Seismic Waves and Locating Earthquakes
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for vocabulary related to seismic waves and locating earthquakes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Seismic Waves
Waves of energy that travel through the Earth, typically caused by geological activity such as earthquakes.
P-waves
- fastest
- smallest amplitude.
S-waves
- slower than P-wave
- greater amplitude than P-wave
Surface Waves
- ~2-4 km/sec
- slower than body waves
- slowest = Rayleigh waves
- largest amplitude
Seismograph
An instrument that records the motion of the Earth during an earthquake.
Seismogram
A graphical record produced by a seismograph showing the time and amplitude of seismic waves.
Epicenter
The point on the Earth's surface directly above the origin of an earthquake.
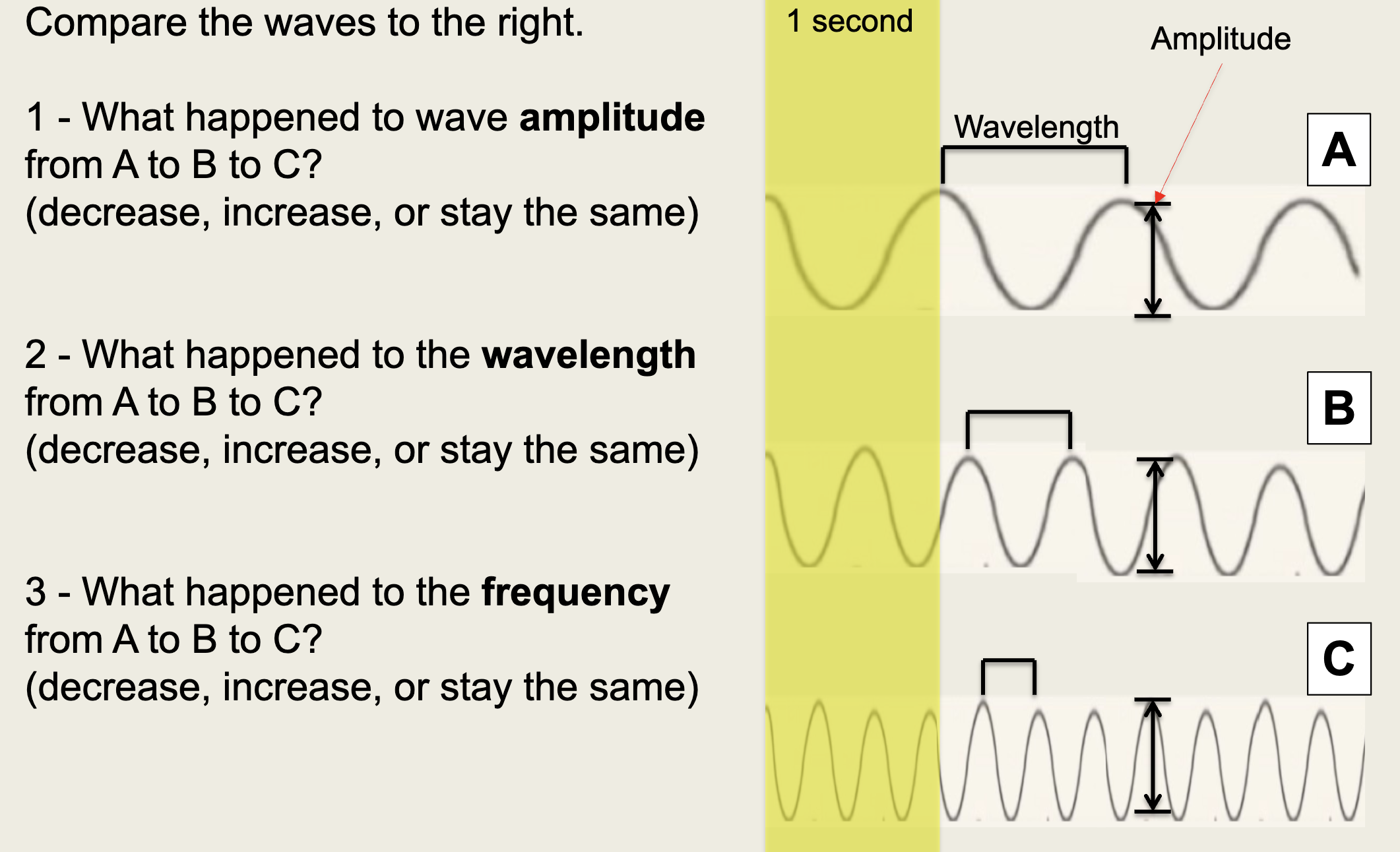
Wave Amplitude
The height of the wave measured from its rest position, indicating its energy and intensity.
Wavelength
The distance between two consecutive crests (or troughs) of a wave.
Frequency
The number of complete waves that pass a given point in a certain amount of time, typically measured in Hertz (Hz).
What happens to seismic wave amplitude, wavelength, and frequency as it passes from consolidated rock to tightly packed ground to loose soil/mud?
As seismic waves travel from consolidated rock to tightly packed ground, amplitude may increase; wavelength decreases due to faster propagation; and frequency increases in loose soil/mud.
How do we measure seismic waves?
Seismic waves are measured using instruments called seismometers or accelerometers, which detect motion caused by the waves.
What are seismographs and seismograms?
Seismographs are instruments that record the motion of the ground during an earthquake, while seismograms are the printed or digital records produced by seismographs.
How do P-waves, S-waves, Love waves, and Rayleigh waves differ in location and particle motion?
P-waves (primary waves) are compressional and travel through all media, S-waves (secondary waves) are shear waves and can only travel through solids, Love waves move horizontally and occur at the surface, while Rayleigh waves create an elliptical motion and also occur at the surface.
Which waves cause the most damage, body waves or surface waves?
Surface waves usually cause the most damage during an earthquake due to their larger amplitudes and longer duration.
How do the P-waves, S-waves, and surface waves differ in speed and amplitude?
P-waves are the fastest and have the smallest amplitude, S-waves are slower and have larger amplitudes, while surface waves are the slowest but can have the largest amplitudes.
How can we use the delay between P- and S-waves to triangulate the source (epicenter) of an earthquake?
The delay in arrival times of P-waves and S-waves at a seismic station allows seismologists to calculate the distance to the epicenter, using data from multiple stations to triangulate its precise location