Validity and Reliability
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
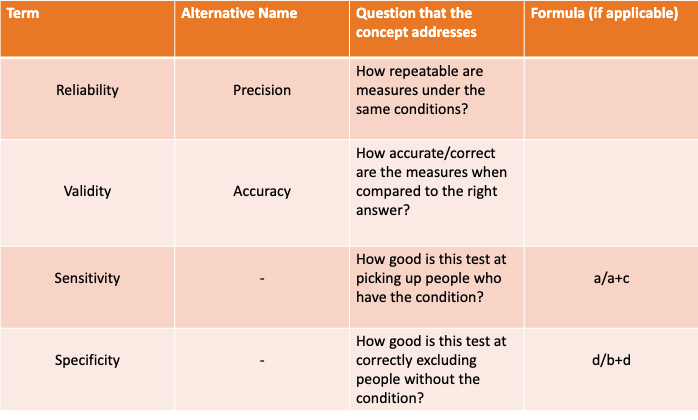
reliability is also known as…?
precision
what term refers to the consistency or repeatability of measurements?
reliability (A test or instrument is reliable if it produces the same results under consistent conditions)
Results are less reliable when there are outside influences that are unknown or difficult to control. In other words, minimizing ________ is important.
random error
Nutritional epidemiology (the relationship of nutrition and health in populations)
Do you eat the exact same foods in the exact same quantities every day?
◦ No!
◦ Your diet varies from day to day, and even month to month.
◦ An epidemiologist would sample data from multiple days
This is an example of what concept?
reliability
validity is also known as…?
accuracy
what term refers to the accuracy of a measurement or whether the test measures what it is supposed to measure?
validity
what is internal validity?
◦ Study results are generalizable to the source population
◦ Required for external validity
what is external validity?
study results are generalizable to populations outside the source population
in order to have validity, we must minimize what 2 things?
bias and systematic error
Nutrition research
Are you able to remember everything you eat?
◦ No!
◦ You will systematically underestimate the amount you eat (what kind of biases could this be?)
This is an example of…?
validity
If you do research where you are measuring something, your protocol may include an analysis to assess reliability and validity
◦ Make sure you are calibrated to yourself
What type of reliability is this?
intraexaminer
If you do research where you are measuring something, your protocol may include an analysis to assess reliability and validity
◦ Make sure you are calibrated to other members of the team also taking measurements
What type of reliability is this?
Interexaminer reliability
If you do research where you are measuring something, your protocol may include an analysis to assess reliability and validity
◦ Make sure that everyone is measuring correctly (compare to an expert)
What is being assessed?
Validity
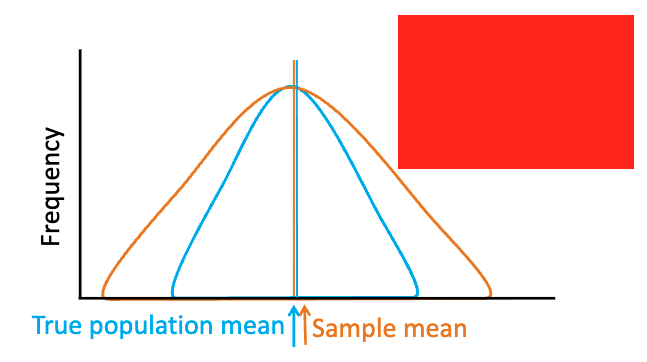
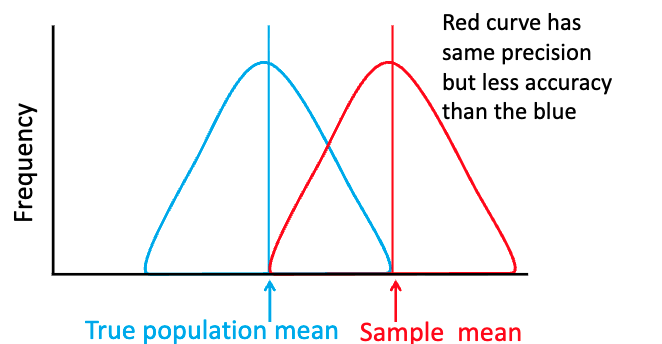
which curve is more accurate? more reliable?
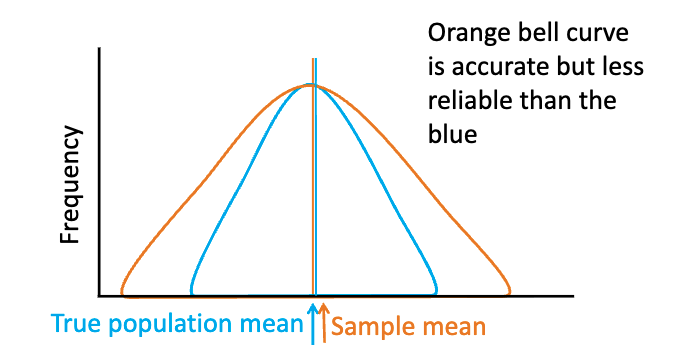
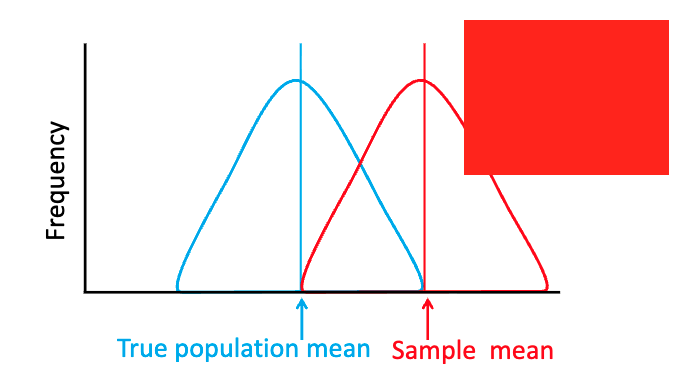
which curve is more precise? more accurate?
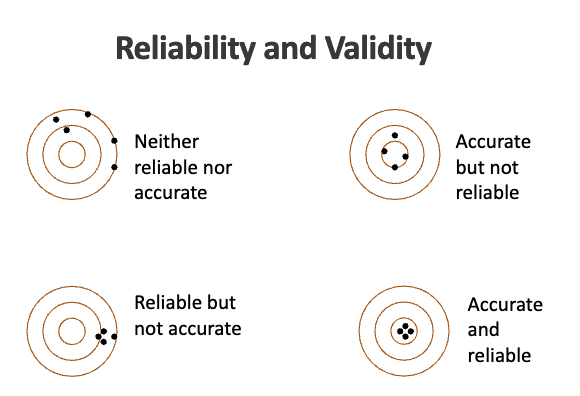
what are 2 ways to assess validity?
sensitivity
specificity
what term refers to the ability to measure the proportion of positives that are true positives (by the gold standard)?
Sensitivity
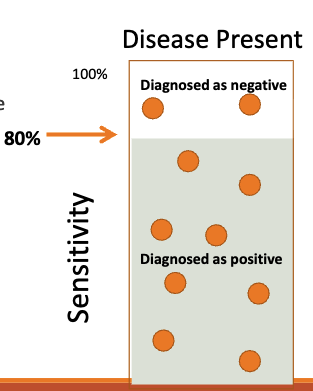
what does a false positive rate (FPR) measure?
Gives you the proportion of people without the condition who are incorrectly identified (by a test) as having the condition.
o The FPR tells you how often a test gives a false alarm. A lower FPR means the test is better at correctly identifying healthy individuals.
what does a false negative rate (FPR) measure?
Gives you the proportion of people with the condition who are incorrectly identified (by a test) as not having the condition.
o The FNR tells you how often a test misses the condition it’s supposed to detect. A lower FNR means the test is better at identifying those with the condition.

(pregnancy tests)
◦ Detect more
◦ Test is more sensitive
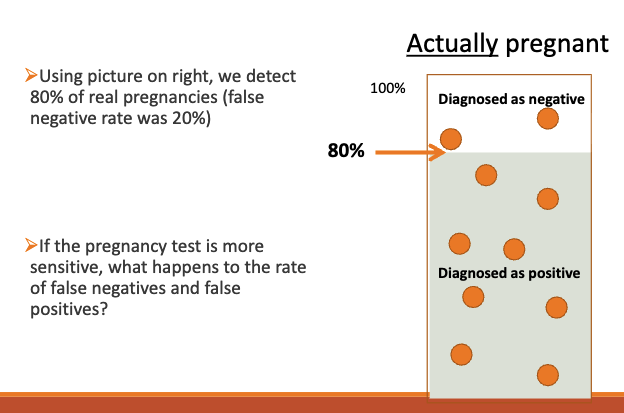
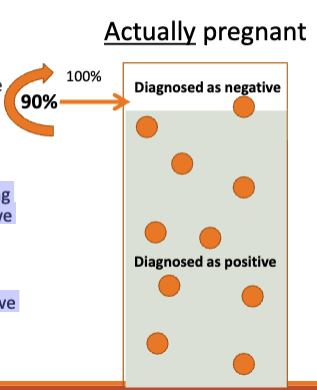
If the pregnancy test is more sensitive, what happens to the rate of false negatives and false positives?
If the test is more sensitive, among those who are actually pregnant, we would have fewer false negatives
When the test is more sensitive, we detected 90% of real pregnancies (false negative rate now 10%)

What happens if we raise the threshold from 25 mlU/ml to 30 mlU/ml?
➢Will we detect more pregnancies or less pregnancies?
Detect less → test is less sensitive (miss some actual pregnancies aka more false negatives)
BUT test becomes more specific (fewer false positives)
draw a 2×2 table (contingency table)
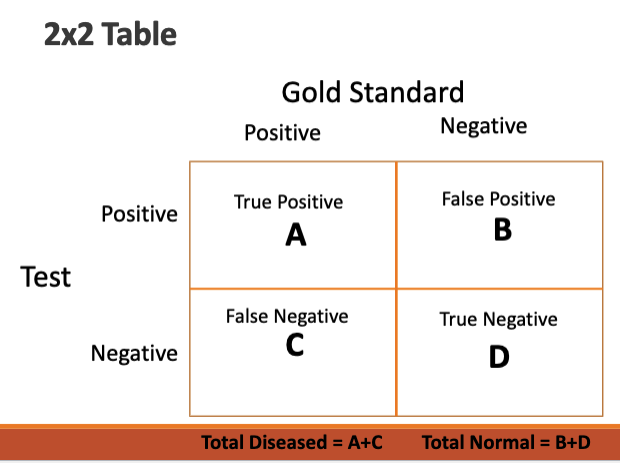
based on a contingency table, how is sensitivty calculate?
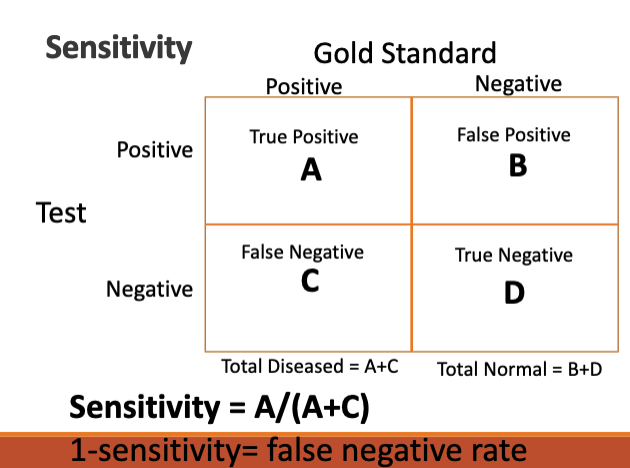
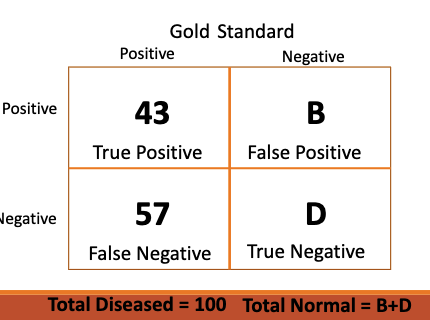
based on this contingency table that shows TMJ sounds to diagnose TMD, calculate sensitivity.
sensitivity = A / A + C
43 / (43+57)
43%
what term measures the proportion of negatives that are true negatives (by the gold standard)?
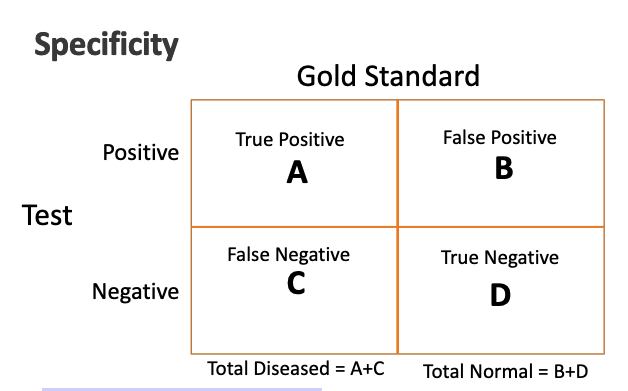
how is specififty calculated using a contingency table?
Specificity = D/(B+D)
1-specificity= false positive rate
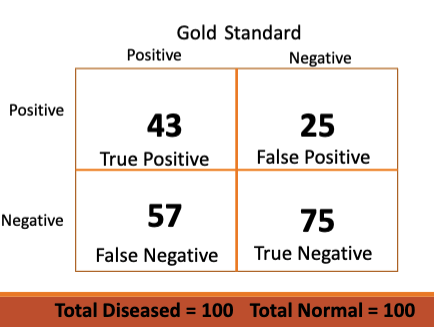
based on this contingency table that shows TMJ sounds to diagnose TMD, calculate specificity.
specificity = D / B + D
75 / (75+25)
75%
how are sensitivity and specificity related?
inversely related
➢As sensitivity increases, specificity decreases
➢As sensitivity decreases, specificity increases
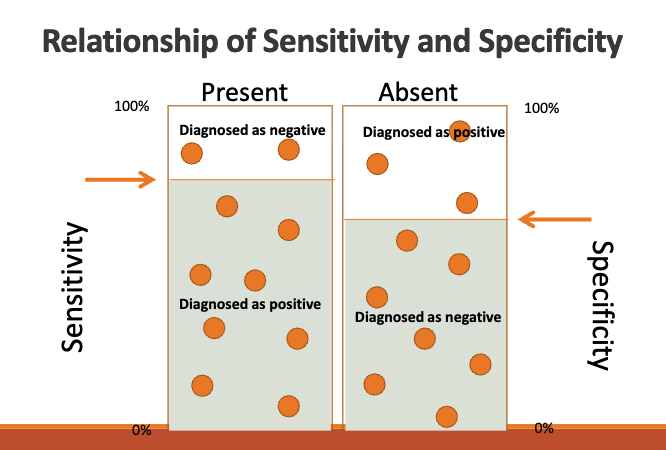

◦ False negative rate = 1-sensitivity = 57%
◦ False positive rate = 1-specificity = 25%
◦ More false negatives
how is false positive rate calcualted?
1 - specificity
how is false negative rate calcualted?
1 - sensitivity
Is high sensitivity always best?
No.
Need to balance sensitivity and specificity with risks of treatment vs no treatment
◦ Example: false-positive mammograms in women under age 40
◦ You don’t want to put patients through unnecessary biopsies
Why not always use the gold standard?
typically, gold standards can be expensive and time consuming
nutrition example:
◦ The more “objective” measures for diet can involve 24 hour urine collections, Blood draws, More expensive
◦ Require going to a clinic/lab
◦ Not practical for very big population studies