Antidepressants
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Response
> 50% improvement in symptoms, the patient is better but not well.
Remission
All symptoms are gone but for < 6mo
Recovery
Remission lasting longer than 6mo.
Relapse
Depression comes back before full remission or after remission
Recurrence
A new episode after the person has fully recovered
What is the modern goal of antidepressants
Full remission
Who is the rate of relape in MDD better for?
Someone who has acheived full remission
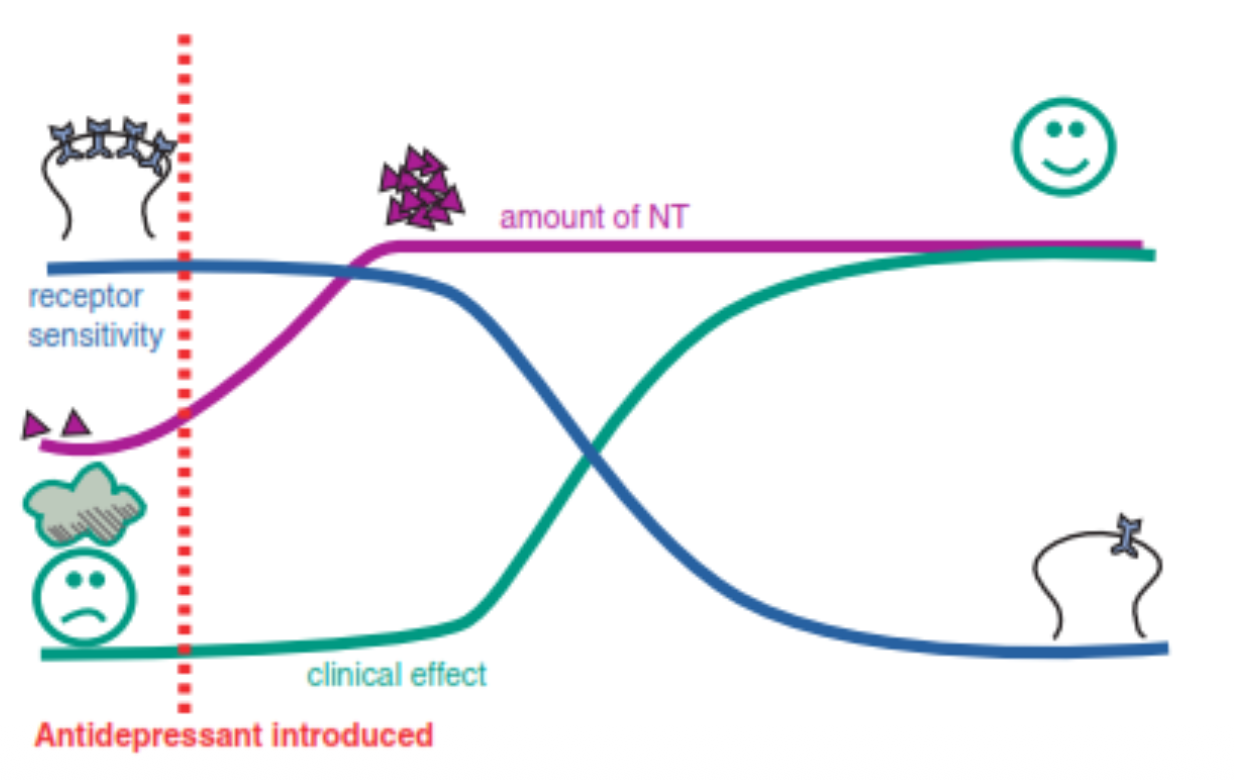
Explain this image
When an antidepressant is introduced, monoamines increase quickly, but theraputic effects in receptor sensitivy take longer
Explain the Neurotransmitter-Receptor Hypothesis
A NT blocks the reuptake in the syanpse which causes increased NT causing receptor downregualtion
What does an SSRI do?
Blocks SERT which causes increase SER in synaptic cleft
What is the actions that causes the theraputic effects of SRRIs
5HT is blocked at the soma and denderites. This causes incraeses SER and action potentials, this causes postsynaptic autoreceptor downregualtion and this is the theraputic effects of SSRIs
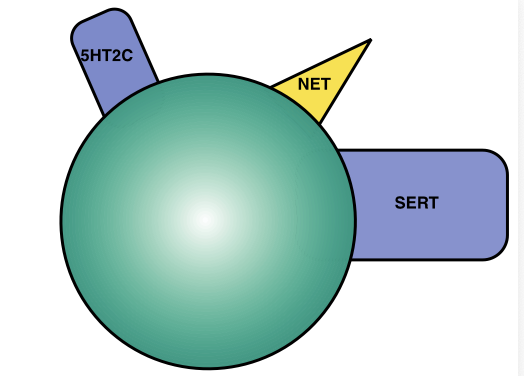
What SSRI is this?
Fluoxetine
Who is Fluoxetine best for?
Low mood and low energy depressed patients
Who is fluoxetine worst for?
Agitated and anxioud patients, insomia and panic disorder patients
Is Fluoxetine generally activating or inhibiting
Activating
How does blocking 5HT2C work in Fluoxetine
5HT2C binds to inhibiting GABA interneurosn which frees up the release of DA and NE
What SSRI has the longest half life and minimal withdrawl
Fluoxetine
Fluoxetine side effects
Sexual Dysfucntion
Decreased apetite
Insomnia
SIADH In adults

Which SSRI is this?
Sertraline
Who is Sertaline best for?
Any anxiety disorder patients (OCD, PTSD, GAD)
What are the mechanisms of Sertraline
SERT Inhibition
Weak DAT Inhibition
Sigma-1 binding
What drug should you start ‘low and slow for’
Sertraline
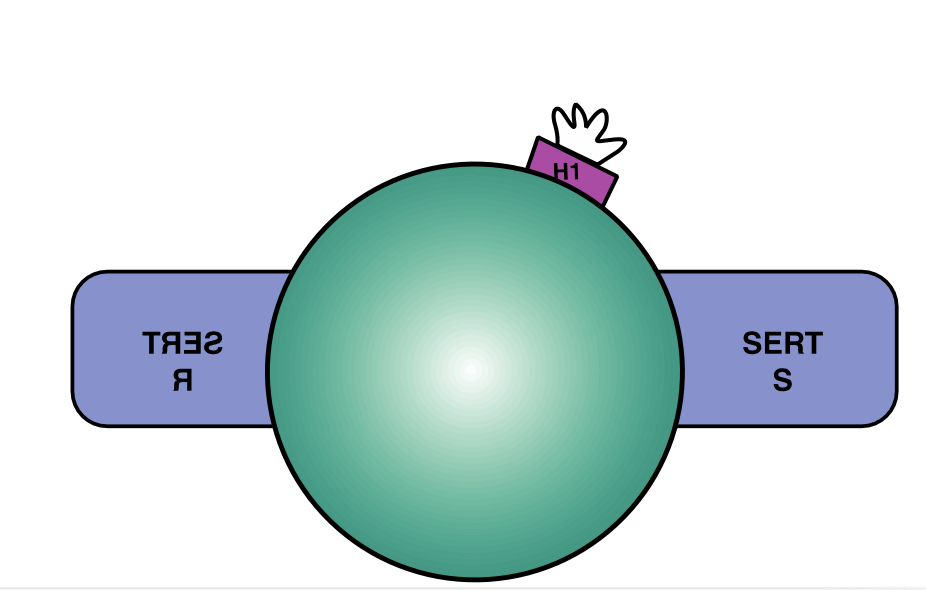
Which SSRI is this?
Citalopram
What is the mechanism of Citalopram
Pure SERT Inhibition of S and R enantiomer
What is the biggest risk with Citalopram
QTc prolongation
What SSRI do elderly commonly use
Citalopram
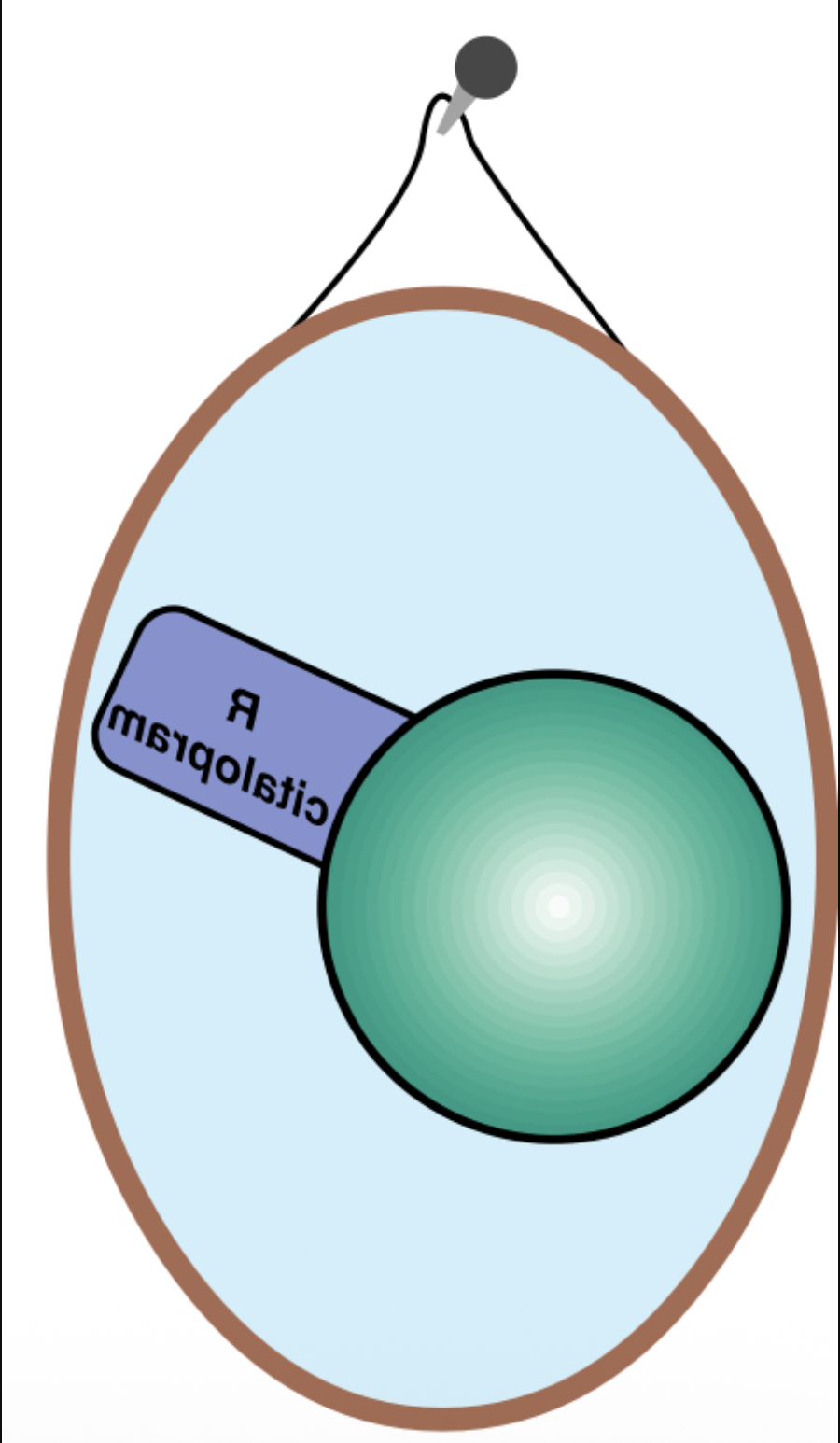
Which SSR is this?
Escitalopram
Which SSRi only contains the S-enantiomer
Escitalopram
What is considered the best tollerated SSRI on the market?
Escitalopram
Why is Escitalopram the best tolerated?
Removes the antihistamin effect, Only s-enantiomer means now QTc and pure SERT inhibition
Which antidepressant is a SARI
Trazodone?
Why, and what side effects, does trazodone avoid?
Through blocking 5HT2A/C it avoids sexual dysfucntion, insomania, and anxiety
What is trazadone (low doses) clinically commonly used for?
Insomnia
What is Trazodone at higher doses used for?
Antidepressant action
How do you get the theraputic effect for Trazadone?
Blocking 5HT2A/C means you stimulate 5HT1A (theruptic effect)
Which antidepressant works by blocking 5HT2A/C to therefore stimulate 5HT1A for MDD improvment?
Trazadone
Inhibiting which MOA has the theraputic effect?
MOA-A (or both)
How does MOA-A have a theraputic effect?
This blocks monoamine oxidase A, which inhibits MOA-A meaning that more monoamines are avaliable inside the enzyme.
Why are MOA’s not taken alot?
Dietary restrictions (Tyramine problem)
What do TCA’s do
SSRI effect with ‘bagage'
What does H1, M1 and a-1 blockage from TCAs cause
H1 = weight gain and sedation
M1 = dry mouth constipation
a-1 = dizziness
What is the biggest risks for TCA’s
Sodium channel blockage can cause death (heart issues)
What is Ketamines mechanism of action?
It blocks NMDA receptors which inhibits glutamate and causes AMPA receptors to fire which leads to a signal cascade and increased synaptic plasticity
What pathway does Ketamine also affact?
mTOR pathway where it is activated and causes synaptogenisis
What is the antidepressant dose of Ketamine?
0.5 mg/kg - 1.0mg/kg IV