Skin and Body Membranes
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Body membranes
Cover surface, line body cavities, and form protective sheets around organs
Epithelial and Connective tissue membrane
Types of Body membranes
Epithelial membranes
Covering and Lining
Includes cutaneous, mucous, and serous membranes
Composed of epithelial layer + Connective tissue
Cutaneous, Mucous, and Serous membrane
Types of Epithelial membrane
Cutaneous Membrane
Composed of the superficial epidermis and underlying dermis
Stratified squamous epi + dense CT
Exposed to air and is dry
Skin
Example of Cutaneous membrane
Mucous membrane
Composed of epithelium resting on a loose CT (Lamina propria)
Lines of body cavities that open to the exterior
Either stratified squamous or stratified columnar
Digestive and respiratory system
Example of Mucous Membrane
Serous membrane
Composed of a simple layer of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer or areolar CT
Line body cavities that are CLOSED to the exterior )except for the dorsal body cavity and joint cavities)
Parietal and Visceral
Serous membrane occurs in: ___ and ____
Serous fluid
Clear fluid that fills the serous membrane
Peritoneum, Pleurae, and pericardia
The 3 location where we can find Serous membrane
Peritoneum
Serosa lining the abdominal cavity and its organs
Pleurae
Membranes surroundings the lungs
Pericardia
Membrane around the heart
Connective tissue membrane
Encapsulate organs and line movable joints
Synovial membrane
Formed solely from connective tissue
Synovial membrane
Composed of loose areolar connective tissue and contain no epithelial cells
Lines the fibrous capsules surroundings joint
Bursae
Synovial membrane line the small sacs of connective tissue called _______
Tendon sheaths
Synovial membrane line the tube like ______
Integumentary system
Composed of skin and its appendages
Contributes to homeostasis
Allows an organism to sense stimuli
Most exposed to infection, disease, and injury
Dermatology
The skin
Also known as cutaneous membrane
Covers the external surface of the body
Epidermis and Dermis
Two types Tissues found in the skin
Epidermis
Superficial, thinner portion
Composed of keratinize strat, squamous epithelium
Avascular
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Intraepidermal macrophages, and Tactile epithelial cells
Four principal types of cells in Epidermis
Keratinocytes
Arranged in four to five layers
Produce lamellar granules
Product is Keratin
Melanocyte
Long and slender projections
Produces pigment melanin
Melanin
A yellow-red or brown-black pigment that contributes to skin color and absorbs UV radiation
Intraepidermal macrophages
Arise from red bone marrow and migrate to the epidermis
Participate in Immune response
Langerhans cell
Cell of the Intraepidermal macrophages
Tactile Epithelial Cell or Merkel cells
Located in the deepest layer of the epidermis
Detect touch sensations
Stratum basale, spinosum, granulosum, lucidum, and corneum
5 layers of epidermis
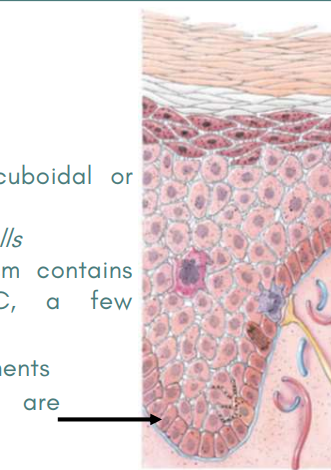
Stratum Basale
Deepest layer of the epidermis
Single row of cuboidal or columnar keratinocytes
Also known as Stratum germinativum
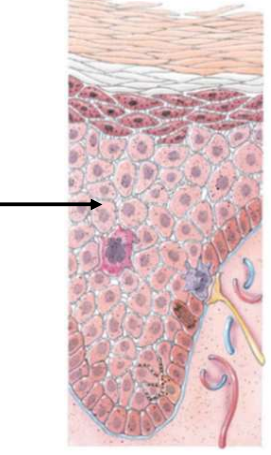
Stratum Spinosum
Superficial to the stratum basale
Consists of numerous keratinocytes
Arrangements provide both strength and flexibility to the skin Langerhans cells are present
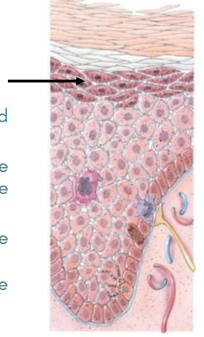
Stratum Granulosum
Middle layer with cells contain “grains”
No longer produced but are becoming more apparent due to organelle regression
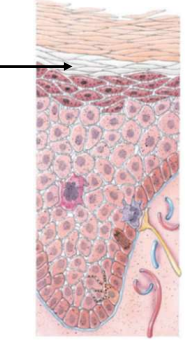
Stratum Lucidum
Clear layer
Present only in the thick skin areas
Four to six layers of flattened, clear, dead keratinocytes that contain large amounts of keratin and thickened plasma membranes.
Stratum Corneum
25-30 layers of flattened dead keratinocytes
Cells are extremely thin, flat, plasma membrane-enclosed packages of keratin
Cells overlap one another like scales
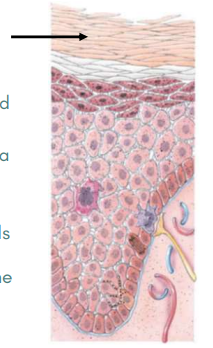
Dermis
Second layer, deeper
Composed of dense irregular connective tissue containing collagen and elastic fibers
Has the ability to stretch and recoil easily
Vascular
Much thicker
Fibroblasts, Macrophages, and Adipocytes
Principal type of cells in Dermis
Papillary region and Reticular region
Division of Dermis into 2 region
Papillary region
Superficial layer
Contain collagen and fine elastic fibers
Surface area greatly increased by dermal papillae
Reticular Region
Attached to subQ layer
Contains bundle of thick collage fibers, scattered fibroblasts, and macrophages
Contains blood vessels, glands, and lamellar corpuscles
Cyanotic
Bluish
Blood not picking up an adequate amount of O2 from the lungs
Jaundice
Yellow
Build up of bilirubin in the skin
Indicates liver disease
Erythema
Red
Engorgement of capillaries in the dermis due to skin injury, heat, infection, inflammation, or allergic reaction
Pallor
Paleness
Shock and Anemia
Loss of decrease of blood flow to the skin
Albinism
Inherited inability of an individual to produce melanin
Results in problem with vision and skin to burn on overexposure to sunlight
Vitiligo
Partial or complete loss of melanocytes from patches of skin
Related to an immune system malfunction in which antibodies attack the melanocytes
Skin Appendages
Hair, Skin Glands, and Nails
Develop from the embryonic epidermis
Holds several important functions
Hair
Present on most skin surfaces except the palms, palmar surfaces of the finger, the soles, and the plantar surface of the feet.
Scalp, eyebrows, axillae, and around the external genitalia
Offers limited protection
Hair anatomy
Composed of columns of dead keratinized epidermal cells
Hair Shaft
Superficial to hair root
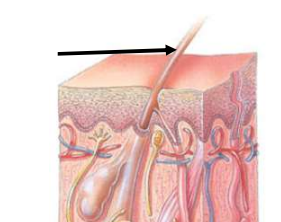
Hair Root
Deep to the shaft
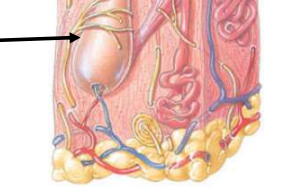
Medulla, Cortex, and Cuticle
Three concentric layers of cells
Cutaneous glands
All exocrine glands that release their secretions to the skin surface via ducts
Sebaceous, Swear, and Ceruminous Glands
3 cutaneous glands
Sebaceous Glands
Oil glands
Simple, branched acinar glands
Some are connected to hair follicles
Sudoriferous glands
Three to four million
Sweat glands
These glands release sweat into hair follicles or onto the skin surface through pores
Eccrine and Apocrine
2 types of sudoriferous glands
Eccrine Sweat Glands
Found all over the body
Secretory portions is located mostly in deep dermis
Excretory duct projects through the dermis and epidermis and ends as a pore at the surface of the dermis
Apocrine Sweat Glands
Simple, coiled, tubular glands that have larger ducts and lumens
Formed mainly in the skin of the axilla, groin, areolae of the breasts, bearded regions of the face in adult males
Ceruminous glands
Modified sweat glands in the external ear \
Produces a waxy lubricating secretion
Athletes foot
An itchy, red, peeling condition of the skin between the toes, resulting from an infection witht he fungus Tinea pedis
Boils
Furuncles and carbuncles
Caused by inflammation of hair follicles and surrounding tissues
Boils often caused by bacterium Staphylococcus aureus
Cold Sores
Fever blisters
Small fluid-filled blisters that itch and sting, caused by human herpesvirus 1 infection
Impetigo
Develop a yellow crust and eventually rupture
Caused by highly contagious Staphylococcus spp or Streptococcus spp. infections
Squamous cell carcinoma, Basal cell carcinoma, and Malignant melanoma
Types of Skin cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Arises from the cells of the stratum spinosum
The lesions appear as scarly, reddened papule that gradually form shallow ulcers with firm, raised borders.
Basal cell Carcinoma
The least malignant and most common skin cancer
Cells that altered the production of keratin, no longer honor the boundary between epidermis and dermis
Malignant melanoma
Cancer of melanocytes
Arises from accumulated DNA damage in a skin cell and usually appears as a spreading brown-to-black patch that metastasizes rapidly to surrounding lymph and blood vessels