Pathology - Block 1
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Block 1 Practical
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
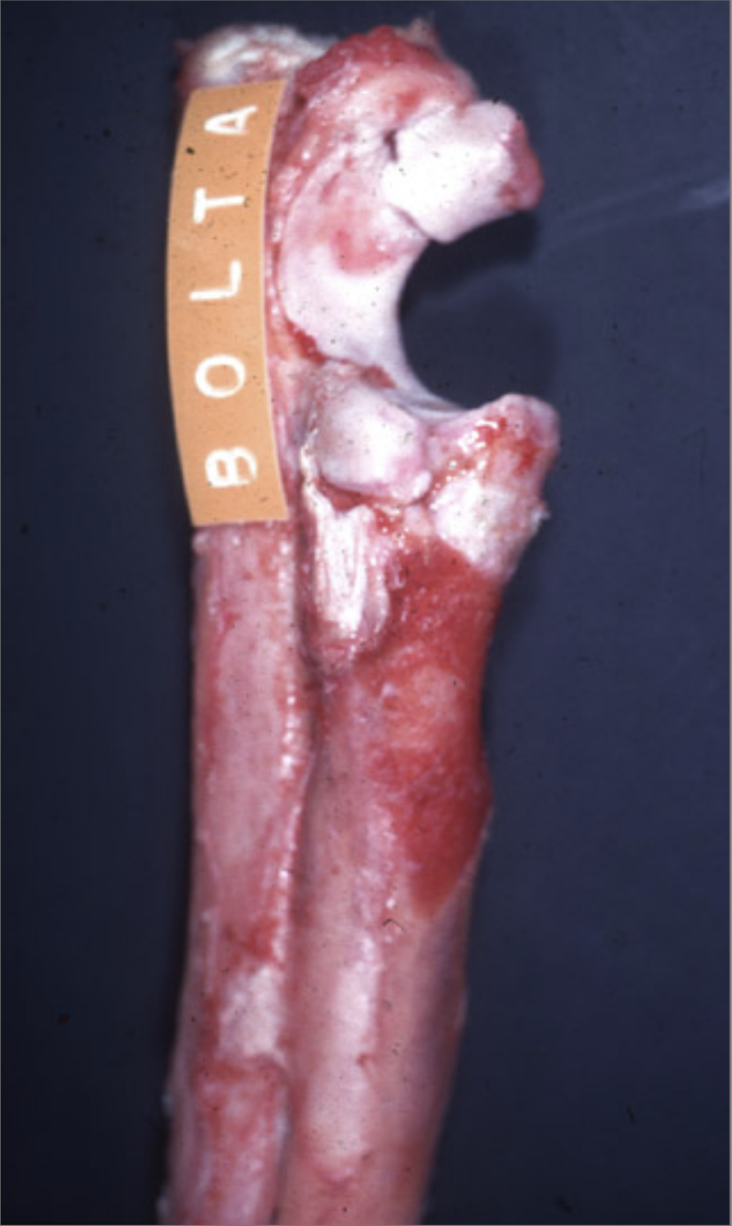
This was taken from a 7 month German Shepherd.
What could cause the lesion presented?
Developmental
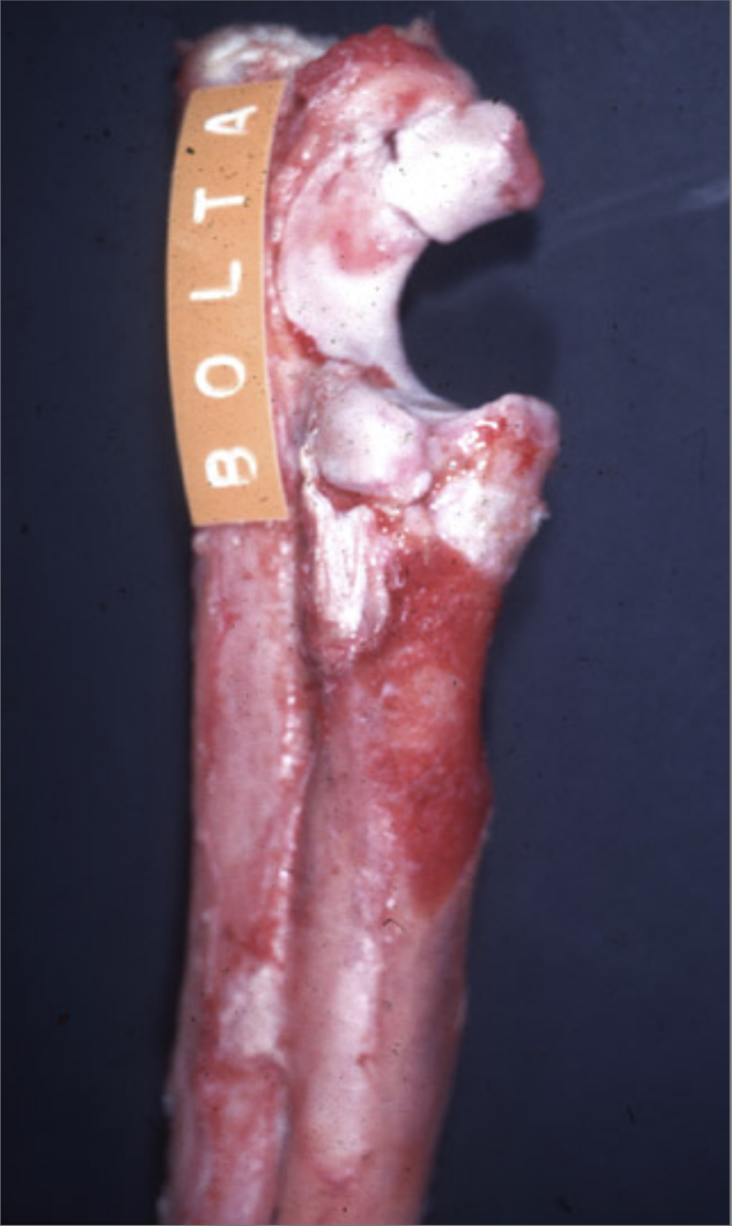
This was taken from a 7 month German Shepherd.
What is the name of the lesion shown?
Ununited anconeal process
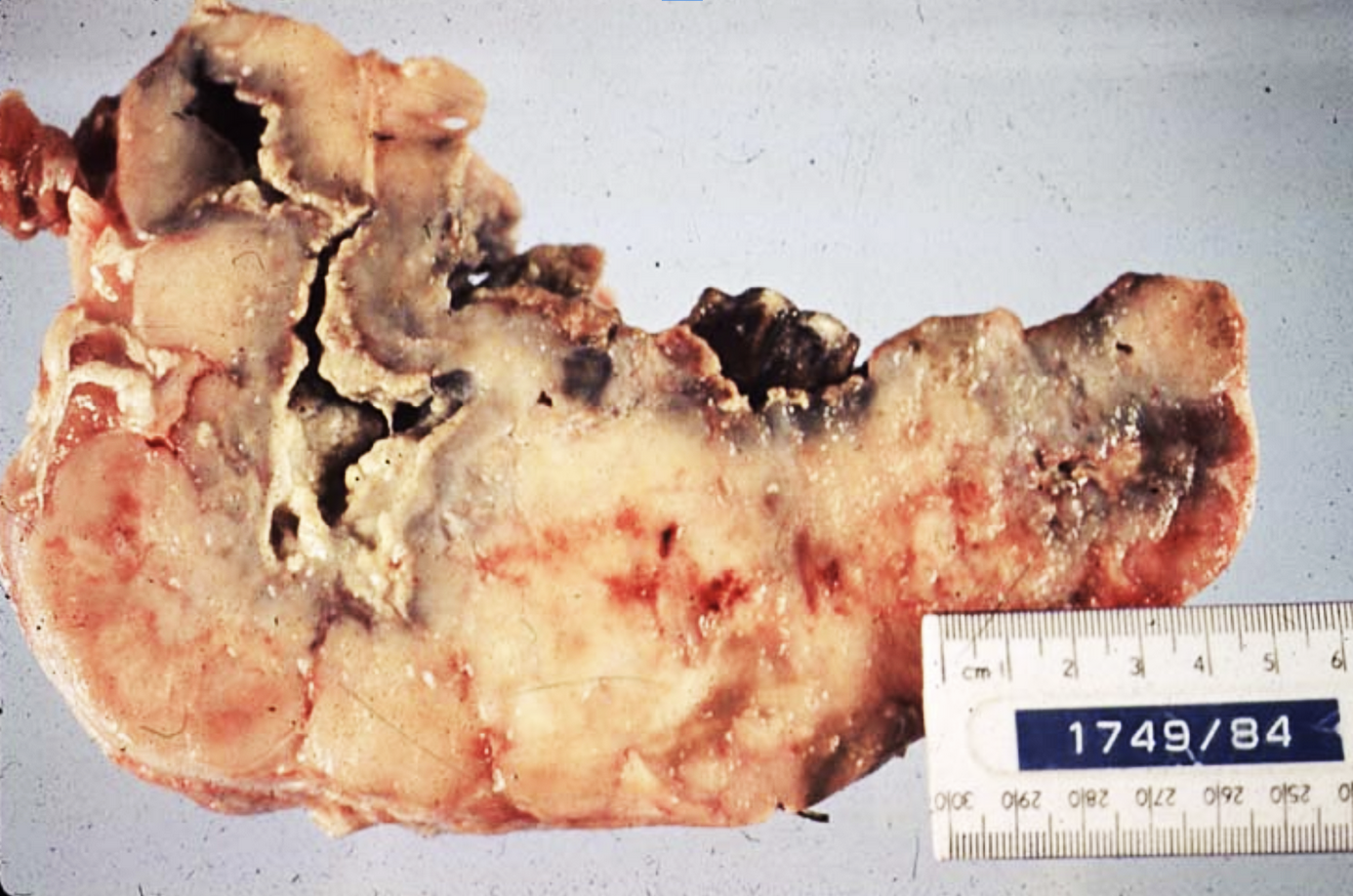
This was taken from a deer.
The lesion is slow growing with purulent exudate draining, caused by mandibular osteomyelitis (“Lumpy jaw”). What is the distribution of this lesion?
Focal + Locally Extensive
Classify the lesion.
Degeneration
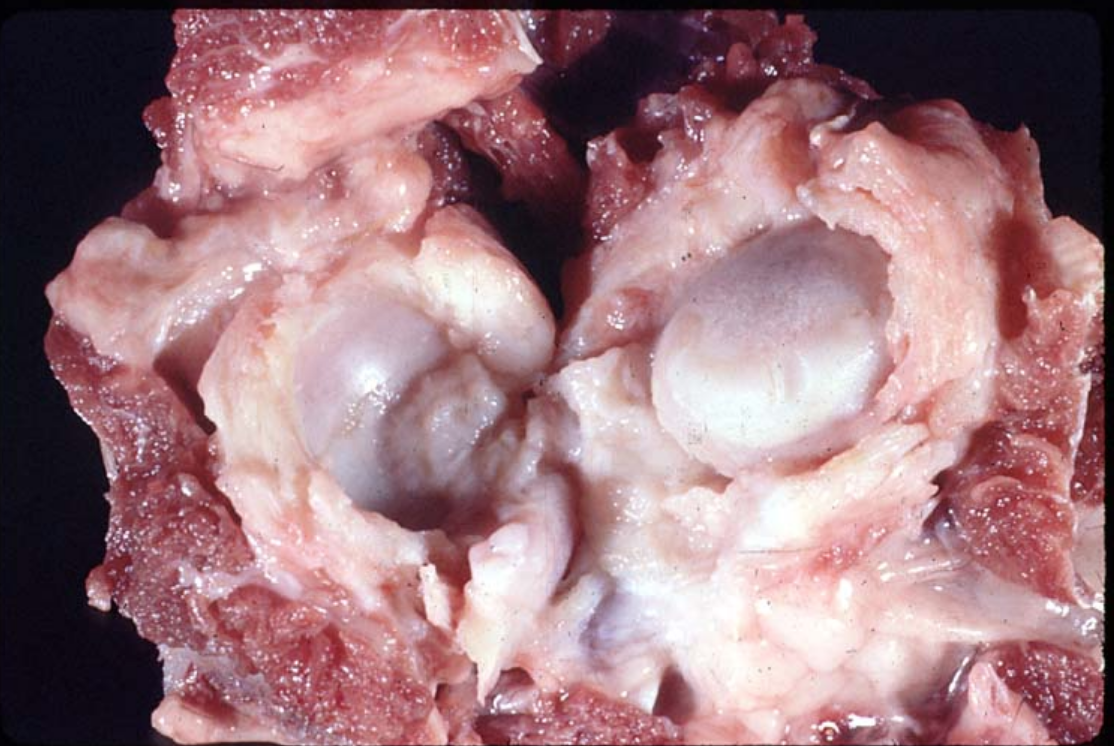
What pathological process has taken place at this coxofemoral joint?
Eburnation - loss of articular cartilage at the femoral head
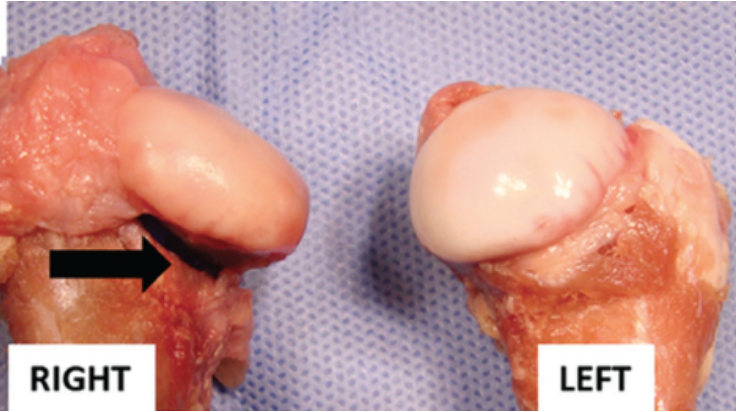
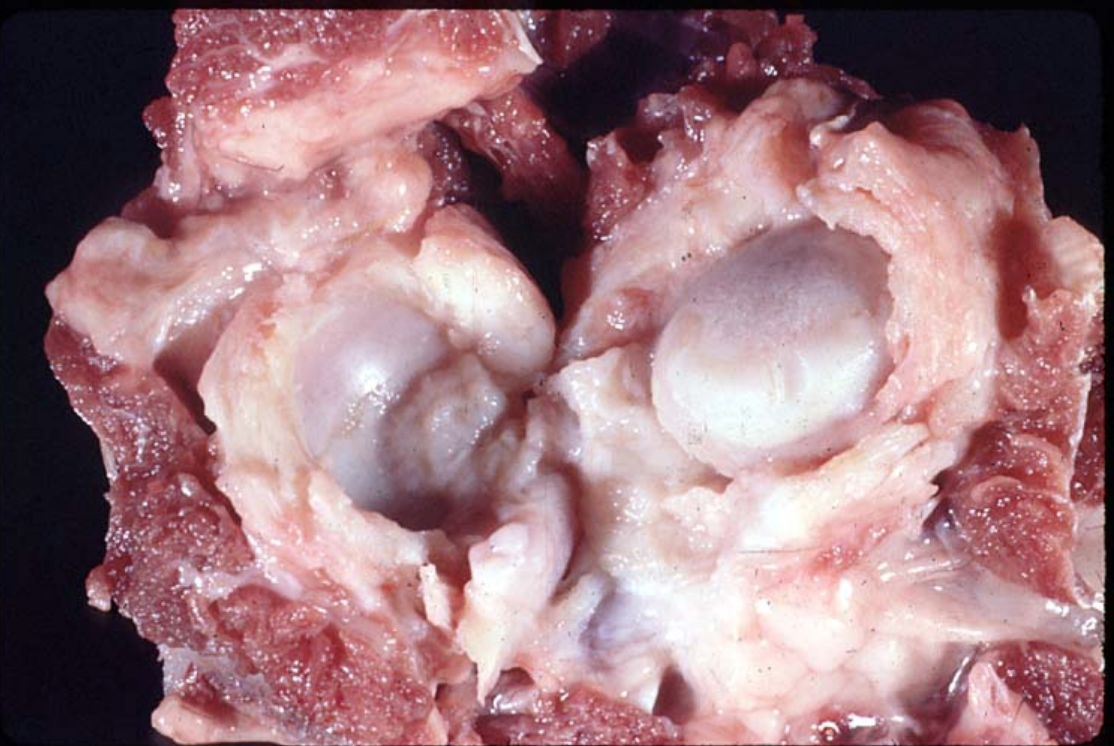
Left and right femoral heads of a piglet.
Where and what is the lesion?
Right - flattening of femoral head due to ischemic necrosis of the subchondral bone
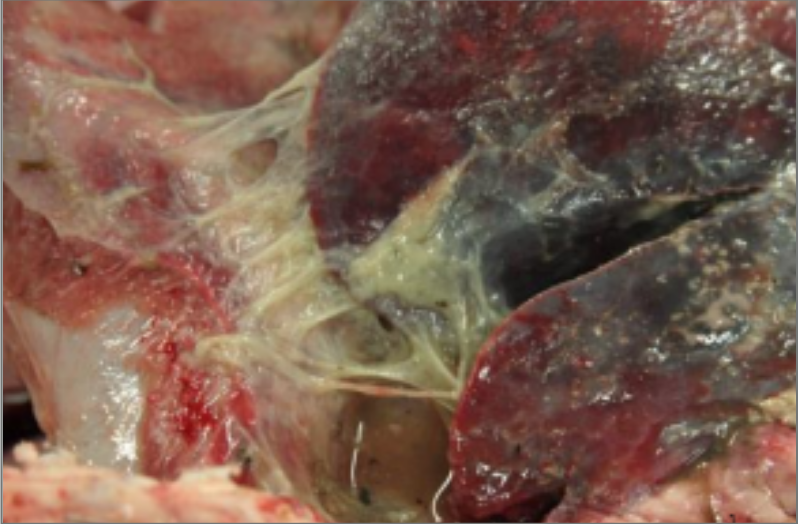
What inflammatory marker is seen here?
Fibrin
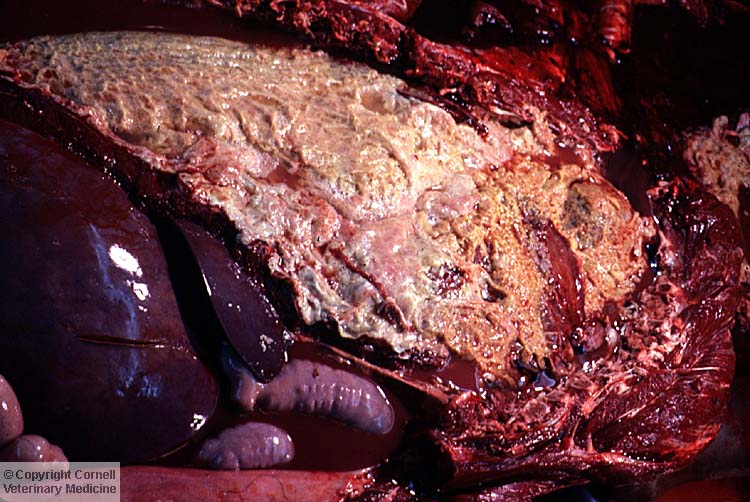
What inflammatory marker is seen here?
Fibrin
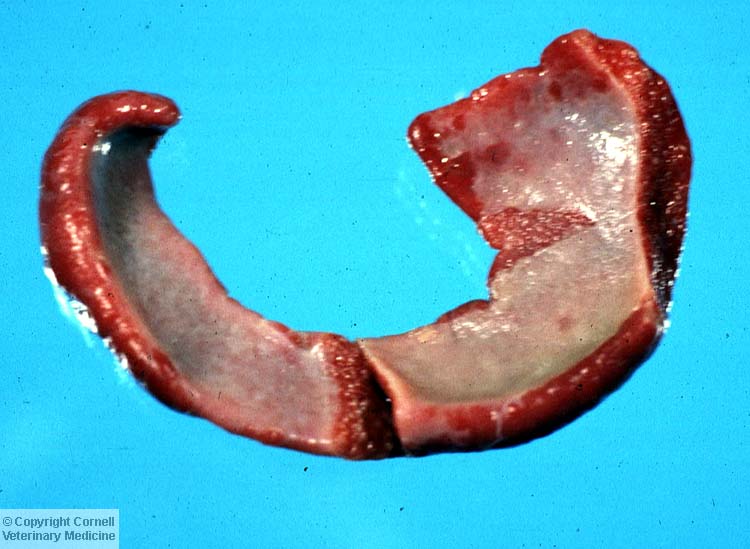
What inflammatory marker is seen here?
Fibrinogen
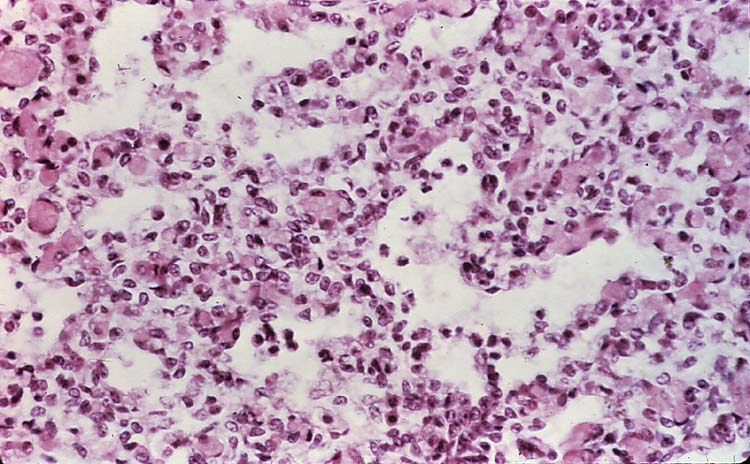
Taken from a fetal lung of a sheep.
Name the predominant cell type seen in this slide (within the alveoli).
Neutrophils
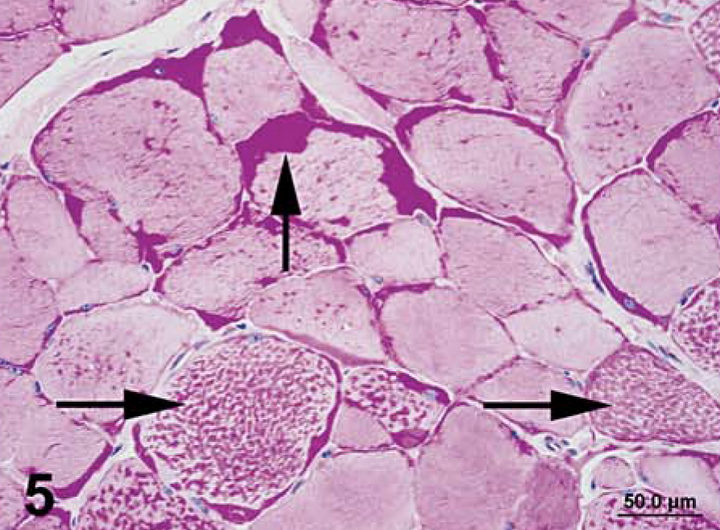
Skeletal muscle biopsy stained with PAS.
What is your diagnosis and why?
Polysaccharide storage myopathy- intracytoplasmic accumulations of abnormal polysaccharide
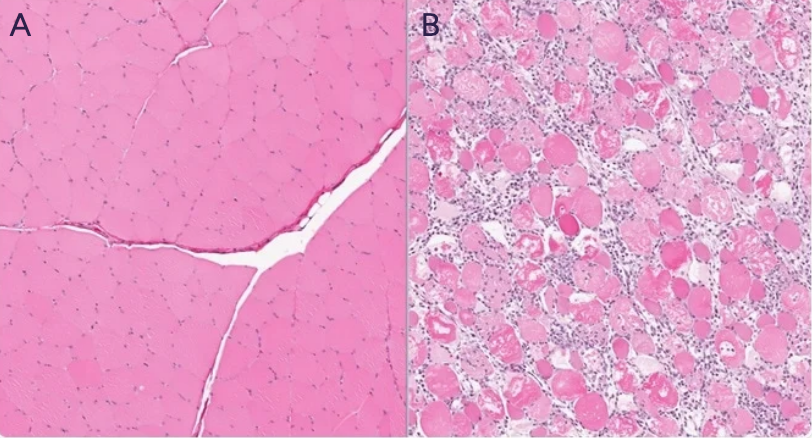
Attached are two different muscle fiber segments.
If Picture A showcases normal skeletal muscle fibers, how would you describe the muscle segment in picture B?
Rhabdomyolysis - macrophage infiltration & necrotic myofibrils, resulting from lysis and severe inflammation
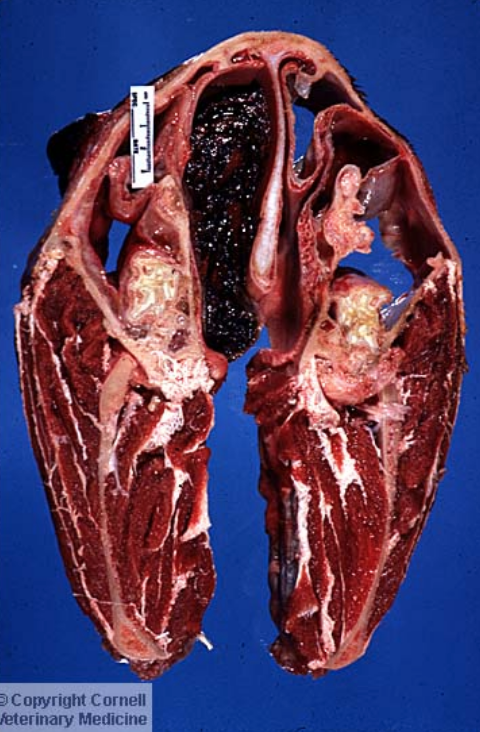
What features would we expect to see on histopathology of the following lesion in the horse nasal cavity?
Granulation Tissue (macrophages, fibroblasts, blood vessels), Fibrous Connective Tissue, Hemosiderophages
Which lesion carries the highest, most IMMEDIATE risk of potentially fatal hemorrhage in horses?
Guttural Pouch Mycosis
Both ethmoid hematomas and guttural pouch mycosis can cause epistaxis in horses.
Which feature most reliably distinguishes guttural pouch mycosis?
Fungal plaques eroding into the internal carotid artery
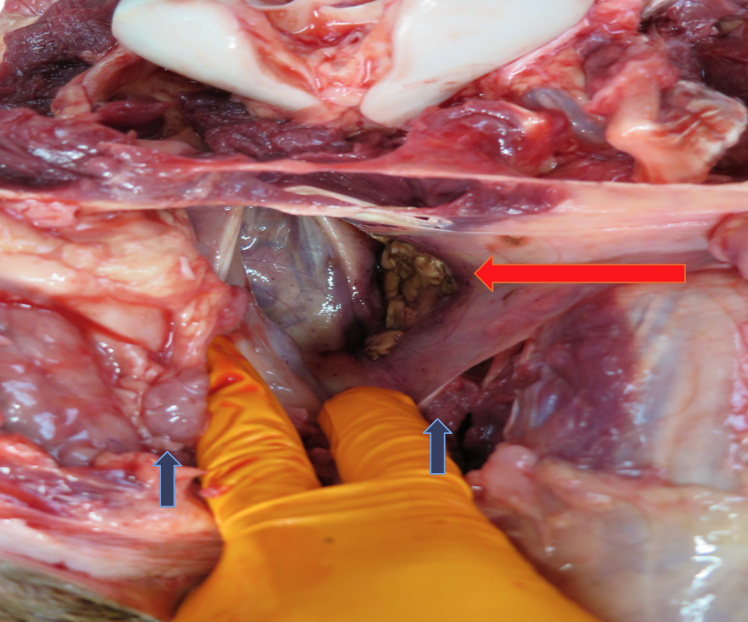
What abnormal structure is observed in the guttural pouch of this mare (red arrow)?
for reference, blue arrows = condyles
Fungal Plaque
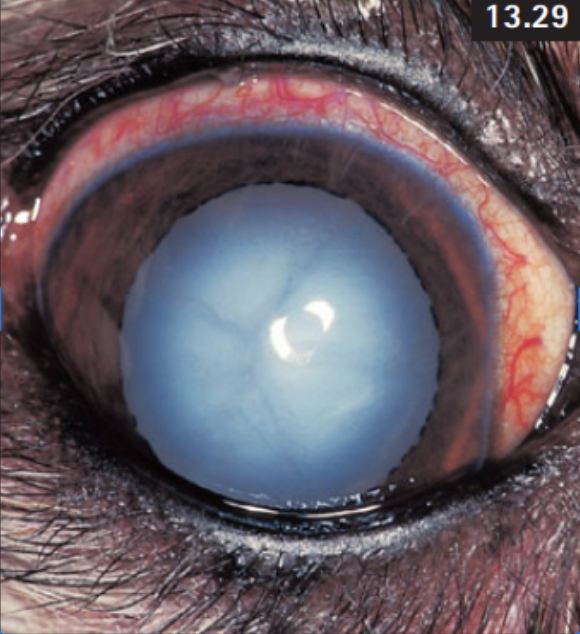
What aspect of the eye is affected + what is the pathology?
Lens + Cataract (cloudiness due to thickening of lens fibers)
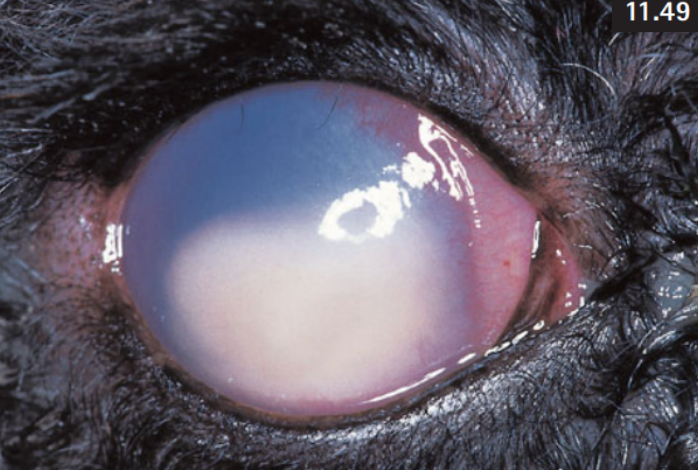
Eye of a dog diagnosed with uveitis and secondary glaucoma.
What pathologies do you see?
Hypopyon, Superficial Corneal Neovascularization
What is the definition of hypopyon?
Accumulation of pus, or white blood cells, within the eye
What is the definition of eburnation (and a common example)?
Bone becomes abnormally dense, hard, and smooth due to chronic friction and the loss of articular cartilage (osteoarthritis)
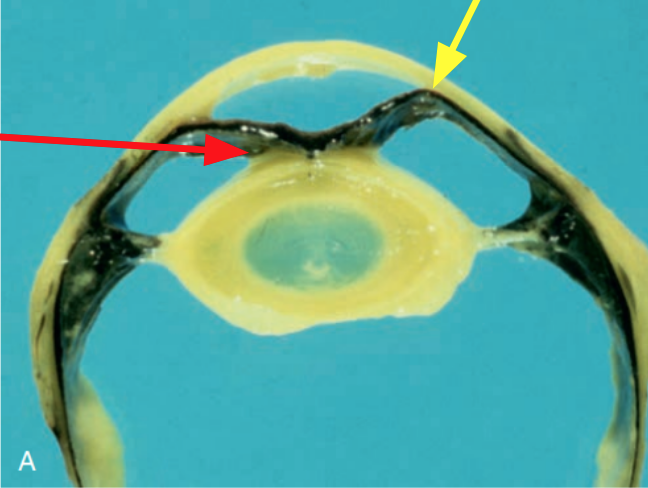
What is the pathology indicated by the red arrow?
Synechiae
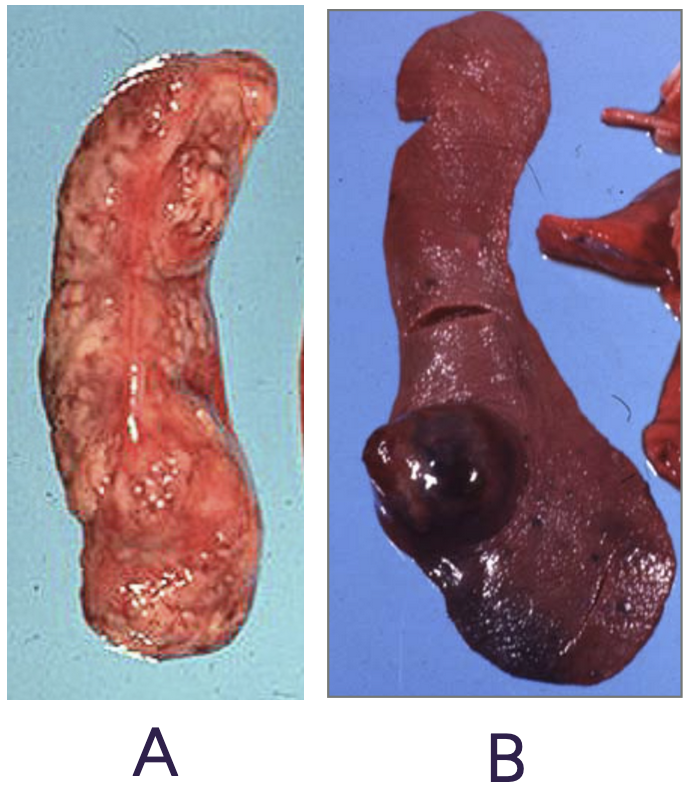
Both of these masses on the spleen are very invasive.
What are the correct distributions of each lesion? + Identify if the mass is more likely to be hemangiosarcoma or lymphosarcoma?
A - Multifocal Lymphosarcoma, B - Focal Hemangiosarcoma
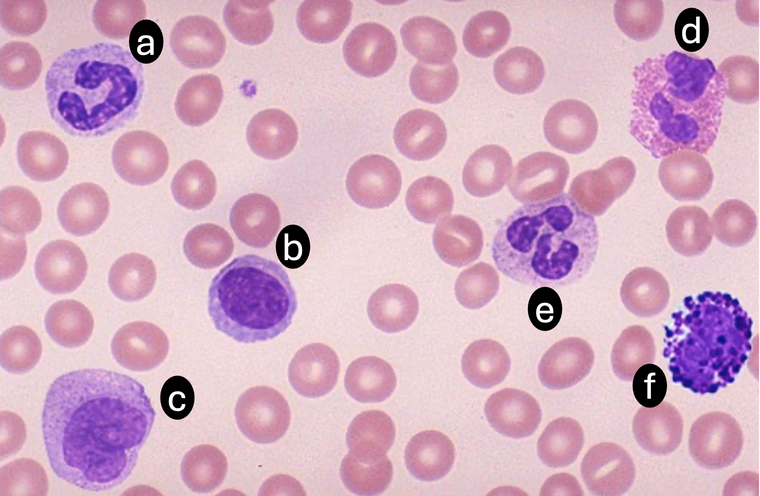
Which is the correct identification of each cell type shown?
A - Band Neutrophil / B - Lymphocyte / C - Monocyte / D - Eosinophil / E - Segmented Neutrophil / F - Basophil
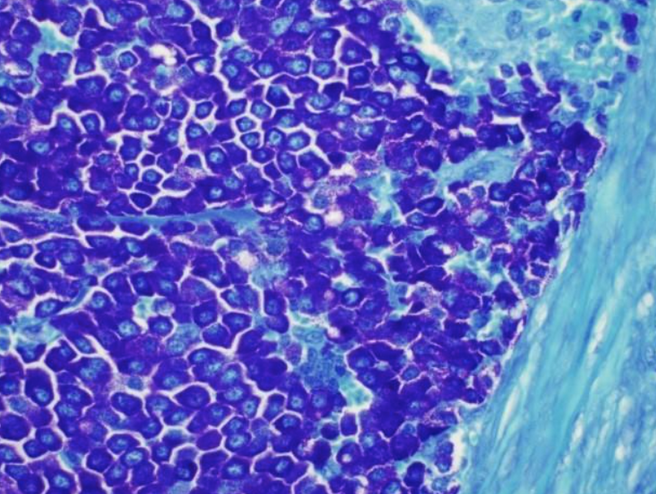
What is the predominant cell type seen on this slide? + What stain was used to visualize them?
Mast Cells, Toluidine Blue Stain
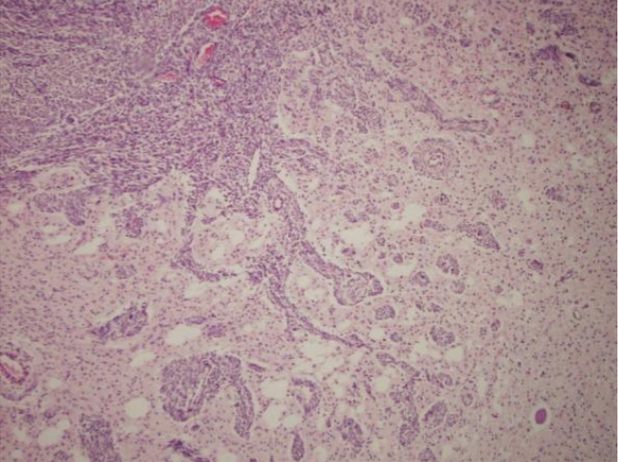
Examine the histological slide of this neoplastic lesion.
Which feature is most indicative that the tumor has metastatic potential?
Tumor cells invading adjacent tissue
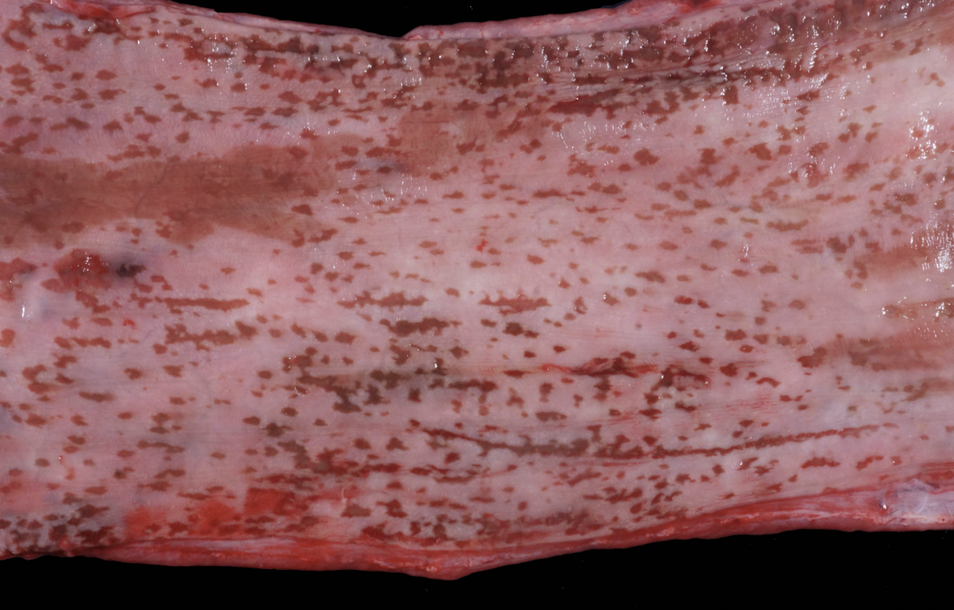
Esophagus of a 6 month old Angus bull calf that was experiencing diarrhea and a low body temperature.
What is the distribution of the lesion? + Using DAMNIT-V, what is the most likely cause of the lesion?
Multifocal + Infectious
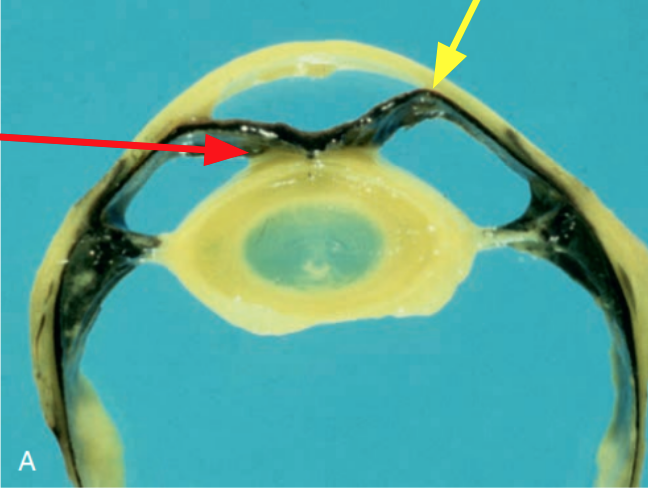
What is the lesion indicated by the yellow arrow? + How does it relate to the pathology indicated by the red arrow?
Iris Bombe + iris ‘bows’ or ‘balloons’ forward due to obstructed aqueuous humor outflow
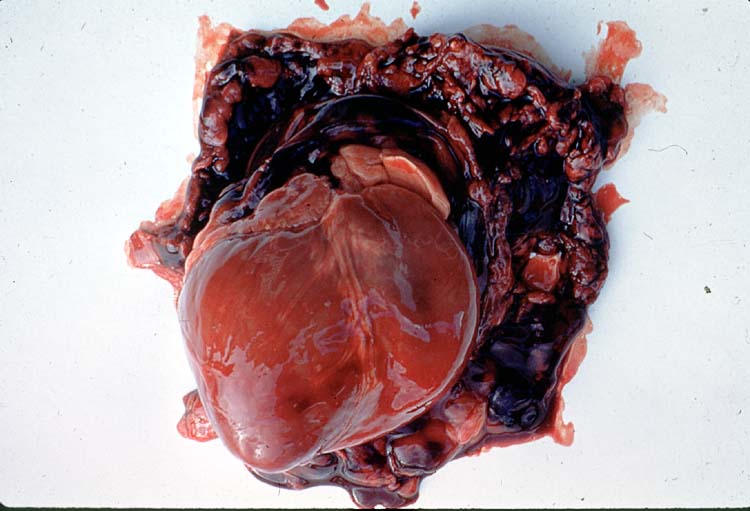
Identify the lesion.
Hemorrhage associated with the thymus
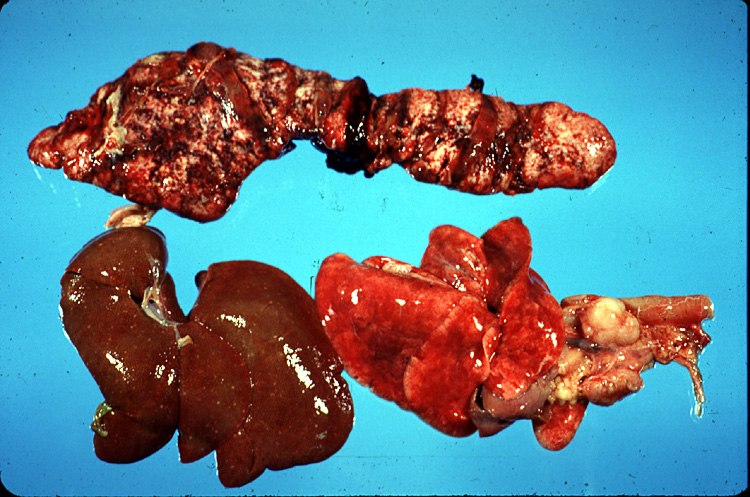
Identify the three organs shown; all are from a cat with lymphosarcoma. (think about pathology of lymphosarcoma & which organs would likely be affected!)
Spleen, Liver, Thymus
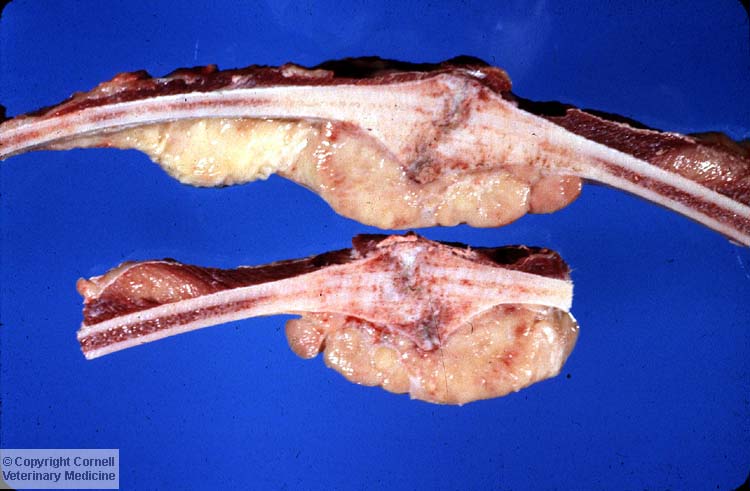
Ribs from an adult cow.
Which of the following can you identify in the photo?
(probably a little too clinical, but thought it was cool to see something that tied together multiple cases from this block!)
Rib Fractures with Callus Formation, Secondary Lymphosarcoma of Reactive Bone
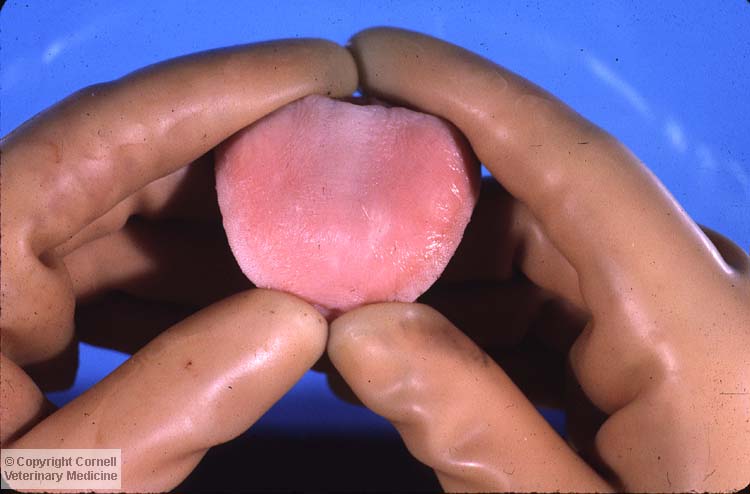
The photo showcases the tongue of a calf that had been diagnosed with muscle degeneration caused by white muscle disease.
Which of the following is a common contributor to this disease process?
Vitamin E & Selenium Deficiencies
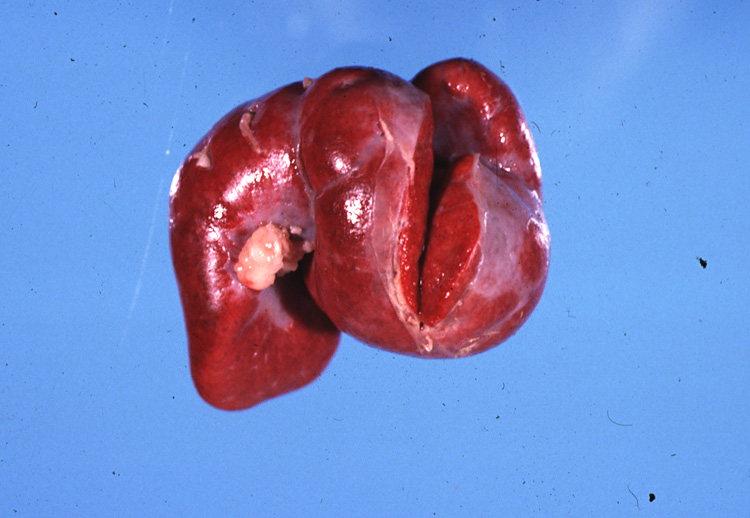
Enlargement and contortion of a feline spleen, both secondary to a mast cell tumor. Which pathology is most likely?
Both are secondary to the expansion of the mast cell tumor.
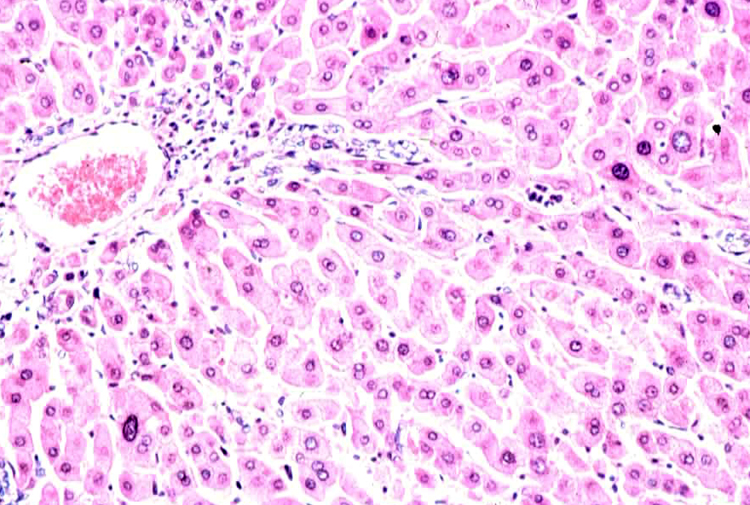
Which of these is the best definition of pleomorphism? (it can be visualized in the photo, which is from the liver of a woodchuck!)
All of these choices define pleomorphism!
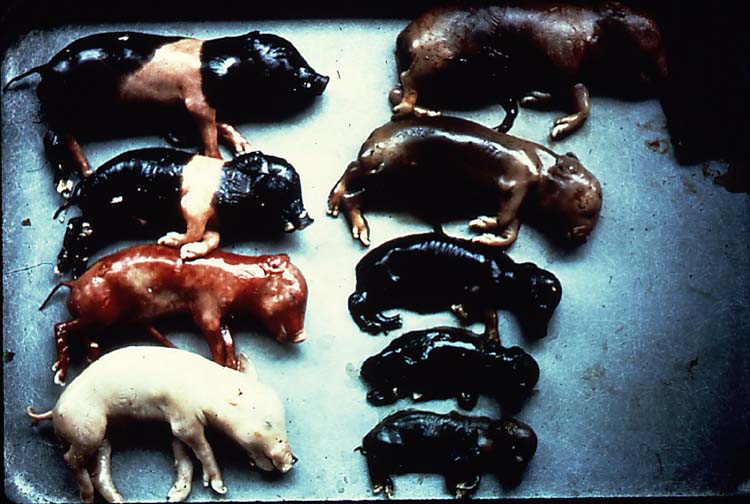
How many mummified feti are in this photo? (Dr. Alcaraz used this photo during pathology rounds and a lot of people guessed incorrectly, so it may make an appearance on our exam)
3
Mummification, maceration, and stillbirth are all types of abortion. Which of these statements about fetuses is correct?
Stillbirths have hair, where macerated or mummified fetuses do not
Mummification of a fetus is caused by which of the following?
Placental Insufficiency
Which of the following IS NOT considered a phase of the wound healing process?
Regeneration
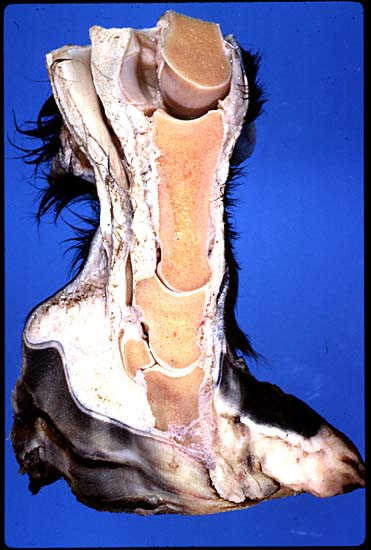
The photo showcases an extreme case of:
Laminitis
Which of these DOES NOT contribute to ‘inflammatory soup’?
Infiltration of Damaged Tissue by Inflammatory Mediators
Are you ready to ace this pathology exam?!!
HELL YEA!!!!!!!!!!!!!