8.4 (done)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
functions of the skeletal system
shape
support
movement
protection
blood + cell production
storage
shape
Bone structure gives shape to the body
Changes as the body grows
Determines height and width
support
Skeleton provides support to the body
Keeps internal organs in place
Vertebra help to stand straight
movement
Bones are held together by ligaments and tendons
points of attachment for muscles via articulations (joints).
Muscles attached to bones
Muscles contract and the skeleton moves
protection
Bones protect vital internal organs
e.g., brain is encased within the cranium + the heart and lungs are protected by the rib cage
blood + cell production
red marrow contained within certain bones contains stem cells that can differentiate into blood cells
storage
stores + releases minerals and fat
e.g., calcium, phosphorus, sodium + potassium
names of bones
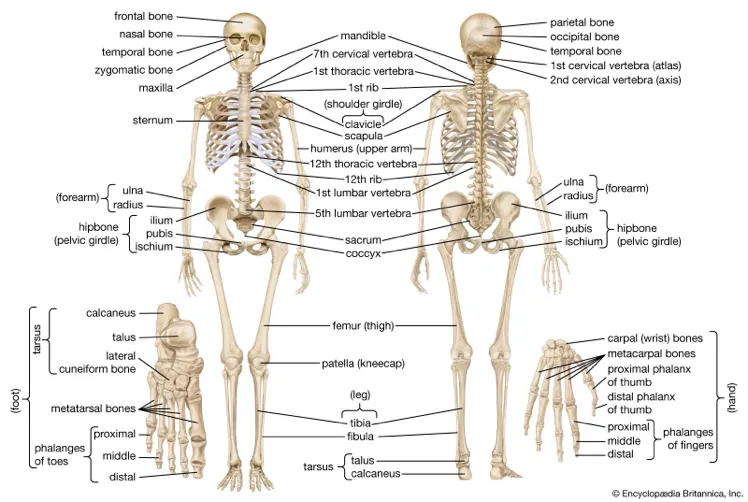
types of bone
long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid.
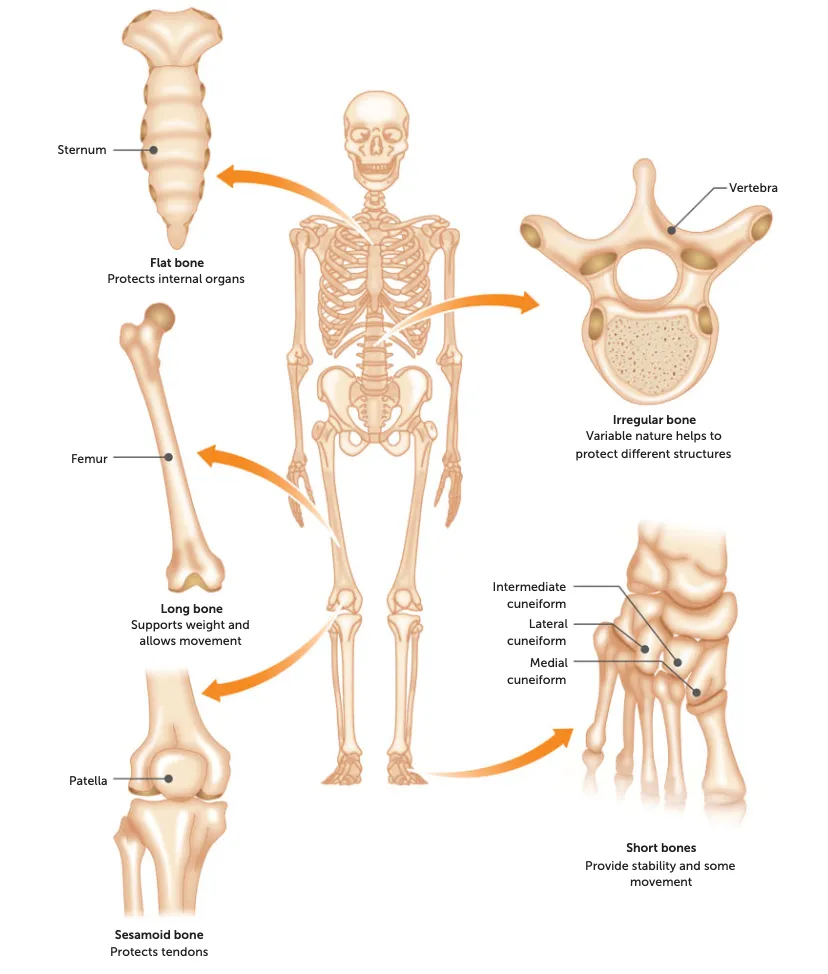
long
shape: long, large and strong.
function: weight-bearing + provide long levers for speed
Eg: long limbs eg. Femur, humerus, tibia etc
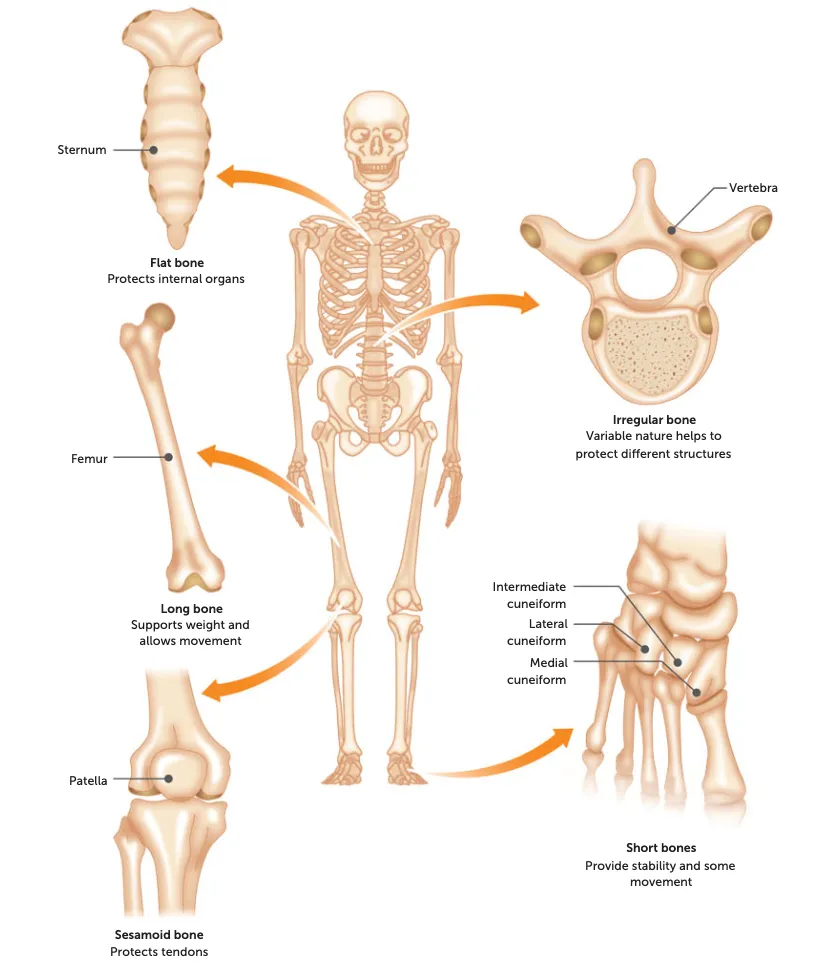
short
shape: cube/round
function: large range of movement
Eg: wrist, feet, knee, hands etc
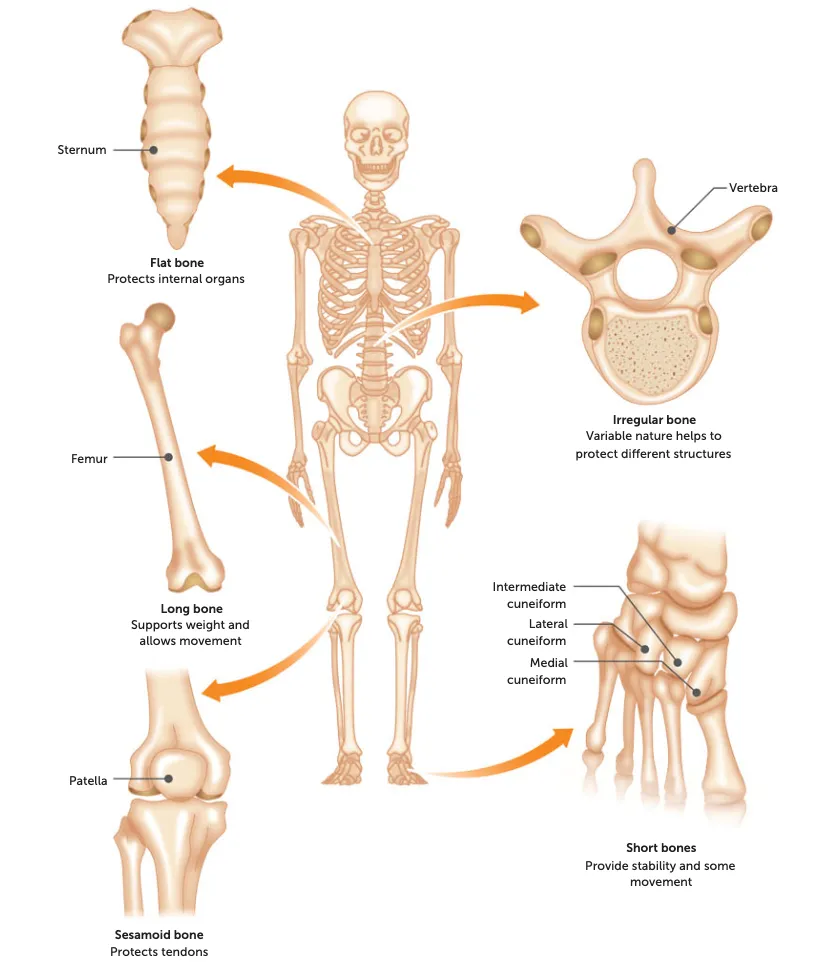
flat
shape: broad, flat surface for muscles to attach to
function: Protecting vital organs
Eg: ribs, skull, sternum
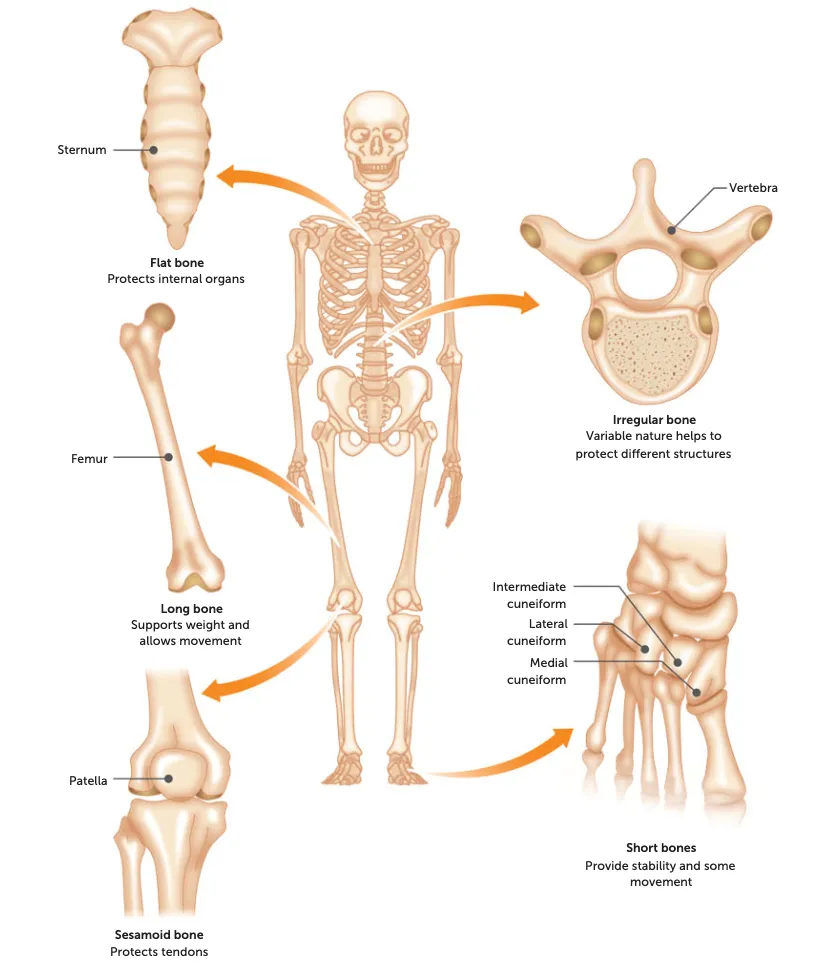
irregular
what: All the rest that aren’t in the above categories
function: areas where more strength is needed
Eg: Vertebra
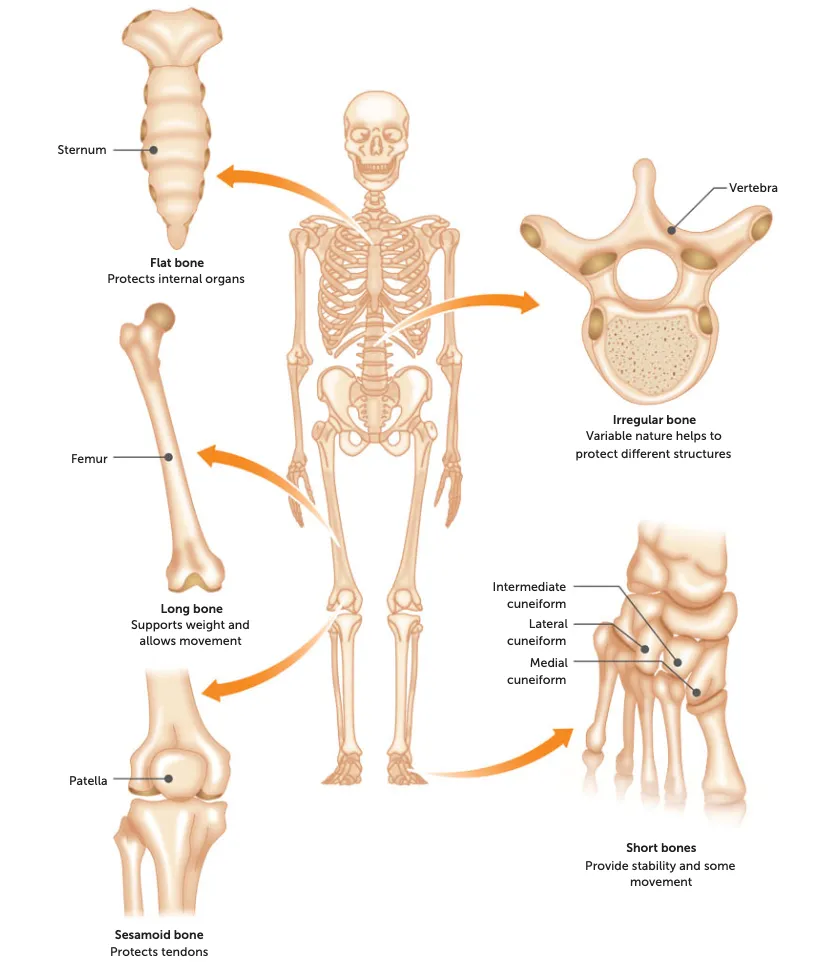
sesamoid
shape: small + oval
function: protect tendons from excessive strain by reducing friction + pressure
Eg: patella
how many bones in adult human skeleton
206
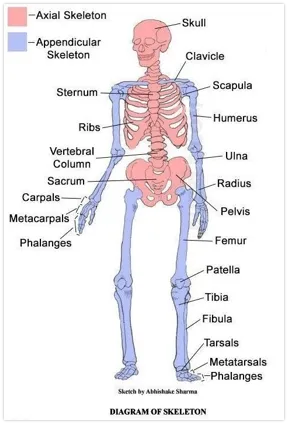
axial skeleton
consists of the bones that lie around the central axis of the body
skull, vertebral column, ribs, sternum.
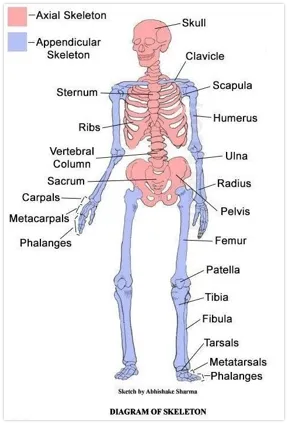
appendicular skeleton
consists of the bones of the upper and lower limbs + shoulders and pelvis
limbs, pectoral and pelvic girdles.