measuring and modeling population change
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
populations are
dynamic and changing
always in flux
carrying capacity can change
biotic potential
Maximum reproductive rate under ideal conditions, no limit factors
carrying capacity (K)
number of individuals the environmental resources can support over a long period of time
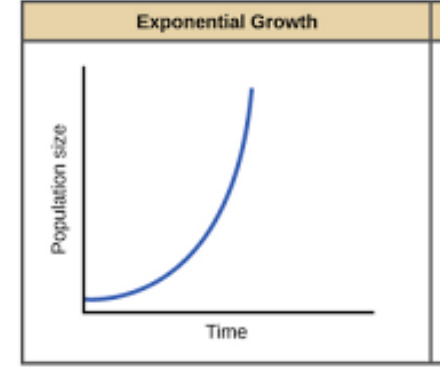
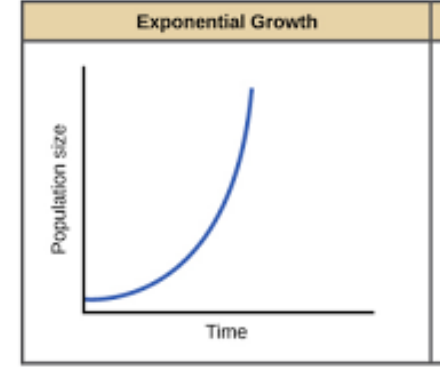
exponential growth model
organisms reproduce continuously at a constant rate
not realistic
doesnt including limiting factors
instantaneous growth rate
change in the rate at a particular instant
like a snapshot of population
doubling time
the amount of time required for population to double in size
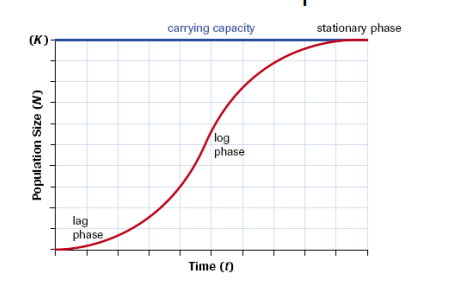
logistic growth model
describes limited population growth
often due to limited resources or predation
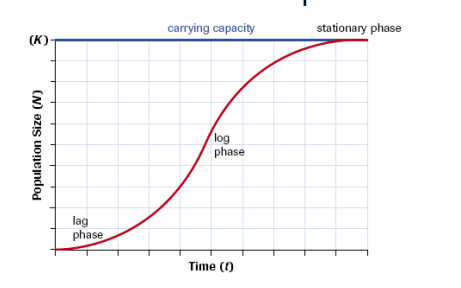
logistic growth model phases
lag phase: rate accelerates
log phase: rate slows down
stationary phase: once carrying capacity is reached
Exponential Vs. Logistic Growth
exponential: unrestricted; growth rate of population accelerates
logistic: restricted; realistic phases
does a decrease in rate mean less offspring produced?
life strategies
species patterns of growth, survival and reproduction
used in order to grow their populations or
to make trade-offs to maximize the number of offspring that survive
r-selected life strategies
spawners
exponential growth
temporarily large populations, followed by sudden crashes in population size
short life span
sexually mature at young age, many offspring
Ex. Insects, bacteria, annual plants, algae
k-strategists
brooders
long life span
sexually mature later in life
produce few offspring and provide care
generally live close to carrying capacity, logistic curve
Ex. Mammals and birds