10R Transport in plants
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Instead of a circulatory system, what do plants have?
A vascular bundle
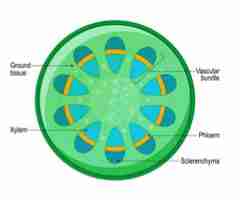
What are the specialized transport vessels in the vascular bundle?
The xylem vessels which transport water and mineral salts from the roots and the stem and then the leaves
The phloem tubes which transport food and hormones
What are xylem vessels?
These are long, very narrow hollow tubes composed of elongated cells joined end to end.
Describe the structure of the xylem vessels
They are located throughout the plant (from the root hairs to the leaf)
They have walls made up of thick lignin
They lack a nucleus and cytoplasm
What are phloem tubes?
Same as xylem
What make up phloem tubes?
These are made up of sieve tube elements and companion cells
What are the end walls of phloem tubes called?
Sieve plates which are perforated with small holes.
Describe the structure of phloem tubes
They have living cells
Their cell walls are porous allowing the exchange of materials with neighbouring cells
Explain how the structure of the xylem and phloem are suited to their function
Xylem vessels are elongated tubes made up of dead cells providing a waterproof vessel for the transport of water and absorbed minerals.
Phloem tubes are also elongated and tubular but made up of living cells which provide energy for the transportation of manufactured food.
What are the five stages in the movement of water through the plant?
The water is absorbed by the root hair cells
The water moves across the root cortex to the xylem
The water moves up the xylem
The water moves across the leaf hair cells
The movement of water from the leaves
What are the 3 main processes directly related to the movement of water through the xylem vessels?
Capillarity
Root pressure
Transpiration pull
Define the term capillarity
This is the process in which water molecules adhere to one another and to the surfaces of narrow tubes, causing the water to rise within the tube.
Define the term root pressure
This refers to the pressure generated in the roots that helps push water and dissolved nutrients upward through the plant. This process occurs when water enters the roots from the soil, creating a pressure that can move water into the stem and leaves, especially during times when transpiration (water loss through leaves) is low
Define the term transpiration pull
This is the process by which water is drawn up from the roots to the leaves through the xylem. This occurs as water evaporates from the surface of the leaves, creating a negative pressure that helps pull more water upward, allowing nutrients to be transported throughout the plant.
Define the term transpiration
This is the loss of water as water vapour from the surface of plants
What are the factors that affect transpiration?
Temperature- the higher the temperature the higher the transpiration rate
Humidity- The higher the humidity the lower the transpiration rate because the air is almost saturated with water vapour
Light intensity- the brighter the light the higher the transpiration rate because at that point the stomata are open
Air movement (wind)- transpiration increases as wind speed increases as during windy conditions water vapour is carried rapidly away from the leaves.
Define the term translocation
This is the movement of manufactured food from the leaves to all the cells of a plant.
What is active transport?
This is the process by which cells use energy to move nutrients and ions from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration, ensuring the plant absorbs essential substances needed for growth and development.
What is the main structure for transpiration through plants?
The leaf
What are the structures through which plants lose water?
The stomata, the cuticles, and the lentils
What is the cuticle?
This is the outer wall of the epidermal cells which is made up of waxy material that protects plants from desiccation (the removal of moisture)
What is the amount of water loss dependent on?
The thickness of the cuticle
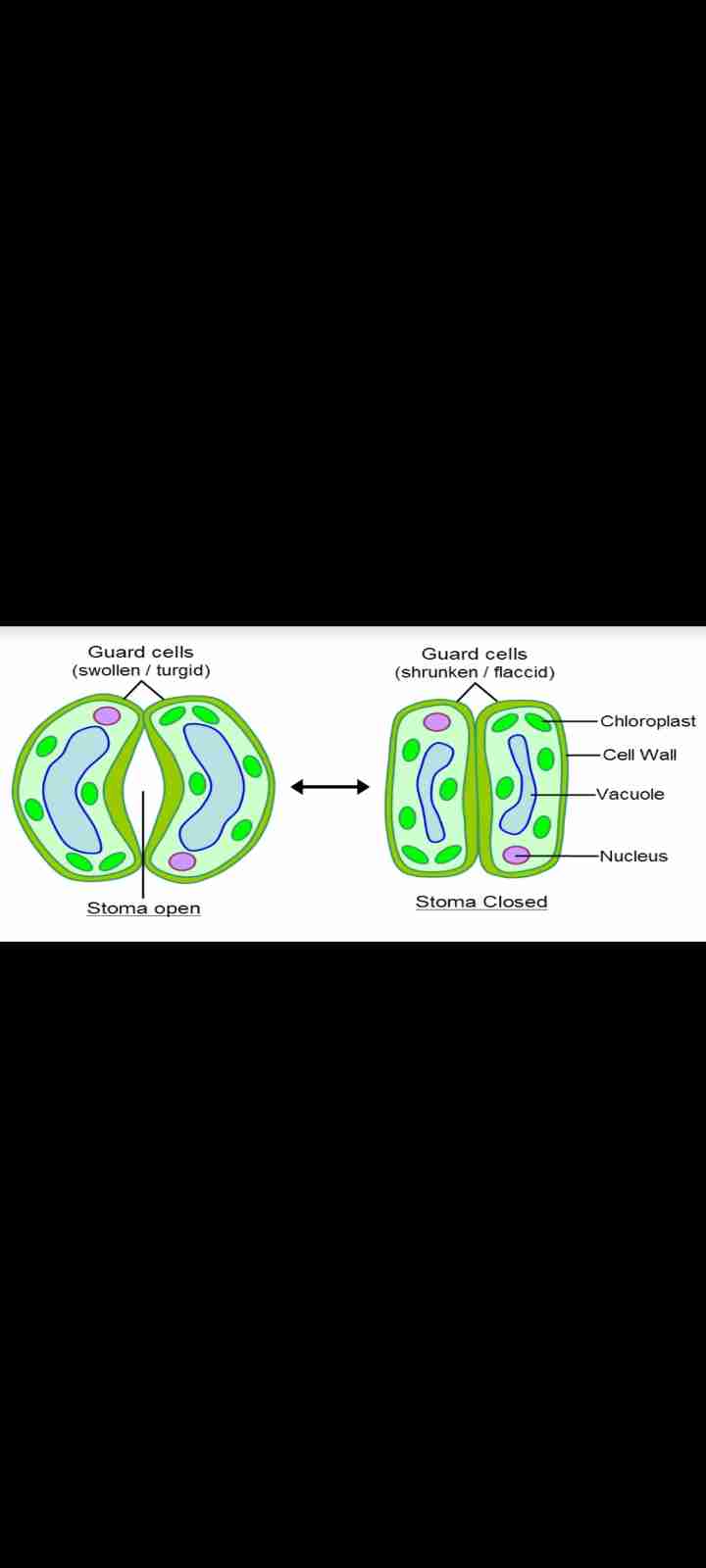
What is a stomata?
These are tiny pores on the underside of leaves through which water is lost as water vapour. 90% of water is lost through the stoma
What surrounds each stoma on a plant?
A pair of guard cells
What is the function of guard cells?
These changes shape to open (becomes swollen or turgid) or close (becomes shrunken or flaccid) the stoma.
What are lentils?
These are small splits on the stems and bark of trees which facilitate gaseous exchange.
