Cranial Nerves 9-12 and blood brain barrier
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
what is CN 9? is it motor, sensory, or both? what does it feel/control?
glossopharyngeal nerve. both. provides sensation to the posterior 1/3rd of the tongue. controls muscles involved in swallowing and secretion of saliva
what is CN 10? is it motor, sensory, or both? what does it feel/control?
vagus nerve (CRITICAL for speech). both.
sensory responsibilities: provides sensation to eh pharynx and larynx, conveys sensory info from the thoracic and abdominal organs
motor responsibilities: controls muscles of the pharynx and larynx involved in speaking and swallowing
parasympathetic: regulates heart rate, digestive processes, and respiratory rate
what is CN 11? is it motor, sensory, or both? what does it feel/control? (4)
spinal accessory nerve. motor. controls 4 things:
neck and shoulder movements
soft palate, larynx, pharynx movements
indirect impact on breathing
overall muscle coordination and balance
what is CN 12? is it motor, sensory, or both? what does it feel/control?
hypoglossal nerve. motor. controls tongue muscle, necessary for speaking, swallowing, and manipulating food
what is the blood brain barrier? what are its functions?
a critical component of the brain’s defense system. protects the brain from toxins/pathogens, ensures that water and oxygen can pass through (selective permeability)
what are the 3 main components of the blood brain barrier? describe them
endothelial cells: line the interior of the vessels. connected by tight junctions
pericytes: encircle the endothelial cells, providing structural support
astrocytic end-feet: cover the outide of the blood vessel, interacting with the endothelial cells (permeability)
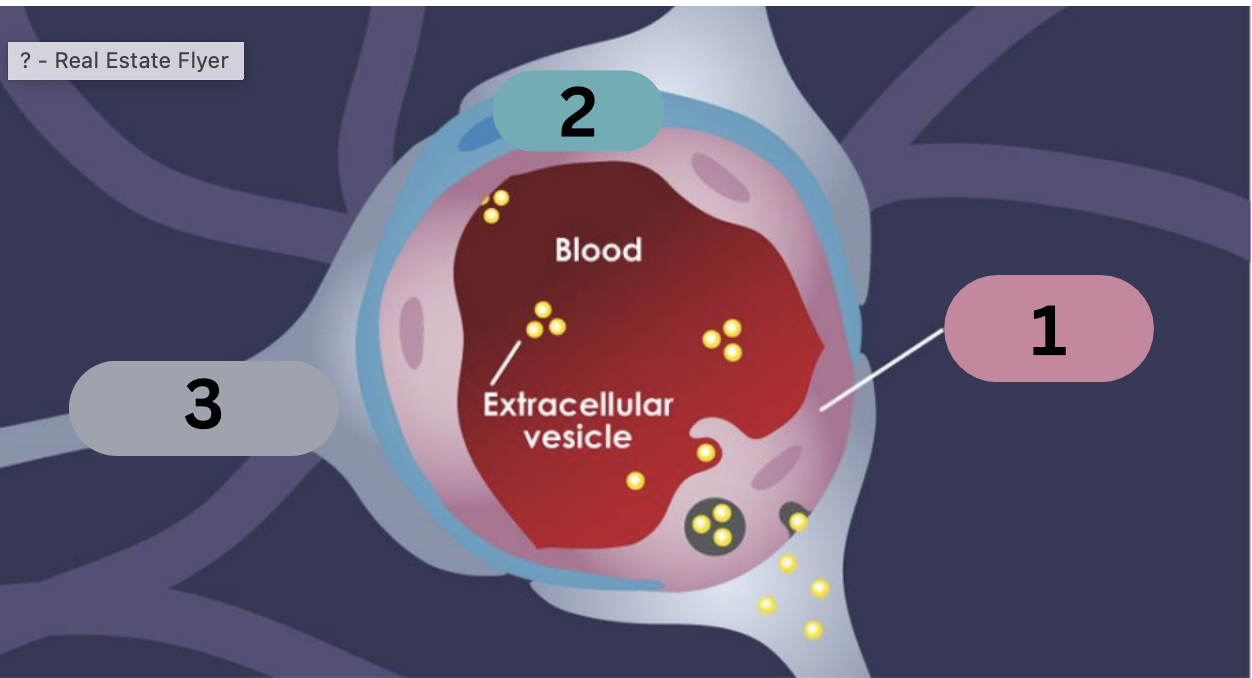
label
1: endothelial cell
2: pericyte
3: astrocytic end feet