physics midterm 1 term 1 gr11b
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
a ray
an arrow that points out in the direction that light travels
the normal to a reflecting surface
a line drawn perpendicular to the surface
incident ray
the ray that hits the surface at the angle (theta1)
reflected ray
a ray that reflects the incident ray at the angle of reflection (theta2)
the law of reflection
the relationship between the angle of reflection and angle of incidence is that they are always equal
specular reflection
reflection from a smooth surface results in all the reflected light moving in one direction
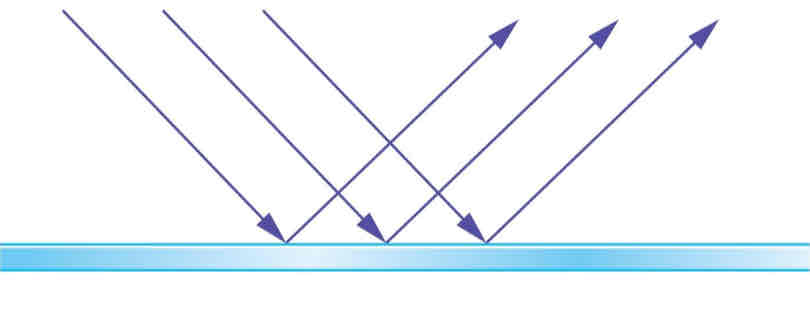
diffuse reflection
reflection from a rough surface results in light to reflect in all directions
plane mirror
a perfectly flat mirror
plane mirror distance equation
image distance = -(object distance)
di = -do
negative image distance means that the image is behind the mirror, known as a virtual image
virtual image
when the image is behind the mirror and no light passes through the image and it cannot be projected on a screen, it looks real to the eyes but it is virtual
plane mirrors height equation
image height = object height
hi = ho
this is always true
corner reflector
if three plane mirrors are joined at a right angle
a light incident ray is sent back in the direction it came from
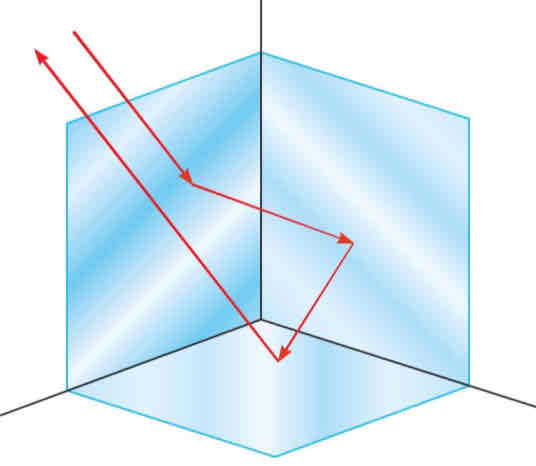
where are corner reflectors usually used
on ships and lifeboats, where they reflect radar waves directly back to the source
often viewed as retroreflectors
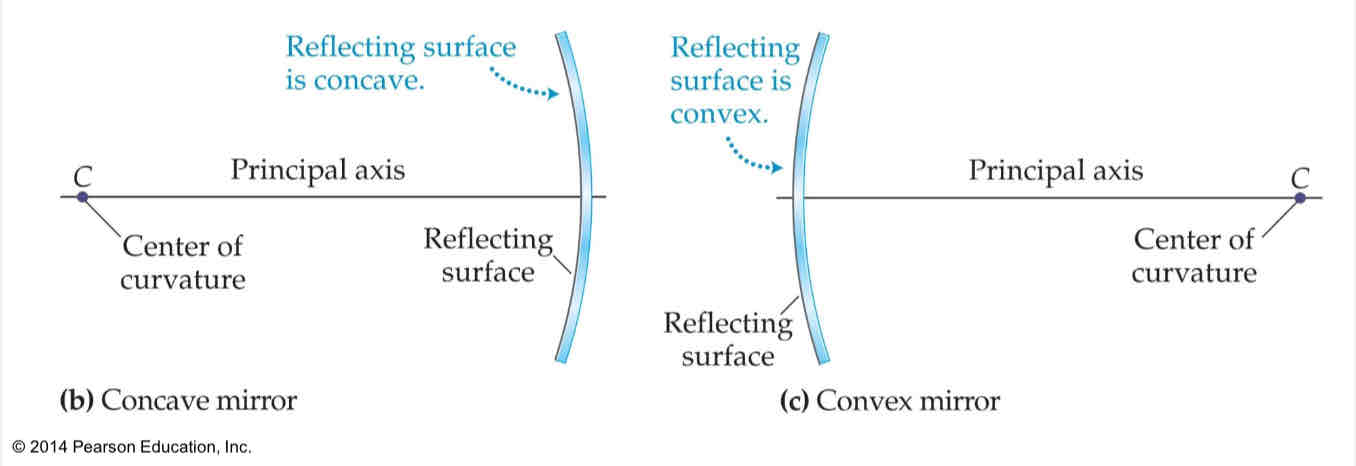
concave mirror
a mirror that moves inwards, forming a cave in the mirror
convex mirror
a mirror taht bulges / curves outward like a ball
curved mirrors
spherical mirrors, another term for convex nd concave
center of curvature
the center of the mirror
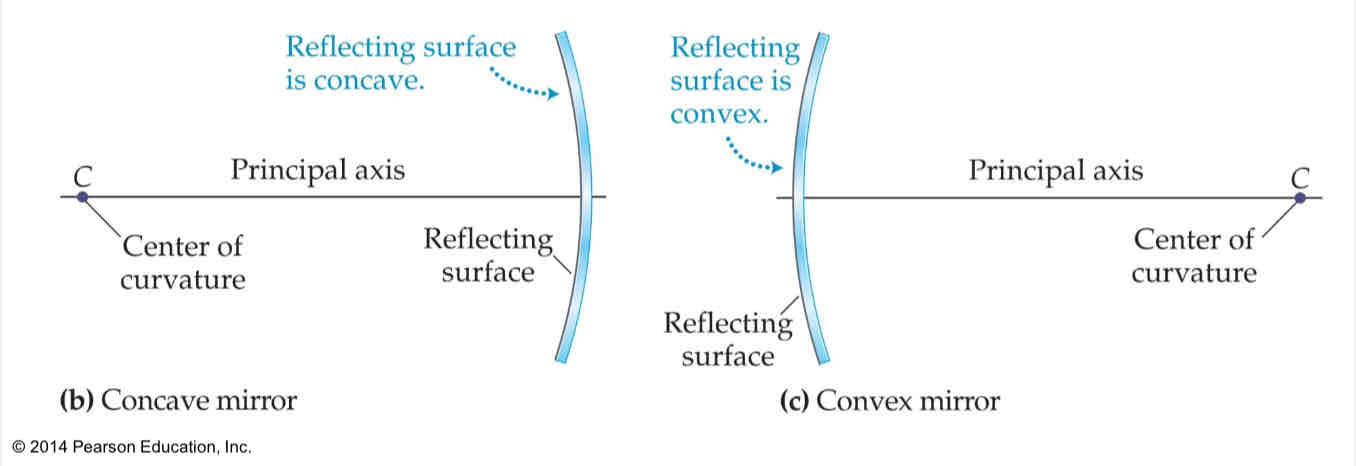
principal axis
a straight drawn line drawn through the center of curvature and the midpoint of the mirror, intersects the mirror at right angles
parallel rays
beams of light directed toward the mirror along its principal axis
the rays reflected from the surface of the mirror and focus / are reflected thru the focal point
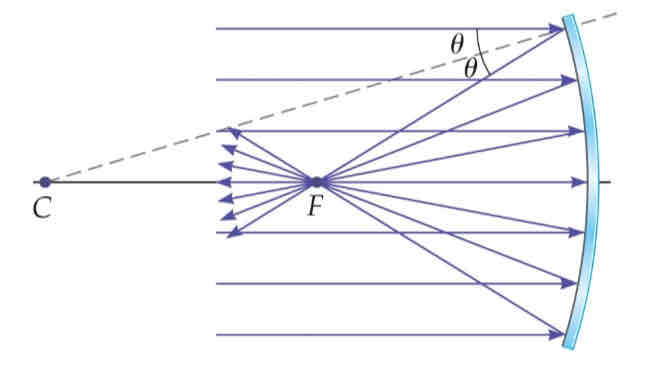
focal point
the point halfway between the center of curvature and the surface of the mirror
focal length equation
focal length = ½ radius of curvature
f = ½ R
(-) the focal point is behind the mirror, all convex mirrors have negative focal length and therefore a focal point behind the mirror
(+) the focal point is in front of the mirror, all concave mirrors have positive focal length and therefore a focal point in front of the mirror
parallel rays are shown approaching s convex mirror
incoming rays of light that are parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror spread outward when they are reflected, just as if they had started from the focal point behind the mirror; however, no light actually passes through the focal point of a convex mirror
ray tracing
drawing the paths of rays of light as they reflect from a mirror and use them to find the location of the image
principal rays
the 3 rays that are used in ray tracing spherical mirrors :
P ray - parallel ray
F ray - focal point ray
C ray - center of curvature ray
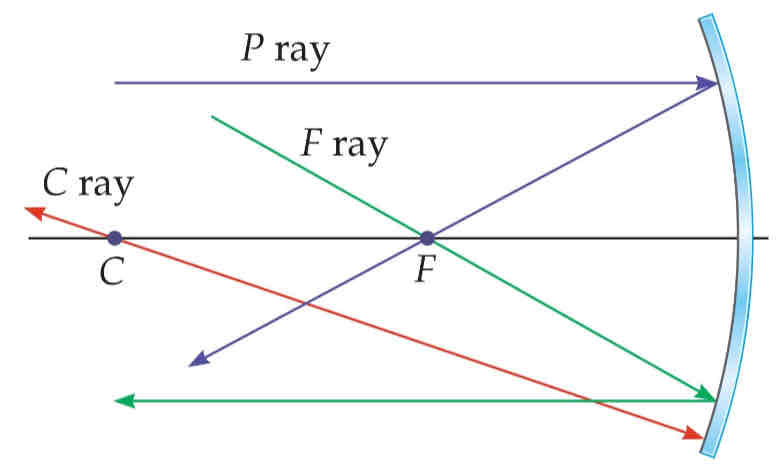
P ray / parallel ray
reflects through the focal point, hits the surface of the mirror parallel to the principal axis
F ray / focal point ray
reflects parallel to the principal axis, hits the surface of the mirror passing through the focal point
C ray / center of curvature ray
reflects back along its incoming path, hits the surface and reflects its own ray by passing through itself (center of curvature)
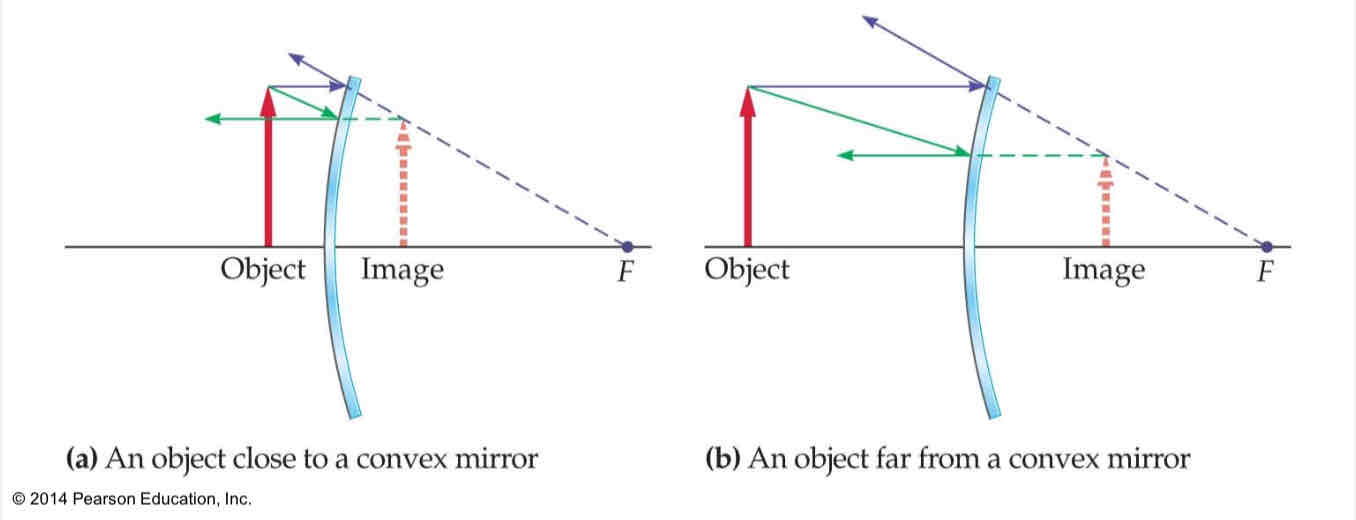
convex mirror cases
object is close to mirror : image is same size and distance from the mirror
object is far from mirror : image is small and close to the focal point
the mirror equation
1/object distance + 1/image distance = 1/focal length
1/do + 1/di = 1/f

magnification equation
magnification = image height/object height = - (image distance/object distance)
m = hi/ho = - (di/do)
