NCEA Level 1 - Mechanics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Velocity (v)
the rate that distance is travelled in a particular direction (ms-1)
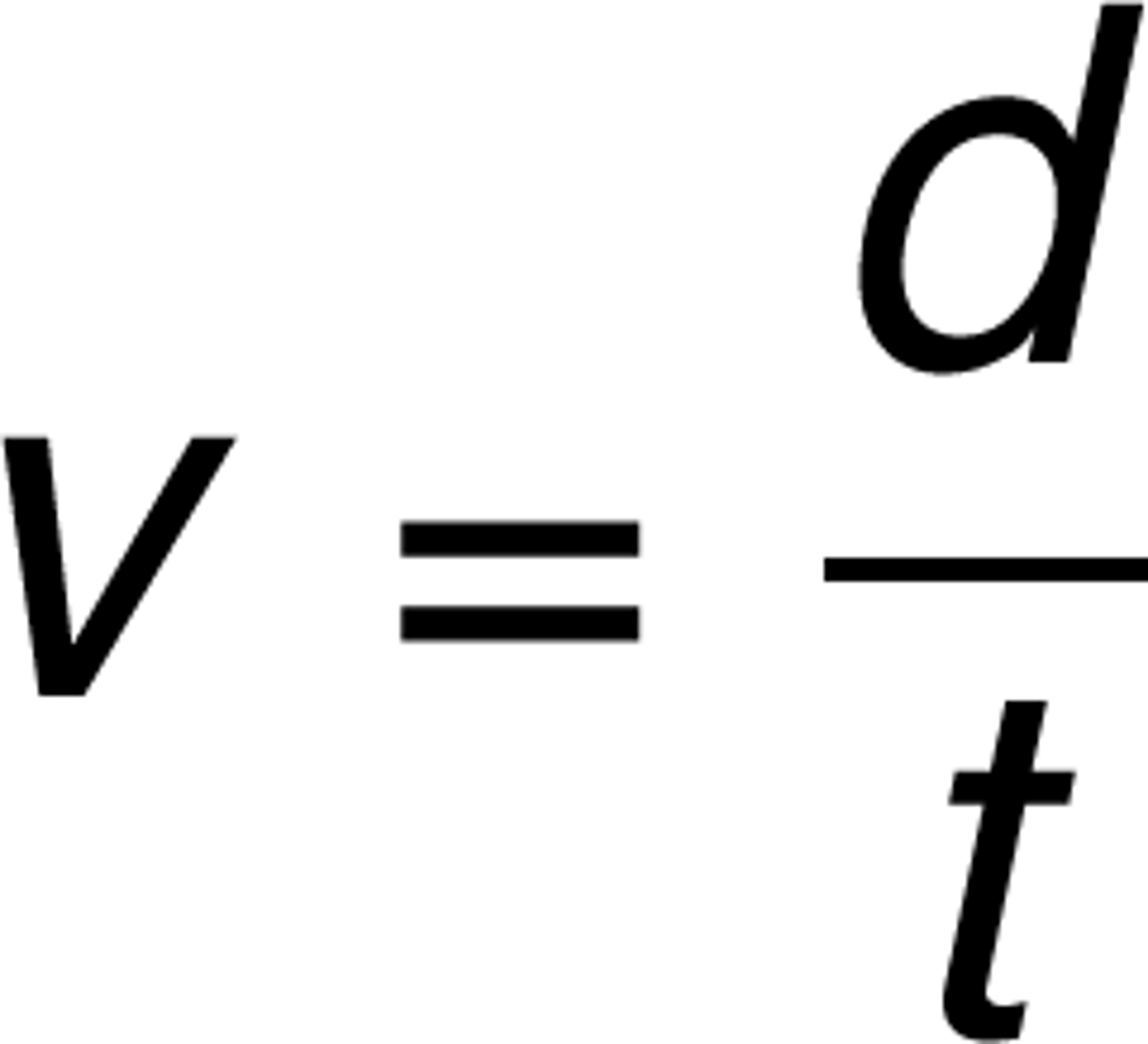
Distance (d)
it is the number of metres (m) between two points or the metres travelled by an object
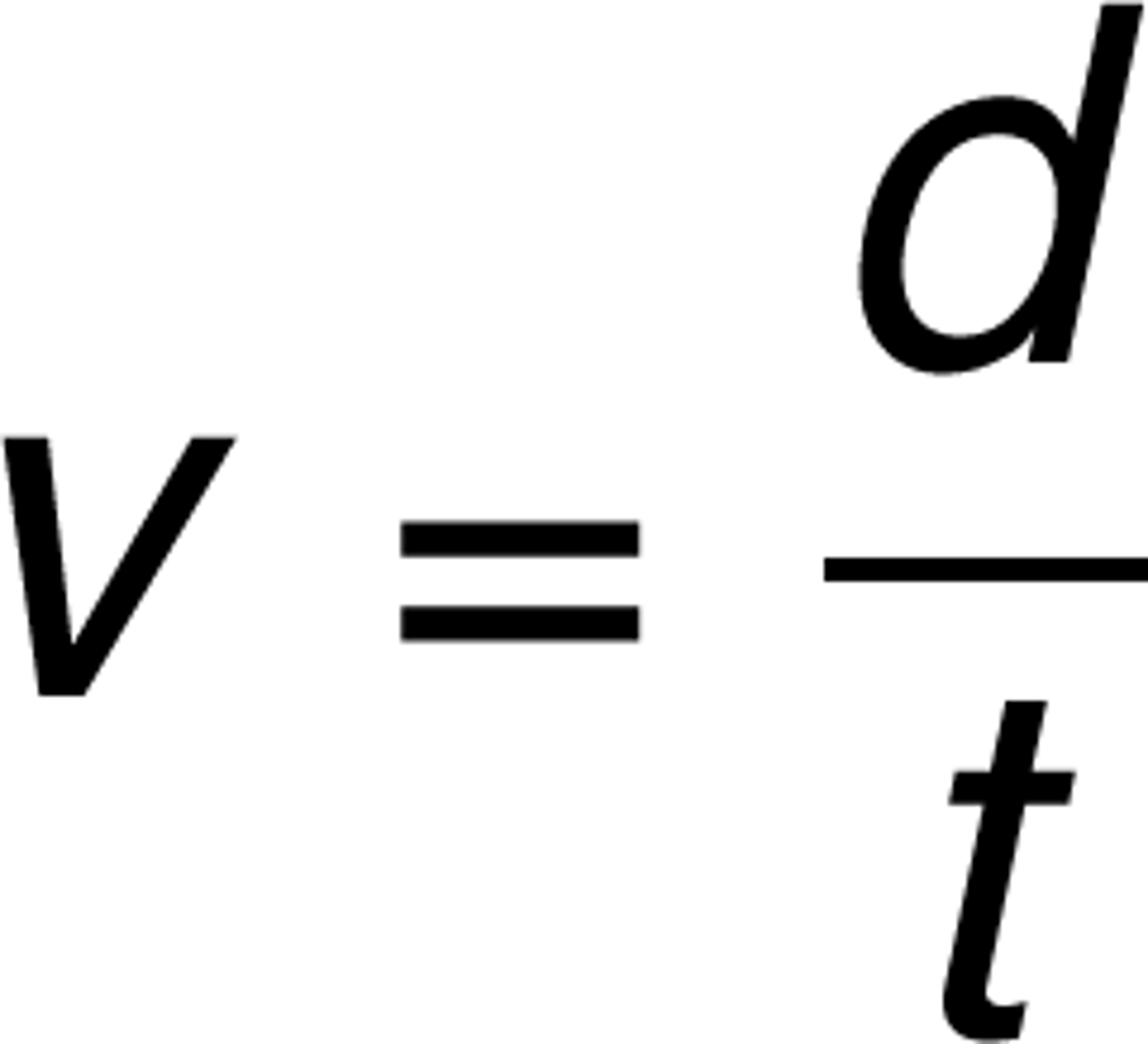
Time (t)
the number of seconds it takes for an event to occur

Acceleration (a)
the rate that speed changes for a moving object, a change in speed : getting faster or slower (ms-2)
-is an increase in speed in a certain time
-can be calculated by dividing the change in speed by the change in time, a=v/t
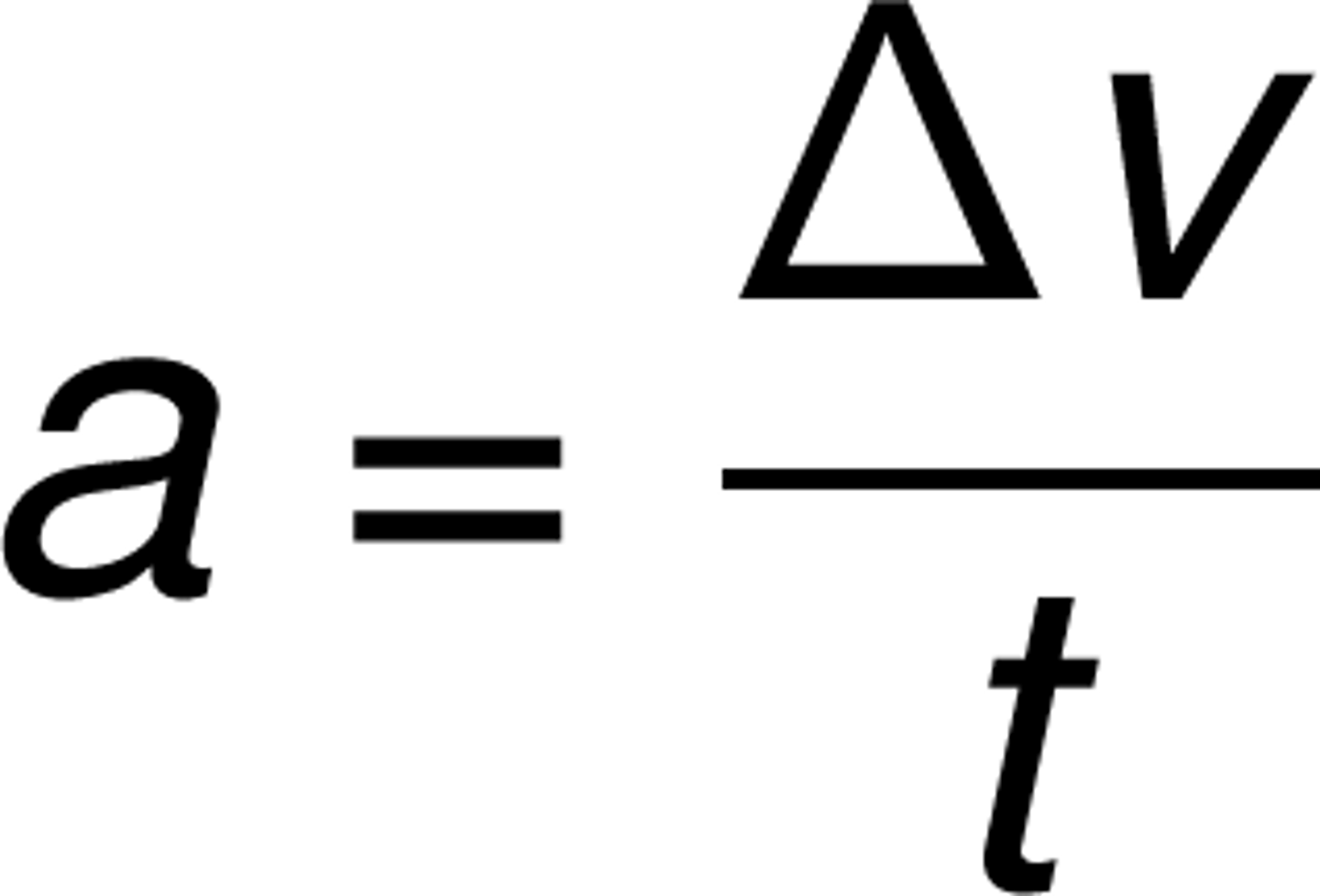
Deceleration
a word used for 'slowing down' or 'negative acceleration' (-ms-2)
-when describing in word answer NEVER say 'it is decelerating at -10m/s2
-deceleration:write using positive value eg- decelerating at 10m/s2
-deceleration with a negative value: eg- accelerating at -10m/s2
Mass (m)
the quantity of matter in an object measured in kilograms (kg)

Weight force
is a force measured in Newtons and it is the force due to gravity. Fw=mg
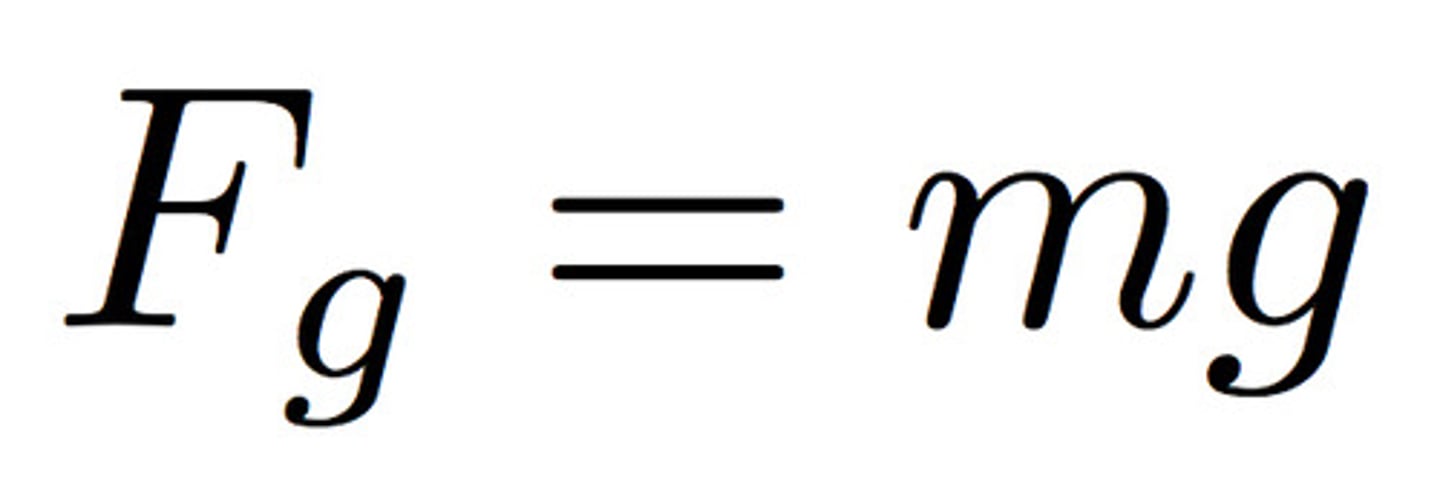
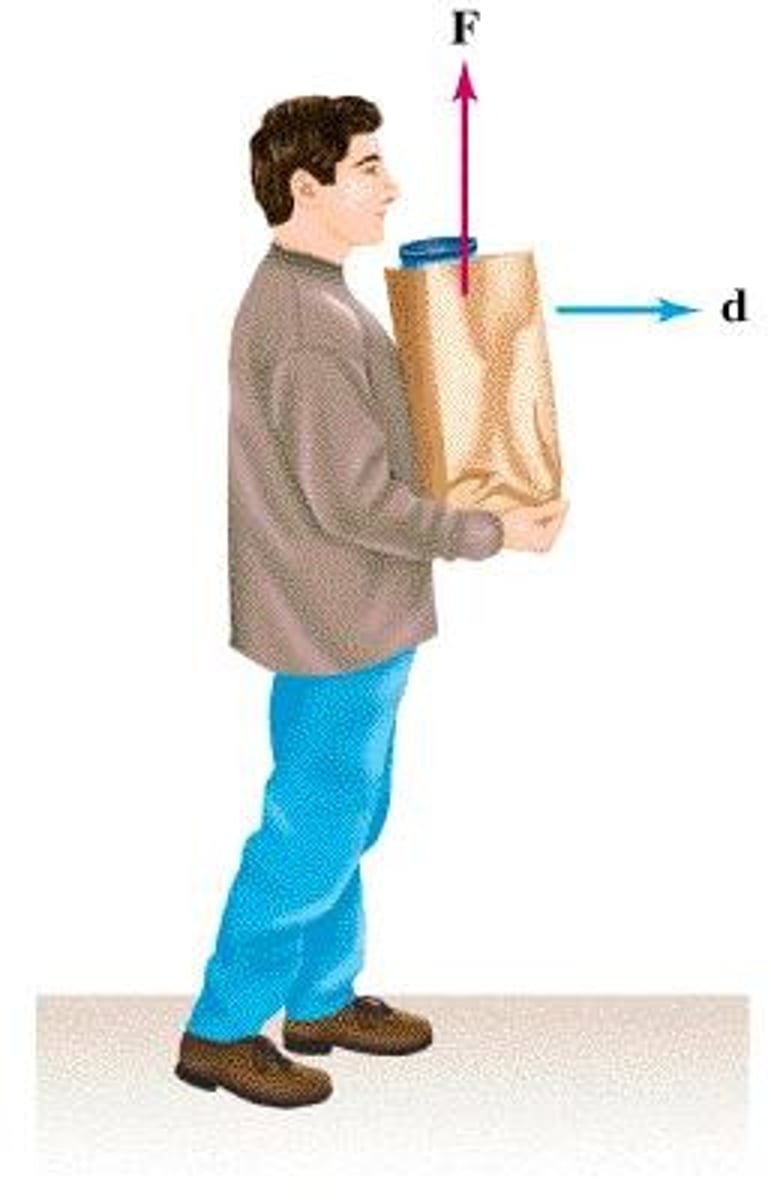
Work (w)
is the energy transferred from one form to another and is work is done whenever an object moves in the direction of the force that is being applied to it, measured in joules (J)
-If you are carrying something "along" there are NO forces acting on it in the direction of motion (no change in speed so no change in energy) so no work is done.
Power (P)
the rate at which work is being done measured in Watts (W)
-work done per second
-A more powerful person/thing does more work in the same time or the same work in less time
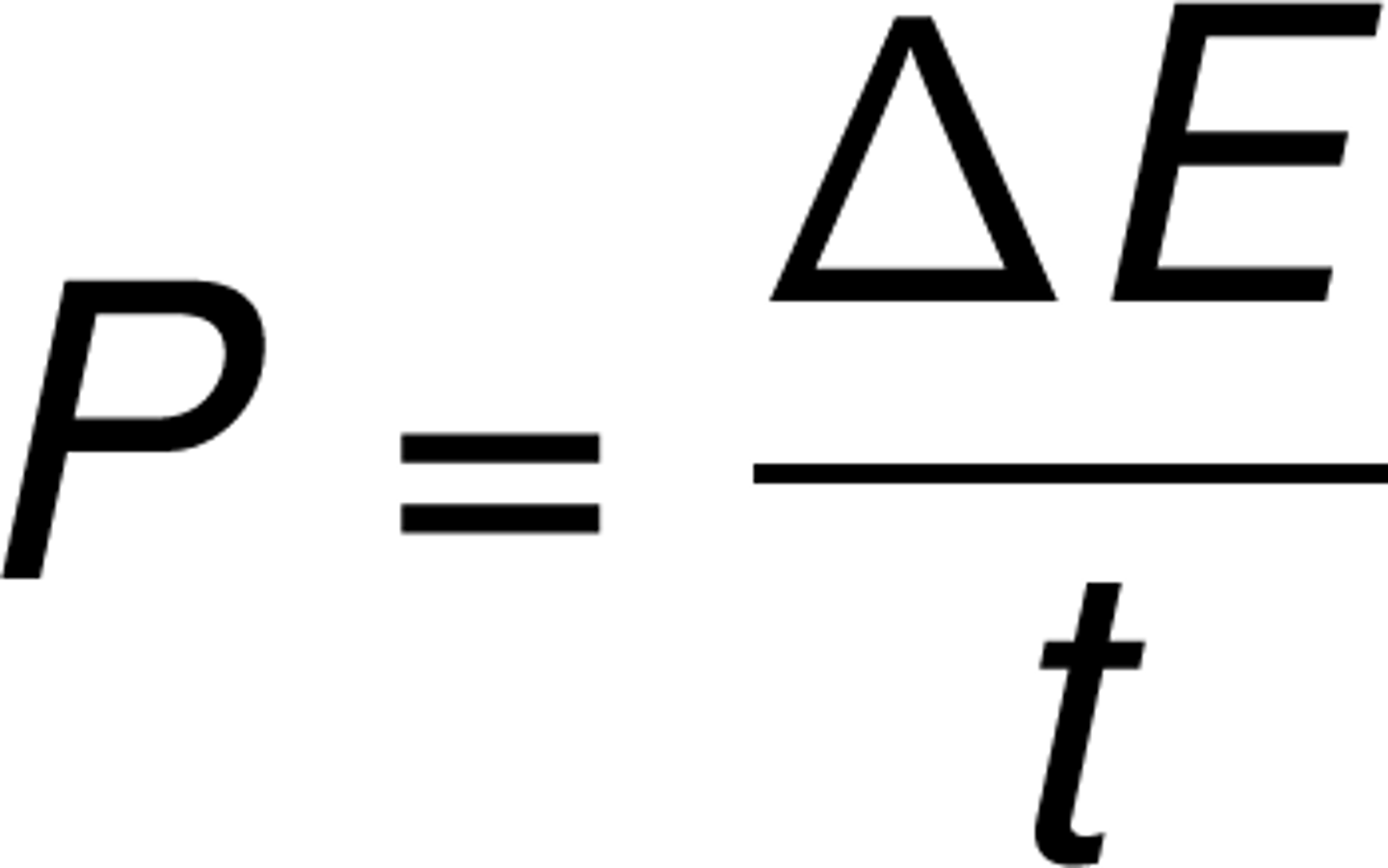
Pressure (P)
pressure depends on the amount of force used and how big an area of force is spread over or force applied to a certain area measured in (Nm-2) or Pascals (Pa)
-is force per unit area
-To turn cm2 into m2 divide by 10,000 (100 x 100) 10^-3
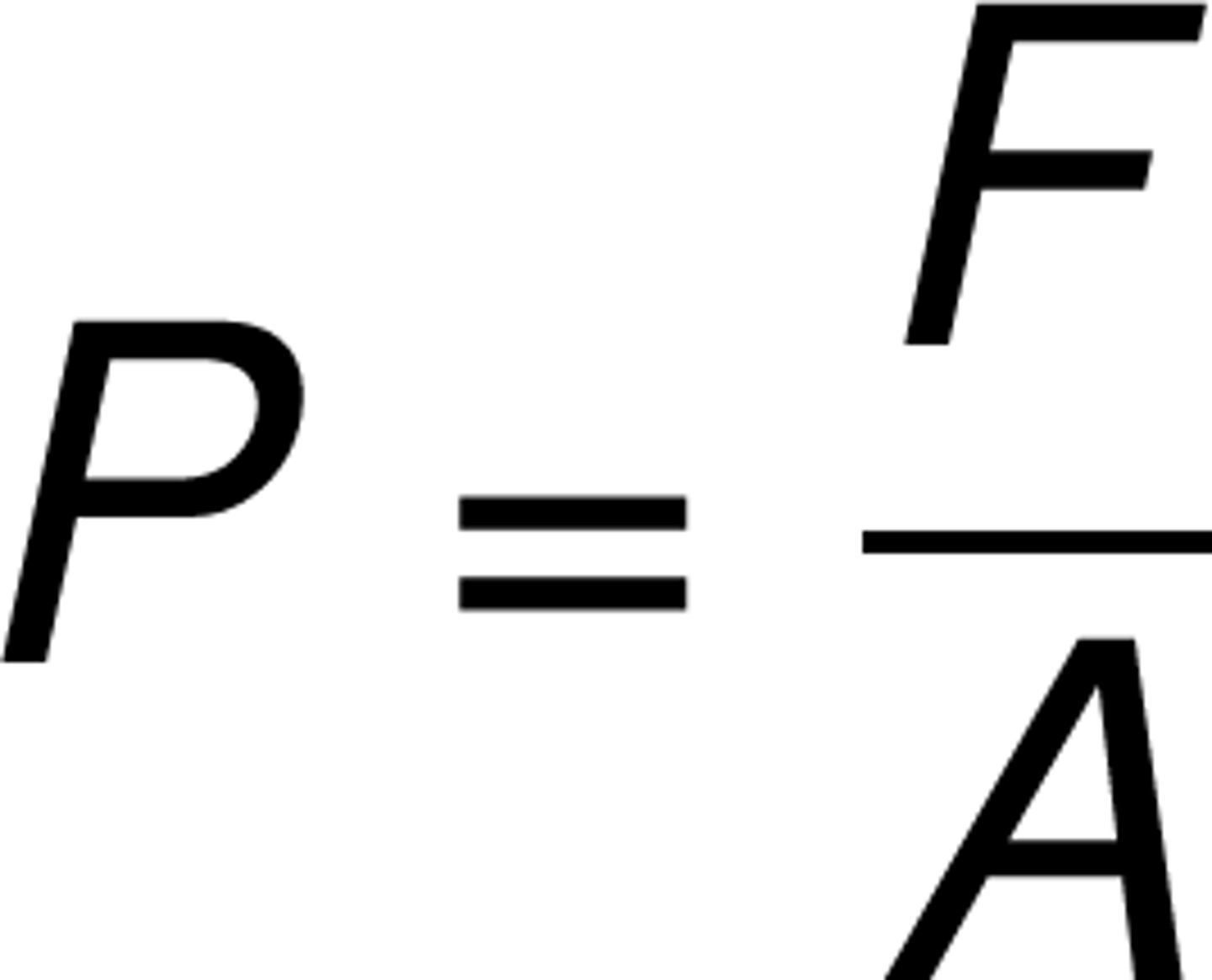
Force (F)
a push or pull measured in Newtons (N)
something that can make an object either speed up, slow down, stop, changes its direction or shape, to work out F=ma
Gravity
is a force that attracts objects towards the centre of the earth, g=10Nkg-1

How to solve physics problems?
-read question carefully
-write equation/formula
-substitute in numbers
-rearrange
-calculate
-correct unit ( make sure to make any conversions if needed)
Stationary
if something is not moving, it is said to be stopped or stationary
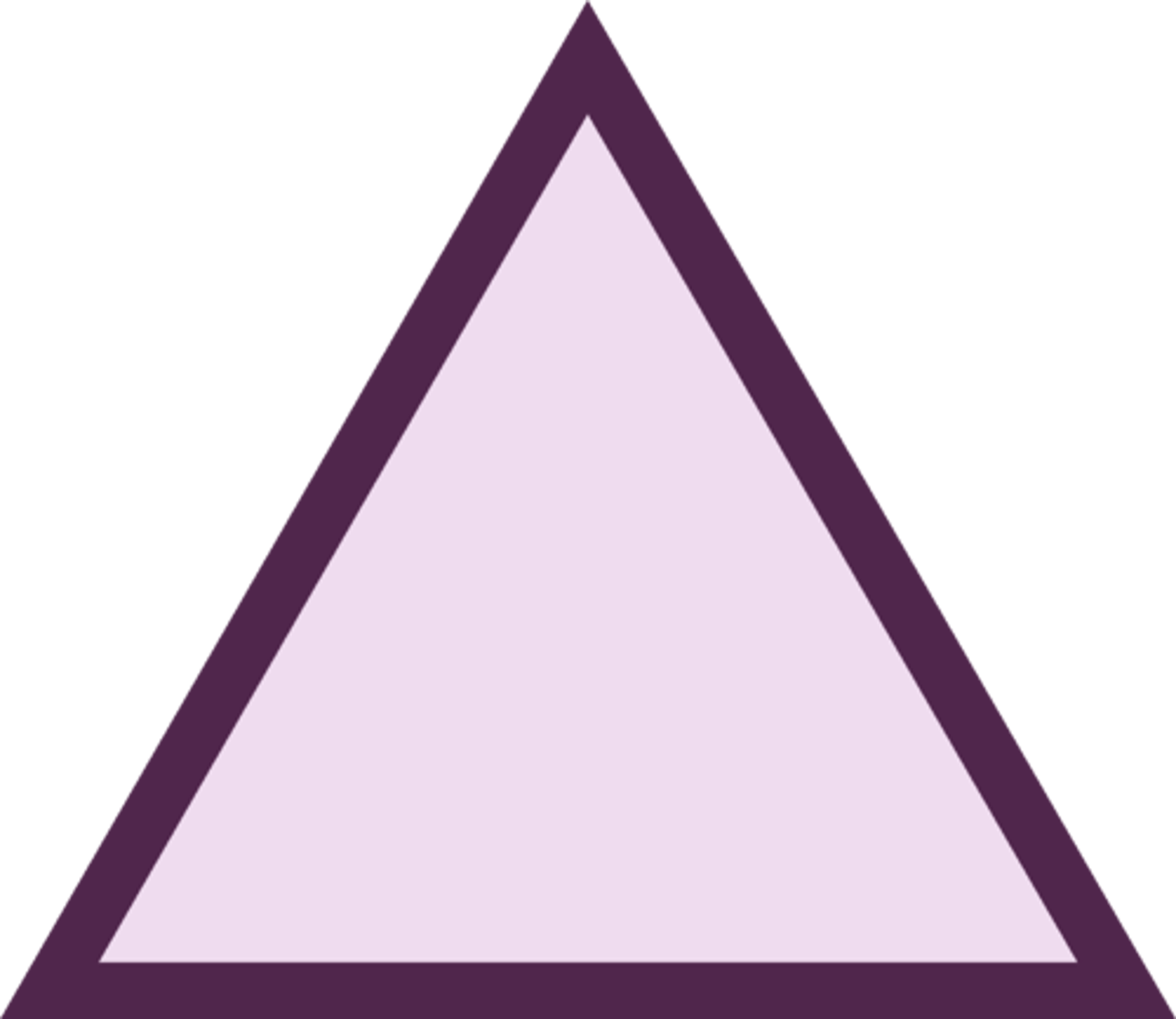
What is the symbol for change in?
TRIANGLE
Constant Speed
if a object is moving at a 'constant speed' then it is covering equal distances in equal time
Average Speed
total distance travelled / total time taken
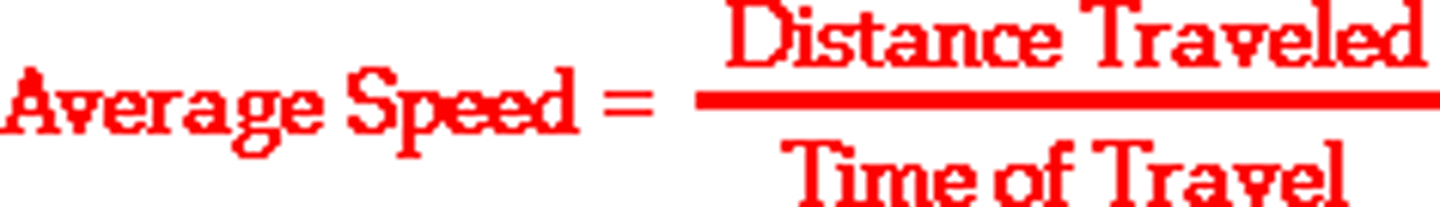
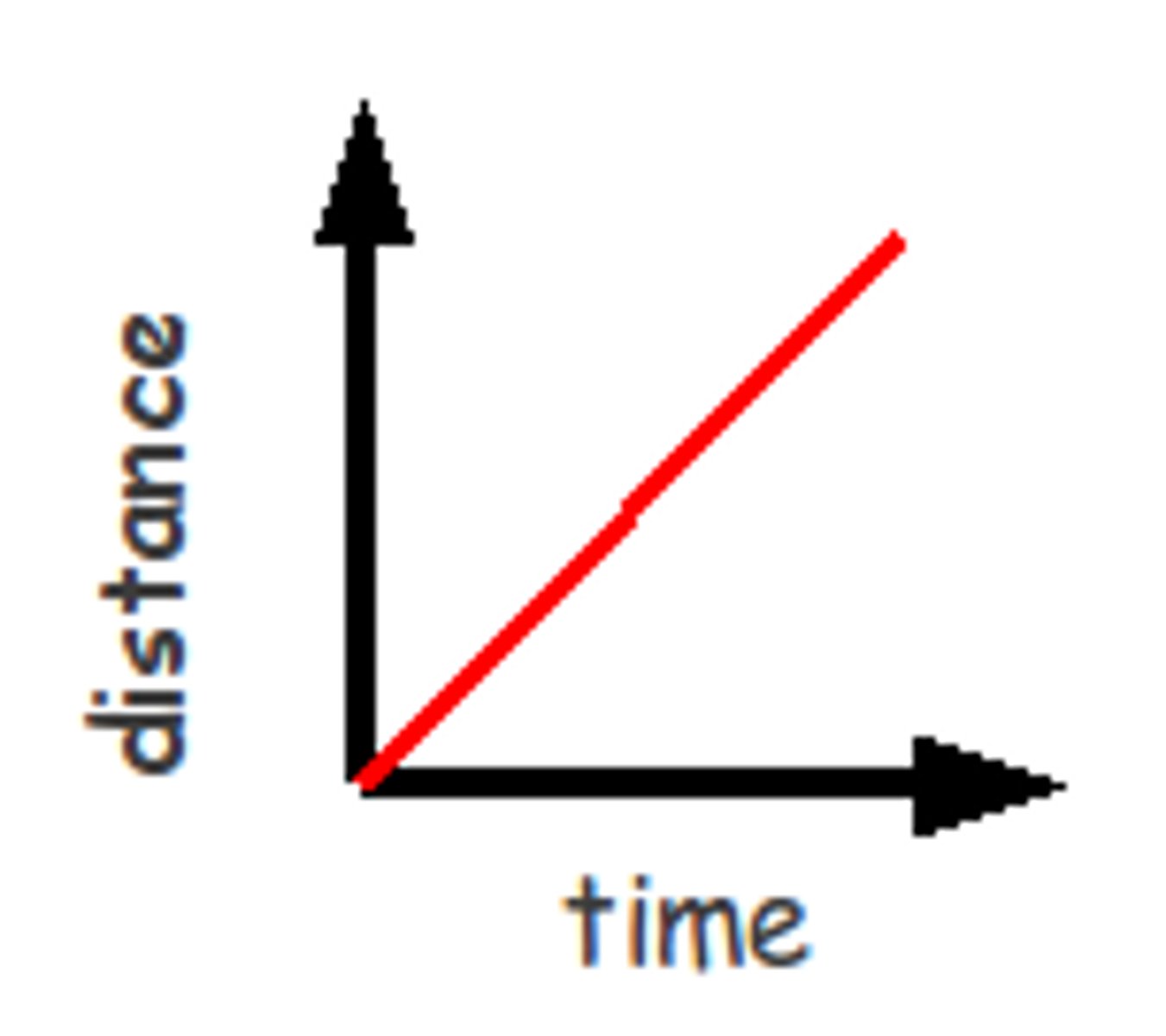
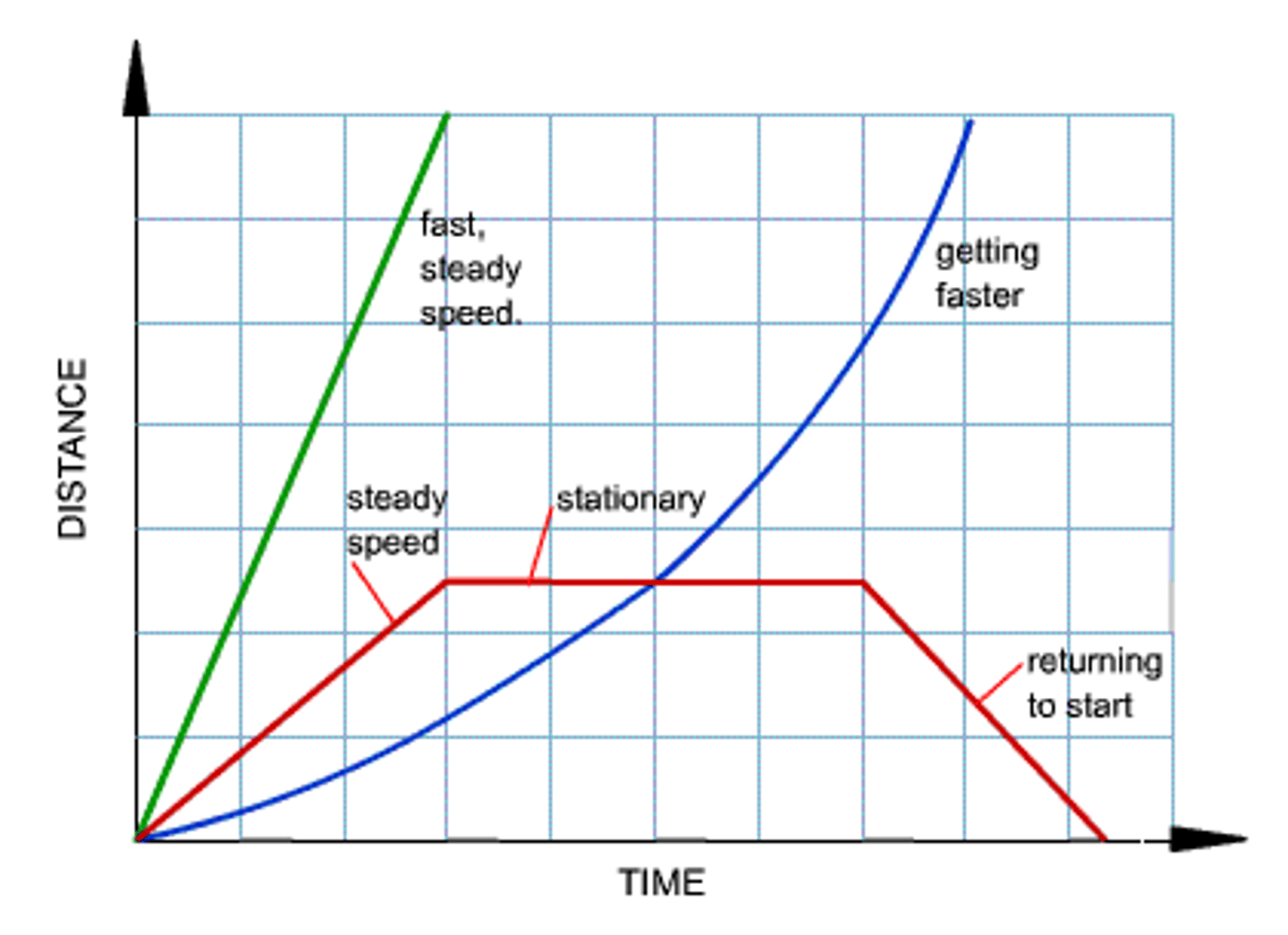
Distance/Time Graphs
-distance an object has moved at different times can be plotted on this graph
-vertical axis (y) is used for distance
-horizontal axis (x) is used for time
-size of slope (gradient) of the graph gives the velocity/speed
-flat sections are where object has stopped
-the greater the slope the greater the speed.
-curves represent acceleration or deceleration
-steep curve means it's speeding up
-a leveling off curve means deceleration
-line going back to the start shows object returning back to starting point
-v= d/t, eg- 500/30 = 16.7m/s
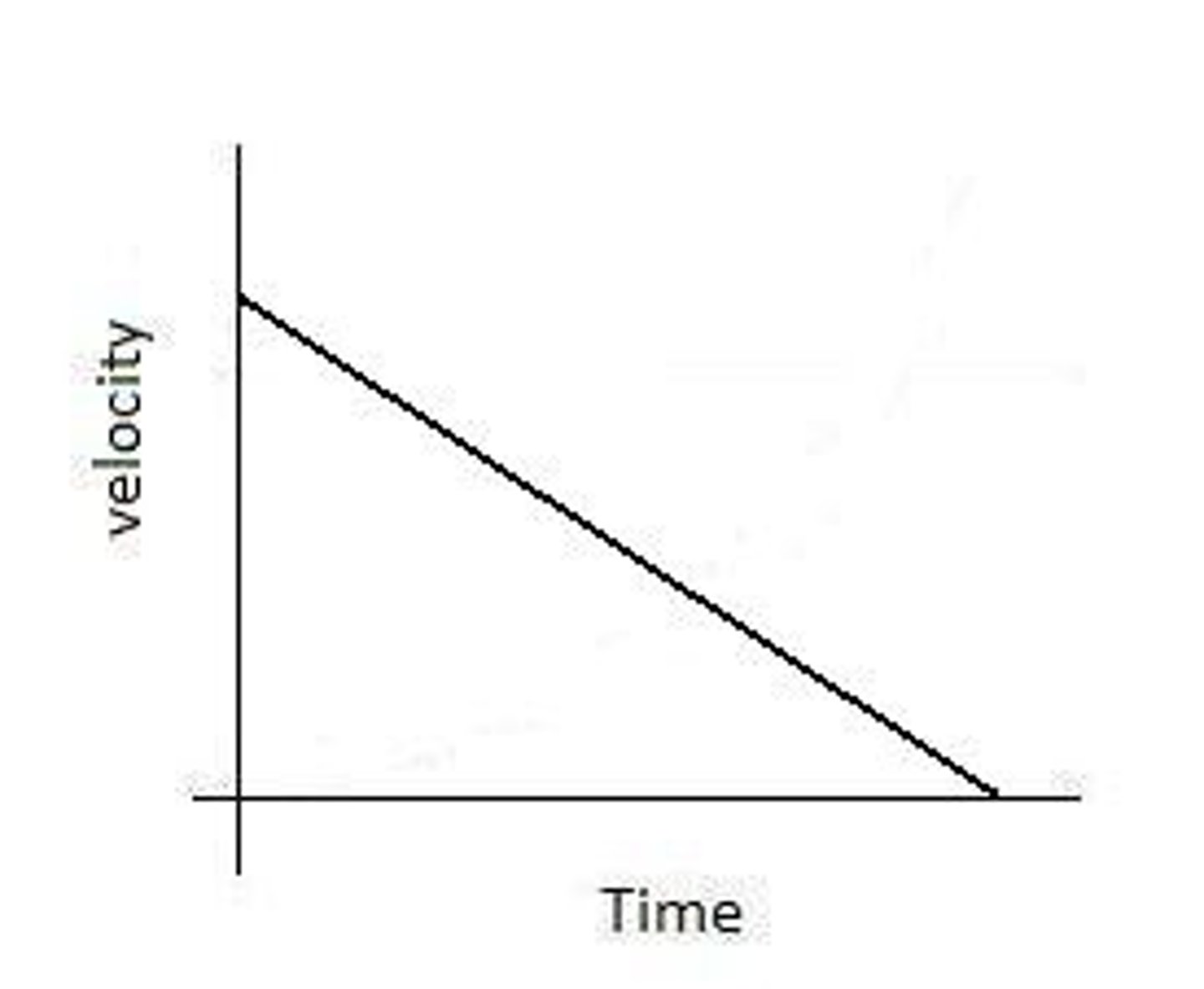
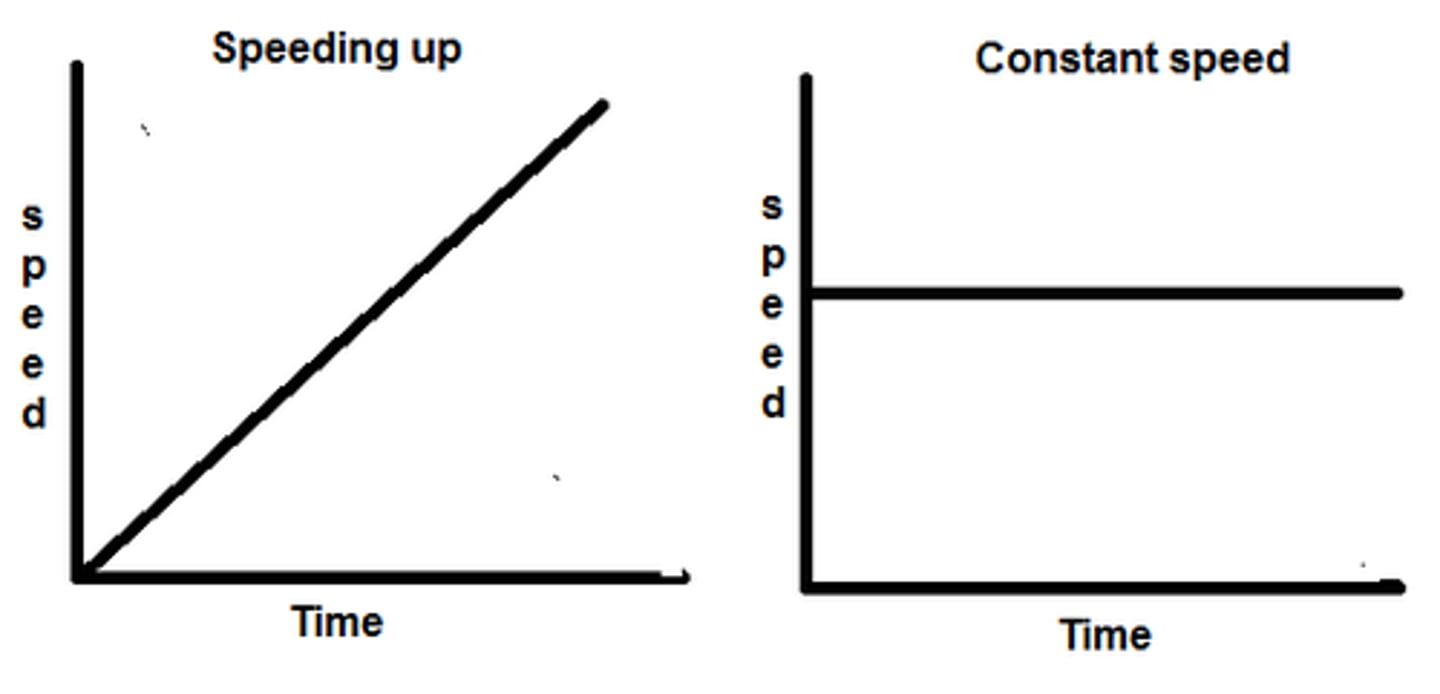
Speed/Time Graphs
-vertical axis (y) is used for speed
-horizontal axis (x) is used for time
-gradient of the slope gives the acceleration
-flat sections represent steady speed
-uphill sections are acceleration
-downhill sections are deceleration
-a curve means change acceleration
-the greater the slope, the greater the acceleration
-negative acceleration=deceleration=slowing down
-the area under the graph line and the time axis gives the total distance travelled (=bh or 1/2bh)
-a= v/t, eg- 30/20 = 1.5m/s2
Gradient (slope)
rise/run
Constant Acceleration
speed is changing by equal amounts in equal times
Net Force
total force
-unbalanced forces make an object speed up (accelerate) or slow down (decelerate)
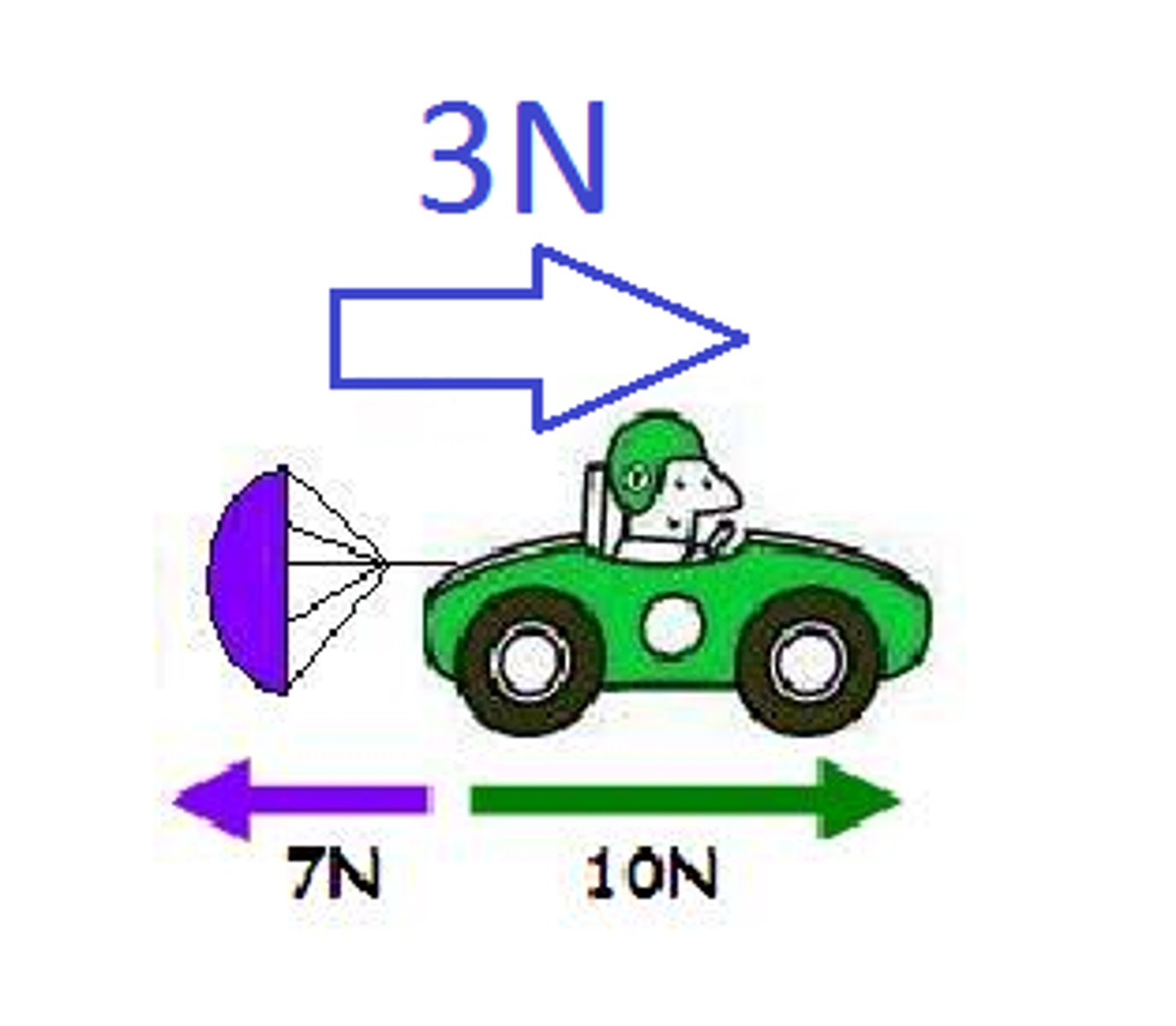
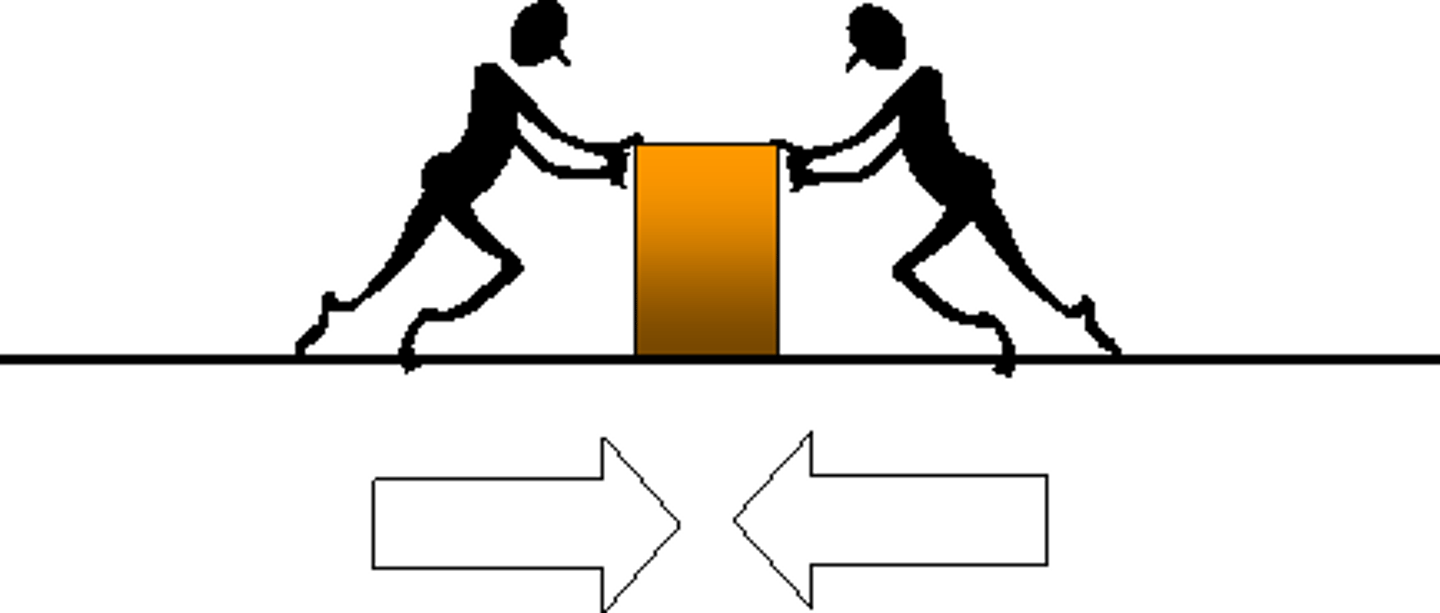
Balanced Forces
-when the forces acting on an object are of the same size (net total:0N)
-equal in size but opposite in direction
-object is either travelling at a constant speed or stationary

Unbalanced Forces
-the forces acting on an object are unequal causing a change in motion
-one force is greater than the other
-will make an object accelerate or decelerate

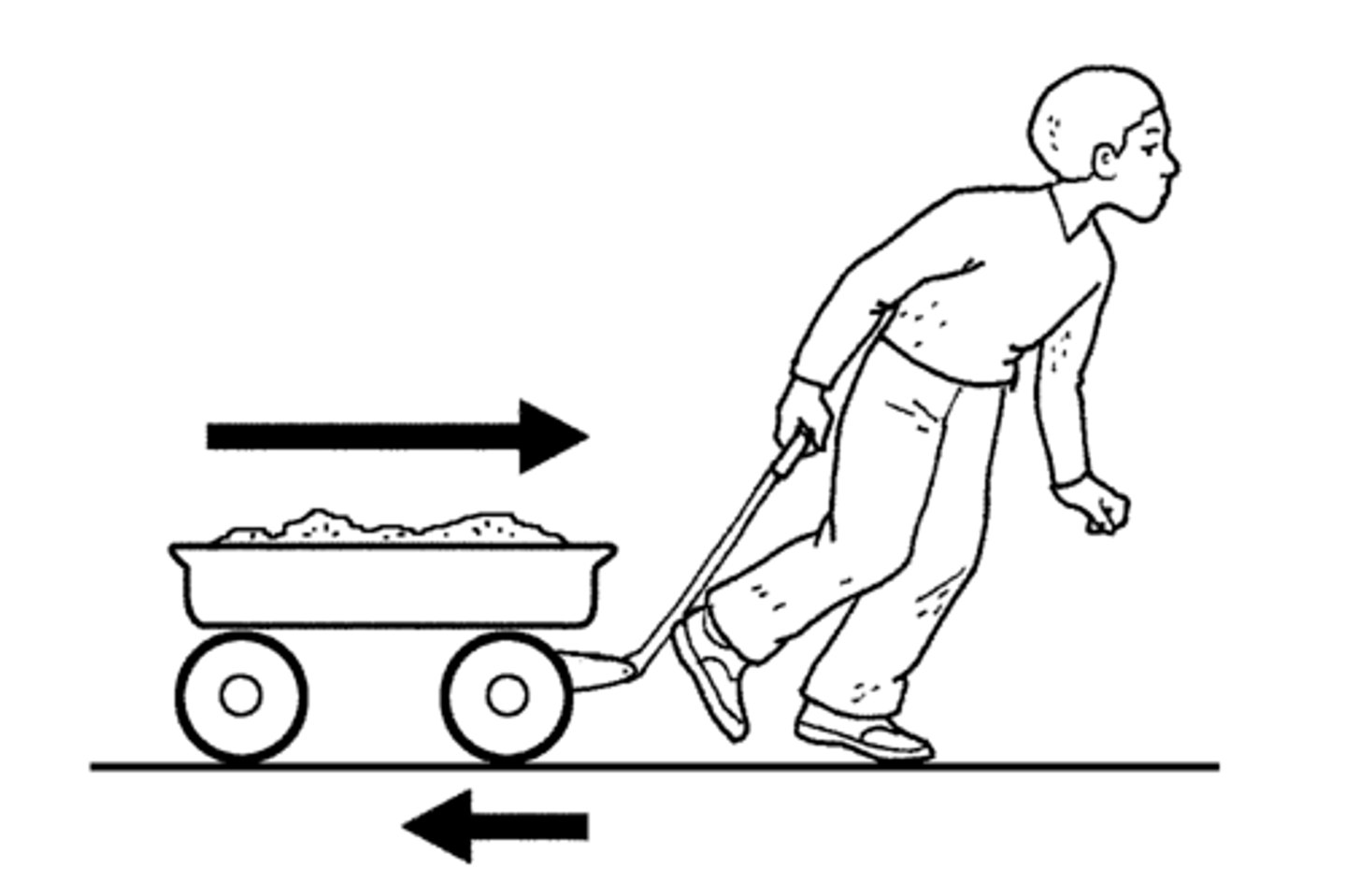
Force Arrows
-size of the arrows show force
-equal sized arrows show balanced forces
upwards force/upthrust/air resistance,
downwards force/weight, buoyancy
sideways forces/thrust/drag/friction
Air Resistance
friction acting on an object moving through air
Contact Force
Thrust, push
Non Contact Force
Weight force,Magnetic Force,
Friction
is a force that opposes motion or one surface moving over another.
-converts kinetic energy that a moving object has into heat energy
-can be reduced by using lubricants, smooth surfaces, aerodynamic shape, less contact surface and less weight force

How to find out Force
Force = Mass x Acceleration

Acceleration due to Gravity
is the acceleration of free falling objects
G= 10ms-2 and always acts in a downwards vertical direction
-the amount of acceleration depends on the size of the mass and the size of the force
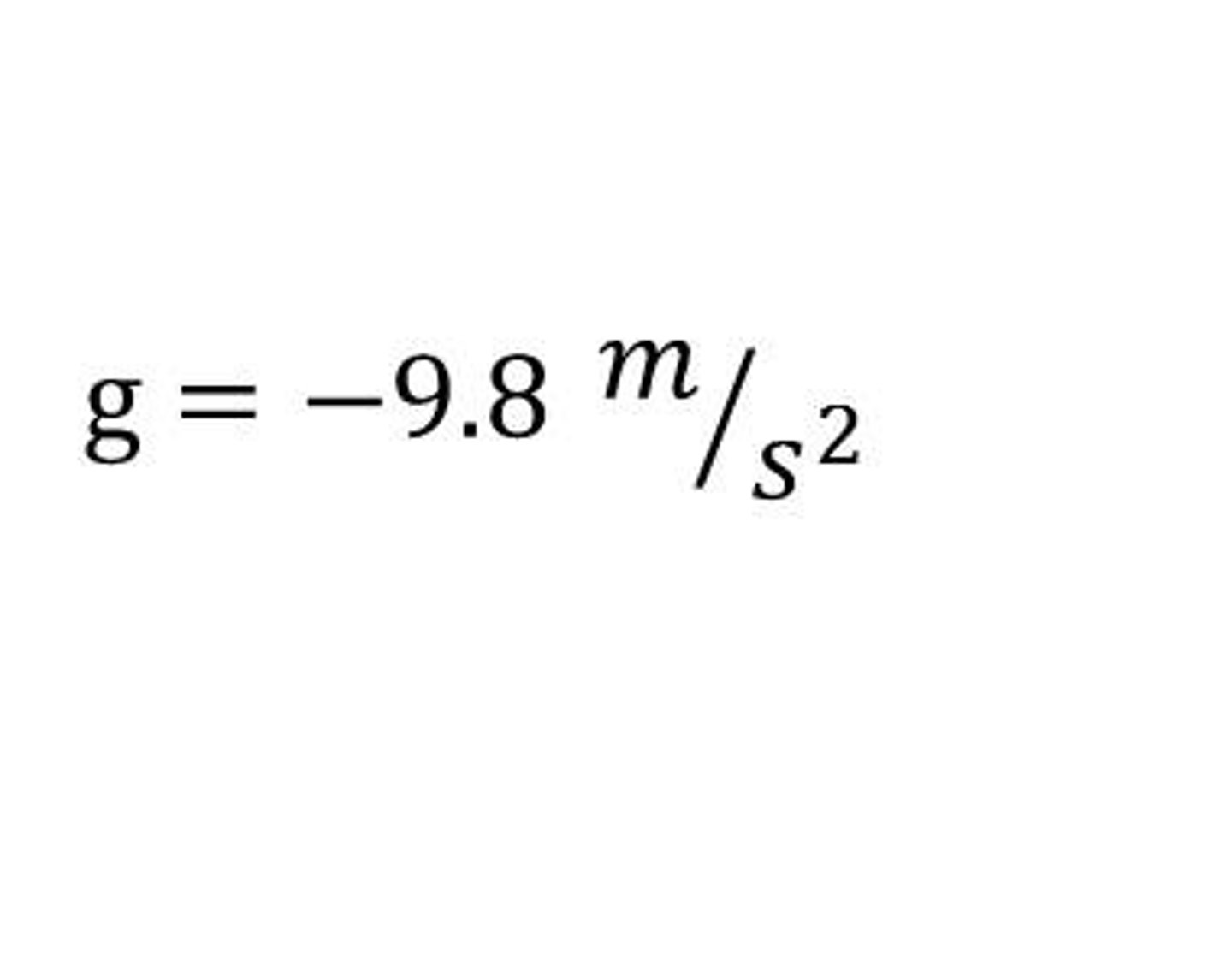
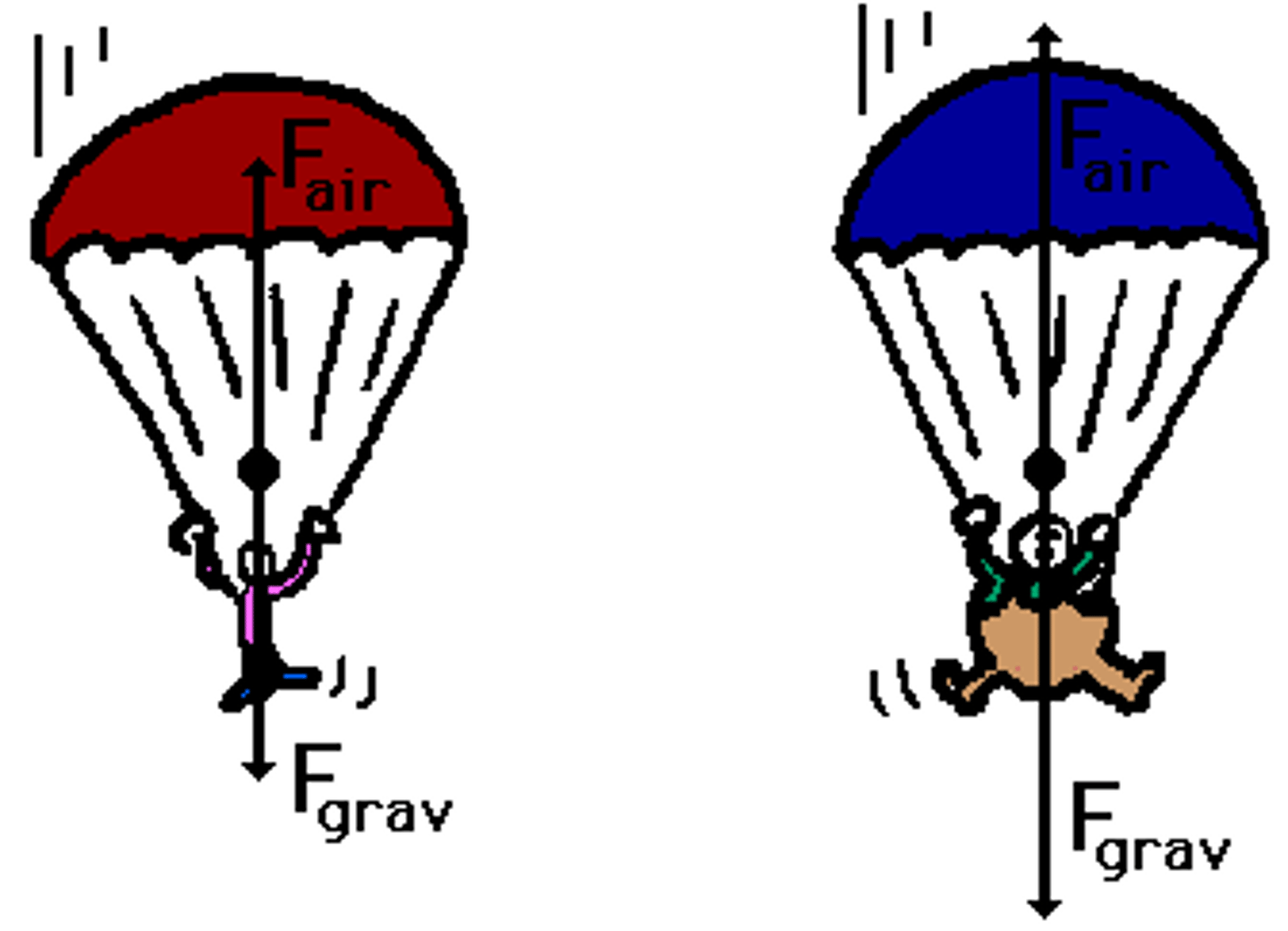
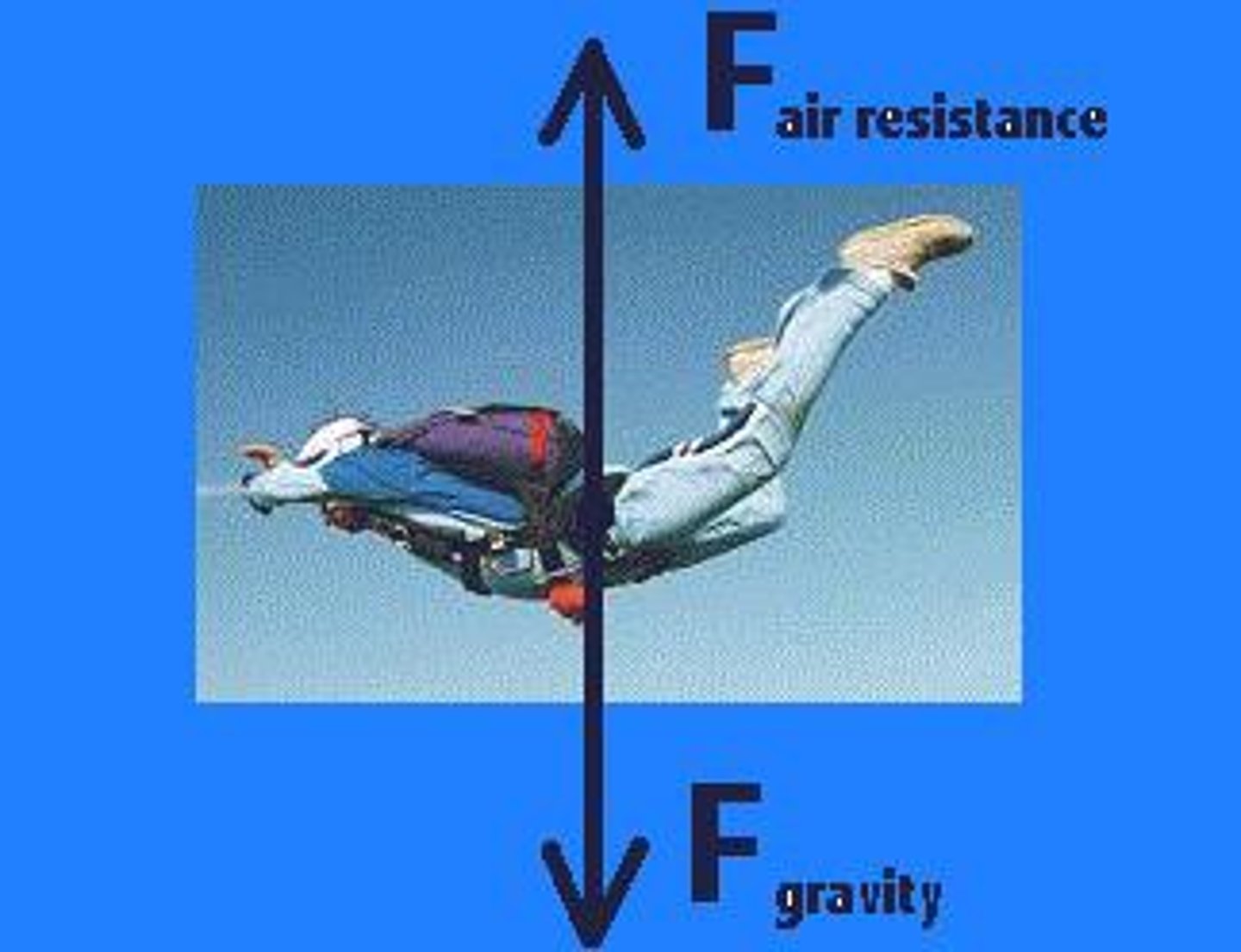
Terminal Velocity
When large objects fall freely through the air from a large height they do not continue to accelerate but eventually reach a constant speed
-terminal speed or terminal velocity
-the downward force (weight) equals the upwards force (air resistance). The forces are balanced so the sky diver falls at a constant
Gravitational Potential Energy
-measured in Joules (J)
-is (Epgrav) is energy stored when an object gains height
-when an object is lifted against gravity it's energy is increased and stored
-when the object falls energy is released transforming Epgrav to Kinetic Energy
- Ep = weight x h or Epgrav= Fgrav x h
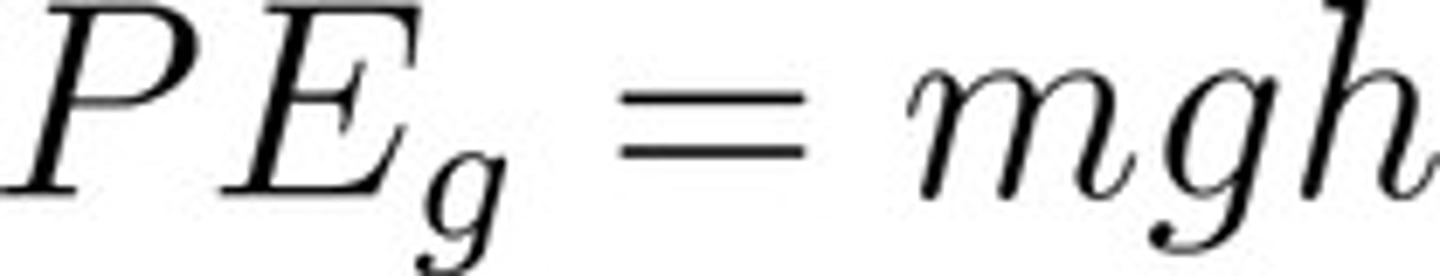
Kinetic Energy
-measured in Joules (J)
-the energy an object has due to motion
-objects not moving have no Ek
-the greater the mass/speed of an object, the greater it's kinetic energy
-double speed = 4x the energy
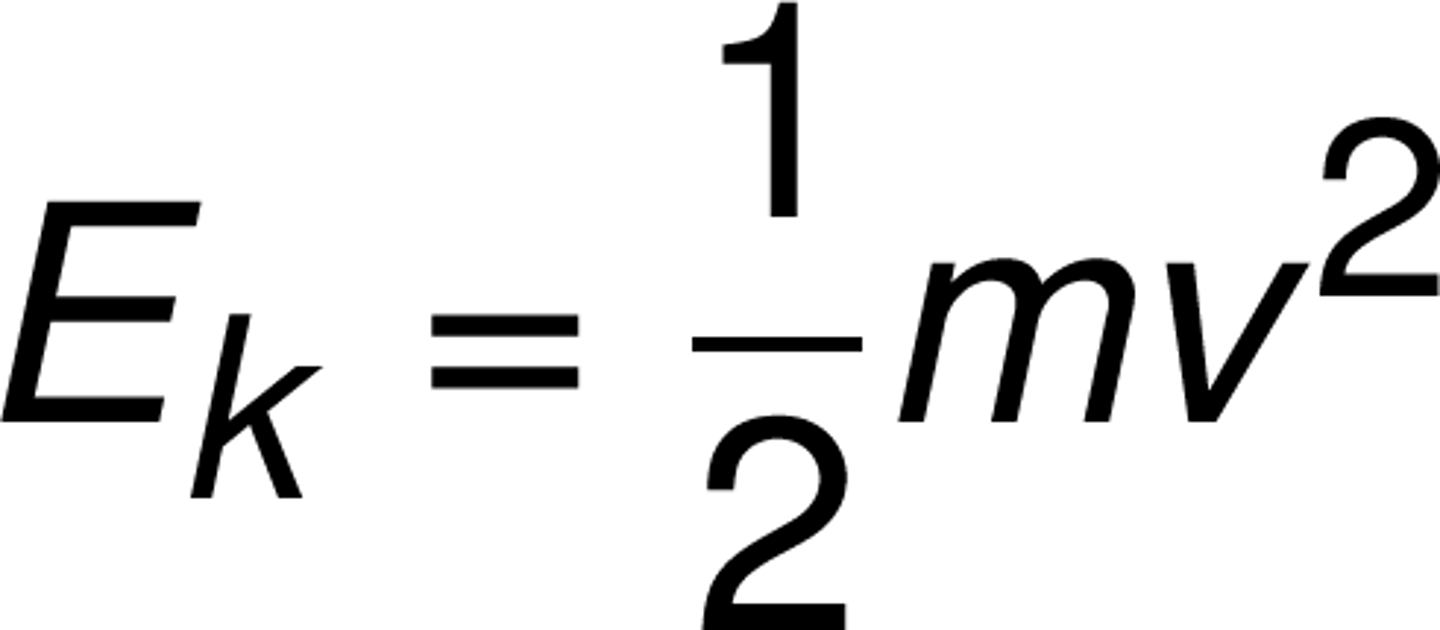
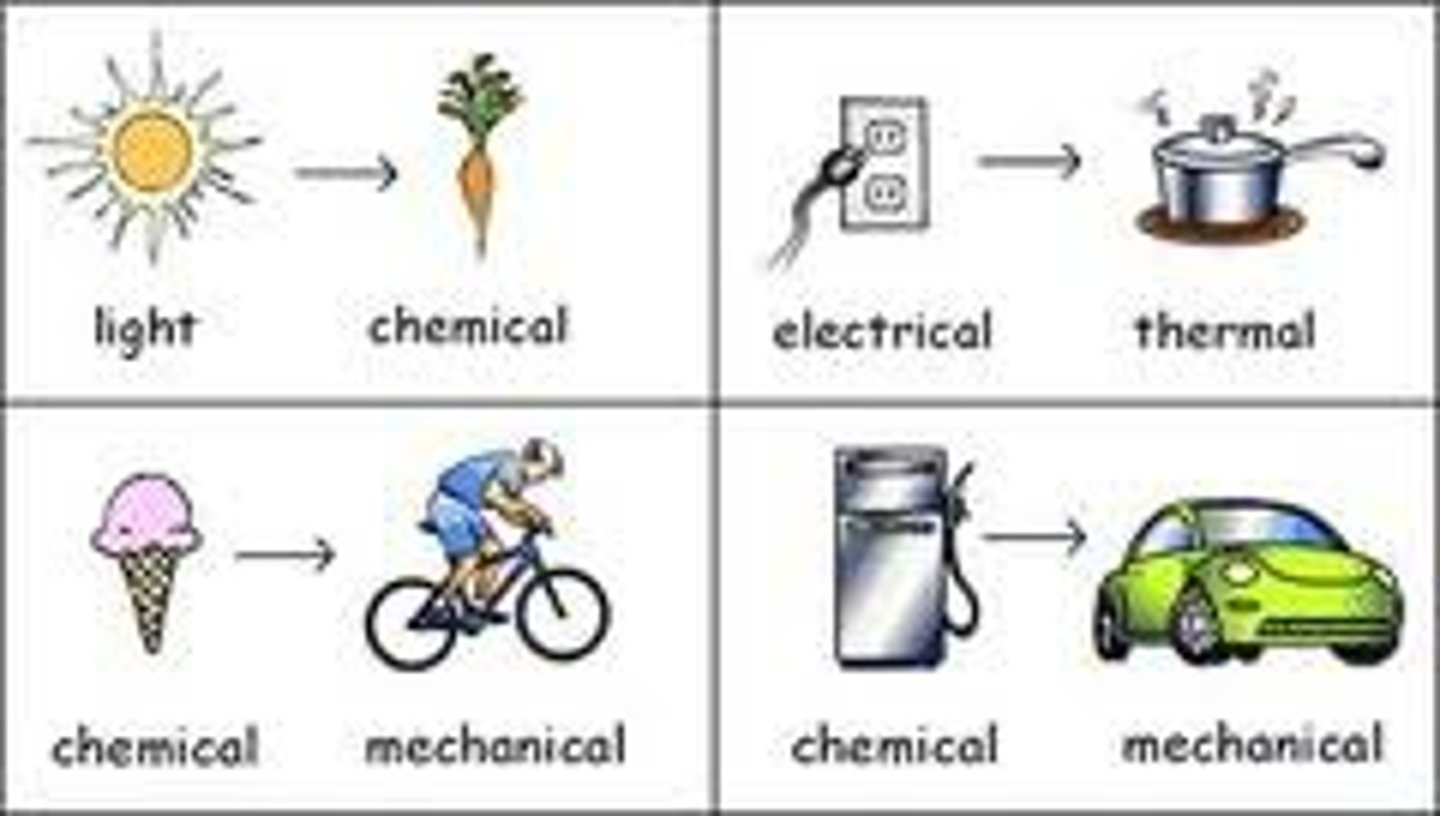
Energy (work)
-the ability to do work and needed to make anything happen, is neither created nor destroyed rather takes the form of another
-during any energy change the total amount of energy is conserved.

A Simple Machine
-the purpose of a machine is to lessen the force needed to do some useful work
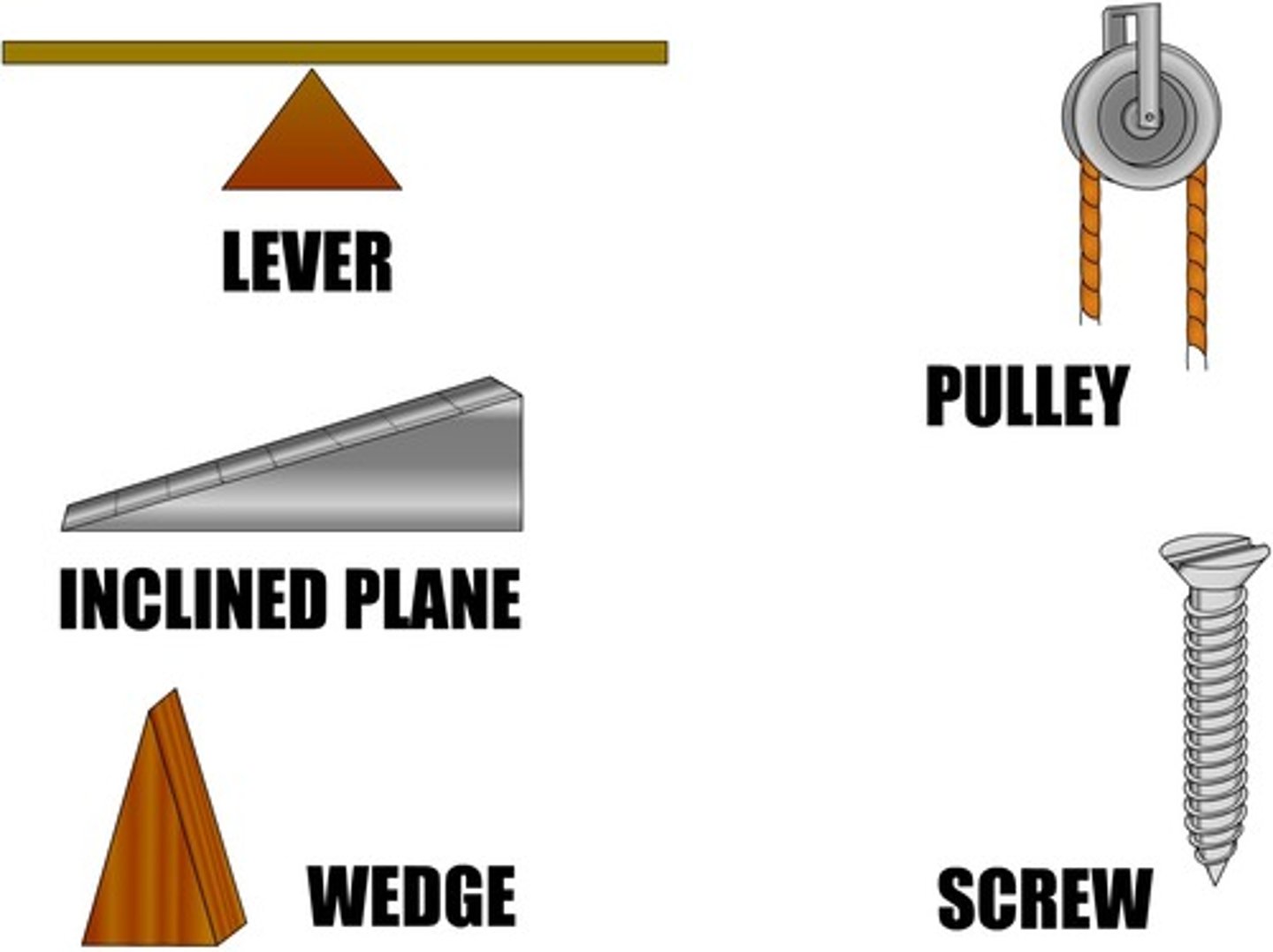
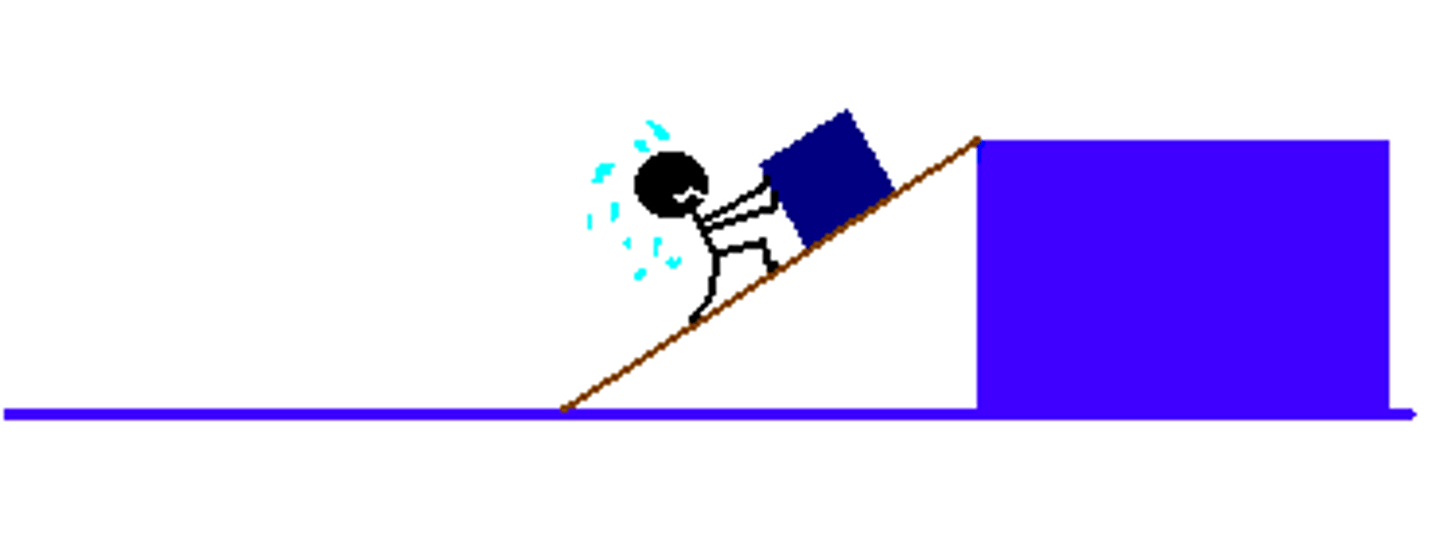
Inclined Plane
-same work can be one as lifting force but less force is required
-but more distance to pull the object
-has to overcome friction
Law of Conservation
Energy is neither created nor destroyed only transformed from one form to the other. The total amount of energy is 'conserved'. This means that no extra energy is created and none of the energy totally disappears.