unit 1 econ final review
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12th grade ap microeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
economics
- science of scarcity
- study of choices
- social science concerned with the efficient use of limited resources to achieve maximum satisfaction of economic wants
scarcity
the condition in which our wants are greater than our limited resources
positive statements
- facts
- avoids value judgements (what is)
normative statements
- opinions
- value judgements (what ought to be)
marginal
- additional
- additional benefit ≥ additional cost
economic assumptions
- society wants are unlimited but resources are limited (scarcity)
- every choice has a cost/trade-off
- maximizers
- MC = MB
trade offs
alternatives that we give up whenever we choose something else (opportunity cost)
opportunity cost
the most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision (second best option)
product market
- firms sell
- households buy
factor/resource market
- firms buy
- households sell
factors of production
capital, land, labor, entrepreneurs
production possibilities curve/frontier
- shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scare resources
- demonstrates scarcity, tradeoffs, opportunity costs, and efficiency
production possibilities curve/frontier assumptions
- only two goods can be produced
- full employment of resources
- fixed resources (ceteris paribus)
- fixed technology
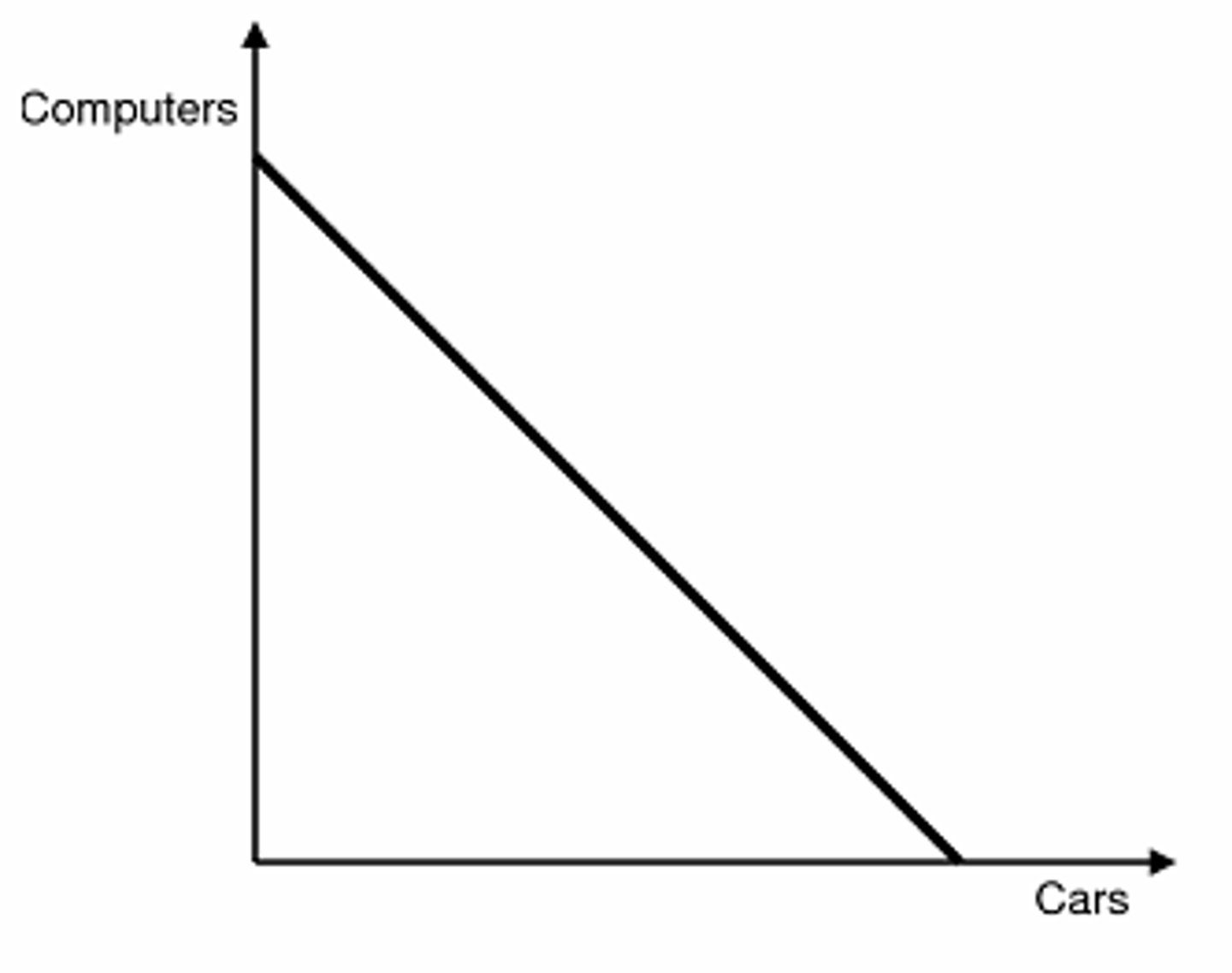
constant opportunity cost
resources are easily adaptable for producing either good
increasing opportunity cost
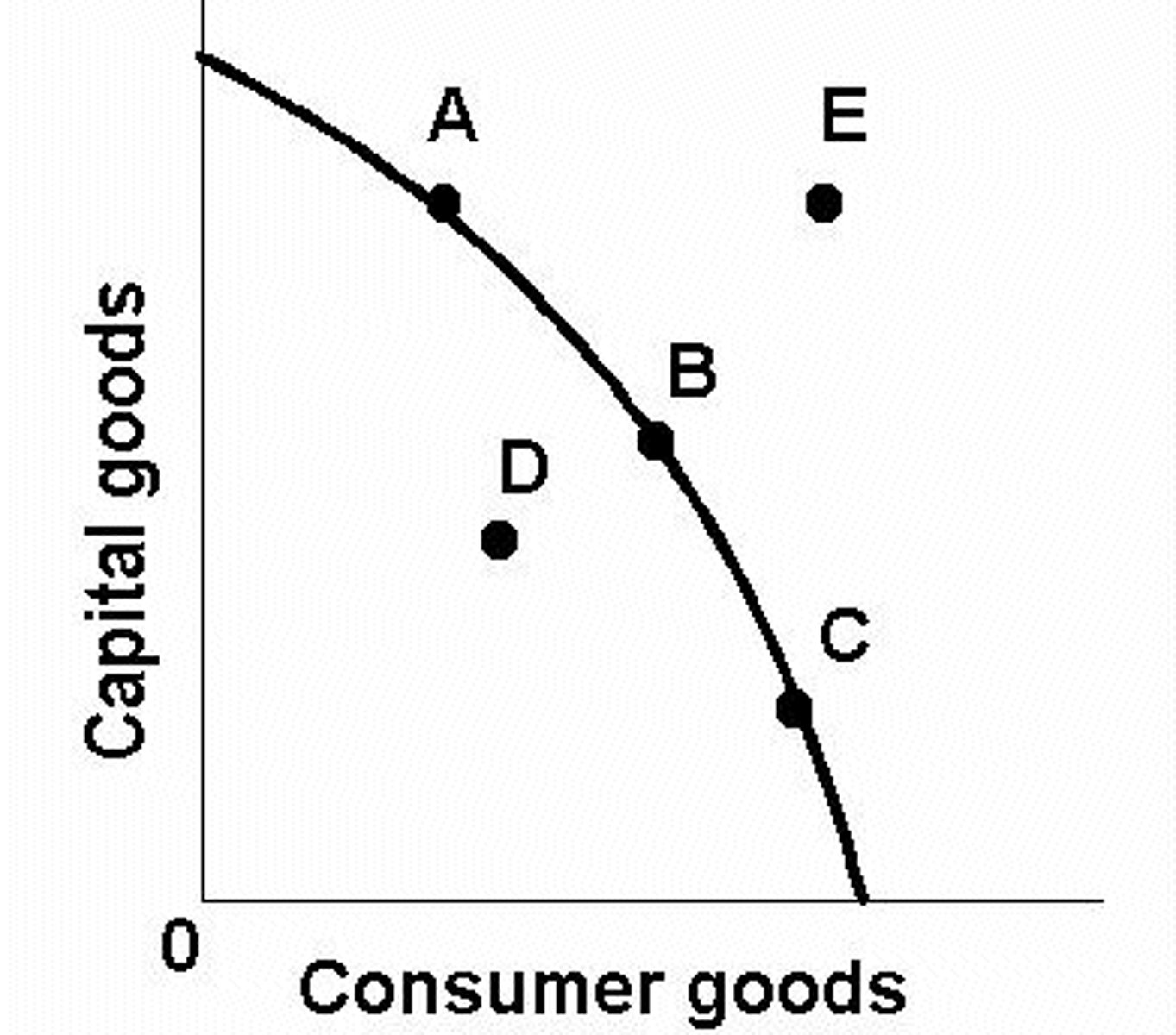
- resources are not easily adaptable to producing both goods
- as you produce more of any good, the opportunity cost will increase
shifters of production possibilities curve/frontier
- resource quantity or quality
- technology
- trade
productive efficiency
- products are being produced in the least costly way
- point on PPC
allocative efficiency
- products being produced are the ones most desired by society
- optimal point on PPC
per unit opportunity cost
opportunity cost/ units gained
absolute advantage
- producer that can produce the most output or requires the least amount of inputs/resources
- input: smallest #
- output: largest #
comparative advantage
- producer with the lowest (per unit) opportunity cost
- input: cross-add -> smallest #/ other goes under
- output: cross-add -> largest #/ other goes over
economic questions
- WHAT goods and services should be produced?
- HOW should these goods and services be produced?
- WHO consumes these goods and services
economic system
method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services
command (centrally-planned) economy
gov owns resources and decides what to produce, how much, and who will receive it
capitalism/ free market system
- laissez faire: little gov involvement
- individuals own resources and determine the economic questions
- ppl can make profit = incentive to produce quality items efficiency
- wide variety of goods
- competition and self-interest regulate economy
invisible hand
society's goals will be met as individuals seek their own self-interest