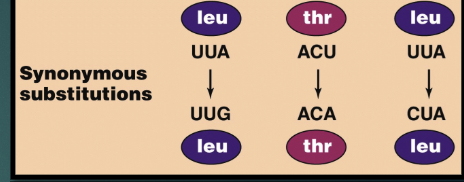
Synonymous mutations
nucleotide is altered but the resulting amino acid stays the same; silent mutations
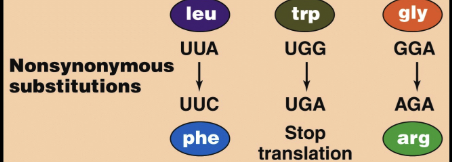
Non-synonymous mutations
nucleotide is altered and the animo acid sequence cahanges as a result
Missense mutation
altetred protein
small change= conservative missense
large change= non-conservative
Nonsense mutation
creates a stop codon that ends translation
Frameshift mutation
Insertion or deletion of nucleotide cause reading frame to shift
Molecular Clocks
mutations accumulate in a fiven seqence at predicatble rates
Neutral theory
many changes are not acted upon by selection
they occur by chance
A gene that codes for a protein that is needed to build structures or perform functions within a cell
Structural gene
A sequence of DNA that does not code for the formation of a protein, but has other functions within the genome
Non-coding Gene
A gene that codes for regulatory proteins that can activate or de-activate other genes
Regulatory Gene
A transposable gene, or transposon, that can move and interrupt gene sequences, leading to dysregulation or a loss of gene expression
Non-Coding Genen
Structural genes
Code for proteins needed to build structures or perfome functions within a cell
Non-coding genes
some contribute to ene regulation and expression
change in phenotype without change in genotype
epigenetics
EVO-DEVO
compare the developmental processes of different species
how these traits evolved
The increased expression of keratin in some reptiles and birds is regulated by histone modification which increases the efficiency of the transcription of the genes necessary to produce keratin proteins in structures like scales, feathers, and beaks
Epigenetics
An alteration to the gene Gap5 controls the expression of eyes in fish and amphibians; modifications to this gene cause eyes not to form during development
Evo-Devo Rule 1
Hox and Gap genes are seen in all species of animal and indicate that all animals evolved from a common ancestor that had homeobox gene sequences
Evo-Devo Rule 2
Evo-devo rule 1: Modular Body plans
changes to developmenttal regulatory genes cause changes tp body segment arrangements
HOX genes
genes in animals contail a similar 180 nucleotide seqence (homeobox)
GAP genes
activate early in embryonic development and help regulate the formationof major body structure
Evo Devo 2 Conserved genes
developmental regulatory genes are highly conserved over time and across species
control the body plans of organims