Concept 22.1: Why Charles Darwin Matters
1/10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms

Charles Darwin
Scientist that proposed evolution by natural selection, changing views of biodiversity
Born 1809 in England
Studied medicine and theology at Cambridge, having a passion for natural history

HMS Beagle
Ship that Charles Darwin went on from 1831 to 1836 for a voyage around the world, studying fossils, species, and geology

Charles Lyell
Geologist that influenced Charles Darwin’s views of the Earth’s age
Galapagos Islands
Where Charles Darwin observed finches with varied beaks, island-specific tortoises, and adaptation to local environments
Sparked his theories of natural selection and evolution

The Origin of Species
1859 book that Charles Darwin published, challenging the belief of a fixed, unchanging species
Introduced evolution as a scientific theory
Created controversy for going against religious creationism
Descent with modification
Idea that species accumulate changes over generations with evolution, explaining the unity and diversity of life
Seen with finches through the islands’ droughts and floods

Genetic variation
Idea in nature where individuals vary in their inherited traits
Overproduction
Idea that more offspring are produced than can survive in a population
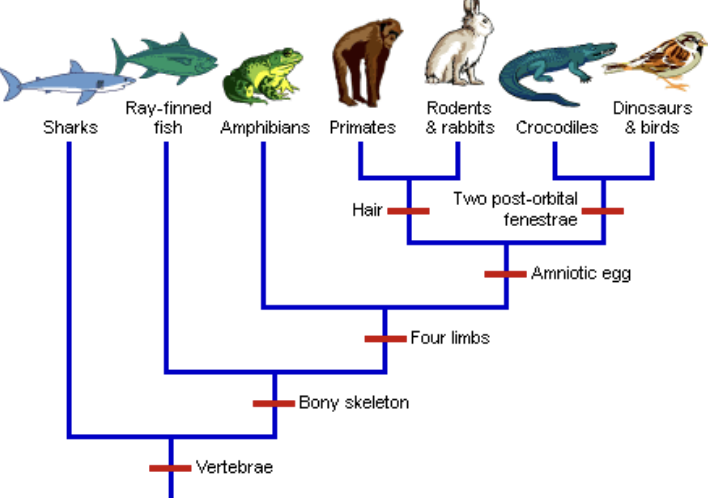
Evidence for evolution
Includes:
Similar fossil records showing homologous structures
Biogeography (location) of a certain species
Molecular (DNA) evidence
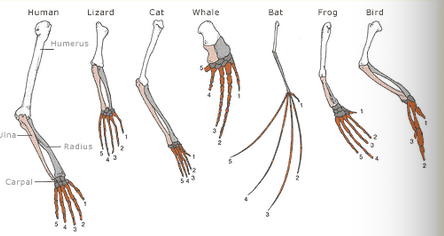
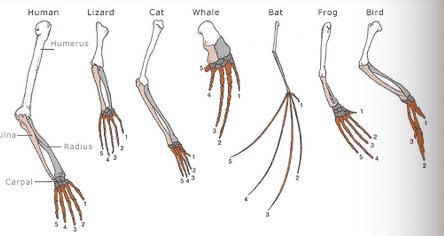
Homologous structures
Structures (typically made of bone) similar across different species used as evidence of evolution
Survival of the fittest
Idea that individuals with the most desirable traits have better reproductive success in a specific environment, resulting in that trait increasing in number across generations
Based on environmental — not planned — factors
Does not necessarily mean that the strongest in a population is the fittest