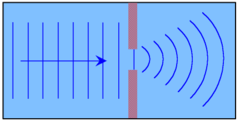
Chapter 6: Waves and Sound
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Last updated 5:07 PM on 10/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
What is a Wave?
-A disturbance that travels from one place to another transporting energy, but not necessarily matter, along with it.
2
New cards
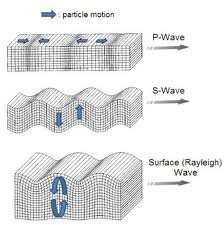
In what kind of wave do particles move up and down perpendicular to the direction of wave travel?
Transverse wave
3
New cards
What term describes the maximum displacement of a particle in a wave?
Amplitude
4
New cards
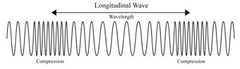
What is used to measure wavelength in a longitudinal wave?
The distance between two adjacent compressions AND the distance between two adjacent rarefactions.
5
New cards
What is the relationship between the period and the frequency of a wave?
They are the inverse of one another.
6
New cards
What do waves carry through matter or space?
Through energy
7
New cards
The highest point on a transverse wave
Crest
8
New cards
The lowest point on a transverse wave
Trough
9
New cards
A region of increased pressure in a longitudinal wave
Compression
10
New cards
A region of decreased pressure in a longitudinal wave
Rarefaction
11
New cards
The distance between any two successive parts of a wave
Wavelength
12
New cards
The units for frequency
Hertz (Hz)
13
New cards
The bending of a wave as it passes from one medium to another
Refraction
14
New cards
Waves bouncing off of a surface
Reflection
15
New cards
What waves travel in the same direction as amplitude.
Longitudinal waves
16
New cards
The rate at which a repeating event occurs is called?
frequency
17
New cards
What is the maximum displacement of a wave from its position of rest is its?
amplitude
18
New cards
Which type of wave contains compressions and rarefactions?
Longitudinal
19
New cards
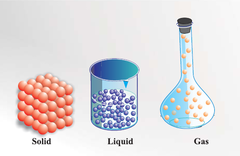
What is a medium
-It is the material through which a wave travels.
20
New cards
What are 3 types of mediums a mechanical wave can travel through?
-Solids, liquids, and gasses
21
New cards
Wavelength
-The distance from two corresponding (or the same) parts of a wave.
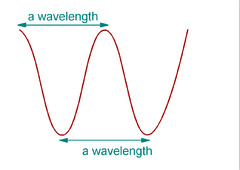
22
New cards
Frequency
-How many waves can pass a given point per second, measured in Hertz (Hz)
23
New cards
Refraction
The bending of a wave as it passes at an angle from one medium to another
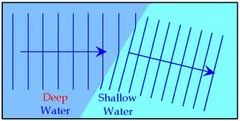
24
New cards
Diffraction
The wave changes direction because it bends around an object