Biology- Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is the chemical formula for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 12H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
What are the reactants in the process of photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide and water
What are the products of photosynthesis?
Glucose, oxygen, and water
What molecules are used in photosynthesis?
ATP, ADP, Hydrogen ions, water, CO2, NADP, NADPH
What molecules are made during/ after photosynthesis?
ATP, Hydrogen ions, O2, NADPH, NADP, glucose
What are the stages in photosynthesis?
Stage 1- light dependent reactions, Stage 2- light independent reactions
What is a Thylakoid?
The organelle in which light dependent reactions take place and coined shapes towers in chloroplast.
What is a Stroma?
Where the light independent reactions take place and is the fluid portion of the chloroplast; between the thylakoids
What are the inputs and outputs of stage 1- light dependant reactions?
Inputs: H2O, NADP, ADP and light
Outputs: NADPH, H+, ATP and O2
What are the inputs & outputs of stage 2- light independant reactions?
Inputs: CO2, ATP, NADPH, H+
Outputs: Glucose, ADP, NADP, H2O
What is the process of photosynthesis?
plants convert solar energy into chemical energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates
Photosynthesis Overview
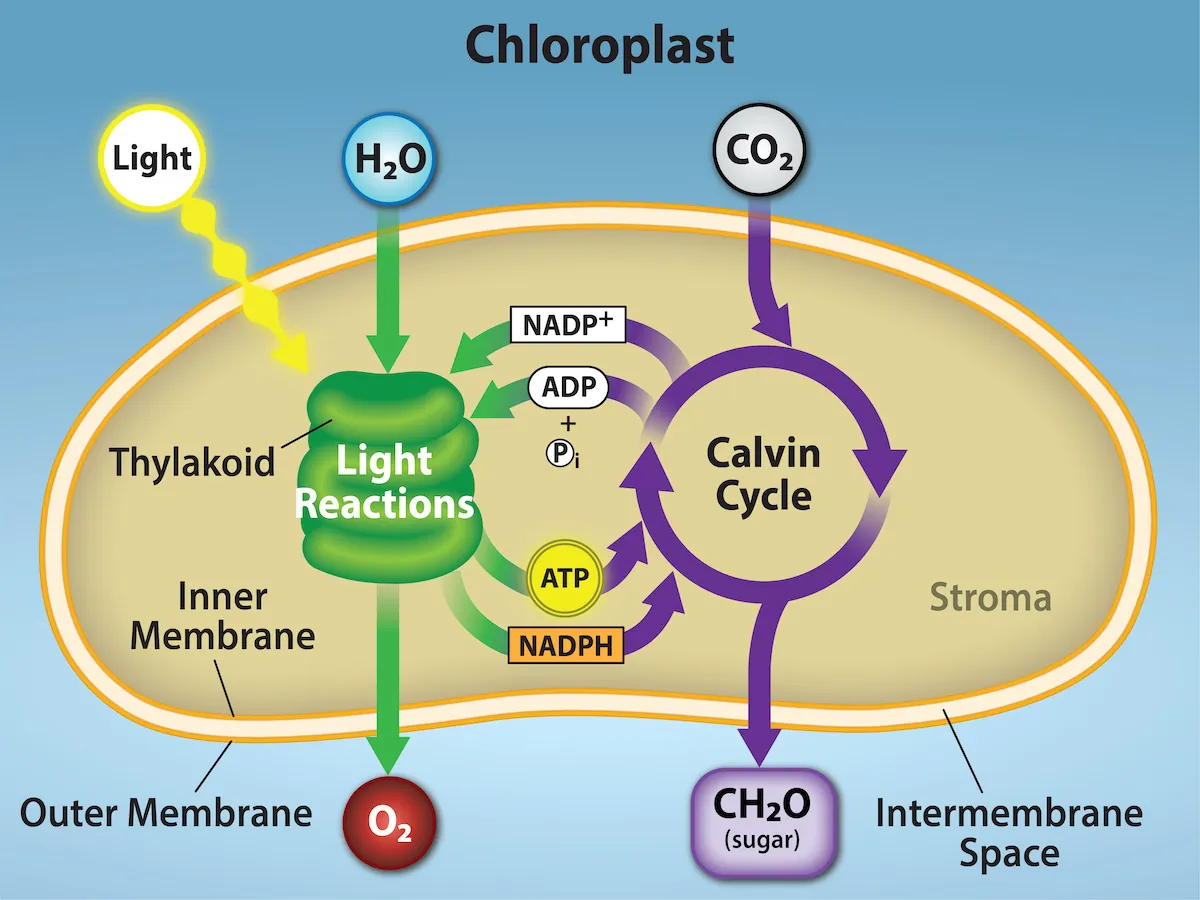
What is Stomata?
Stomata are small pores on the bottom surface of leaves that regulate gas exchange, allowing water vapour & CO2 to enter and O2 to exit.
What are Guard Cells?
They surround the stomata and control the opening and closing of the stomata and regulate gas exchange and water loss in plants.
What happens when water is low, at night time and the CO2 needs are low?
The stomata will close to conserve water and reduce gas exchange, limiting CO2 intake and minimizing water loss during times of scarcity.
What happens when the need for CO2 is high (at day time)?
The stomata will open to allow increased gas exchange, facilitating the intake of CO2 for photosynthesis while releasing oxygen.
Why is the stomata on the bottom side of the leaf?
Is to reduce water loss of evaporation and to control water loss.
How does leaf size affect stomata density?
Larger leaves have less stomata density because they have more surface area, making them spread out.
What is transpiration?
The loss of water vapour through the stomata of leaves. From soil to leaves to atmosphere.
What happens to the stomata when transpiration is high?
The stomata will open
What happens to the stomata when transpiration is low?
The stomata will close
What are the factors affecting transpiration?
wind, temperature, light, humidity
Which factors increase transpiration?
wind, temperature, light
Why does humidity decrease transpiration?
The air in the atmosphere is already saturates with water vapour, making it harder for plants to evaporate more water from it's leaves and harder to move out the plant.
What is the aerobic respiration chemical equation?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36-38ATP
What are the reactants and products for aerobic respiration chemical equation?
Glucose+ oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + energy
What are the 2 phases that occur in cellular respiration?
anaerobically and aerobically
What is aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration uses oxygen from the air to release energy from glucose.
What is anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is the release of energy from glucose without using oxygen. This produces lactic acid.
What is step 1 called in cellular respiration?
Glycolysis
What is step 2 called in cellular respiration?
Fermentation and Krebs Cycle
What is step 3 called in cellular respiration?
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Where does Glycolysis (step 1) occur?
It occurs outside of mitochondria in the cytoplasm.
Does Glycolysis (step 1) use oxygen or no oxygen?
It uses no oxygen therefore, anaerobic
What are the inputs, outputs & net ATP of Glycolysis (step 1)
Inputs: glucose, 2x ATP
Outputs: 4x ATP, 2x pyruvate, NADH (the pyruvate is used/powers the next step)
Net ATP made: 2 ATP (lactic acid gets used for fermentation)
Where does Fermentation (step 2) occur?
Occurs in cytoplasm.
Does Fermentation (step 2) use oxygen or no oxygen
It uses no oxygen therefore, anaerobic
In alcohol fermentation (plants) what are the inputs and outputs?
Input: 2x pyruvate
Output: Alcohol
In lactic acid fermentation (animals) what are the inputs and outputs?
Input: 2x pyruvate
Output: Lactic acid
Where does the Krebs cycle (step 2 also) occur?
It takes place in the mitochondria matrix (liquid)
Does Krebs cycle have oxygen or no oxygen present?
Krebs cycle requires a presence of oxygen, therefore aerobic
What are the inputs, outputs and net ATP made of Krebs cycle (step 2 also)?
Inputs: 2x pyruvate (from glycolysis- step 1)
Outputs: 2x ATP, CO2, NADH, FADH (NADH & FADH are needed to power next step)
Net ATP made: 2x ATP
Does electron transport chain (ETC) (step 3) need oxygen or no oxygen?
ETC needs oxygen therefore aerobic
What are the inputs and outputs and net ATP made of electron transport cycle (step 3)?
Inputs: O2, NADH, FADH
Outputs: 32-34 ATP, H2O
Net ATP made: 32-34 ATP (ranges because sometimes the 2 ATP in glycolysis gets used up in fermentation even with O2 present)
What are the similarities of anaerobic & aerobic respiration?
Both make ATP, both make NADH, both go through glycolysis,
What are the differences between anaerobic & aerobic respiration?
Anaerobic is in cytoplasm and aerobic is in mitochondria. One uses O2 and one doesn’t.
What are the significance between anaerobic & aerobic respiration?
Aerobic makes more ATP and is more efficient. Anaerobic still allows organisms in low-oxygen environment to to breathe. They both allow small organelles to still get O2 with no mitochondria