Overview of Tissues, Membranes, and the Integumentary System
1/450
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
451 Terms
What is a tissue?
A group of similar cells that perform a common function.
What is the extracellular material that tissues are often embedded in?
The matrix, which is often made out of protein or mineral composites.
What is histology?
The biological study of tissues.
What are the principal types of tissue?
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nervous tissue.
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Covers and protects the body's surface, specializes in secretion, excretion, and absorption, and forms many glands.
Where is epithelial tissue commonly found?
In areas with borders, such as the skin, inside the mouth, and lining the tubes in the body.
What is connective tissue responsible for?
Supporting the body and its parts, connecting body parts together, transporting substances, and protecting from foreign invasion.
Why is connective tissue considered strong?
It has relatively few cells in ratio to the extracellular matrix.
What are examples of connective tissue?
Bones, cartilage, and adipose tissue.
What is the primary function of muscle tissue?
Produces movement resulting in locomotion.
What is the role of nervous tissue?
Specializes in communication between various parts of the body and their integration.
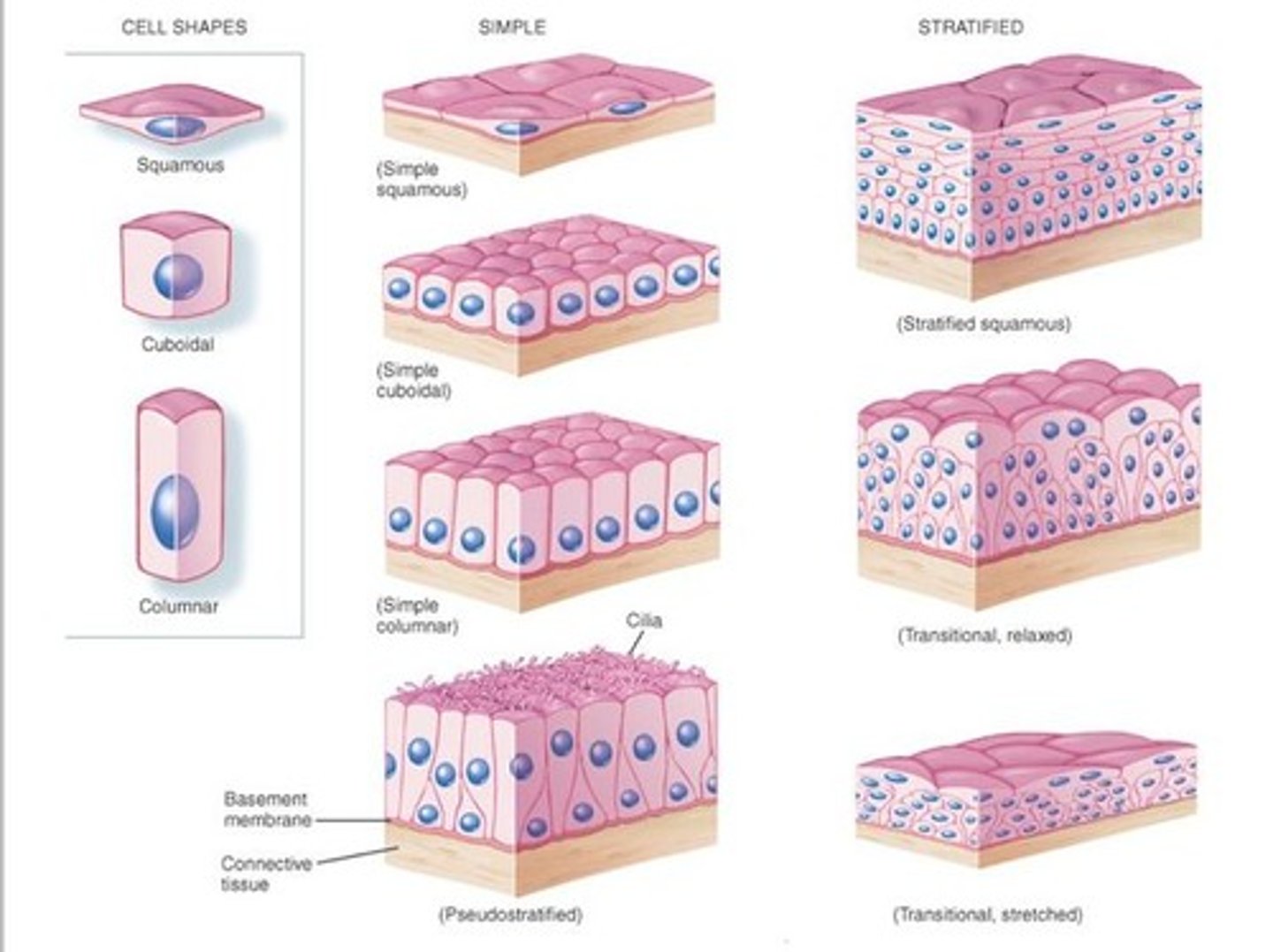
What are the two types of epithelial tissue based on cell layers?
Simple epithelium (one layer) and stratified epithelium (multiple layers).
What is the function of simple epithelium?
Lines the body's cavities, ducts, and tubes where absorption and diffusion are key.
What is the function of stratified epithelium?
Typically functions in a protective capacity in areas with more mechanical stress.
How can epithelial tissue be classified?
As membranous or glandular.
What does glandular epithelium do?
Forms secretory units of glands.
What does membranous epithelium cover?
Covers the body and lines cavities such as pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal cavities.
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
Protection, Sensory, Secretion, Absorption, and Excretion.
How does epithelial tissue relate to its environment?
It deals with borders, focusing on protection, secretion, and sensation.
What is an example of epithelial tissue's protective function?
The skin provides a tough and impermeable covering that protects against injuries.
What type of epithelial tissue is involved in absorption of nutrients?
Simple epithelium, typically found in the gut.
Where is excretion performed by epithelial tissue?
In the lining of kidney tubes.
What shape are squamous cells?
Flat and plate-like.
What is the shape of cuboidal cells?
Cube-shaped.
Describe the shape of columnar cells.
Higher than they are wide, appearing narrow and cylindrical.
What characterizes pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
It has one layer of oddly shaped columnar cells where nuclei may appear to overlap.
What is the meaning of 'pseudostratified'?
It appears stratified but is actually a single layer of cells.
What is simple epithelium?
Epithelial tissue arranged in a single layer.
What defines stratified epithelium?
Cells are layered one on top of another.
What is transitional epithelium?
An arrangement of differing cell shapes in a stratified epithelial sheet.
What is located underneath epithelial layers?
A basement membrane that connects epithelial cells to connective tissue.
Where are stratified squamous cells typically found?
In the production of skin.
What is the function of transitional stratified tissues?
They allow cells to stretch and pull apart without mechanical tearing.
What is the relationship between form and function in simple squamous epithelium?
Very thin tissue facilitates diffusion but is not good for protection.
How does stratified squamous epithelium differ in function?
It is thicker, providing good protection but not facilitating diffusion.
Where is simple squamous epithelium found?
In alveoli of lungs, lining of blood and lymphatic vessels, and surfaces of pleura, pericardium, and peritoneum.
What are the locations of simple cuboidal epithelium?
Glands, gland ducts, and kidney tubes.
What modifications can be found in simple columnar epithelium?
Goblet cells, cilia, and microvilli.
What is the function of goblet cells?
They produce mucus.
What is the role of cilia in epithelial tissue?
They are hair-like structures that move and produce a rhythm.
What do microvilli do?
They have projections that increase surface area.
Where is pseudostratified columnar epithelium located?
In the lining of air passages and segments of the male reproductive system.
What contributes to the protective qualities of stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium?
The presence of keratin.
Where can stratified squamous epithelium be found?
In the lining of the vagina, mouth, and esophagus.
Where is stratified columnar epithelium located?
In segments of the male urethra and in the mucous layer near the anus.
Where is transitional epithelium found?
In areas subjected to stress and tension changes, such as the urinary bladder.
What is connective tissue primarily composed of?
Extracellular matrix (ECM) with relatively few cells.
What determines the structural characteristics of connective tissues?
The qualities of the fibers and components in the ECM.
What are collagenous fibers?
White fibers made of collagen, providing great tensile strength.
What are reticular fibers?
Delicate fibers that occur in networks, supporting capillaries and nerve fibers.
What are elastic fibers made of?
Elastic fibers are made of the protein elastin, which is a rubbery protein with memory.
What type of connective tissue is found between tissues and organs?
Loose or ordinary connective tissue.
What is the primary function of adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue stores energy and provides padding around organs, including the eyes and kidneys.
What are adipocytes?
Adipocytes are cells that store fat primarily for energy storage and padding.
What is the function of reticular connective tissue?
Reticular connective tissue forms the inner framework of the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow.
Where is dense irregular connective tissue found?
Dense irregular connective tissue is found in deep fascia, the dermis of the skin, and scars.
What are the functions of dense regular collagenous connective tissue?
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue connects muscles to bones (tendons) and bones to bones (ligaments).
What type of connective tissue is found in the walls of certain arteries?
Dense regular elastic connective tissue.
What is the difference between compact bone and cancellous bone?
Compact bone forms the outer shell of bones, while cancellous bone is found inside bones and interacts with the marrow.
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
Hyaline cartilage is found in the nasal septum, articular surfaces, larynx, and rings in the trachea and bronchi.
What is fibrocartilage and where is it located?
Fibrocartilage is found in vertebral disks and the symphysis pubis.
What is the unique feature of elastic cartilage?
Elastic cartilage is found in the external ear and the auditory tube.
What are the three types of muscle tissues in the body?
Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissues.
What characterizes skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle has many cross striations, is multinucleated, long and narrow, and well innervated.
What are the characteristics of smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle fibers are narrow, long, have one nucleus per fiber, and are non-striated.
What unique features does cardiac muscle have?
Cardiac muscle has cross striations, intercalated disks joining fibers, and is unique to the heart.
What are the two types of basic cells in nervous tissue?
Neurons and neuroglia.
What is the function of neurons?
Neurons are responsible for receiving and sending information, with axons carrying information away and dendrites carrying signals toward the soma.
What role do neuroglia play in nervous tissue?
Neuroglia connect, protect, and support neurons.
How do tissues repair themselves?
Tissues repair themselves through the action of phagocytic cells that remove dead or injured cells, followed by regeneration of new cells.
Which types of tissues have the greatest capacity to regenerate?
Epithelial and connective tissues have the greatest capacity to regenerate.
What is a fibrous mass that remains after an injury called?
A scar.
What is a keloid?
An unusually thick scar that may develop in the lower layer of the skin.
What factors can cause scarring?
Radiation exposure, deep tissue damage, and burning.
What does the term 'membrane' refer to in the context of tissues?
A thin, sheet-like structure serving various functions related to its composition.
How does the term membrane differ from the plasma membrane?
The term membrane in this context refers to tissues, not the plasma membrane of cells.
What are some functions of membranes?
Covering and protecting body surfaces, lining body cavities, covering inner surfaces of hollow organs, anchoring organs, secreting lubricating substances, and decreasing friction between bones and joints.
What are the two major types of membranes?
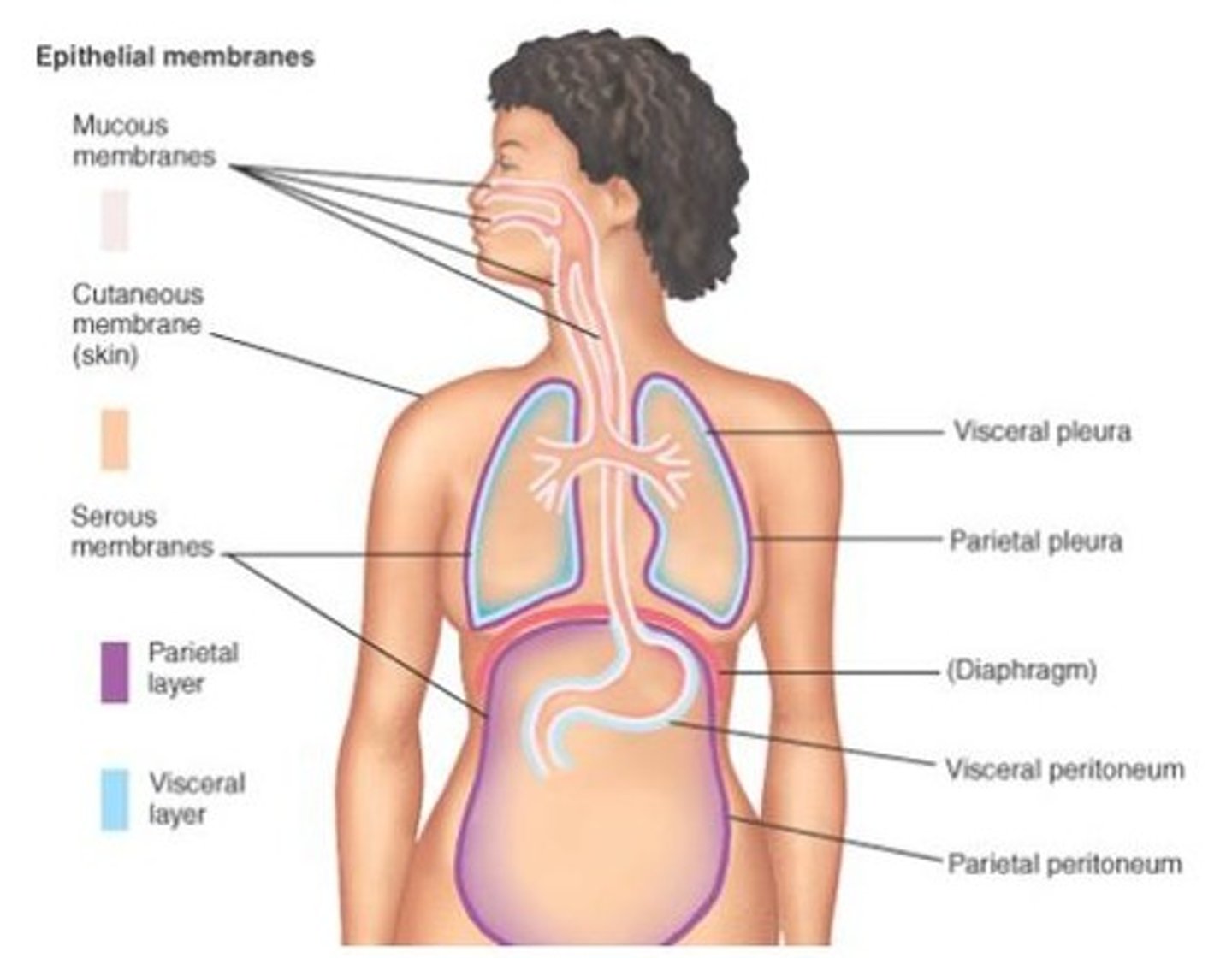
Epithelial membranes and connective tissue membranes.
What are the three types of epithelial membranes?
Cutaneous membranes, serous membranes, and mucous membranes.
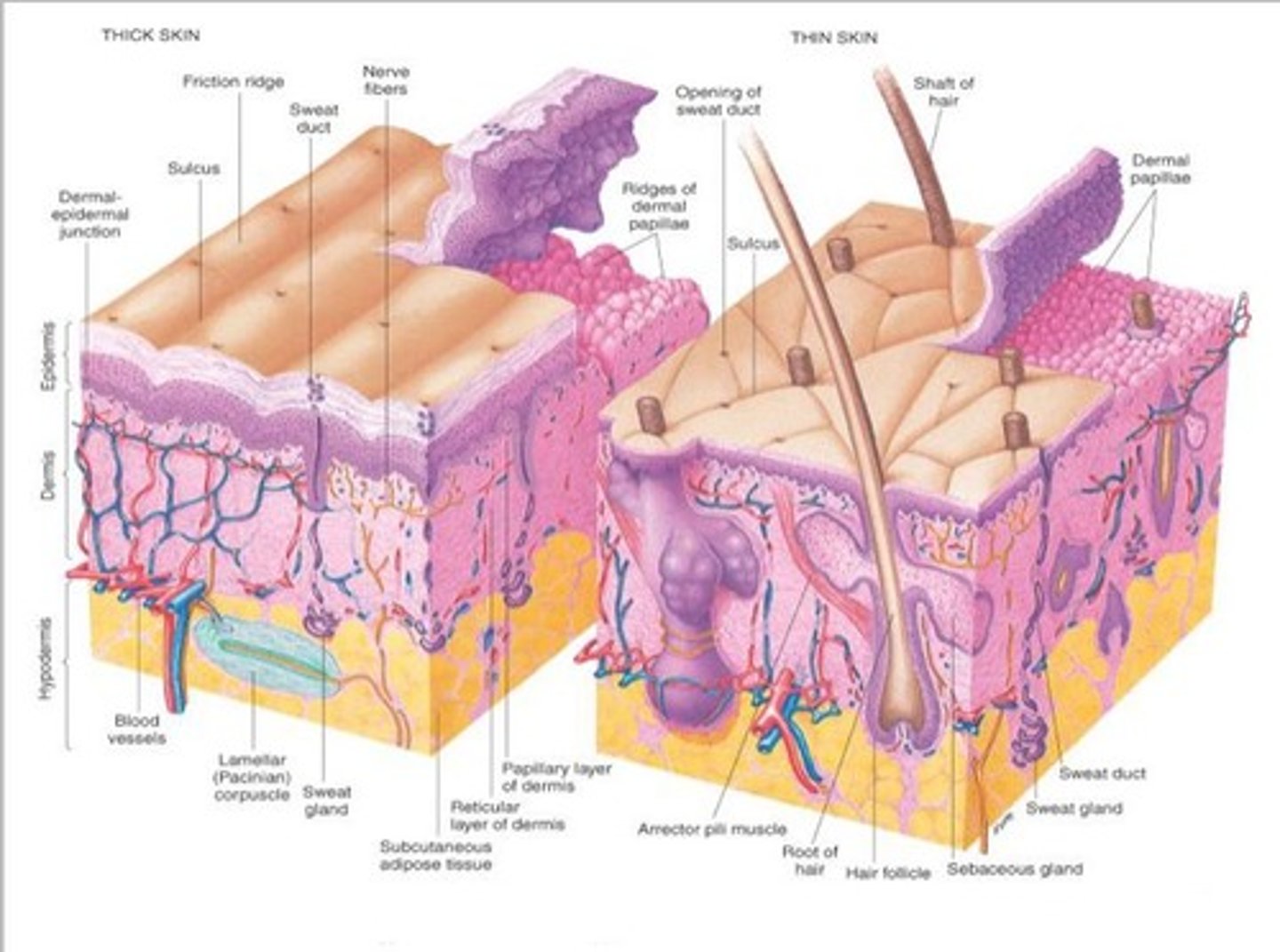
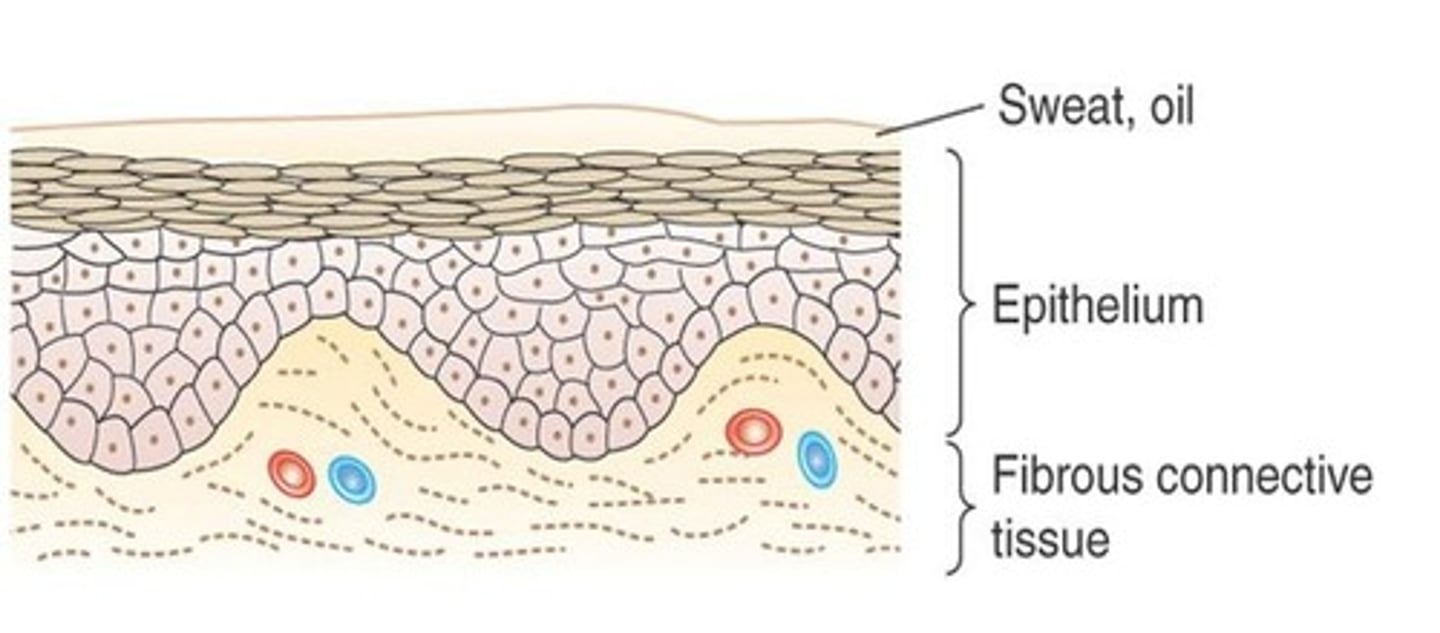
What is a cutaneous membrane?
The skin, which covers body surfaces exposed to the external environment.
What percentage of an individual's body weight does skin typically compose?
Approximately 16%.
What does the cutaneous membrane contain that aids in protection?
Sweat and oil glands that produce a mixture including ammonia, urea, and lactic acid.
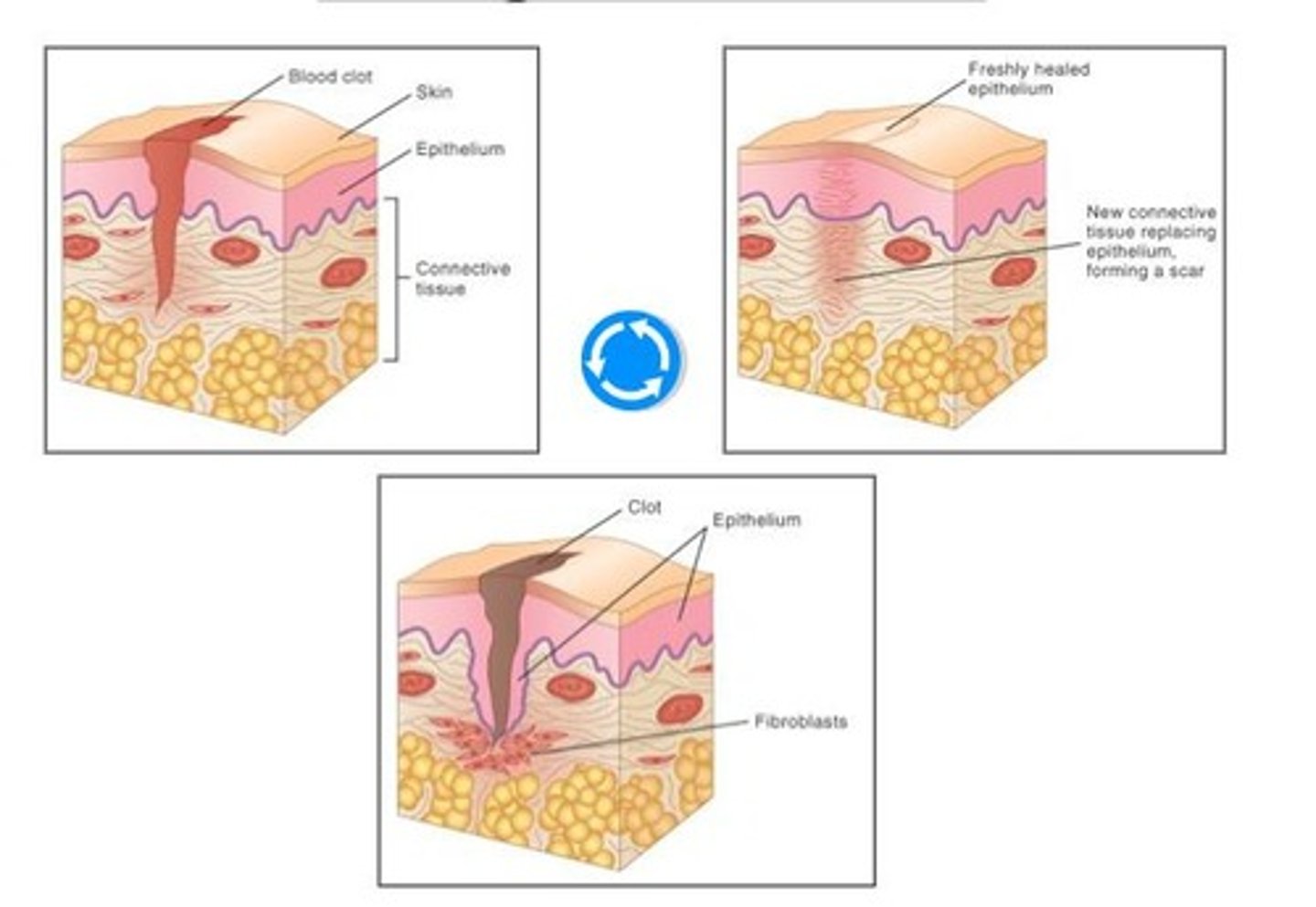
How does the cutaneous membrane heal a minor wound?
A blood clot forms, hardens, and fibroblast cells repair new connective tissue and replace the epithelium.
What is dermatitis?
Inflammation of the skin.
What is psoriasis?
A condition where skin cells multiply 10 times faster than normal, leading to buildup in various locations.
What is vitiligo?
A condition where portions of the skin lose the capacity to produce pigment.
What is basal cell carcinoma?
A cancerous growth of the skin.
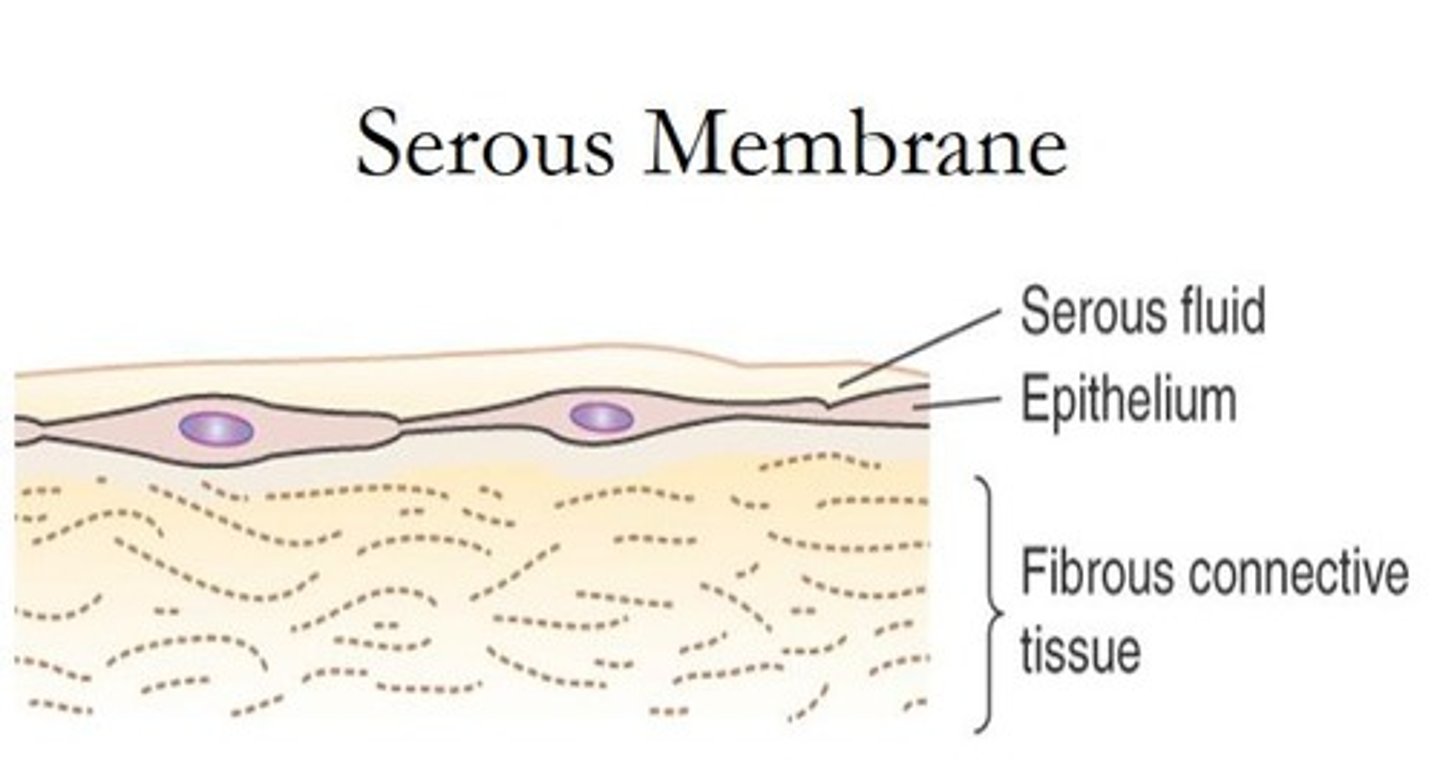
What are serous membranes?
Membranes that line cavities not open to the external environment.
What is the difference between parietal and visceral membranes?
Parietal membranes line the wall of the organ cavity, while visceral membranes cover the actual surface of the organ.
What are the three major serous membranes?
The pleura (surrounds lungs), peritoneum (covers abdominal viscera), and pericardium (surrounds the heart).
What do serous membranes secrete and what is its purpose?
Serous membranes secrete a watery fluid that lubricates organs as they rub against each other and against the walls of cavities.
What is the role of serous fluid in the body?
Serous fluid reduces surface tension and friction.
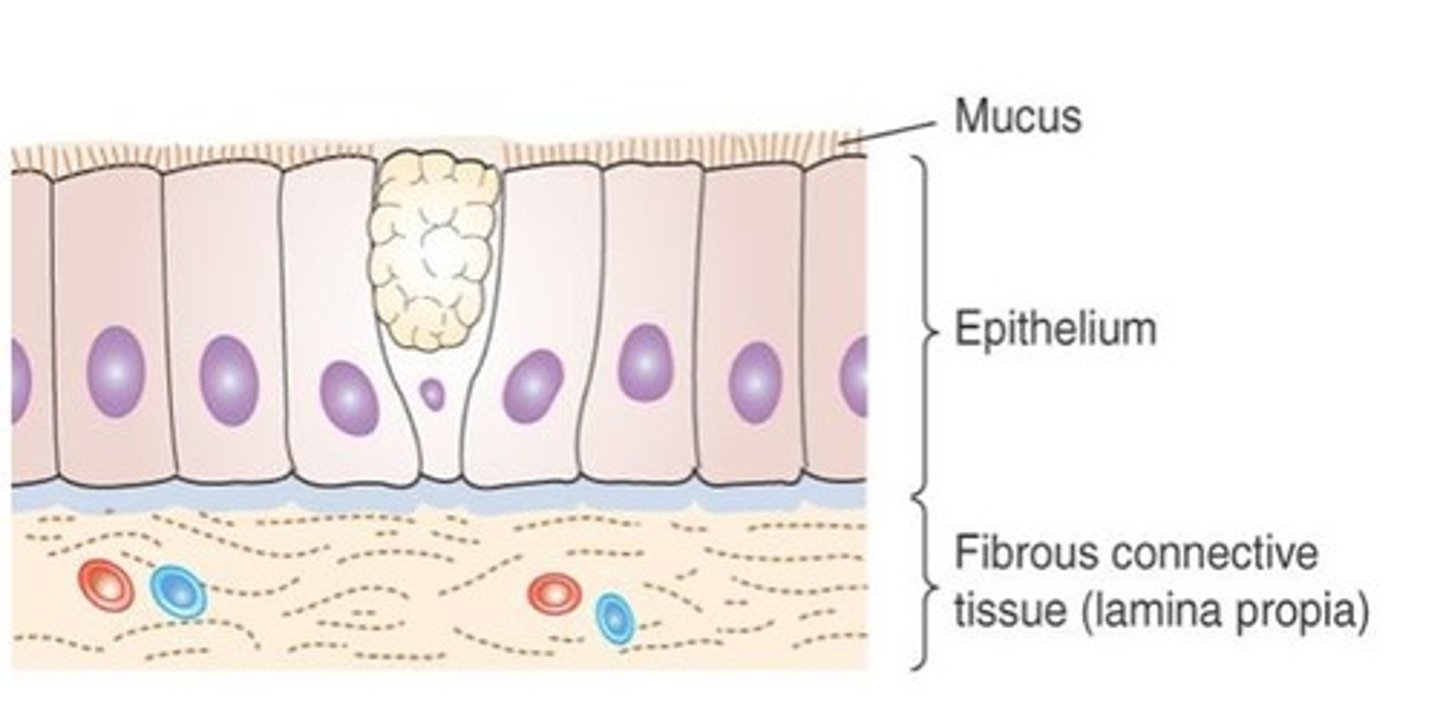
What are mucous membranes also called?
Mucosa.
Where do mucous membranes line in the body?
They line body surfaces opening directly to the external environment, including the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive tracts.
What is the underlying fibrous connective tissue in mucous membranes called?
Lamina propria.
How does the epithelial component of mucosa vary?
It varies depending on its location and function; for example, the esophagus has stratified squamous epithelium, while the lower digestive tract has simple columnar epithelium.
What is the function of mucus produced by mucous membranes?
Mucus coats and protects the underlying cells.
What is mucus composed of?
Mucus is a watery secretion containing a mixture of water and mucins, which are proteoglycan molecules made of protein and polysaccharide.
How are mucins related to epithelial cells?
Mucins can be attached directly to the plasma membranes of epithelial cells or secreted by goblet cells to form a lubricating gel.
What are some auxiliary functions of mucus?
Mucus serves as a lubricant for food passage and a trapping agent for contaminants in the respiratory tract.