Overview of Developmental Psychology Concepts
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Heredity
Genetic blueprint starting at conception.
Prenatal Development
Development begins at conception, forming a zygote.
Zygote
Fertilized egg, the first human cell.
Embryo
Zygote attaches to the uterus wall.
Fetus
Developing human after 3 months gestation.
Teratogens
Toxins disrupting development via placental barrier.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
CNS issues from alcohol exposure during pregnancy.
Critical Periods
Times of heightened vulnerability to teratogens.
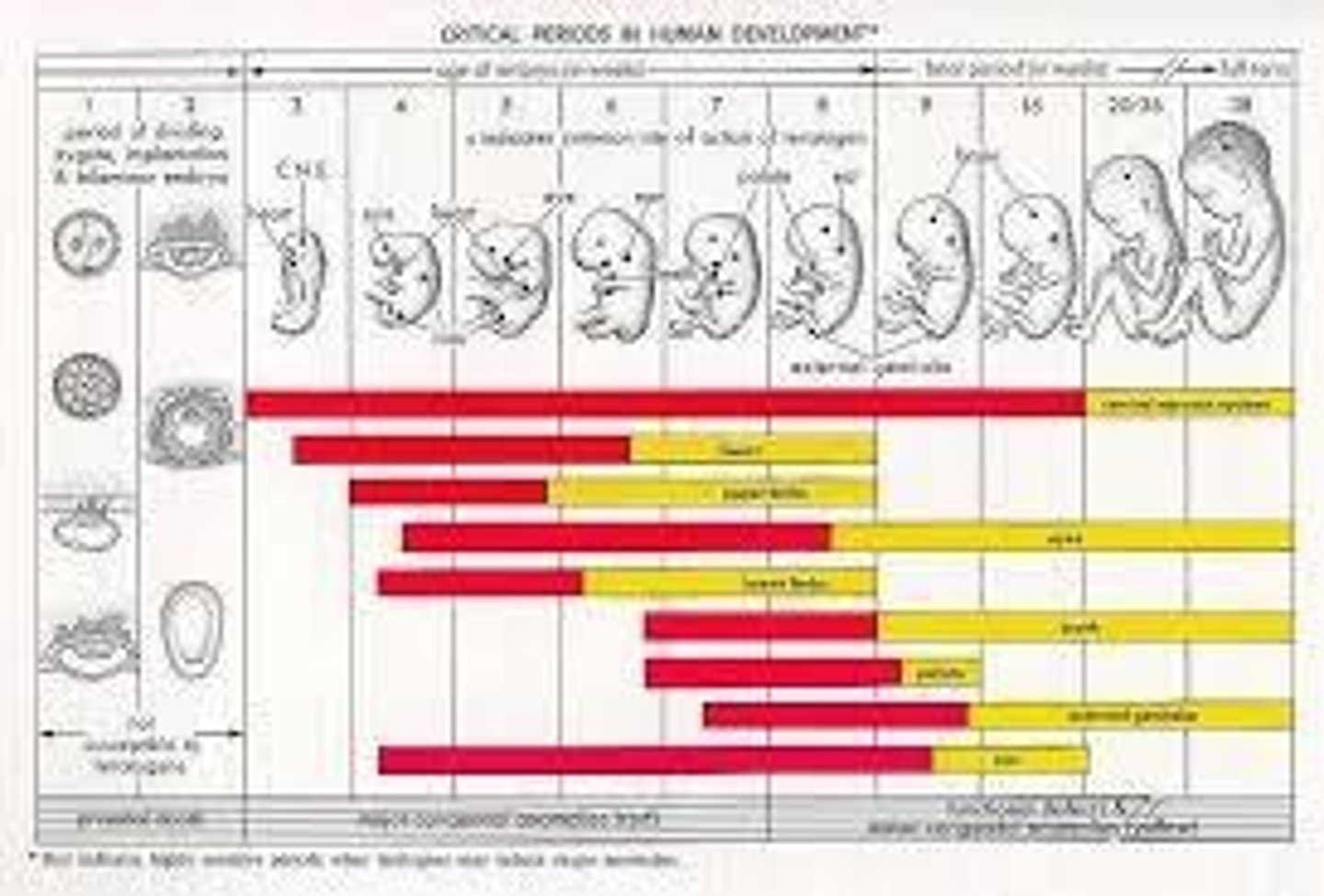
Brain Development
All neurons present at birth, grows rapidly.
Motor Development
Skills develop from center outward, head to tail.
Auditory Perception
Infants respond to sounds within minutes of birth.
Habituation
Decreased response to repeated stimuli.
Visual Perception
Infants are nearsighted, prefer human faces.
Depth Perception
Understanding distance; develops after crawling.
Visual Cliff
Experiment showing depth perception in infants.
Cognitive Development
Growth in knowing, thinking, and understanding.
Jean Piaget
Studied children's cognitive changes across ages.
Sensory-Motor Stage
0-2 years; ends with symbolic thought.
Object Permanence
Understanding objects exist when out of sight.
Preoperational Stage
2-7 years; symbolic and language development.
Concrete Operational Stage
7-11 years; logical reasoning and conservation.
Laws of Conservation
Quantity remains unchanged despite physical alterations.
Formal Operational Stage
Cognitive development stage for abstract reasoning.
Hypothetical Thought
Ability to think about possibilities and scenarios.
Social Development
Process of personal growth and relationships.
Harry Harlow
Studied attachment in rhesus monkeys.
Surrogate Mothers
Substitutes providing food or comfort to infants.
Contact Comfort
Preference for physical comfort over basic needs.
Mary Ainsworth
Developed the Strange Situation Paradigm.
Strange Situation Paradigm
Test for attachment styles in children.
Secure Attachment
Child seeks comfort from parents when frightened.
Insecure Ambivalent
Clingy children who reject caregiver interactions.
Insecure Avoidant
Children avoid contact with distressed attachment figures.
Puberty
Physiological changes from ages 8-18.
Primary Sex Characteristics
Reproductive organs like ovaries and testes.
Secondary Sex Characteristics
Non-reproductive physical changes during puberty.
Moral Reasoning
Development of understanding right and wrong.
Lawrence Kohlberg
Identified levels of moral reasoning.
Heinz Dilemma
Moral dilemma assessing reasoning for stealing.
Premoral Stage
Obey rules to avoid punishment or gain rewards.
Conventional Morality
Conformity to societal norms and laws.
Postconventional Morality
Moral principles based on individual conscience.
Parenting Styles
Different approaches to child-rearing.
Authoritarian Parenting
Emphasizes obedience with strict rules.
Permissive Parenting
Few guidelines, allowing children freedom.
Authoritative Parenting
High responsiveness with consistent limits.
Erik Erikson
Focused on psychosocial development stages.
Trust vs Mistrust
Infant's trust develops from reliable care.
Autonomy vs shame & doubt
Ages 1-3; developing personal control and independence.
Initiative vs guilt
Ages 3-5; asserting self through play and social interaction.
Industry vs inferiority
Ages 5-11; learning skills and facing feelings of inferiority.
Identity vs role confusion
Adolescence; exploring personal values and identity.
Intimacy vs isolation
Early adulthood; forming intimate relationships.
Generativity vs stagnation
Middle adulthood; contributing to society and caring for others.
Integrity vs despair
Late adulthood; reflecting on life accomplishments.
Physical Peak
Before age 30; gradual decline in physical abilities.
Cognitive skills
Sharpened through adulthood; metacognition improves.
Crystallized intelligence
Knowledge accumulated over time; increases with age.
Liquid intelligence
Problem-solving ability; decreases with age.
Empty Nest Syndrome
Adjustment phase after children leave home.
Health in elderly
Increased susceptibility to fractures and health issues.
Dementia
Abnormal brain deterioration affecting memory and judgment.
Alzheimer's disease
Common form of dementia; memory impairment.
Dying process
Elderly often adjust well to death's prospect.
Kubler-Ross stages of grief
Five stages: Denial, Anger, Bargaining, Depression, Acceptance.
Social influences in adolescence
Parents influence major decisions; peers influence lifestyle.
Metacognition
Ability to monitor and evaluate one's own thinking.
Job satisfaction in older adults
Older individuals report greater job satisfaction.
Vocational Tests
Help predict career stability and direction.
Aging effects on recall
Recall ability declines in late adulthood.
Elderly health maintenance
Good health maintained through fitness and diet.