Unit 9 Exam - Quality Management
1/83
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
After what act did the US Fed. Government initiate radiologic and imaging sciences quality management regulations?
Radiation Control and Safety Act of 1968
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
Continually improves quality by focusing on improving the system or process in which individual workers function rather than on the individuals themselves
Who should be actively involved in continuous quality improvement (CQI)?
Every employee
Standards for Quality
A high standard of safe and effective imaging practices; specifies requirements for a quality management system and demonstrates the ability to consistently provide products/services that meet customer and regulatory associations
Who set forth the standards for quality?
FDA
Communication
Must occur between the entire imaging department and also inter-departmentally
Elements of a Quality Management Program
Standards for Quality
Communication
Quality Manual
Responsibility & Administration
Test Equipment, Procedures & Training
Record Keeping
Evaluation
Continuing Education
Quality Manual
Assures the integrity of QMS is maintained and focused on meeting the intended outcomes; describes the structure and interaction
When should the quality manual be reviewed?
Anually
Responsibility and Administration
Professionals who can participate in QM; staff technologist, physicists, supervisory technologists, QC technologists and staff service engineers
Test Equipment, Procedures and Training
QC monitoring, preventive maintenance and corrective maintenance; specific for each procedure and must be trained to perform test accurately
Record Keeping
Data must be recorded after each performance tests and kept on file
Test Review
Review the test was performed accurately; analyze the data obtained
How many levels of evaluation is there?
2
First Level of Evaluation
Results from the monitoring procedures - used to evaluate performance of equipment; analysis of trends and data to determine corrective action
Second Level of Evaluation
Evaluating the effectiveness of their program; study of retake rate and causes of repeats, examination of equipment repair and replacement costs, occurence and reasons for complaints by radiologists
Continuing Education
Keeps the entire department updated to equipment specifications; should include orientation and periodic updates
Quality Assurance Program
Organized effort by the staff operating a facility to ensure the diagnostic images produced are of a sufficiently high quality
Objectives of a QA Program
Maintain optimal quality of images
Reduce unnecessary exposure
Be cost effective
Components of a QA Program
Quality Control Tests
Administrative procedures
Preventative maintenance procedures
Training
Quality Control Tests
Refers specifically to the calibration and monitoring of equipment along with discussion of the continuing value of repeat analysis
Variables that Frequency of QC Test Depend On
Inherent variability of the process or equipment
Age, reliability and frequency of use of the equipment
Criticality of the element in the image chain
Administrative Procedure
Designed to verify that the QC testing is effective; test performed regularly and correctly, results evaluated promptly and accurately and necessary action taken
Preventive Maintenance Procedure
Performed on a regularly scheduled basis with the goal of preventing breakdowns due to eqipment failing without warning signs detectable by monitoring
Training
Must provide appropriate training for all personnel with QA responsibilites to ensure the level of competence is there to perform QC testing correctly and consistently
Quality Assurance Committee
Medical physicists
Radiologist
Biomedical engineer
Radiographer
Information technology technician
Medical Physicist
Advise the facility on radiation protection of the patient, staff and members of the public; conduct tests to ensure the safety and proper performance of imaging equipment used
Who develops and implements a radiation protection program?
Medical physicist
Biomedical Engineer
Corrective and preventative maintenance & fault reporting
Image Quality Control
Exposure indicator accuracy
Image integrity
Exposure Indicator Accuracy
Exposure to the image receptor and helps in evaluating image quality and determining whether the image meets standards
Image Integrity
Verification that images are saved to PACS; performed at the end of every procedure
Who is the first at line of defense in preventing, recognizing and reporting QC issues?
Technologists
The quantitative acceptance for CR erasure is an EI values of _________ in the re-exposed image.
0-80
At a minimum, when should CR facilities erase all CR cassettes?
Weekly
Reject Analysis
Repeat exposures are identified (reason, # and tech responsible); allows for solutions to be found to minimize repeats
Causal Reject Analysis
% of repeats from a specific cause
Total Reject Analysis
All repeats no matter what the cause
Repeat rates for radiographic procedures should not exceed ____________?
4-6%
What is the main reason for repeat imaging?
Positioning
What ASRT Practice Standard relate to quality control?
9
Equipment Calibration
Checking of the equipment’s accuracy based on the manufacturer’s recommendations
Uniformity Corrections
Evening out the overall signal or brightness across the entire area of the imaging field
PAPP states use the ROI to check brightness at various points throughout the image should be within _______ of each other.
10%
Spatial resolution test tools are used to indicate ____________.
LP/mm
DoseWatch
Automatically collect and analyze patient radiation and iodine exposure across multi-facility, multi-modality and multi-vendor imaging environments
Benefits of Quality Management
Patient safety
Reduced radiation exposure
Efficacy of patient care
Departmental efficiency
Consistent image quality
Cost-effectiveness
Protective Filtration
Used to remove low-energy x-rays from the beam that cannot penetrate the body
What is the only true measure of actual x-ray beam penetration?
HVL
What material is used for HVL testing?
Aluminum
According to the FDA, the x-axis value should be _________ than the minimum required HVL.
Greater
If HVL falls below the minimum requirement it indicates:
Calibration of kVp is off
Insufficient filtration in the beam
When is a kVp accuracy test done?
Annually
For a kVp accuracy test, the acceptable range is _______ kVp of the set kVp.
+/- 5
Exposure Linearity Test
Alignment of a particular mA station relative to other stations in its output of radiation
When should an exposure linearity test be done?
Annually
Each time the mA is doubled the mR/mAs should double within _____ %?
+/- 10
If kVp or mAs are not in range after testing, what must be done?
Calibration
Exposure Reproducibility Test
Ability to repeat the same technique setting and obtain the same results in exposure
Exposures for an exposure reproducibility test should be within _________?
+/- 5%
When should exposure reproducibility test be done?
Annually
What is the acceptable range of a timer accuracy test?
+/- 5% (unless time is > 10 ms)
When is a timer accuracy test done?
Annually
What is the acceptable range of a beam alignment perpendicularity test?
Within 1 degree (5 mm) of vertical alignment
When should a beam alignment perpendicularity test be done?
Semi-annually
When should a collimator accuracy test be done?
Semi-annually
Collimator accuracy test must be within ____% of the SID.
2
How is the collimator accuracy test done?
9 penny test
AEC exposure must be repeatable within an accuracy range of __________.
+/- 10%
When should an AEC exposure test be done?
Annually
When should QC of protective apparel be done?
Annually
T/F: You can keep defective protective apparel.
False
When should exposure rate test for fluoro be done?
Semi-annually
Standard fluoro air kerma rate is _______________?
> 88 mGy/min
High level fluoro air kerma is __________________?
> 176 mGy/min
Who sets forth the air kerma levels for standard and high level fluoro?
FDA
Mobile Fluoro SSD
12 in (30 cm)
Stationary Fluoro SSD
15 in (32 cm)
ABC or AERC Test Acceptable Range
10 - 40µR/s
When should an exposure reproducibility test in fluoro be done?
Semi-annually
What is the exposure reproducibility guideline in fluoro?
+/- 5%
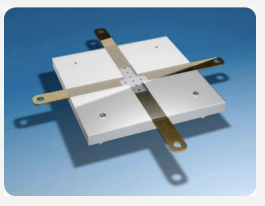
Beam Alignment Test
When should visual/audible monitor testing be done?
Quarterly
T/F: Some quality control begins with the last step instead of the first step.
True