Aviculture test 1
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
What are some ways birds are used in our culture
Symbolism
Music
Migration signals in the changing of the seasons
Downs are used for blankets/jackets
Canaries in the coal mines
Pets/companions
Released for sport hunting
Bird watching and ecotourism
What do birds of prey equal
War or Power
what do doves equal
Peace or love
what does the common raven equal
betrayal/guidance/death
what do storks equal
childbirth
Why were humans first interested in birds
first as a source of food
There were legends, folklore, myths concerning birds
the first human references were in cave drawings
What does the bald eagle equal
USA
What significance did the southern ground hornbill hold
it was believed to be protection from lighting, drought, and evil and it signified death, also consuming parts of the bird like placing it under our tongue can allow humans to harness powers such as seeing the future or hard-to-locate food items, the feathers could also bring rain
What does canary in the coal mine mean
canaries were used to detect carbon monoxide in mines before they hurt other people because they were affected first due to their small size
Where did birds come from
Dinosaurs
What are some things all birds have in common
feathers
no teeth
bipedal
Digitigrade feet (walk on toes)
Fusion and reduction of bones (platform for flight muscles)
Pneumatic bones (direct connections to air sacs)
small size
forelimbs specialized for flight
centralized body mass
high metabolism
highly developed central nervous system/vision
What is the taxonomy of birds
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Aves
How many bird orders are there
41
How many bird tags are there
14
What are some good places to look at information on birds
Cornell birds of the world
AZA
ASAG
Anseriformes TAG
Ducks (waterfowl)
Charadriiformers TAG
Shorebirds
Ciconiiformer/pheonicopteriformes/pelicaniformes (c/p&p) TAG
Storks
Flamingos
Ibis
Spoonbills
Herons
Hamerkop
Shoebill
Pelicans
Columbiformes TAG
Pigeons and Doves
Coraciiformes TAG
Motmots
Bee-eaters
Rollers
Kingfishers
Hornbills
Galliformes TAG (julie's baby)
Pheasants
Qual
Partridges
Gruiformes/eurypygiformes/cariamiformes/otidiformes TAG
Cranes
Rails
Sunbittern
Bustards
Passerine TAG
Perching birds
Hummingbirds
Mousebirds
frogmouths
trogons
Parrot TAG
Parrots
Penguin TAG
Penguins
Piciformes TAG
Toucans
Aracaris
Toucanets
Woodpeckers
Barbets
Raptor TAG
Eagles
Vultures
Owls
Hawks
Falcons
Struthioniformes TAG
Tinamou
Ostrich
Rhea
Emu
Cassowary
Turaco and Cuckoo TAG
Turaco and cuckoo
What was the earliest unambiguous fossil bird
the Archaeopteryx (the feathers are indistinguishable from modern feathers)
Where was the Archaeopteryx found
Limestone beds in Germany
Did feathers evolve from scales
yes
Did feathers evolve quickly
No they evolved very slowly after many many decades
Where did feathers evolve from
it developed from passive gliding flight in early bird-like animals
Where feathers also developed for a means of insulation
Yes
What is the bottom part of the feather called
the Shaft/calamus
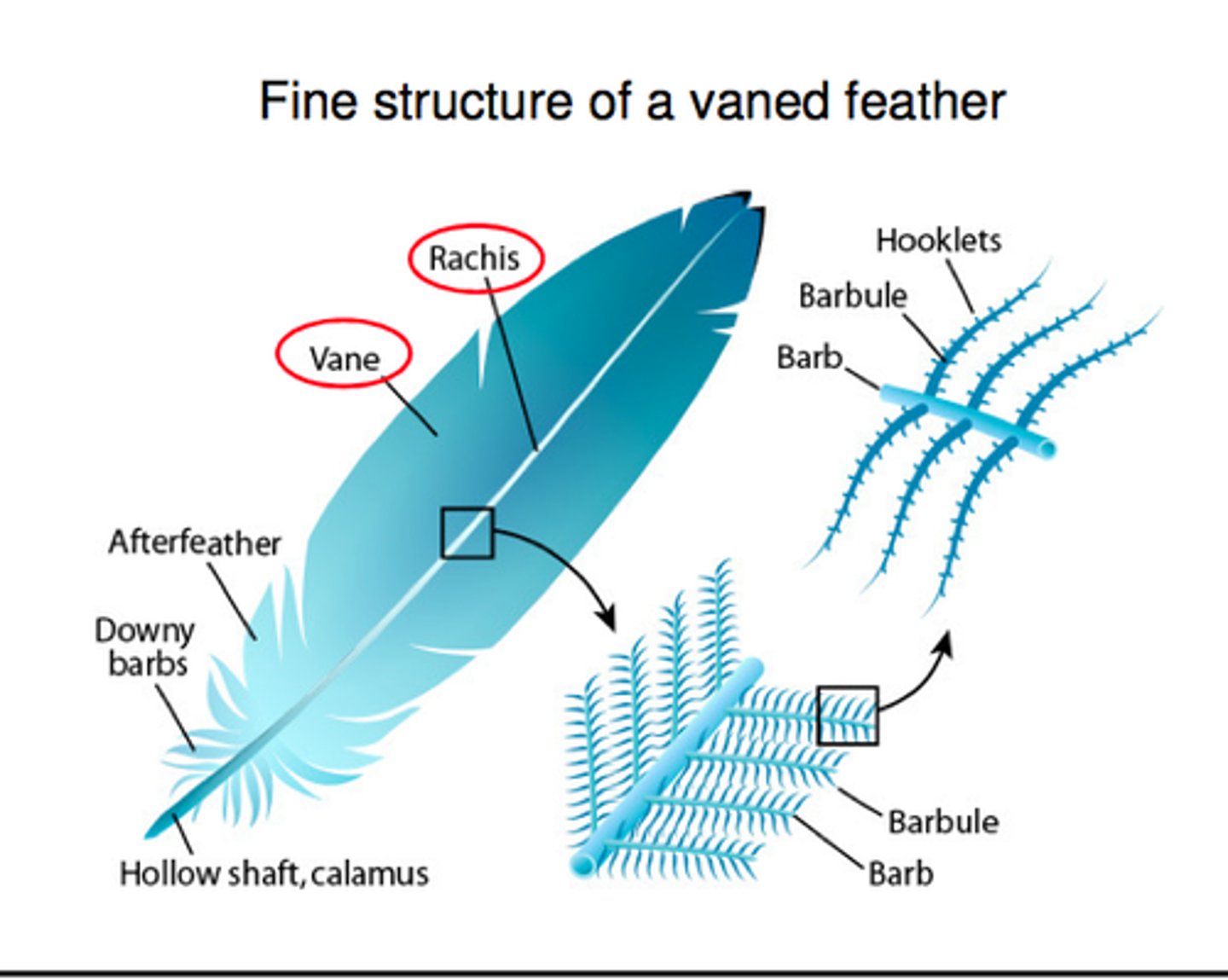
What are feathers made of
Keratin
what is the upper part of the feather called
Rachis
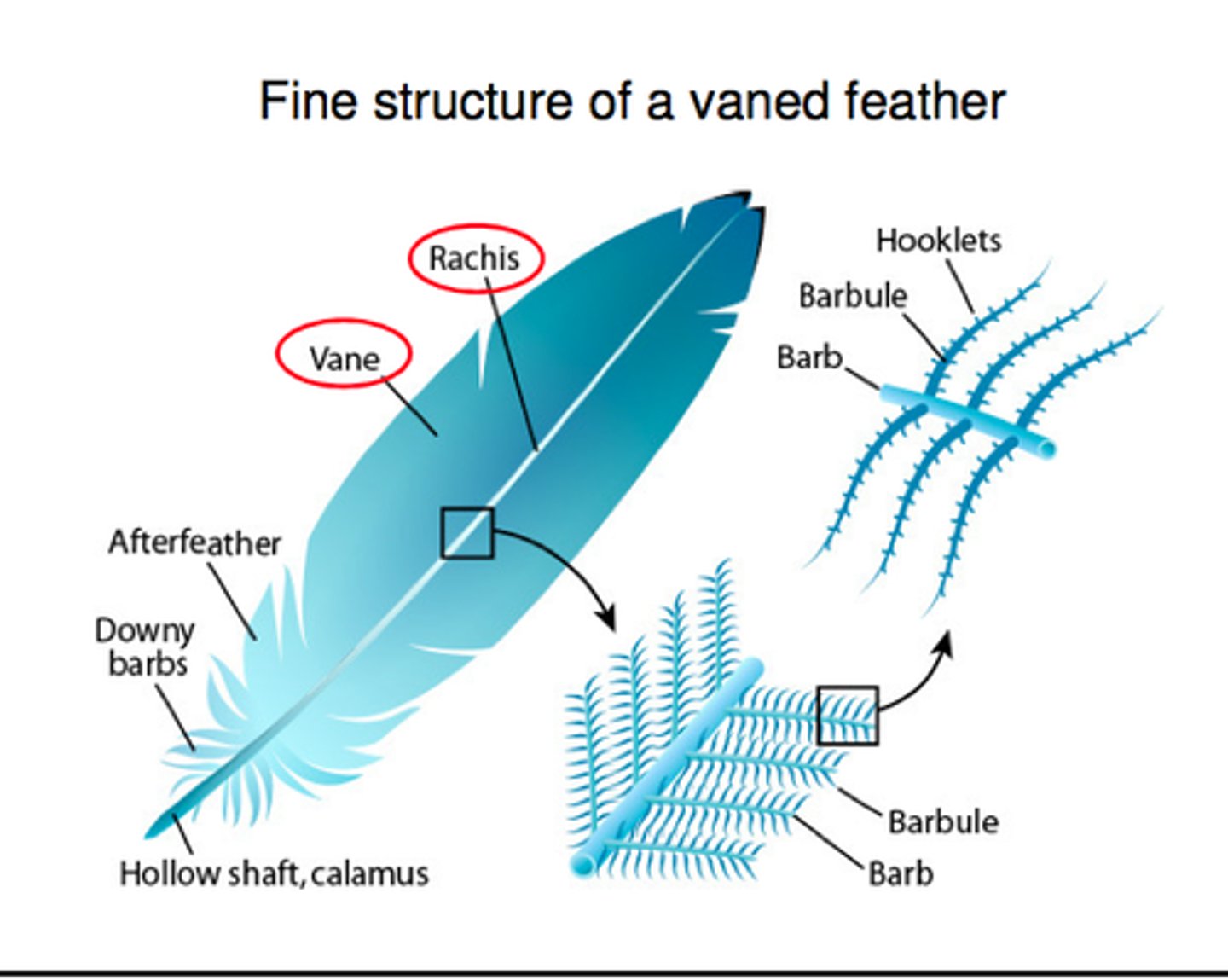
What are the feathers closest to the shaft and don't zip called
Down feathers

What are the parts of the feather that cause the zip
the barb and the barbules with hooklets on them

What are the two types of feathers
Contour feathers and down feathers
How do you tell the difference between tail feathers and flight feathers
the placement of the rachis in the feather
What are powder down feathers
they are never molted and grow continuously and then the tips break off forming powder
they help with waterproofing
Its found in herons/parrots/tinamous/bustards
Do birds have hair
no
What are feather tracts
Feathers don't grow around the body equally they are grown in specific patterns on the body through the tracts
There are no feather tracts of ratites and pheasants
What are the importance of feathers
Flight
Camouflage
Insulation
Display/courtship
Predator deterrent
What is special about the Hooded pitohui
They have poisonous feathers that are developed from the beetles that form part of its diet
What does plumage refer to
The feathers collectively
What colors are structural colors
White, green, and blue
It comes from the reflection of light off the feathers
what colors come from pigments in the feathers
brown, black, yellow, and red
What colors are produced by Melanin
Black, brown, grey
the darker the color the more melanin
What type of birds have different red, red-brown, and green
turacos its caused by the porphyrins produced by the liver
yellows and bright red have to come from the diet
What is molting
shedding and replacing feathers that is related to growth and seasons
Some drop all flight feathers at once (waterfowl) and down from 1-2 at a time (birds of prey)
What is eclipse in birds
When the male has its feathers molt and change into dull colors that look like the female outside of breeding season
Is juvenile plumage different from adults
yes they are different in colors and types of feathers
How long do juveniles have to develop adult plumage
the next migration season they have to be ready
Birds will also molt during chick rearing because they don't have to go anywhere
What are some issues with feathers
Parasites
Nutrition
Stress
Disease
Poor husbandry
What could cause plucking
Stress, nutrition, and mites
They can pluck themselves or others
What are stress bars
a bar that shows across feathers due to lack of nutrition, stress, etc while growing that portion of feathers
What is preening
It keeps feathers in good condition by setting them back on track and zipping them back
It also coats with oil out of their preening gland that helps with waterproofing
Evolution of birds
single fossilized feather found in germany
almost complete feathered skeleton found in the same region and that was the predicted "missing link" predicted by Darwin
Vegavis iaai (modern Anseriformes) was found in vega island that suggested modern birds survived extinction event
What are some features of the archaeopteryx
Feathers consistent with flight but more of a glider
claws meant for climbing
toes like modern perching birds so it perched
strong lets for running
bird like skeleton aka no keel and reduced pelvis and enlarged furcular
Teeth and large eyes suggest carnivorous
Habitat was scrubby islands in shallow lagoons
Is the archaeopteryx the ancestor of modern birds
No the branch died out before the end of the jurassic
What was the vegavis iaai
a bird fossil from vega island
the "modern" anseriformes
Is the phylogeny of birds complicated
Very no definitive agreement on how to classify because morphology is not enough
When did modern birds diverge from each other
123 mya
What is adaptive radiation
diversification of a group of organisms into new forms that fulfill different ecological niches
members relocate and colonize new areas and become separated from original population and evolve into a new species
what were darwins finches
14 species on galapagos islands and 1 on cocos
they evolved from the same ancestor and each population evolved to fill a specific niche and exploiting a certain resource and eventually diverged into separate species
What is the closest living relative to darwin's finches
the dull-colored grassquit
if a bird hops instead of walks where does it generally spend most of its time
trees
What do you have to think about when creating perching for birds
The size of their feet
if they have webbing
The purpose of their perching (roosting or all the time)
the size of the bird and perch
the texture of the perch
an ideal perch allows the bird to close toes almost completely around the perch
What can poor perching cause
callouses and sores on feet
What are different substrates that can be found in aviaries
mulch
sand
dirt
coconut fiber
mats
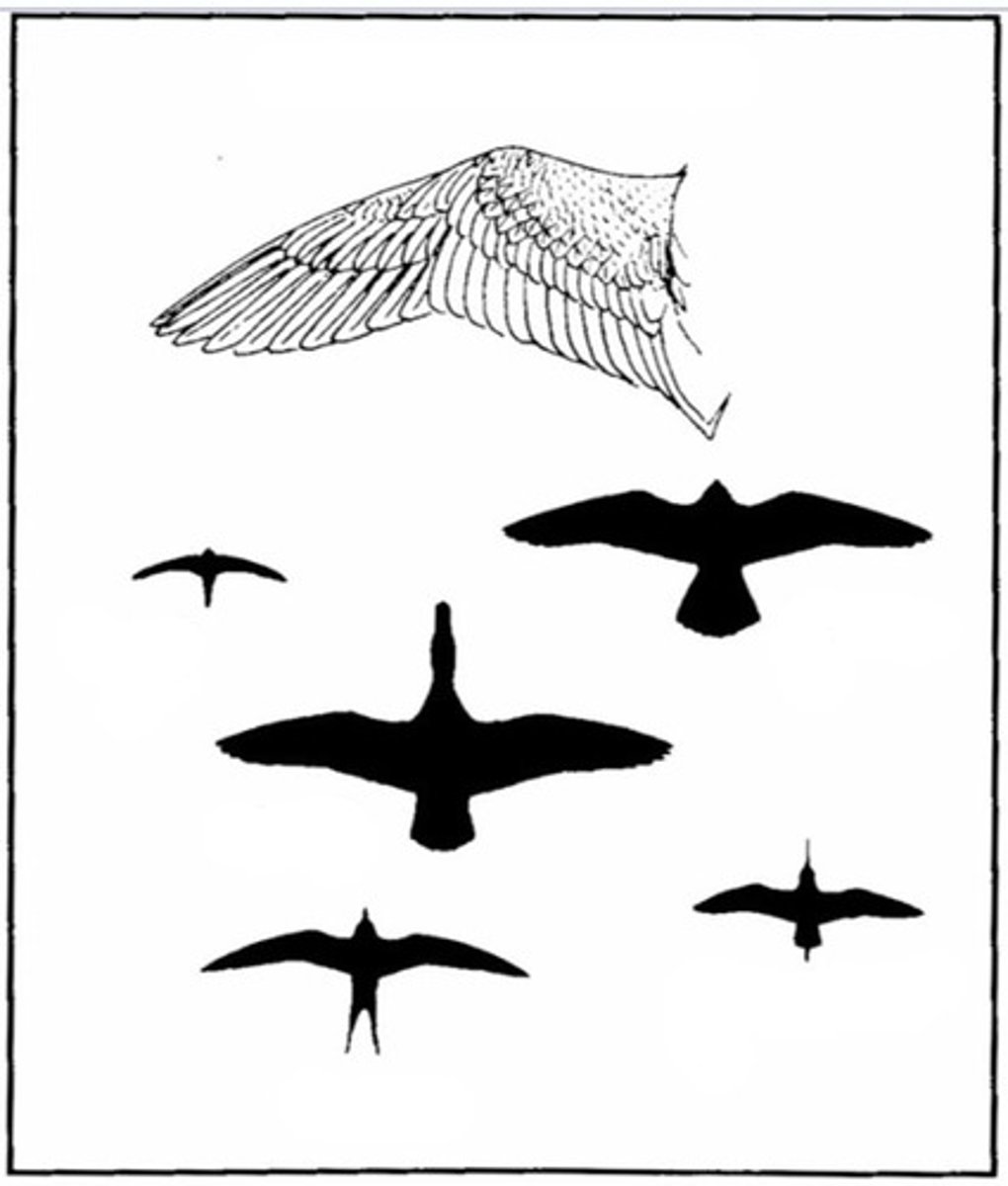
Slotted high lift wing
Passive soaring wings
Long broad wings ending in long primary feathers with wide gaps in between allowing it to soar without reliable wind currents
Eagle and stork
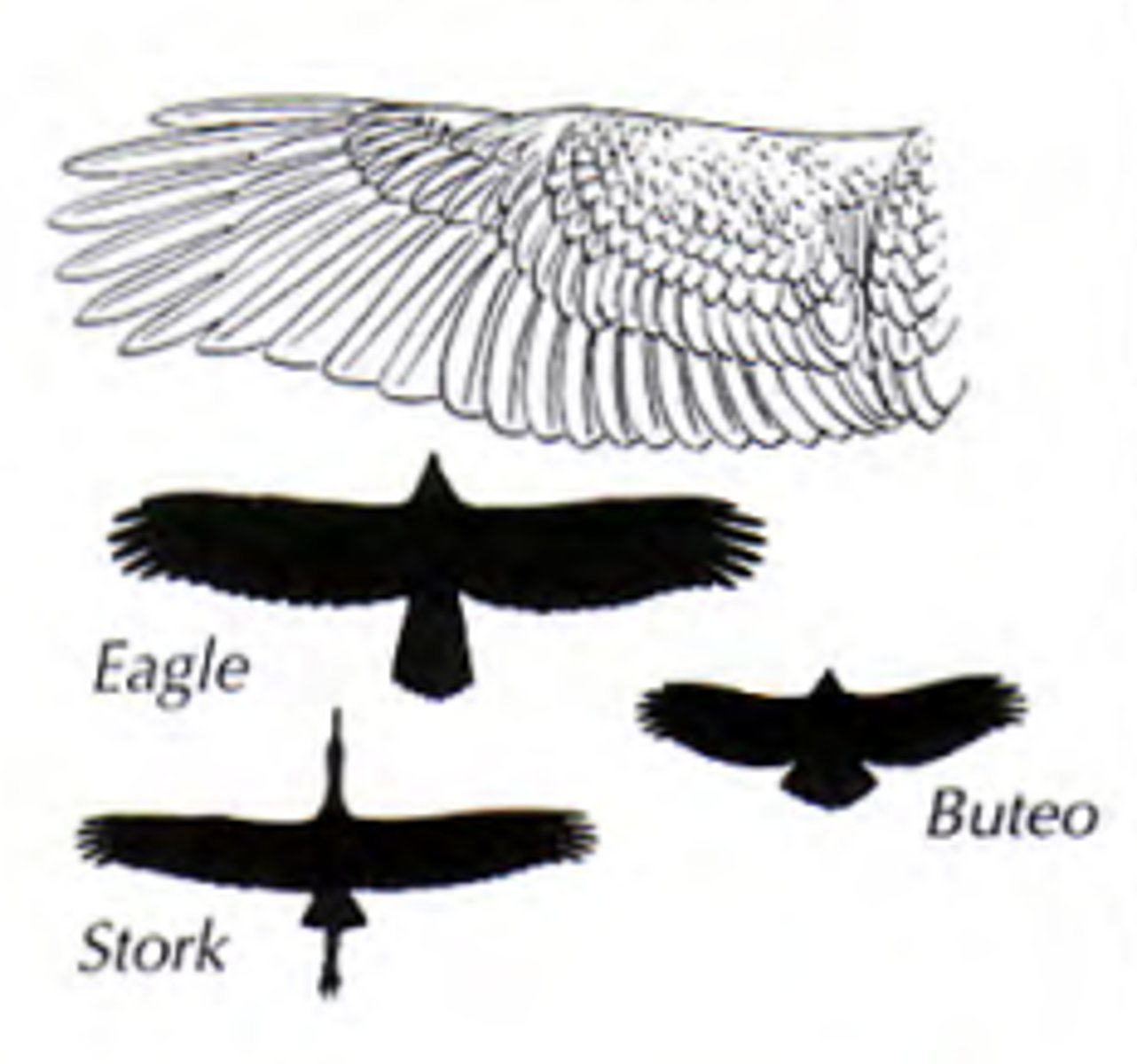
High aspect Ratio wing
Active soaring wing
long and narrow excellent for soaring over water
albatross and gull
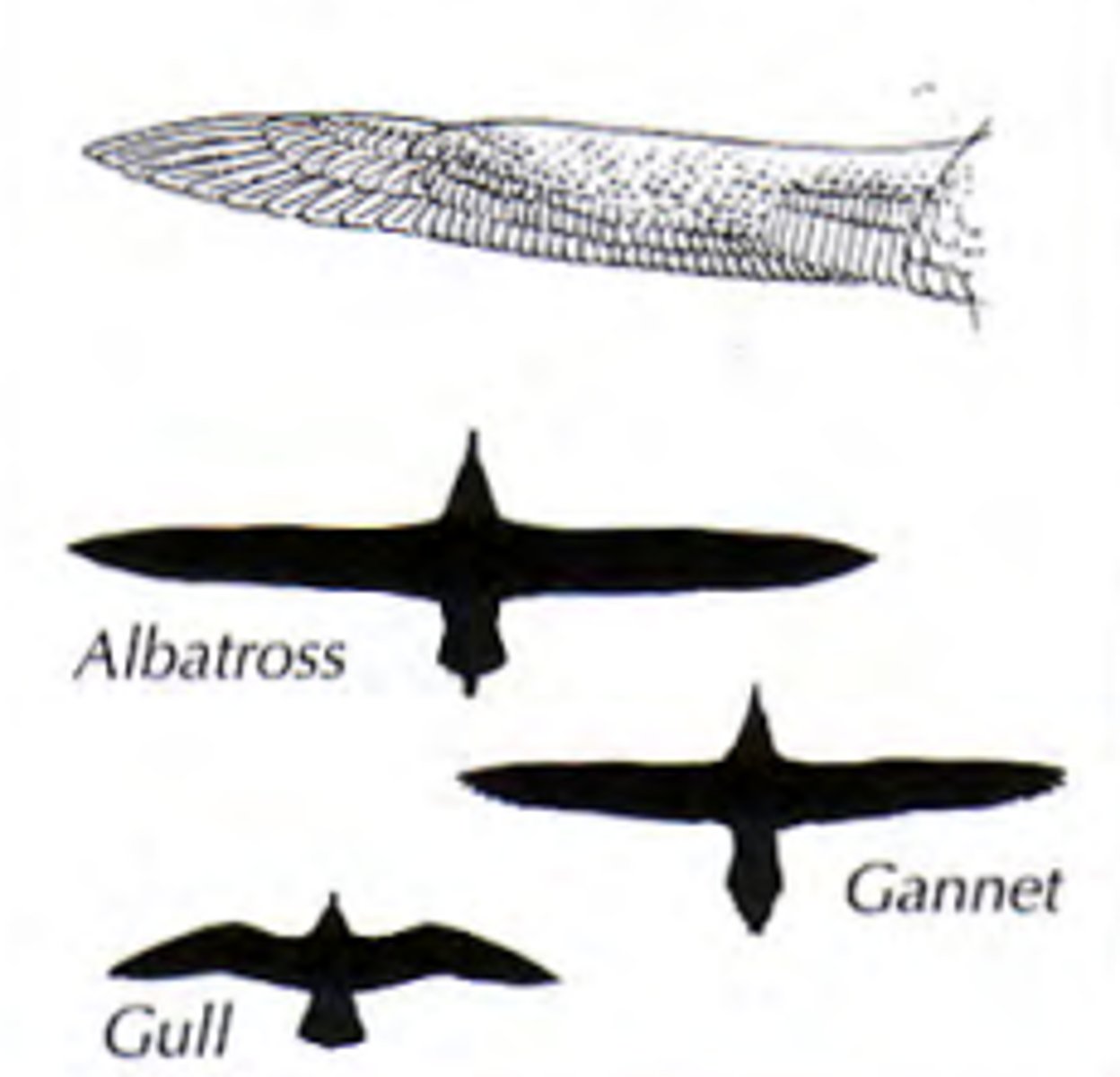
Elliptical wing
Perfect for bursts of fast and tightly controlled flight but ordinary flight is slow and requires a lot of flapping
sparrow and crow
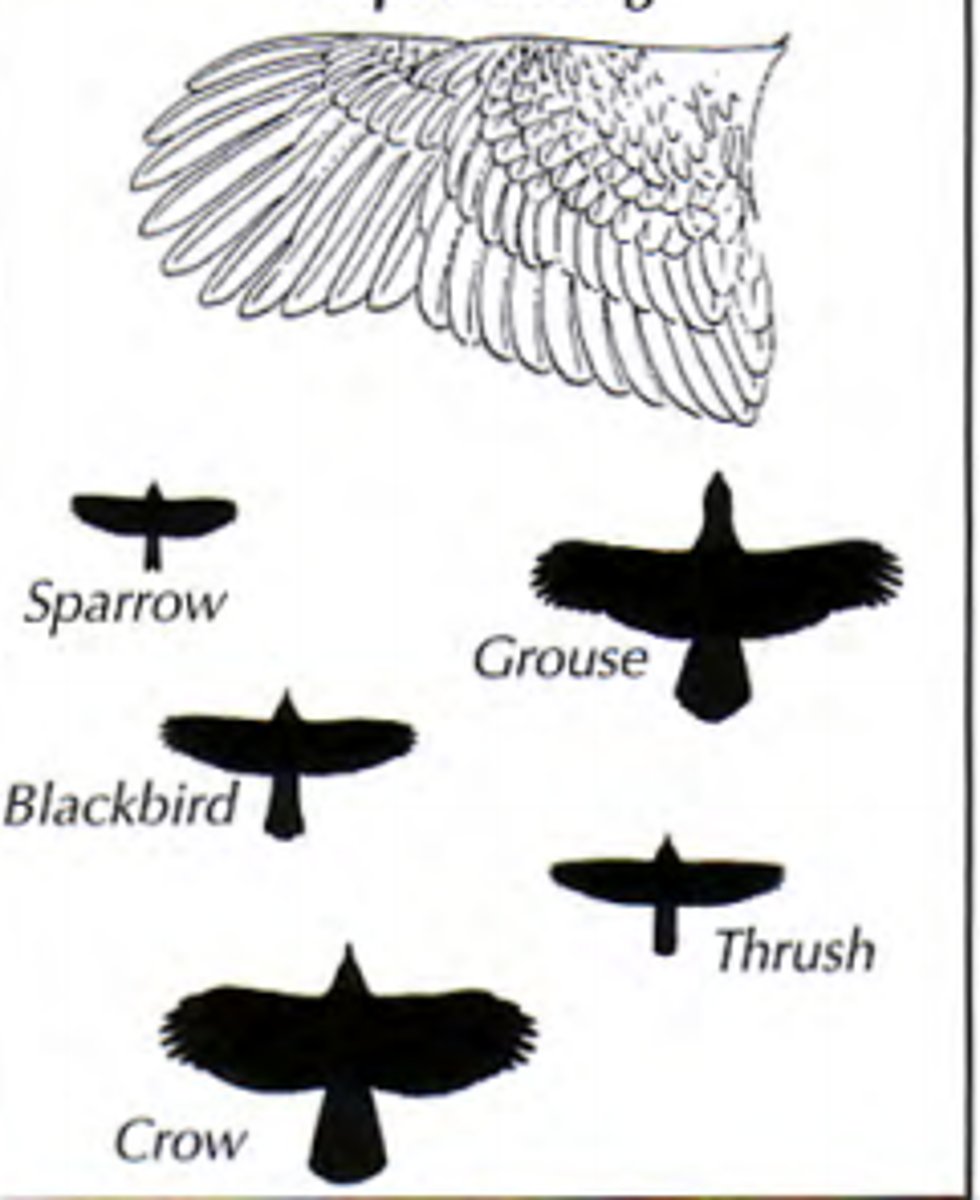
High speed wing
Medium long and narrow optimized for sustained speed
Falcons and terns
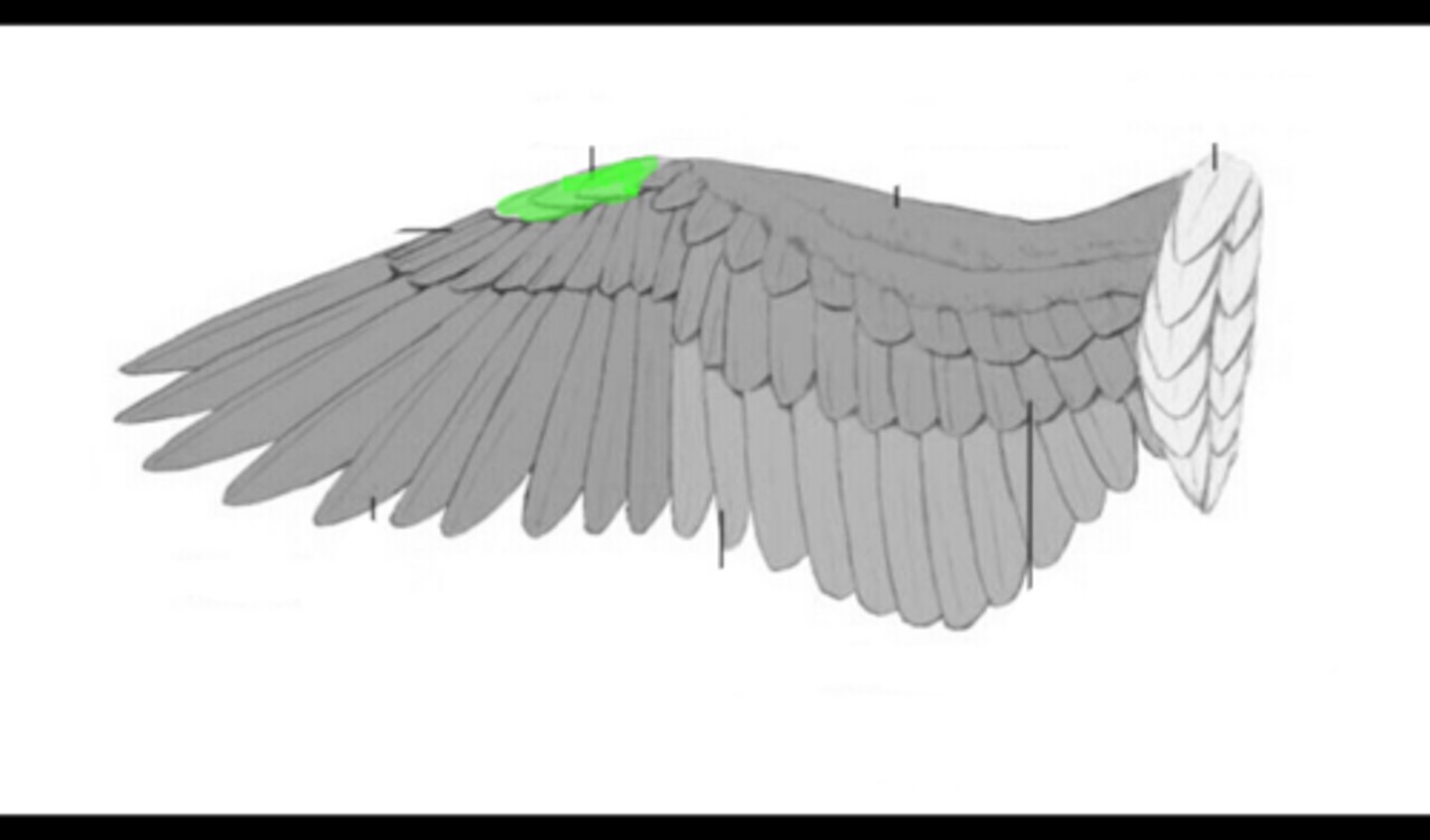
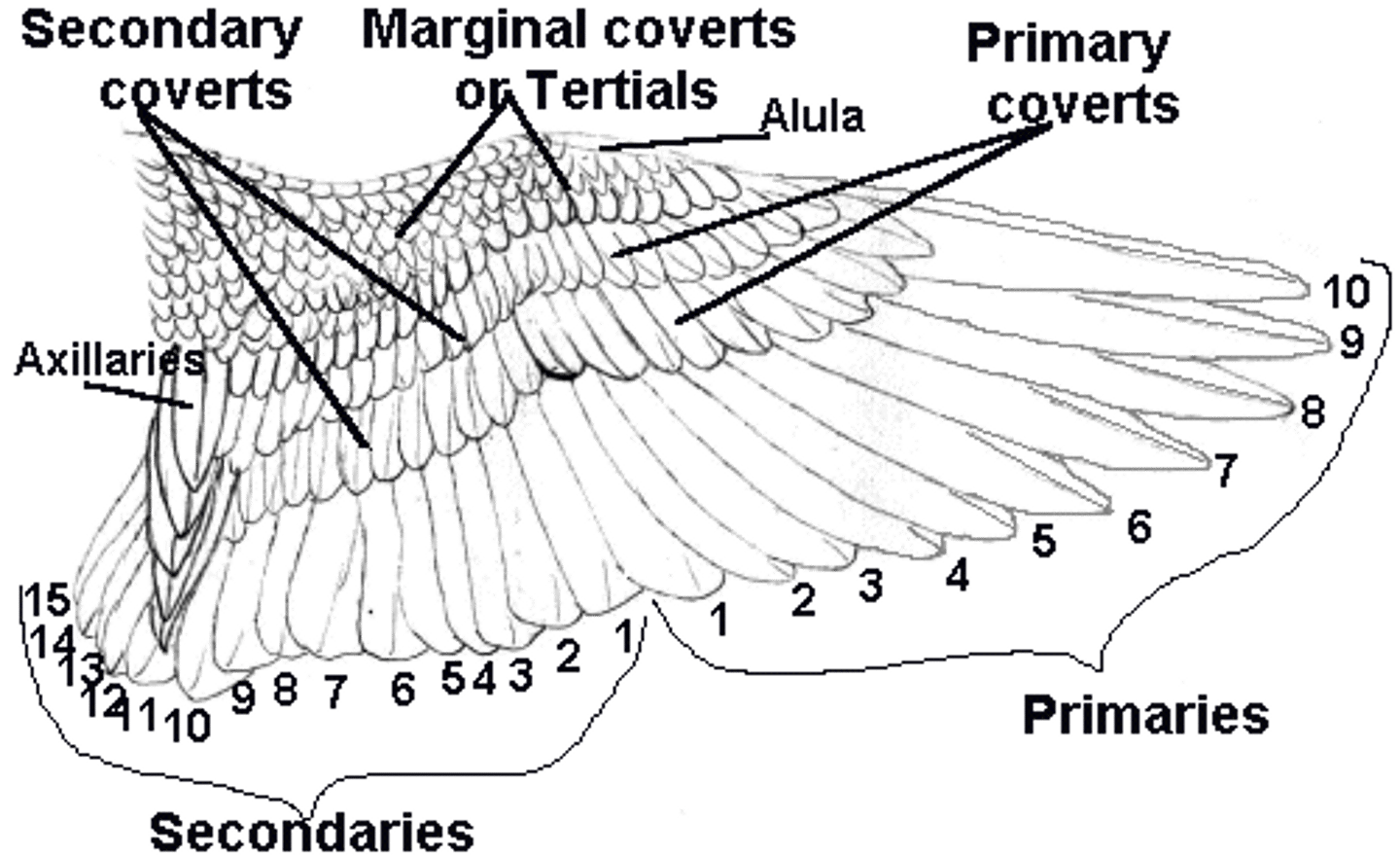
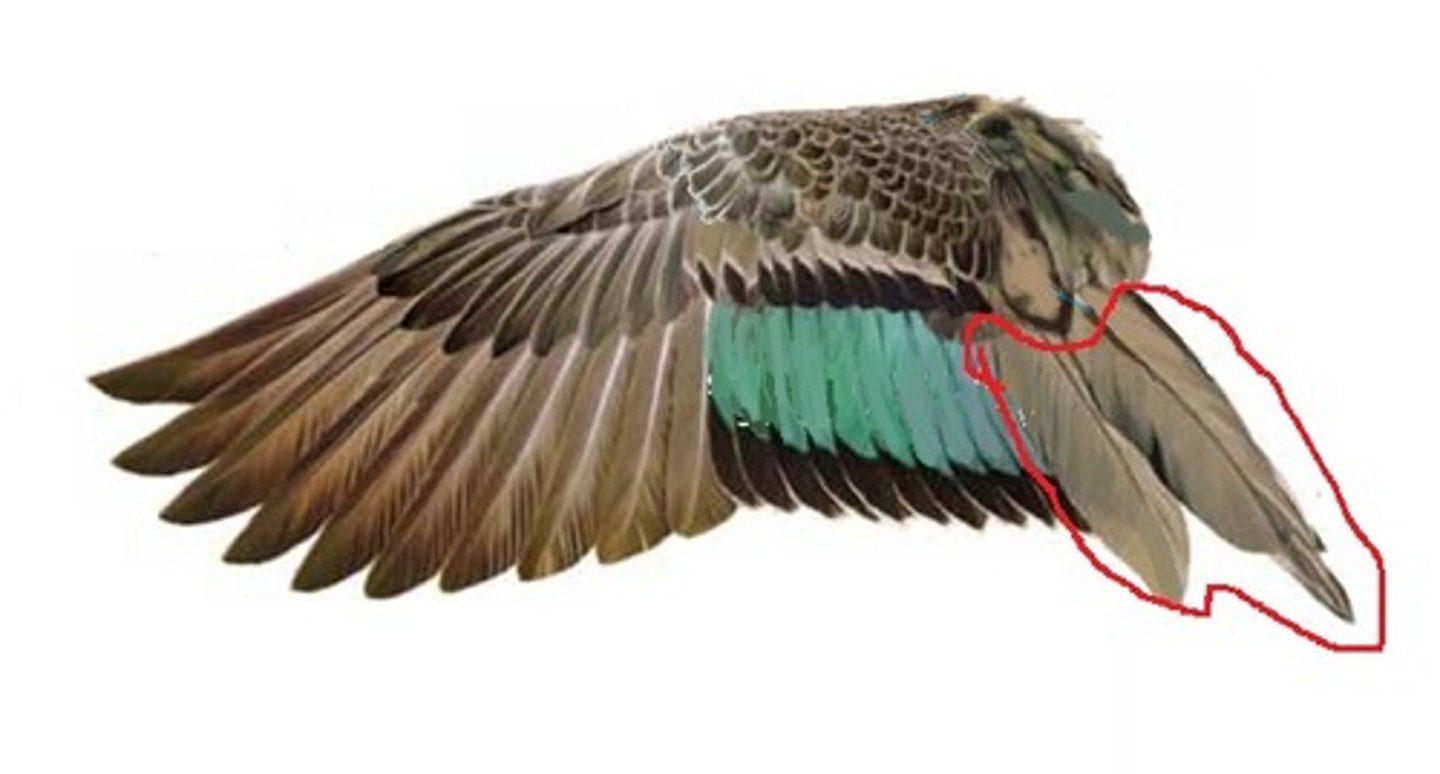
What part of the wings are the primaries, secondaries, and covets
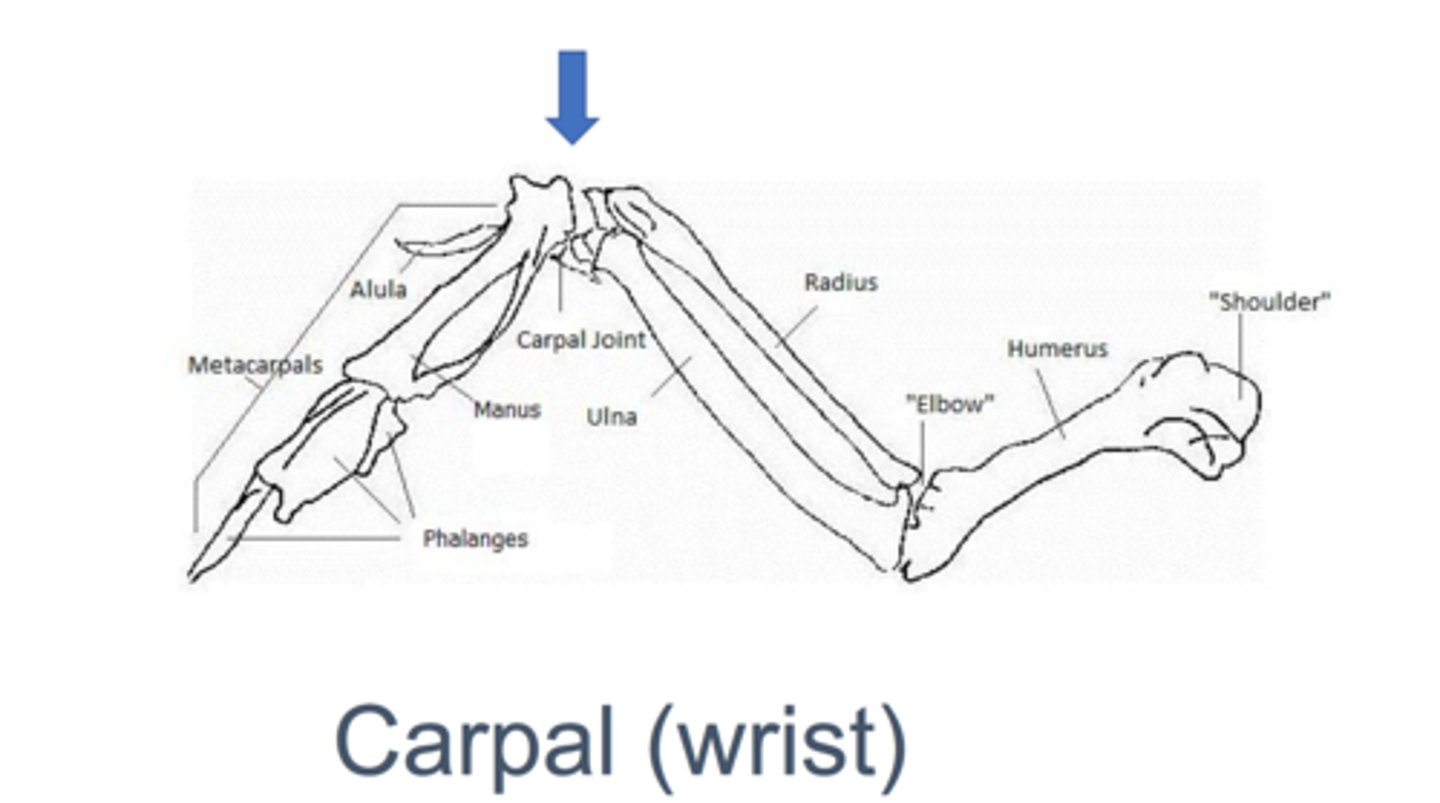
What is the carpal
the wrist
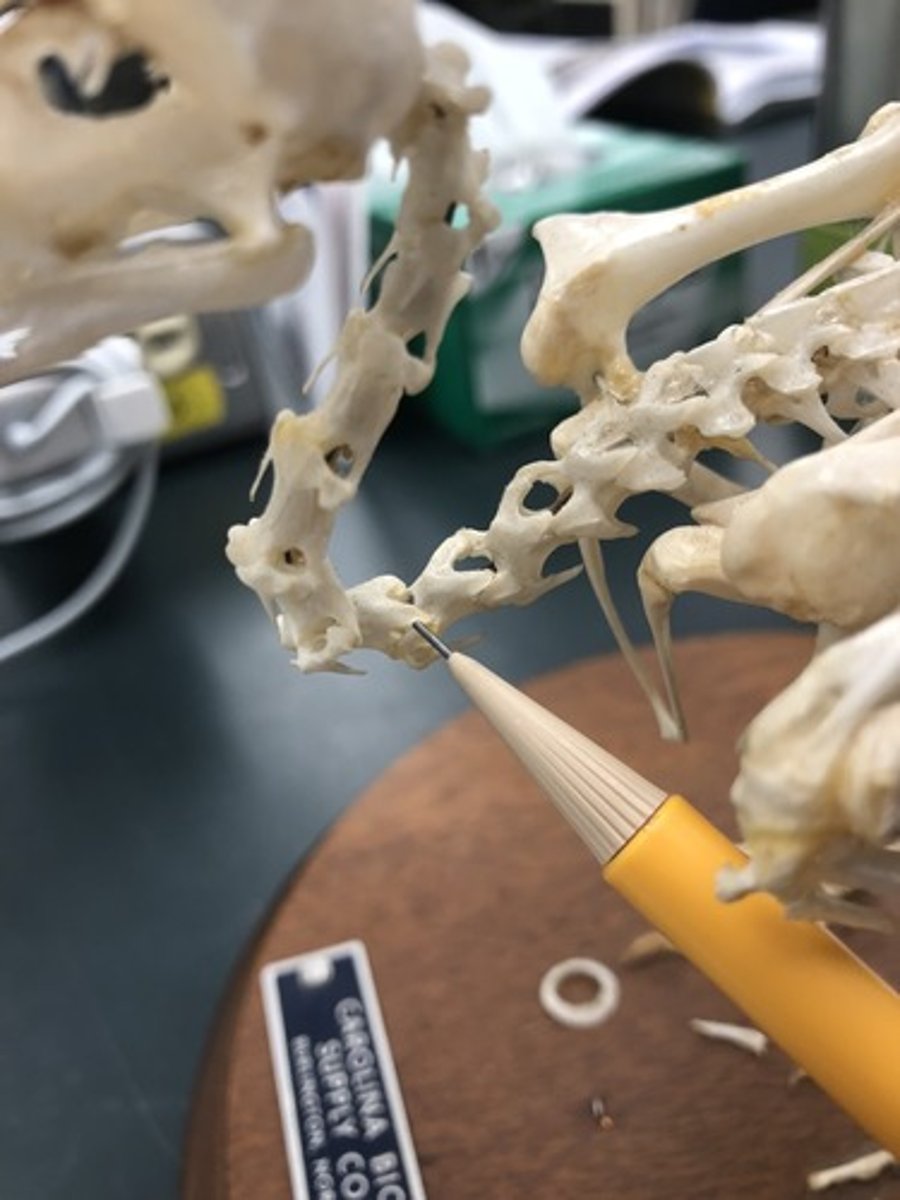
What is the cervical
the neck
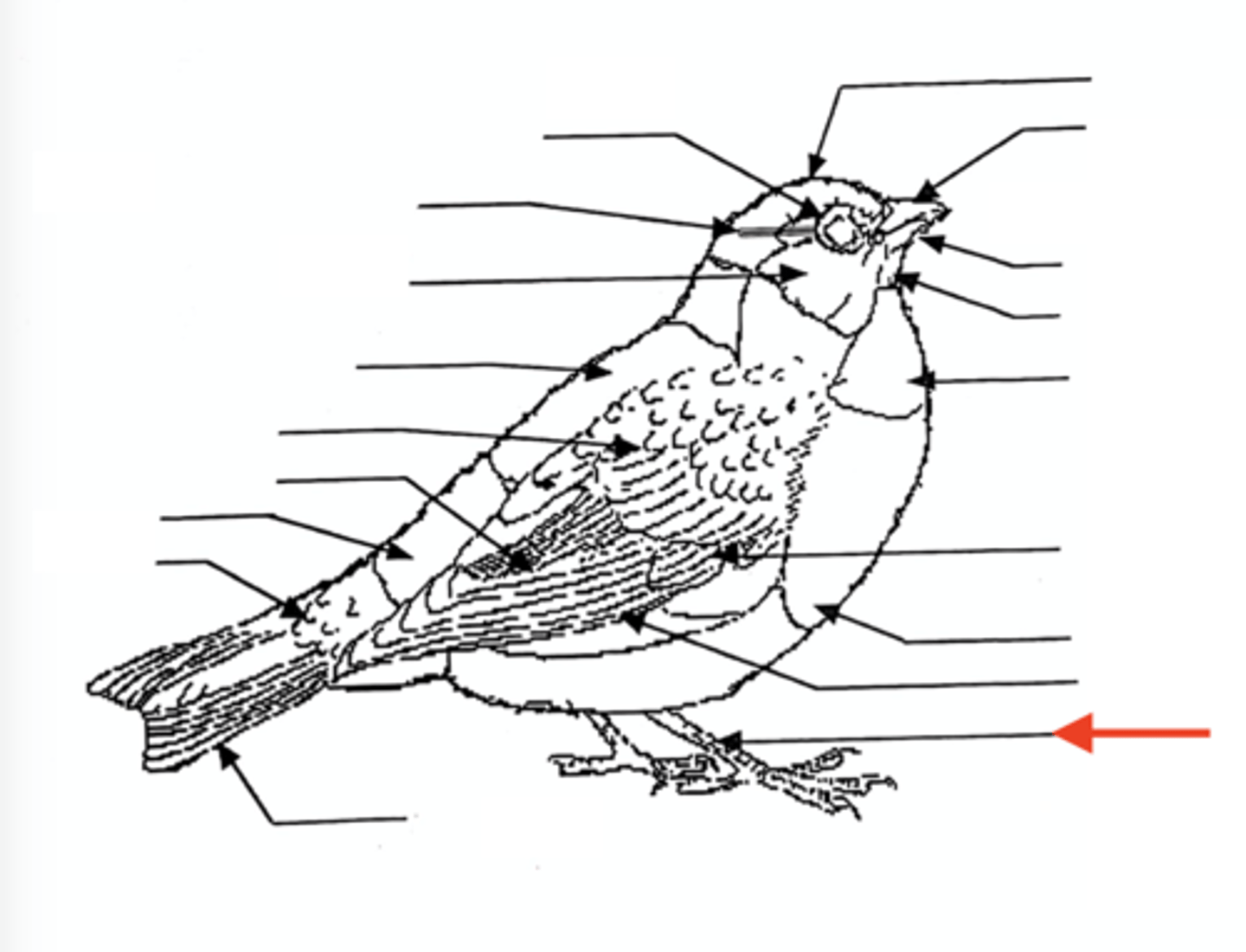
What is the cranial
the head
What is the tarsal/tarsus
the place between the ankle and digits
Anisodactyl
one toe faces the rear, other three face forward (pigeons)
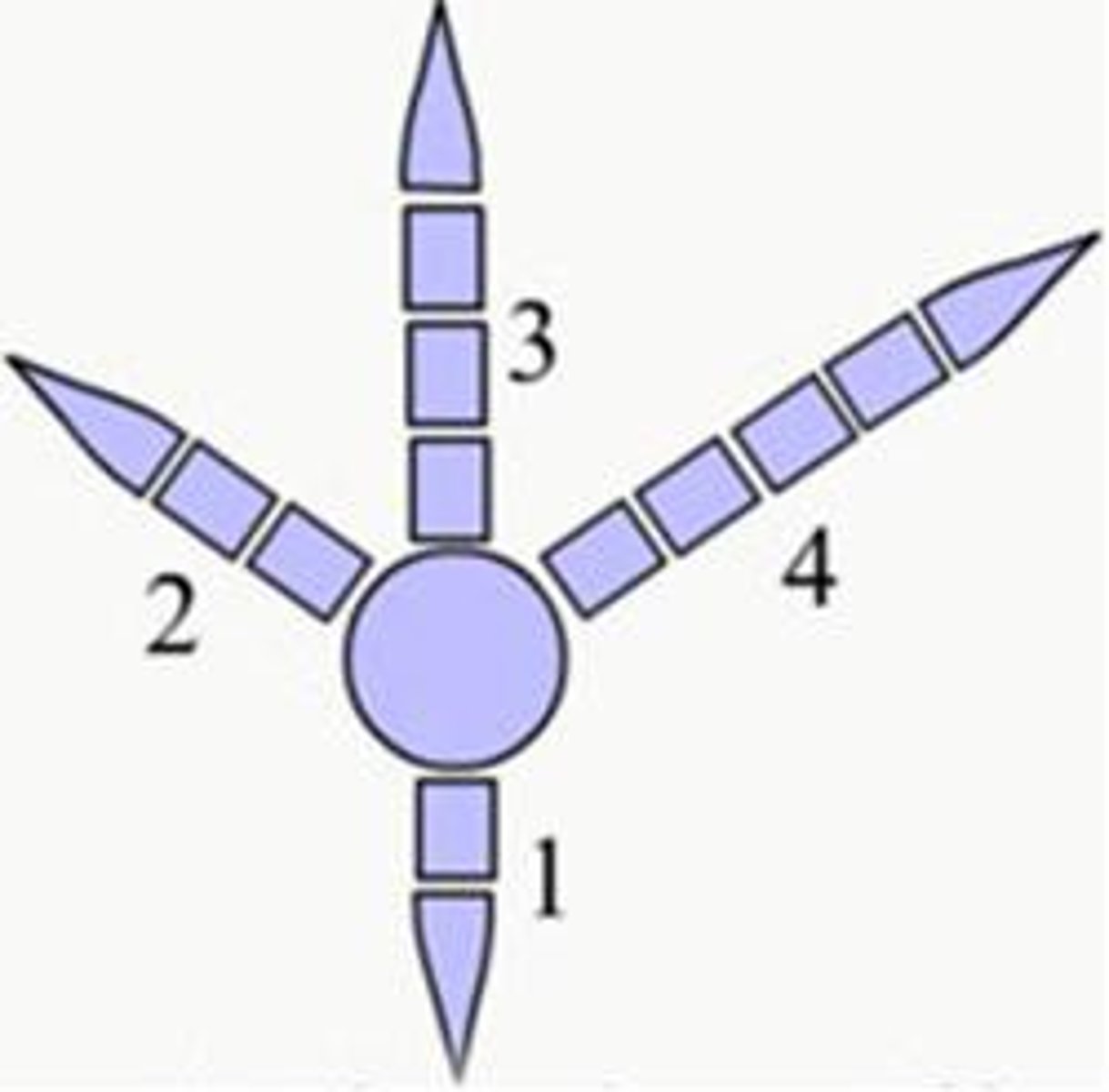
Zygodactyl
having the toes arranged two in front and two behind (owls)
Tridactyl
having 3 digits (emu)
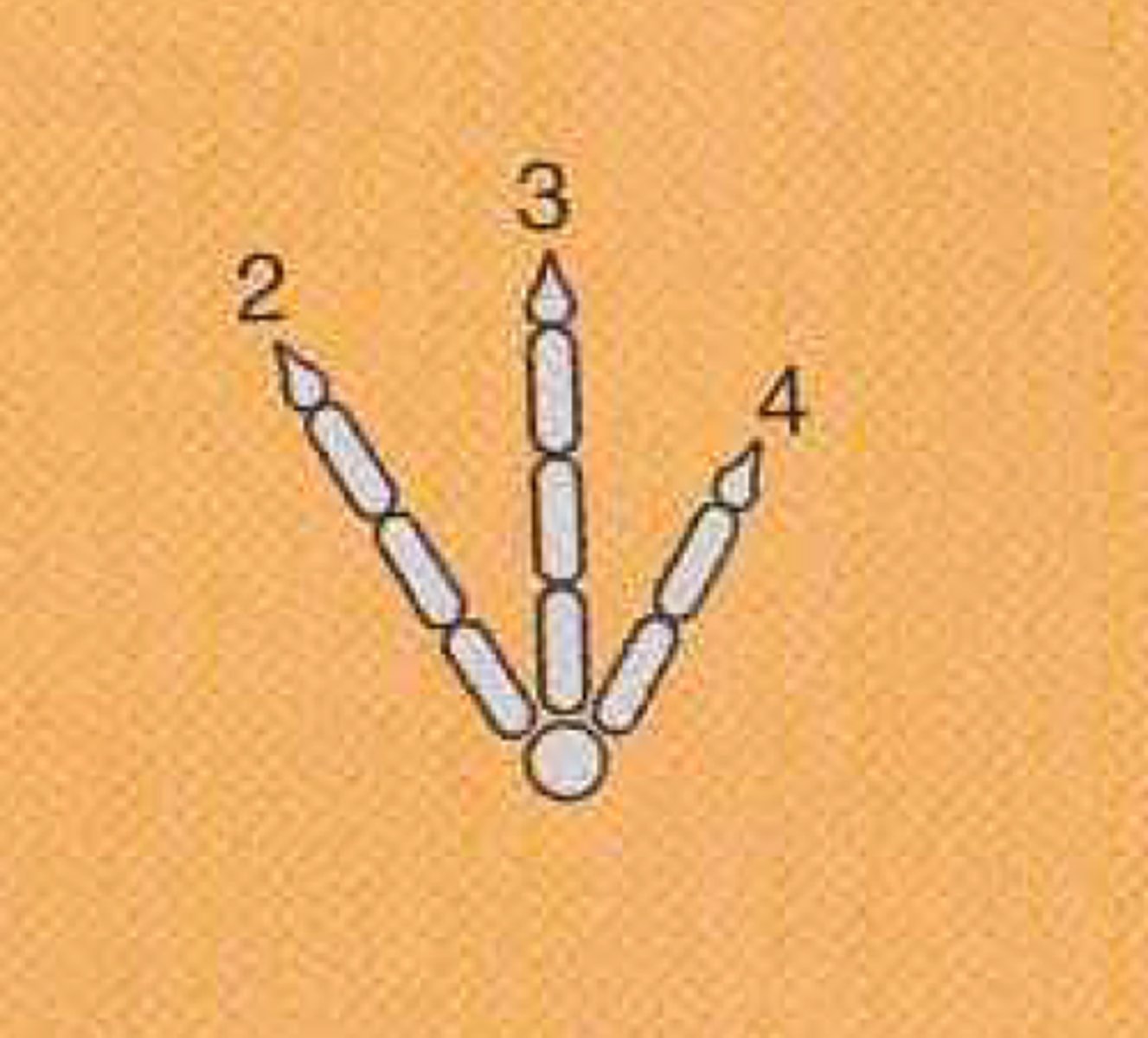
Didactyl
Two digits (ostrich)
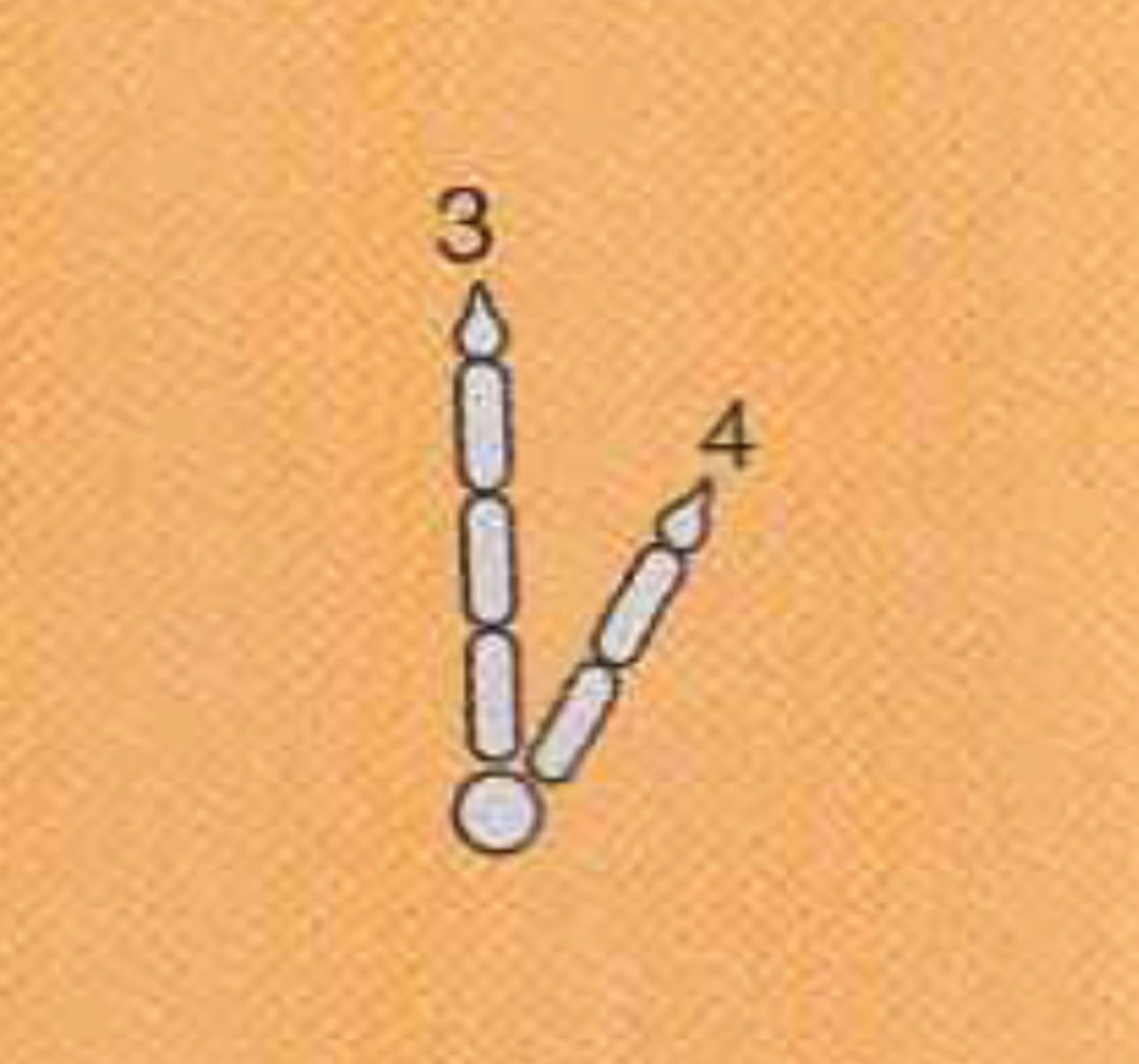
Sindactyl
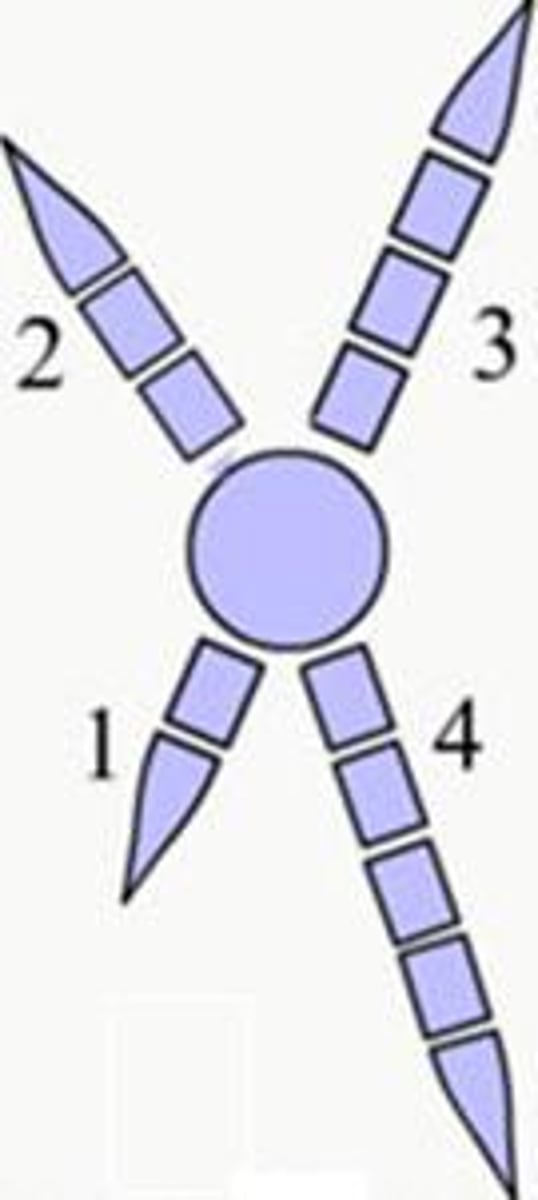
digits 2 and 3 are almost fused together but they have 4 toes (kingfishers)
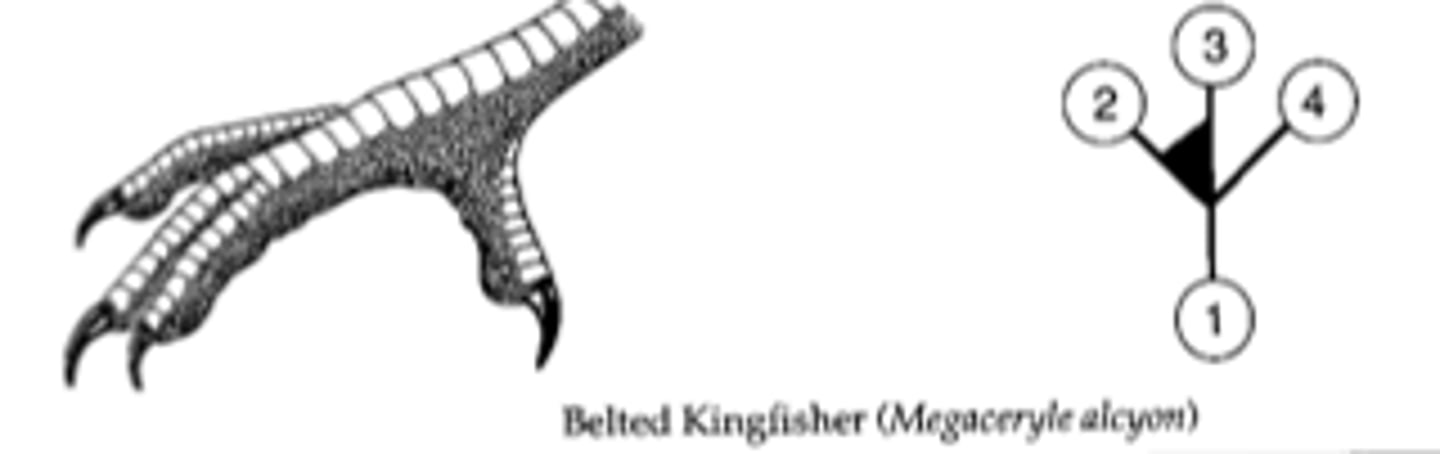
Pamprodactyl
all toes forward (1st toe and hallux can pivot from front to back) Ex: most swifts
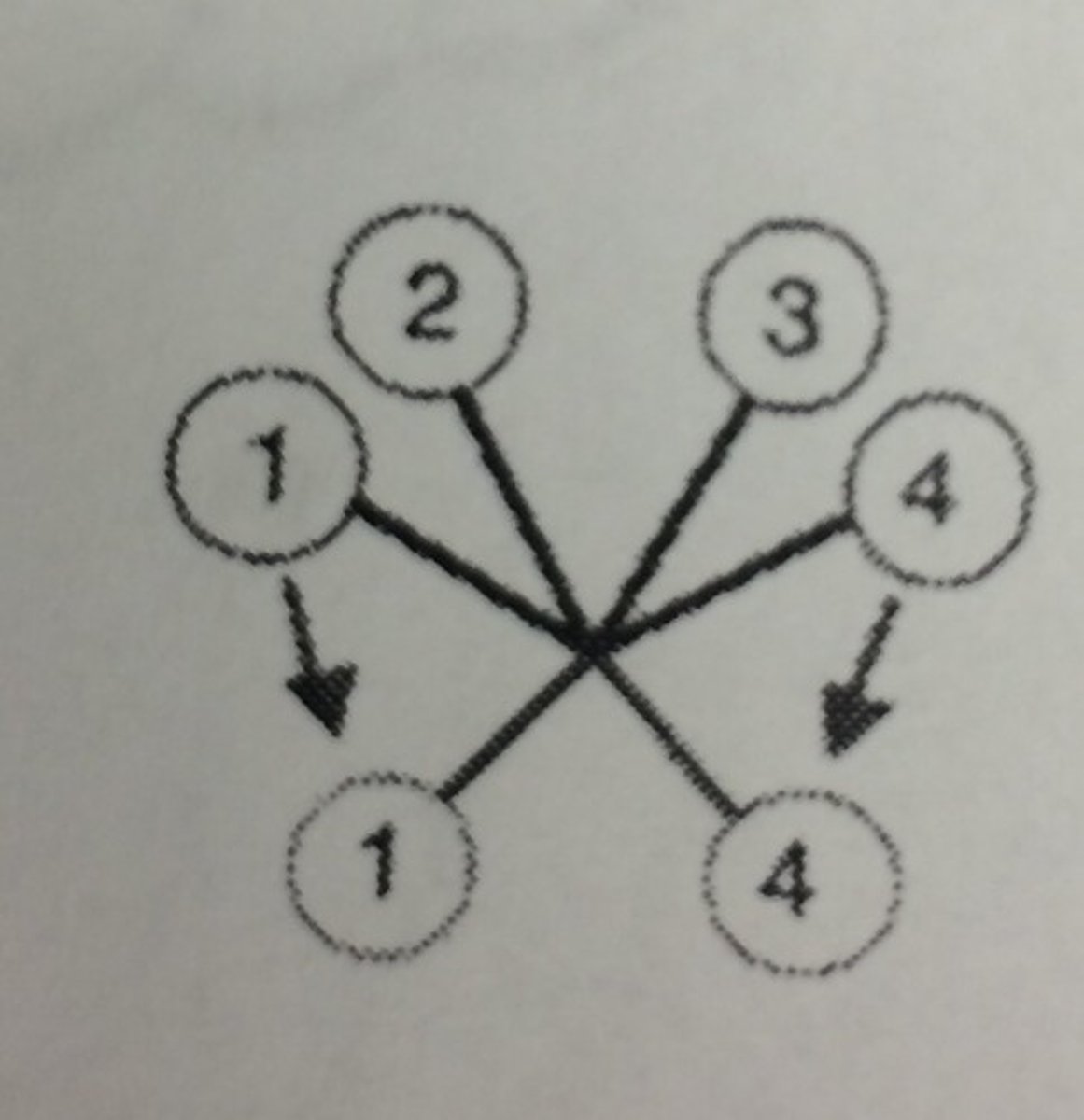
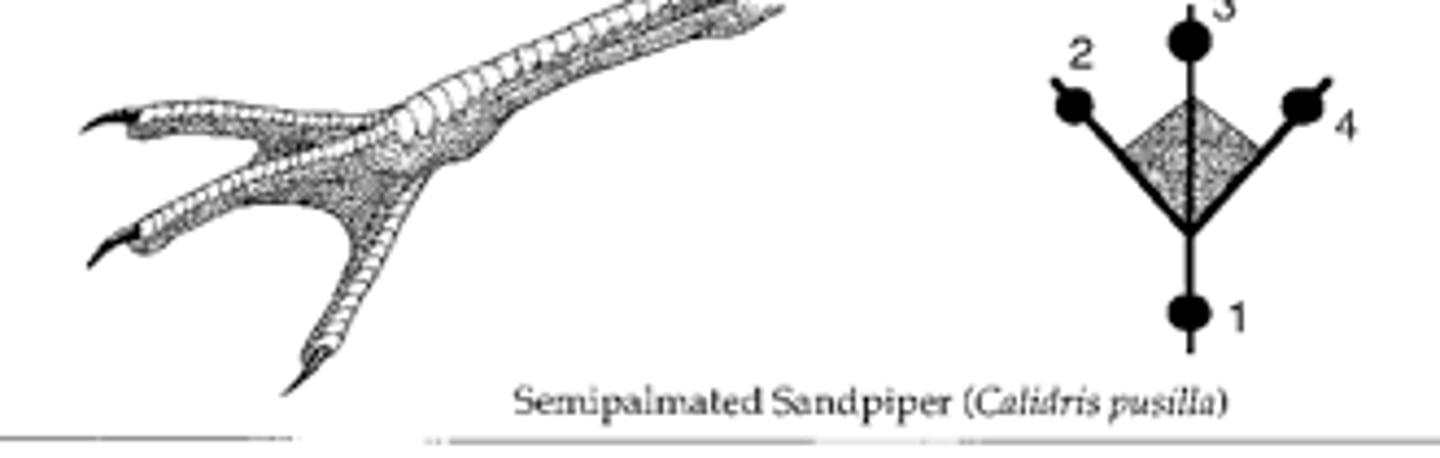
Lobate
Having lobes on each digit (grebes)
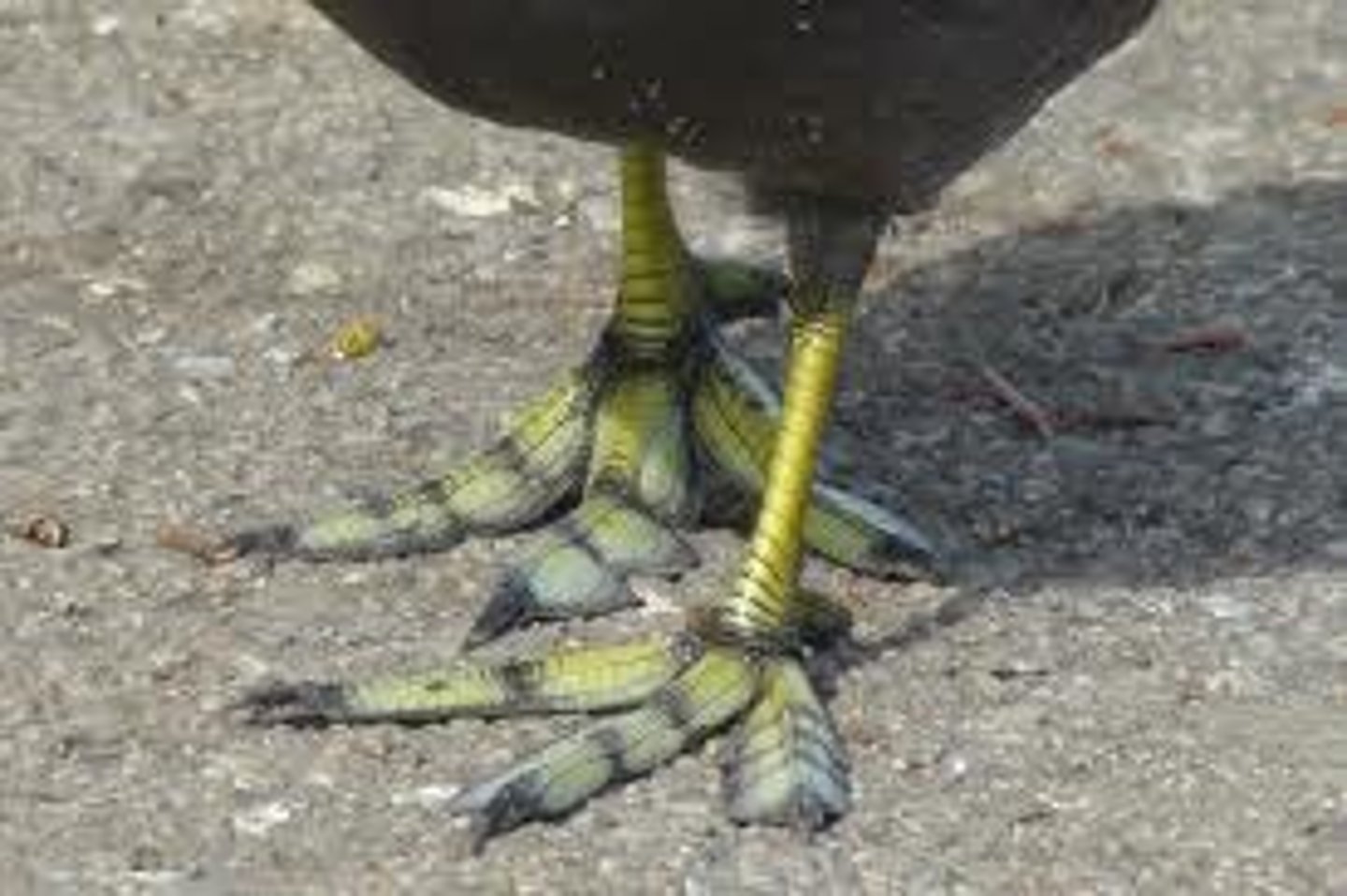

Semipalmate
Incomplete webbing between front three toes (spoonbills)

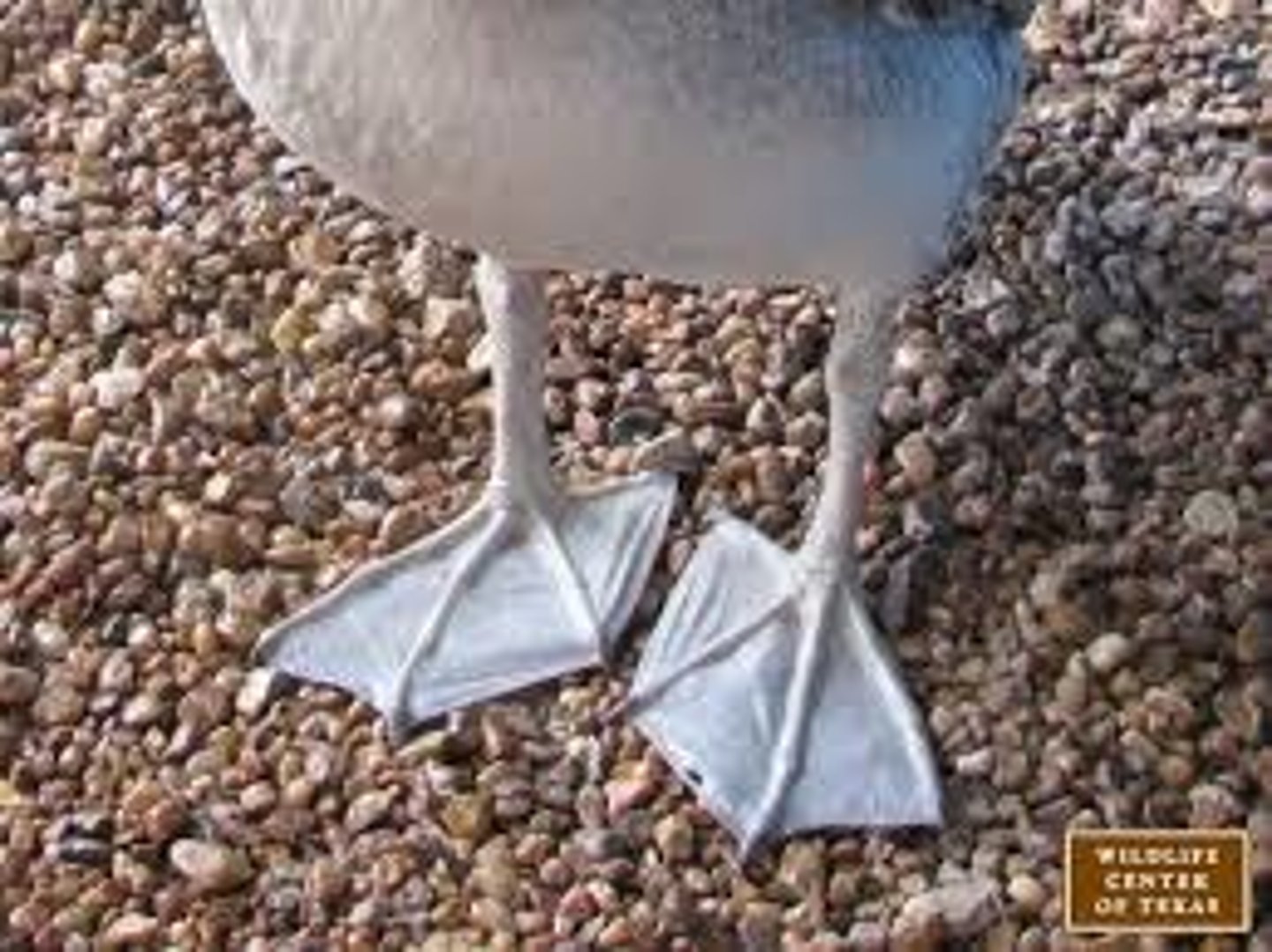
Palmate
Almost full webbing but does not include the hallux (ducks)
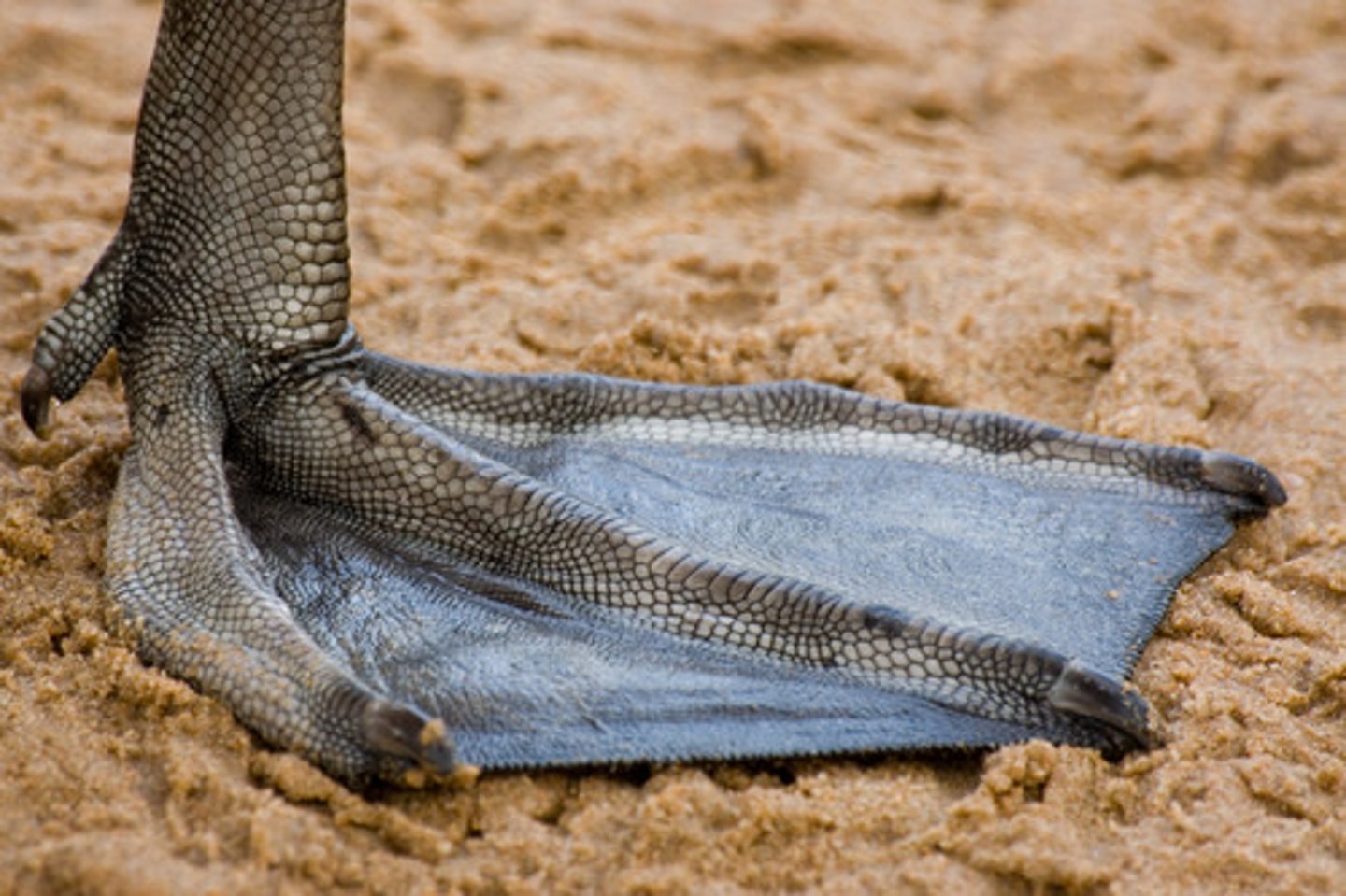

Totipalmate
all four toes webbed (pelicans)

Do primaries shafts go off to the side while secondaries are centered
yes
What is the most common foot arrangement
Anisodactyl
Why are all beaks different
each beak is shaped to what kind of food they have to eat
what are tertials
the innermost flight feathers on the wing
Where is the humerus
Closest to the shoulder
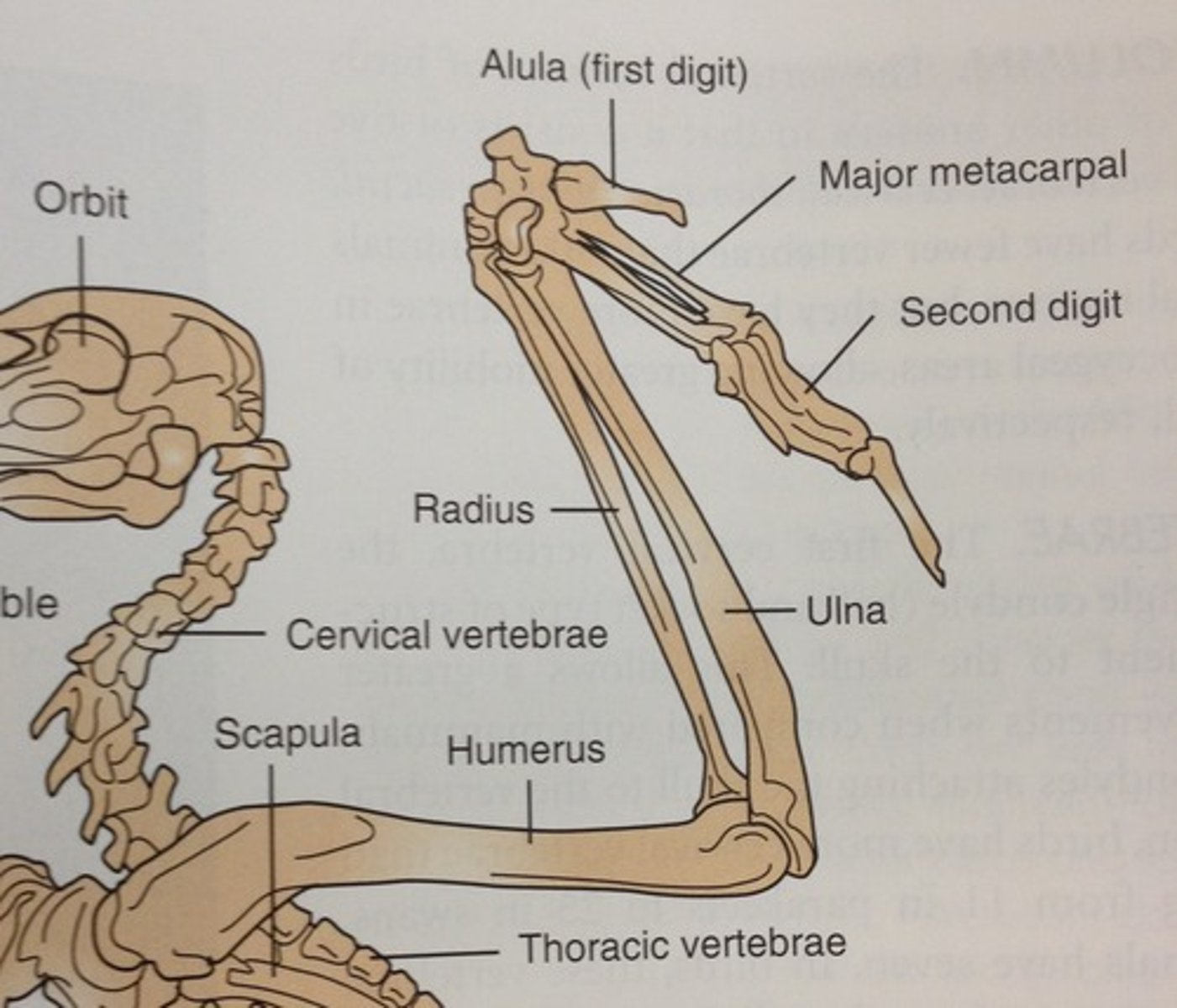
Where is the radius
Below the carpal (the thinner one, the thicker one is the ulna)
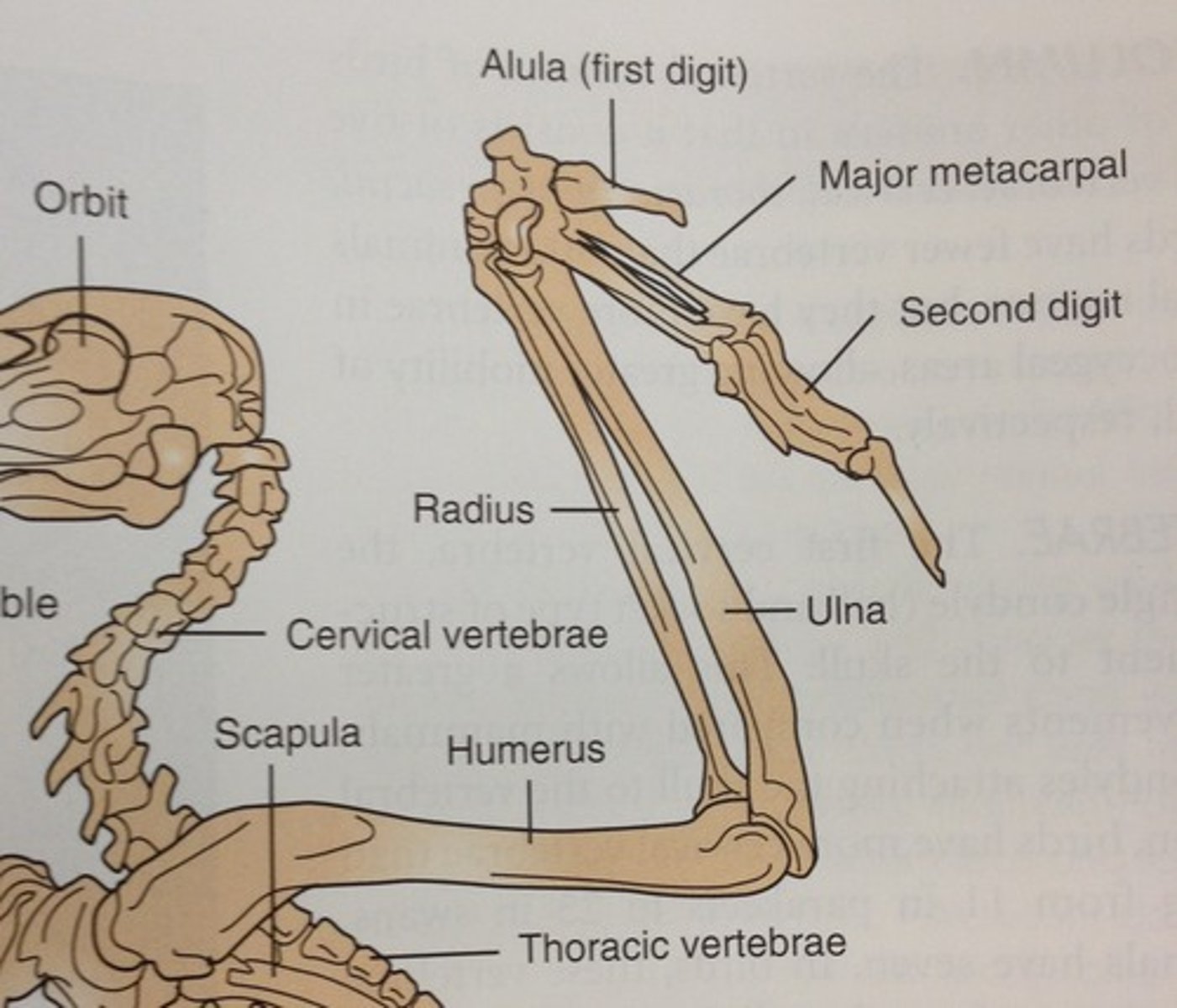
What are metacarpals
The upper part of the digits
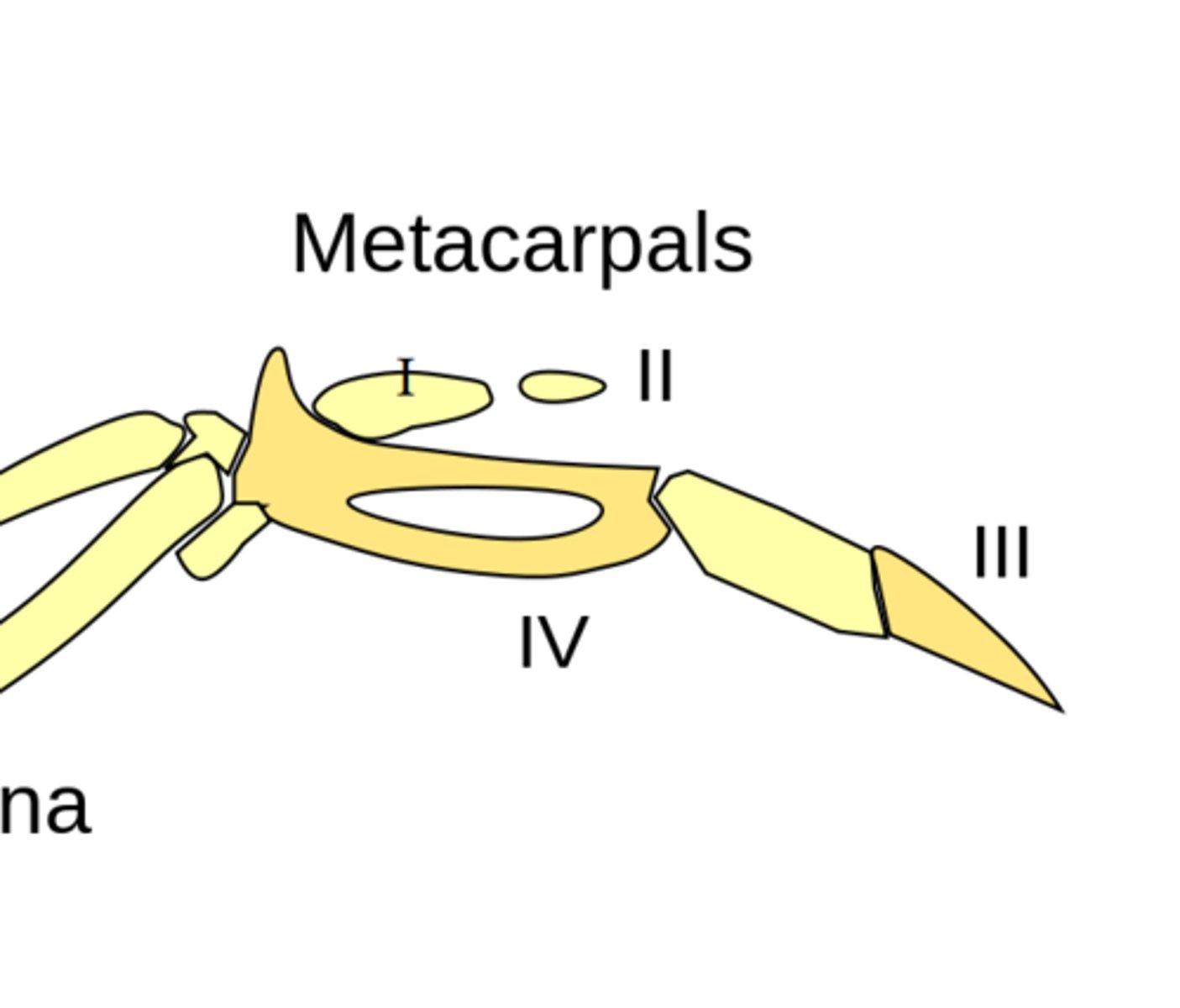
what is the alula
Basically the thumb