learning theory of attachment- classical and operant conditioning
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
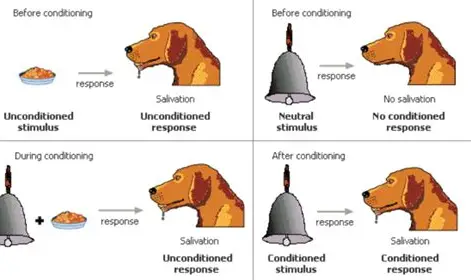
What is classical conditioning
Learning through association a neutral stimulus is consistently paired with an unconditioned stimulus so produces A conditioned response
What is learning theory
The idea that proposes or behaviour is learned rather than in born
What is operant conditioning
Learning through enforcement and consequences
Classical conditioning example with attachment
The unconditioned stimulus is food and the unconditioned response is the baby feeling pleasure of food.
The mother is the neutral stimulus which the baby in the beginning has no response to.
During conditioning the neutral stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus or paired
the mother then becomes the condition stimulus as the baby associate's then with the unconditioned stimulus and their pleasure. Seeing the mother gives the baby a conditioned response of happiness
What are the four types of operant conditioning
positive and negative reinforcement and punishment
positive reinforcement meaning and relate to attachment
when a behaviour is made more likely when receiving a pleasurable stimulus
when a parent feeds a crying baby, the baby is more likely ot repeat the crying behaviour to get food
negative reinforcement meaning and relate to attachment
when a behaviour is made more likely when removing an unpleasant stimulus
parents feeding behaviour is negatively reinforced by the baby stopping its crying behaviour when fed
positive punishment
Positive punishment involves causing a punishment following an undesirable behavior to decrease the likelihood of that behaviour occurring again.
negative punishment
Negative punishment is a behavioural strategy that involves removing a desirable stimulus to decrease the likelihood of an unwanted behaviour being repeated
how is attachment a secondary drive
primary drives are instinctive eg eating and sleeping
secondary drives ae learnt, according to cupboard love, we learn as infants to want attachment becuase we learn that the secondary drive will satisfy a primary drive eg babies and hunger
How can operant conditioning and drive reduction theory be explained with attachment
When an animal is uncomfortable this creates a drive to reduce that discomfort
when the infant is fed the drivers reduced in this produces a feeling of pleasure this is rewarding and called negative reinforcement
the behaviour is more likely to be repeated in the future because it was rewarding
through the process of classical conditioning the person who supplies the food is associated with avoiding discomfort and becomes a secondary reinforcer
What is a pet evaluation point about learning theory being reductionist
It reduces the complex emotional bond between infant and caregiver to stimulus response associations and reinforcements
a review of 17 studies found that oxytocin plays an important role in attachment the levels inquiries during skin to skin contact and parents with higher levels exhibit more responsiveness to infant interactions
therefore it learning theory is oversimplified and fails to convey the depth of human attachment
What is a pet point about learning not being supported from animal studies
Lack of support from studies conducted on animals
Lorenz is geese imprinted on first moving object regardless of food
harlow's research suggest is wasn’t important who gave them food as monkeys were more attached to mother who gave comfort
this shows that factors other than association with food are important in the formation of attachments
this suggests attachment is not learnt but instinctual
What is a pet point about learning not being supported by human studies
Lack of support from human babies studies
schaffer and emerson studied mother baby interactions over 18 months and interviewed mothers about baby separation anxiety and stranger anxiety. Their results were that babies tended to form their main attachment to their mother regardless of whether she was the one who usually fed them
this suggests that food is not the main factor in the formation of human attachments
EVALUATION: learning theory makes intuitive sense
learning theory has face validity. it makes intuitive sense that babies cry more when they learn crying gains them attention and then food
EVALUATION: good and bad of behaviourist principles.
behaviourist principles used to explain attachment are backed up by a long history of well controlled research such as pavlov and skinner.
however such highly controlled research on human babies is impossible for ethical and practical reasons
EVALUATION: how does bowlby disagree with learning theory
bowlbys monotropic theory which gives an evolutionary explanation for caregiver- infant attachment.
this argues babies have an instinct to attach to their primary caregiver as they provide security