Physics - Waves
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What is a progressive wave?
A wave that transfers energy without transferring material
Made up of oscillating particles.
Define Amplitude, Frequency and Wavelength of a wave.
Amplitude - Max displacement from equilibrium position
Frequency - Number of complete oscillations passing through a point per second
Wavelength - Length of one oscillation = distance between peaks/troughs
What is phase?
Position of a certain point on a wave cycle.
When are two waves in phase?
Both waves at same point in cycle
Same displacement
Same velocity
Phase difference is a multiple of 360 degrees
When are waves out of phase?
when they are an odd integer of half cycles apart.
a single half cycle is 180 degrees
Wave Speed equation
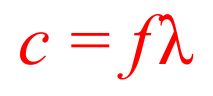
Frequency of a wave.
Where T is period
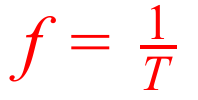
What are Transverse Waves?
Oscillation of particles at right angles to direction of energy transfer.
ALL ___ waves are _________ & travel at _____ metres per second in a _______
EM, Transverse, 3 × 10^8, vacuum
How can Transverse waves be created?
Demonstrated by shaking a slinky vertically or through waves on a string, when attached to signal generator.
What are Longitudinal Waves? Example?
Oscillation of particles parallel to direction of energy transfer.
Made up of compressions and rarefactions
can’t travel in vacuum.
e.g. Sound → Demonstrated by shaking slinky horizontally
What is a polarised wave?
Wave that only oscillates on one plane.
True or False: Only Longitudinal waves can be polarised.
False; Only transverse waves can be polarised.
Polarisation provides evidence for what and How?
Provides evidence for nature of transverse waves because polarisation can only occur if wave oscillation is perpendicular to direction of travel.
Give a single application of polarisation.
Polaroid sunglasses
→ Reduce glare by blocking partially polarised light reflected from water and tarmac.
TV and radio Signal
Plane-polarised by rods on aerial. Thus, receiving aerial must be aligned in the same plane of polarisation to receive signal at full strength.
What is superposition?
Displacements of two waves combining as they pass eachother.
Resultant displacement = vector sum of each wave
What are the two types of interference and explain them.
1 - Constructive interference
2 waves have displacement in the same direction
2 - Destructive interference
+ and - Displacements combine, meaning less resultant displacement.
If waves have equal but opposite displacements, total destructive interference occurs.
What is a stationary wave?
Superposition of 2 progressive waves, travelling in opposite direction in the same plane, with the same frequency, wavelength and amplitude.
Stationary waves do not transfer…
Energy
Describe a stationary wave.
Where waves meet in phase
Constructive interference → antinodes formed (Max amplitude)
Where waves completely out of phase
Destructive interference → nodes formed (no displacement)
What is the first harmonic of a _____ wave?
It is the lowest frequency at which a stationary wave forms.
Distance between adjacent nodes is…?
Half a wavelength.
Give formula for frequency of standing wave.
L is length of string
T is tension
μ is mass per unit length
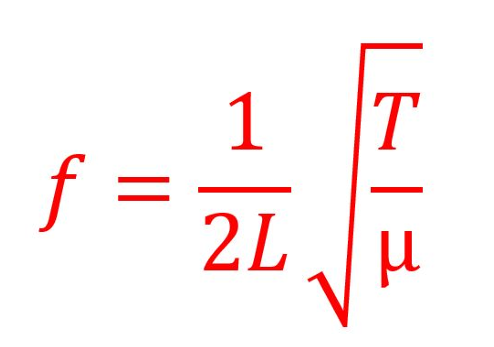
How can you relate the first harmonic to the nth harmonic?
Multiply by two to get second harmonic, multiply by three to get third harmonic, multiply by four to get fourth harmonic and so on…

Give two examples of stationary waves.
1 - Stationary microwaves
Reflect microwave beam of a metal plate, before finding nodes and antinodes using a microwave probe.
2 - Stationary sound waves
Place speaker at one end of a closed glass tube, lay powder across bottom of tube. Powder will be shaken at antinodes and settle at nodes.
SO, distance between each node is half a wavelength and frequency is the same as signal generator.
thus, by c=fλ, speed of sound in air can be found.
What is path difference?
Difference in distance travelled by two waves.
What is a coherent light source?
Same frequency and wavelength and fixed phase difference.
e.g. Lasers
Briefly describe the procedure of Young’s double slit experiment.
Shine coherent light through 2 slits about the same size as wavelength of laser light to enable diffraction
Each slit is a coherent source, making pattern of light and dark fringes.
Light fringes formed via constructive interference → Occurs when path difference between waves is a whole number of wavelengths.
Dark fringes formed via destructive interference. → Occurs when path difference is a whole number and a half wavelengths.
Give formula for fringe spacing. Where is it used?
Used in Young’s Double Slit Experiment.
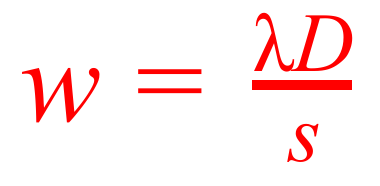
What happens if you use white light instead of laser light in Young’s experiement?
Wider maxima
Less intense diffraction pattern
Central white fringe
Give safety precautions for Young’s experiment?
Wear laser safety goggles
Don’t shine laser at reflective surfaces
Display warning sign
Never shine laser at a person.
What wave, other than light, can demonstrate Young’s double slit? how?
Sound waves →
Two speakers used as coherent sources
Intensity of wave measured using a microphone →
Maxima = light fringes
Minima = Dark fringes
What provided evidence for wave nature of light? And how?
Young’s Double Slit Experiment.
Showed Diffraction and Interference (wave properties)
EM radiation must act as a wave
What do we need to remember as scientists about concepts and theories of the present day?
Knowledge and understanding of any scientific concept changes over time in accordance to experimental evidence gathered.
What is diffraction?
Spreading out of waves when passing through or around a gap.
True or false; Greater diffraction occurs when gap is higher than the wavelength
false; The greatest diffraction actually occurs when the gap is roughly the same size as the wavelength.
A larger gap would mean less noticeable diffraction!
A smaller gap would result in more reflection.
What happens when gap is smaller than wavelength?
More waves are reflected.
Describe what happens when a wave meets an object?
Diffraction around edges.
If object is wider compared to wavelength = less diffraction
Monochromatic light forms a….
patter of light and dark fringes where it has a bright central fringe, double the width of all other fringes.
Bright fringes = Constructive Interference
Dark fringes = Destructive Interference
Explain what happens to white light as it is diffracted?
White light is made up of all colours.
Thus, all different wavelengths of visible light will split as they all diffract by a different amount.
Spectrum of of colour is formed.
White light always has a central white maximum with spectra on either side. (violet is closest to central maximum while red is furthest).
Describe diffraction pattern of white light?
Central white maximum. With spectra of different colours on either side.
Violet is closest to maximum
Red is further away from maximum
How can we adjust central maximum?
Change its width by…
1 - varying slit width
→ Increase slit width = decrease diffraction = central maximum becomes narrower and intensity increases
2 - wavelength
→ Increases Wavelength = increase diffraction = slit is closer to light’s wavelength = central maximum becomes wider and intensity decreases
What is a diffraction grating?
Slide containing many equally spaced slits very close together.
Monochromatic lights that passed through grating will created a sharper and brighter interference pattern than being passed through a double slit.
→ This is because more rays reinforcing the pattern. So, measurements of slit widths are much more accurate as they are easier to take.
Draw out a diagram for rays of light passing through a diffraction grating.
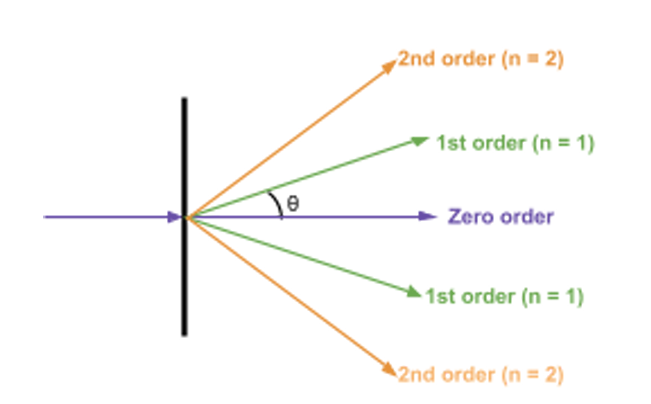
Write down the formula associated with diffraction gratings.
where d is distance between slits
theta is angle to normal made by maximum
n is order
lambda is wavelength
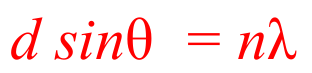
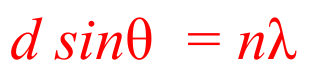
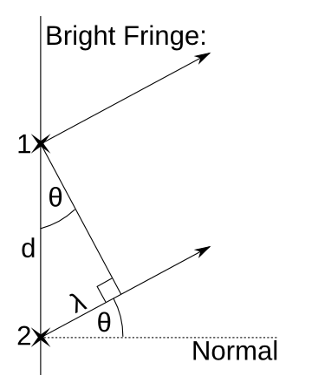
Derive this formula.
1 - Consider first maximum, where path difference between two adjacent rays of light is one wavelength.
2 - Right angle will be formed with side lengths d and lambda, so upper angle will be theta as well.
3 - First maximum = sin θ = lambda/ d
4 - Other maxima occur when path difference between two rays of light is n x lambda
Give applications of diffraction grating.
1 - Split up light from stars to get line absorption spectra, used to show elements are present in the star.
2 - X-ray crystallography
What is a refractive index
property of a material which measures how much it slows down light passing through it.
Calculated by… speed of light in vacuum divided by speed of light in substance
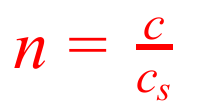
A material with lower r_____ i____ is ____ o_______ d____
A material with lower refractive index is less optically dense.
Refractive index of air is…? And why?
approx. 1, because light doesn’t slow down significantly when travelling through air, compared to vacuum.
Give formula for refraction of light and name.
Snell’s Law
where n1 is refractive index of 1st material
n2 is refractive index of 2nd material
θ1 is angle of incidence of 1st ray
θ2 is angle of refraction of 2nd ray
What happens to light ray during refraction?
Speed changes.
n1 > n2 → Speeds up (further from normal) →
θ1 < θ2
and vice versa!
What is Critical angle, and when does it occur?
Critical Angle Equation.
Occurs when angle of refraction is exactly 90 degrees, thus meaning light is refracted along the boundary.

What is TIR, when does it occur.
Total Internal Reflection occurs when…
angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle. and
AND Incident refractive index is greater than refractive index of the material at the boundary.
GIve application of TIR
Optical Fibres
Optically denser core than cladding that surrounds it
cladding protects core from damage, prevents signal degradation by light escaping the core.
What are the causes of signal degradation?
Light escaping core
Absorption → energy absorbed by fibre, reducing amplitude
Dispersion → causes pulse broadening which can cause overlap of signals
Two type of Dispersion:
1 - Modal
light rays enter fibre at different angles and so take different paths. This leads to rays taking different amounts of time to travel along fibre.
2 - Material
Caused by light having different wavelengths, so light rays will travel at different speeds → Prevented vis using monochromatic light.
How can A____ and D____ be reduced?
Absorption + Dispersion → Via optical fibre repeater.