bone histology
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
what is the name of the cell that forms bones
osteoblast
what is the name of the cell that maintains the structure of the bone after formation
osteocyte
what is bone called when it is first secreted from the osteoblast
osteoid
how is osteoid mineralized
collagen binds with calcium hydroxyapatite
what cell dissolves the boney matrix
osteoclasts
where are osteocytes housed within the bones and how to they communicate with each other
They are house in lacuna and communicate through canaliculi
how are osteoclasts able to break down the boney matrix
through the secretion of carbonic anhydrase
on a macroscopic scale what are the two types of bone
cortical bone
trabecular bone
on a microscopic scale what are the two types of bone
woven bone
lamellar bone
what is woven bone
it is rapidly produced immature fragile bone
what is lamellar bone
mature organized bone
what is the outer layer of the bone called
periosteum
what are the two sections of the periosteum
fibrous layer
osteogenic layer
inside the bone itself what is the lining called
endosteum
what are the functional units of bone called
Osteons
what do osteons do
contain blood vessels, nerves and other cells
what type of bone contains osteons
cortical bone
what are the tunnels in osteons called
haversian canals
what connects two osteons
volkmann’s canal
what are secondary osteons
these are osteons formed on top of preexisting osteons
how are secondary osteons formed
a tunnel is dug with osteoclasts and new bone is formed by a lagging edge of osteoblasts and maintained by osteocytes
what does the bone as an organ do
facilitates normal growth
regulates mineral homeostasis
adapt to stress
repairs microinjuries
responds to macroscopic injuries
what is modeling of a bone
the process in which a bone changes shape
what is remodeling of a bone
the process in which an old bone is replaced by new bone
why is remodeling necessary
normal growth
repair of wear and tear
to accommodate moving vasculature
mineral homeostasis
what are the two types of embryonal bone formation
membranous ossification
endochondral ossificatoin
what bones utilize membranous ossification
flat bones
what bones use endochondral ossification
long bones
what type of bone is formed through membranous ossification
cortical bone
what type of bone is formed though endochondral ossification
trabecular bone
what are the steps of membranous ossification
primitive mesenchyme
differentiates into osteoblasts
lays bone on top of old bone
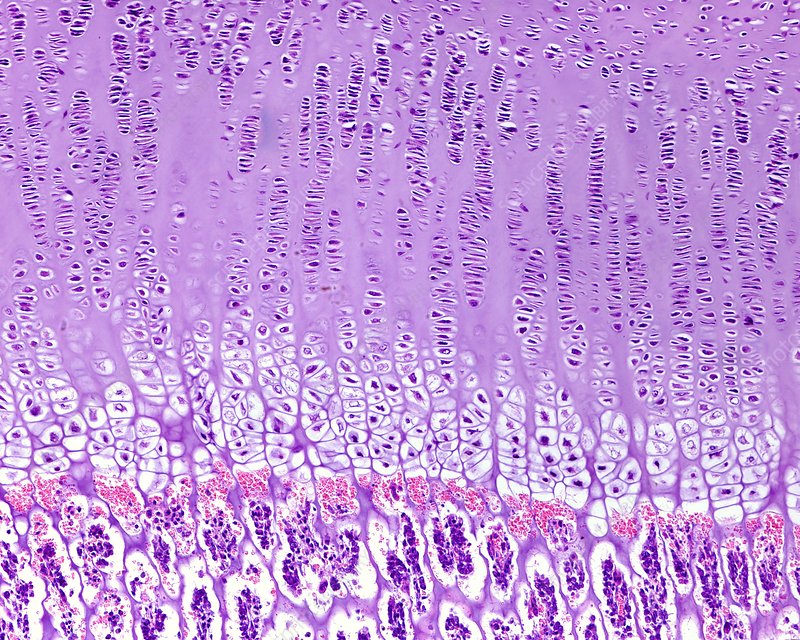
what are the zones in endochondral ossification
zone of reserve cartilage
zone of proliferation
zone of hypertrophy
zone of calcification
where does endochondral ossification take place on a long bone
at the physis
what type of cartilage is present at articular surfaces and physes
hyaline cartilage
what type of cartilage is present at the attachment point of tendons and ligaments
fibrocartilage
what cartilage is present in the ear and nose
elastic cartilage
what is the name of the cell that produces cartilage
chondrocytes