Microbiology-Exam 1 Study Guide-MSSU
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Microbiology
The study of microscopic organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye
5 Major Groups of Microbes under the Umbrella of Microbiology
Bacteriology, Virology, Mycology, Protozoology, Helminthology
What are the names of the specific discipline that research each of these major groups?
Six branches of Microbiology
Medical Microbiology, Public Health Microbiology, Immunology, Industrial Microbiology, Agricultural Microbiology, Environmental Microbiology
Medical Microbiology
Deals with microbes that cause diseases in humans and animals
Public Health Microbiology and Epidemiology
monitor and control the spread of diseases in communities
Immunology
study of the immune system
industrial microbiology
branch of microbiology in which microbes are manipulated to manufacture useful products. Safeguards our food and water; biotechnology used to create amino acids, beer, drugs, enzymes, and vitamins
agriculture microbiology
relationships between microbes and domesticated plants and animals
Enviromental Microbiology
relationships between microbes and among microbes, other organisms, and their environment
What does LUCA stand for?
Last Universal Common Ancestor
(Branch points in the tree of life)
Compare and Contrast Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Eukaryotes are animal and plant cells. They have a nucleus and membrane bound.
organelles.
Prokaryotes are bacteria. They have no nucleus and no membrane bound
organelles.
Are humans eukaryotes or prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes; humans have multicellular organisms having a membrane band nucleus which encloses genetic material of the organisms
ubiquitous
present, appearing, or found everywhere
Describe why the Great Oxygenation Event led to mass extinction.
Massive amounts of built up O2 in the atmosphere, warming the planet and causing likely the first great extinction
What organisms acount for =70% of all O2 production on Earth today?
Bacteria and Algae
What would happen if microbes did not decompose organic matter?
Nutrients would not be able to recycle back into the environment, we would be buried in our own waste.
Two examples of ancient uses of microbes to make products
biotechnology and genetic engineering
Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.
genetic engineering
The direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes.
3 products that were used in genetic engineering.
human insulin, human growth, and hepatitis b vaccine
How was Bioremediation used in the world?
Crime scene cleanup. Bioremediation in this sense involves the cleanup of blood and bodily fluids that can pose health risks such as hepatitis, HIV, and MRSA;
The cleanup of contaminated soil;
Oil spill cleanup.
Most Microbes cause disease. True or False?
False- the vast majority of microbes cause no harm; in fact they provide benefits
emerging disease
disease that appears in the population for the first time, or an old disease that suddenly becomes harder to control
reemerging diseases
infectious diseases that existed in the past but for a variety of reasons are increasing in incidence or in geographic range
parasite
An organism that feeds on a living host
Where do majority of microbes live?
soil and water
Where do majority of microbes obtain their food and other factors ?
nonliving environment
How do viruses differ physically from prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
Viruses are neither prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Viruses are not made of cells. Viruses cannot replicate on their own. Most scientists do not consider viruses to be living.
The majority of Microbes are -celled?
single
Structure of Prokaryotes
Extremely small: 1-1.5 μm wide and 2-6 μm long
Occur in three basic shapes:
Spherical coccus,
Rod-shaped bacillus,
Spiral spirillum (if rigid) or spirochete (if flexible).
Structure of Eukaryotes
1) Cell interior is divided into functional compartments including a nucleus
2) Has membrane bound organelles
Biogenesis
the production of living organisms from other living organisms; asexual reproduction
Biogenesis
Sexual Reproduction
Abiogenesis
spontaneous generation (development of life from lifeless matter); nonliving matter
Example of spontaneous generation
1) Flies coming from meat
2) Mice coming from rice or grain
3) Worms falling from the sky

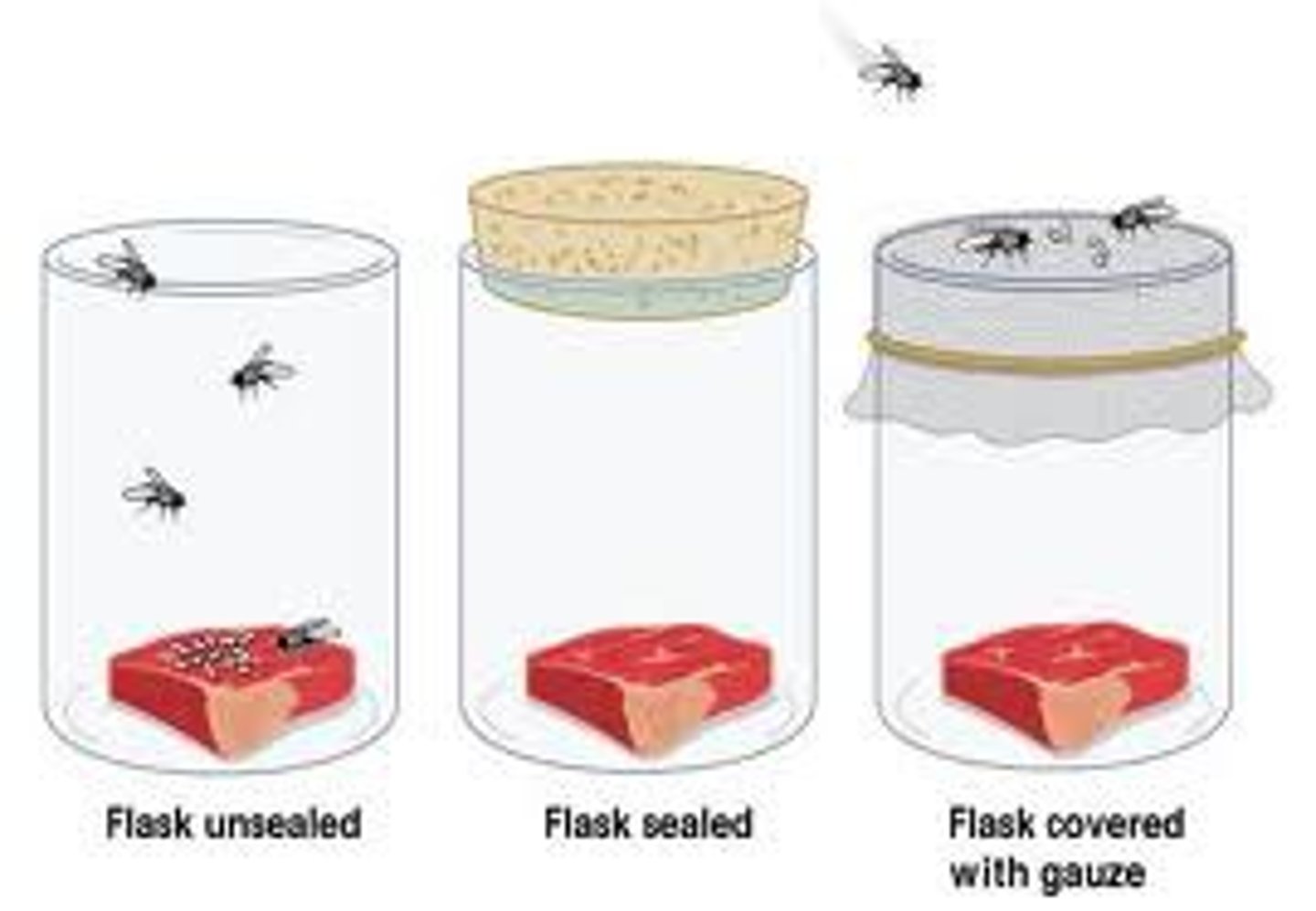
What was Redi's experiment?
Tested the theory of spontaneous generation - placed pieces of meat in two jars—one sealed and one open to the air. Maggots found only in the control jars that were open to air because that was the only place where adult flies could reach the meat to lay eggs.
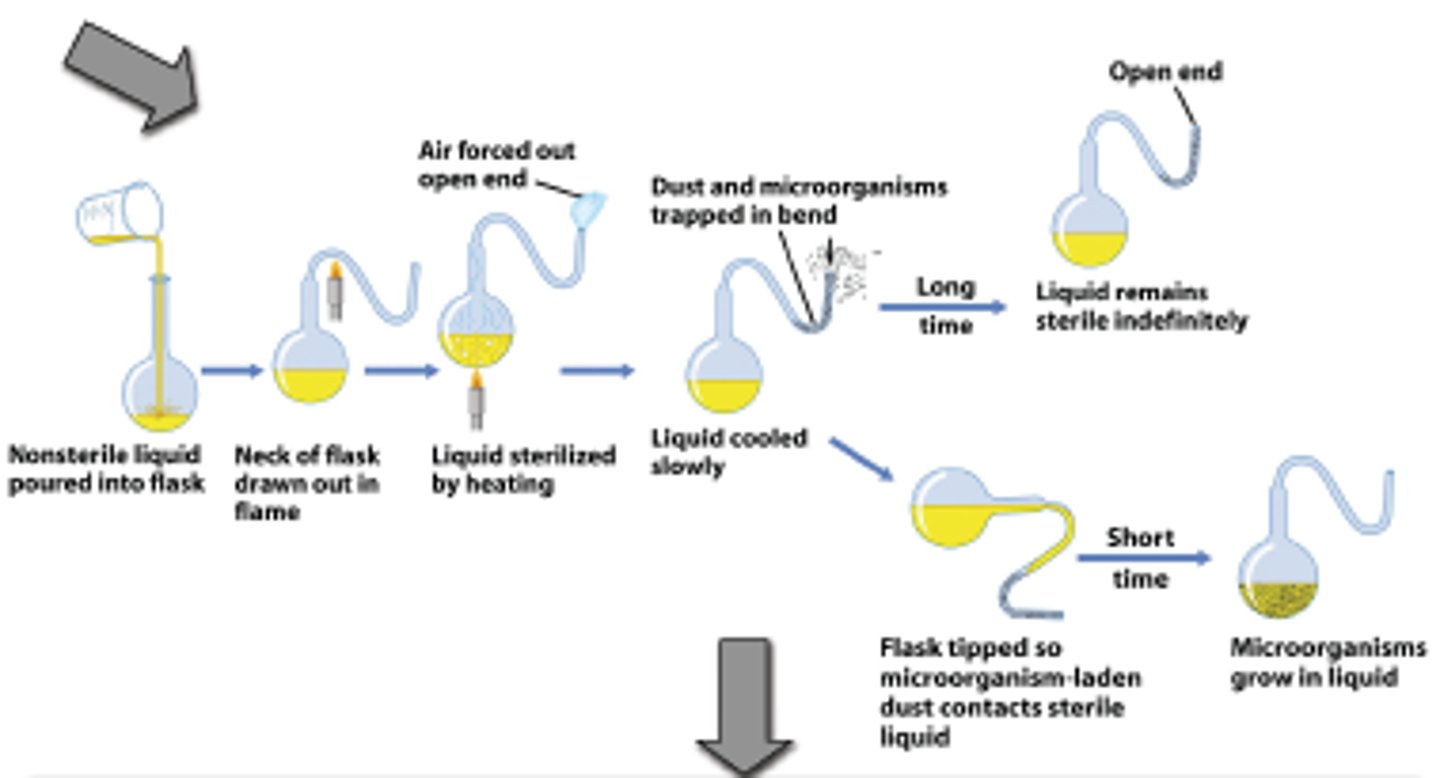
How did Pasteur disprove spontaneous generation?
Using his swan necked flask experiment
What did Robert Hooke do?
He named cells by looking at cork after viewing them under a microscope.
What did Leeuwenhoek do?
First to observe cells in greater detail
deductive reasoning
reasoning in which a conclusion is reached by stating a general principle and then applying that principle to a specific case (The sun rises every morning; therefore, the sun will rise on Tuesday morning.)
inductive reasoning
reasoning from detailed facts to general principles
Atmosphere of Victorian surgery
Surgery in the Victorian era was lethal, but not due to the fast-handed surgeons. Instead, it was the high probability of infection after the patient left the operating table.
Why is Liston famous for his amputations?
Two of the operations for which Liston is most famous involve the story of an amputation he performed in under two and a half minutes which resulted in a 300% mortality rate: the patient died of infection, as did his young assistant whose fingers Liston accidentally amputated, and a witness died of shock when the knife came too close to him.
Microbiology Advancement by Pastuer
Pasteur demonstrated that microorganisms cause disease and discovered how to make vaccines from weakened, or attenuated, microbes. He developed the earliest vaccines against fowl cholera, anthrax, and rabies.
Microbiology Advancement by Koch
building on the work of Pasteur and Lister, set bacteriology on its way to being a modern science. He discovered the causative organisms of anthrax, septicæmia, tuberculosis and cholera.
nomenclature
naming system
What are the 8 taxonomic categories?
1. Domain
2. Kingdom
3. Phylum
4. Class
5. Order
6. Family
7. Genus
8. Species
binomial system
Identifying organisms by their genus and species names
Why is the SSU rRNA gene used for molecular phylogenetic studies of distantly related organisms?
What are the 3 domains?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
What are the six kingdoms?
Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
What physical traits are common for most bacteria?
appendages, flagella, pili, fimbriae; cell envelope; cell wall; cell membrane; internal characteristics include ribosomes, cytoplasm and cytoskeleton.
Colonies
Collections of autonomously replicating cells.
Biofilms
Colonies of bacteria that adhere together and adhere to environmental surfaces.
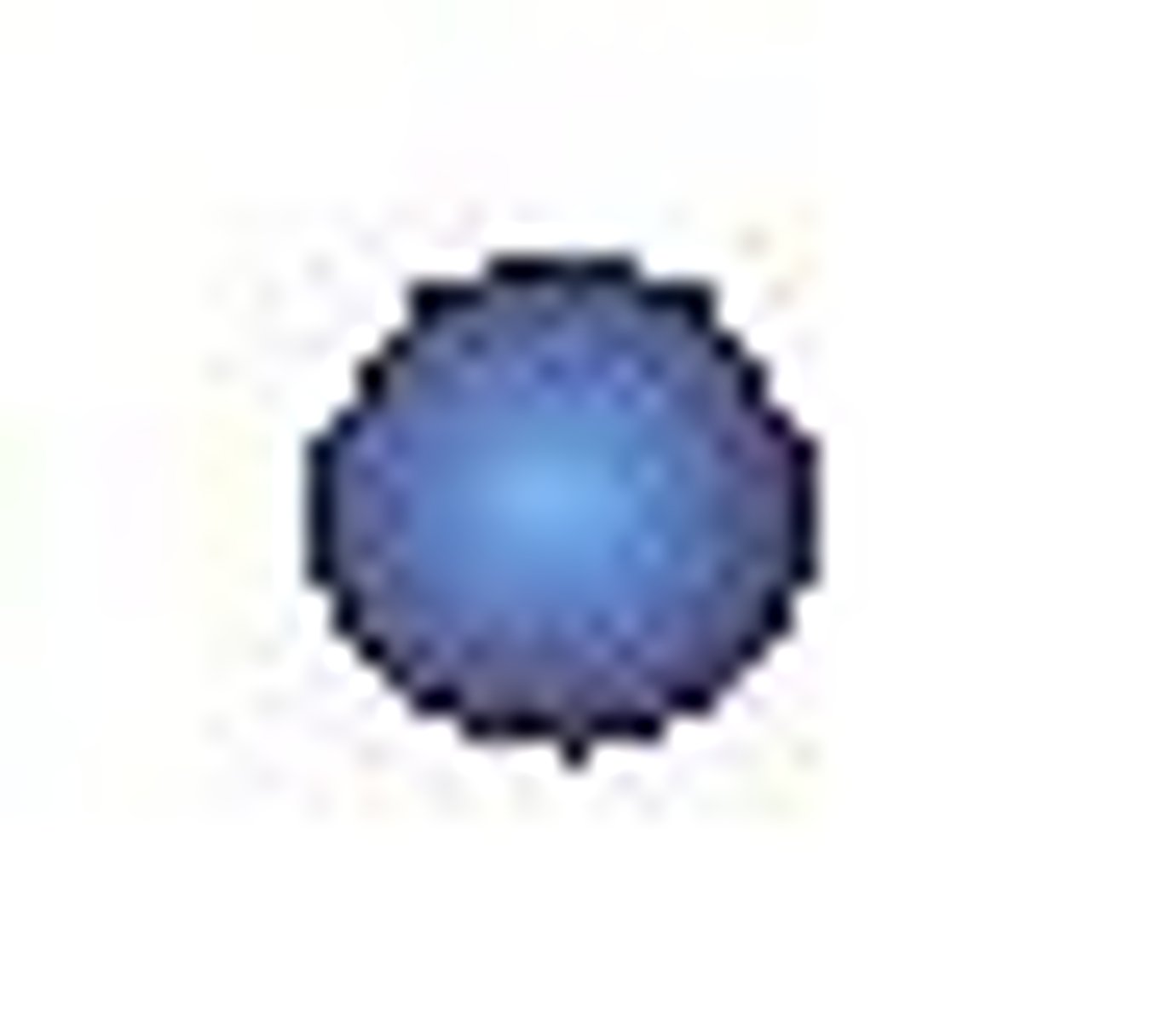
Coccus
A spherical bacterium.

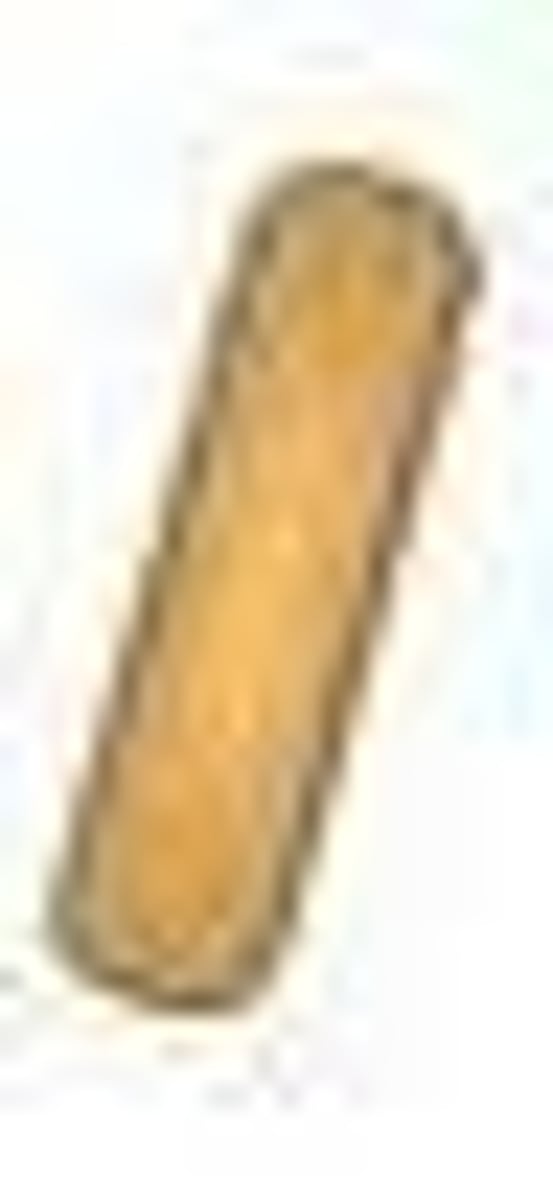
Bacillus
Rod shaped bacteria

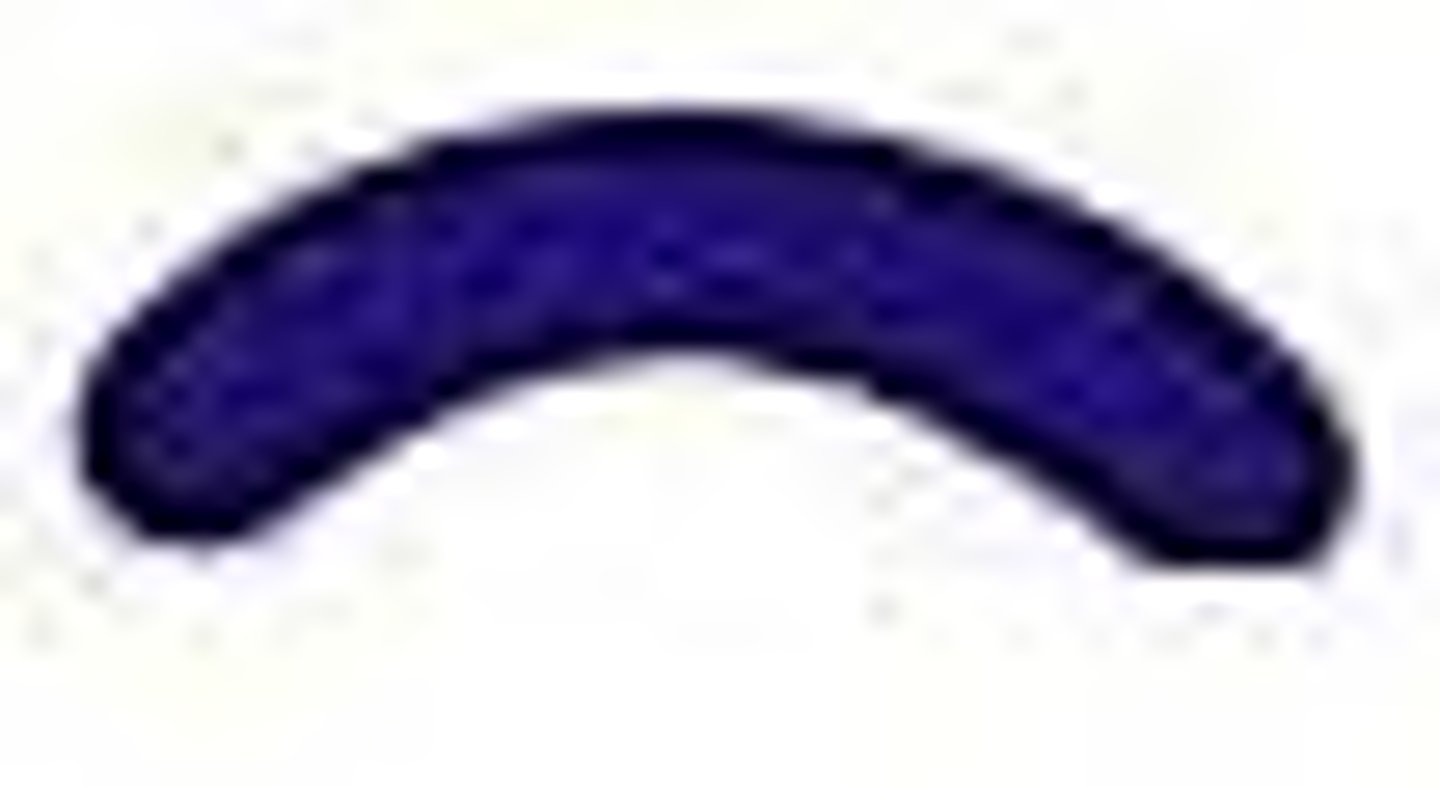
Vibrio
comma shaped bacteria

Spirillum
spiral shaped bacteria
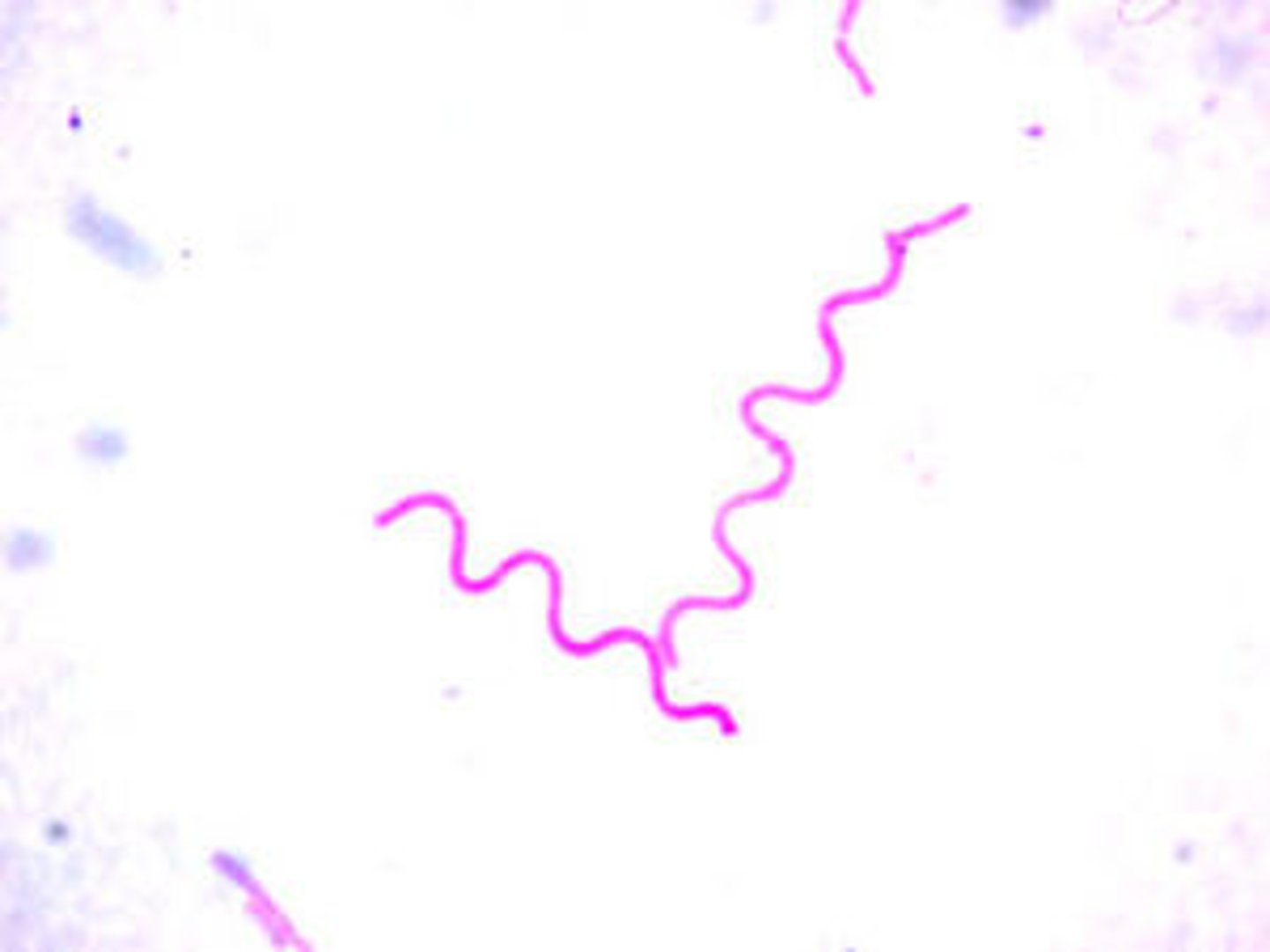
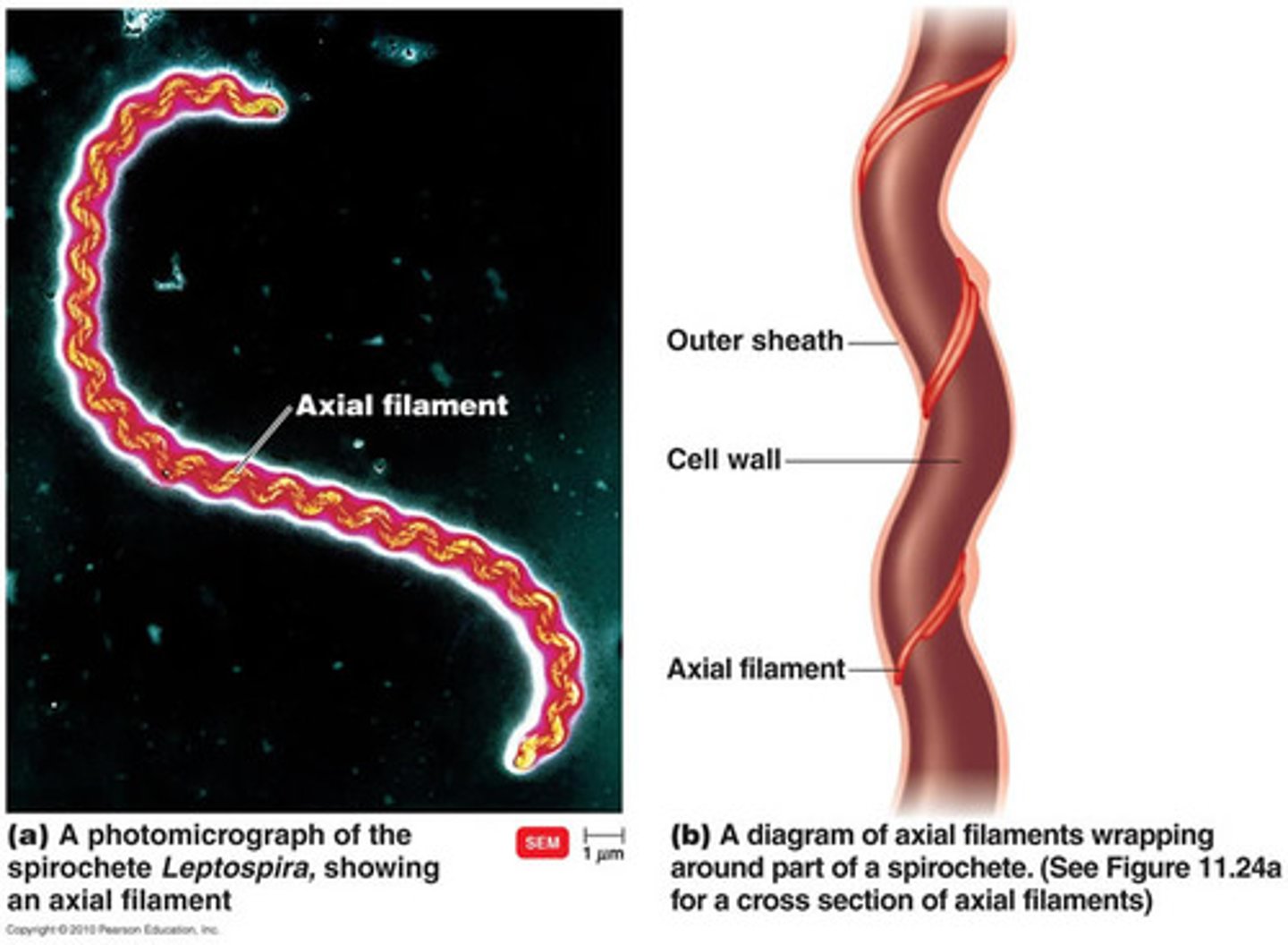
Spirochetes
spiral-shaped bacteria that have flexible walls and are capable of movement
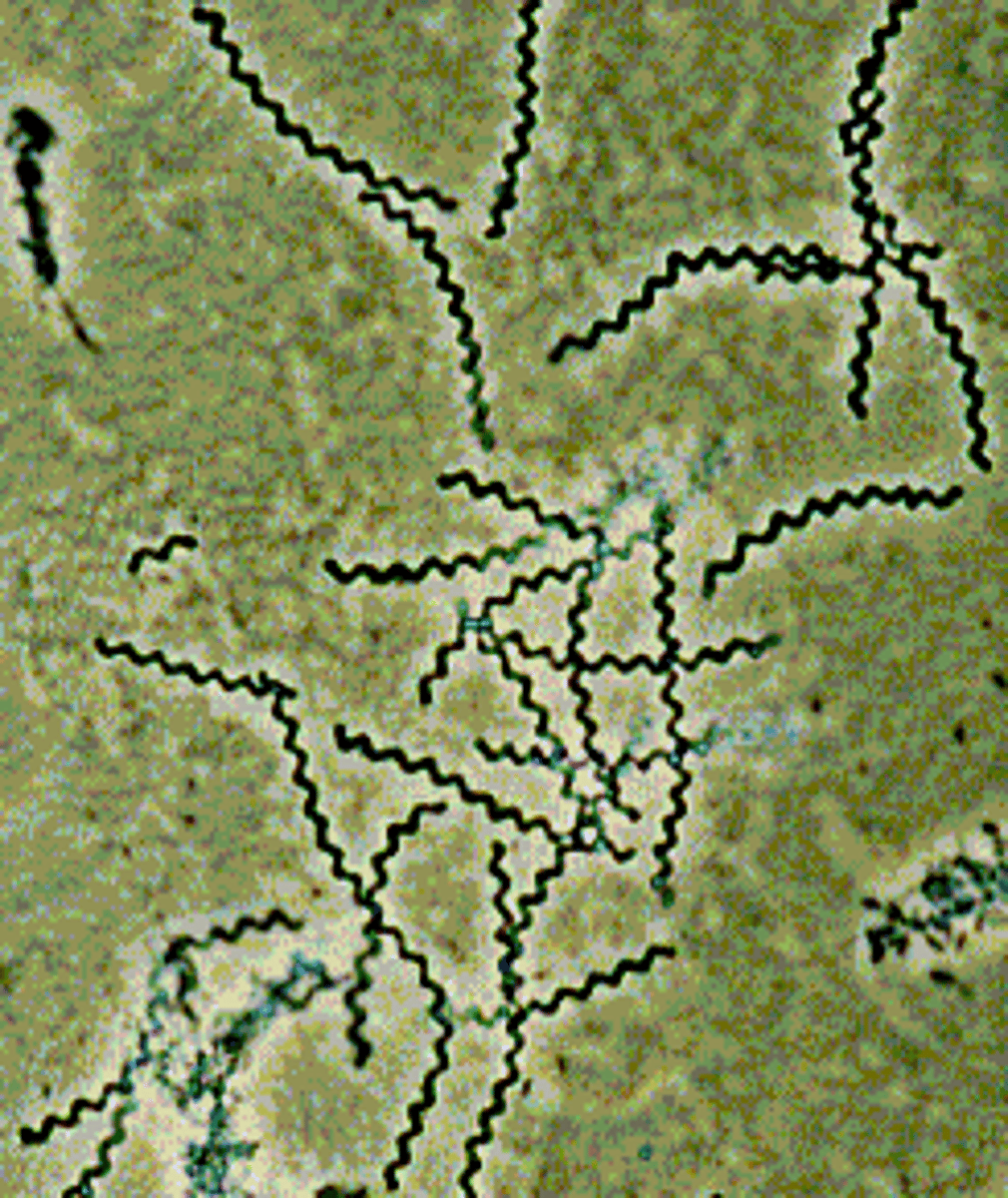
branching filaments
multiple branches off a basic rod structure
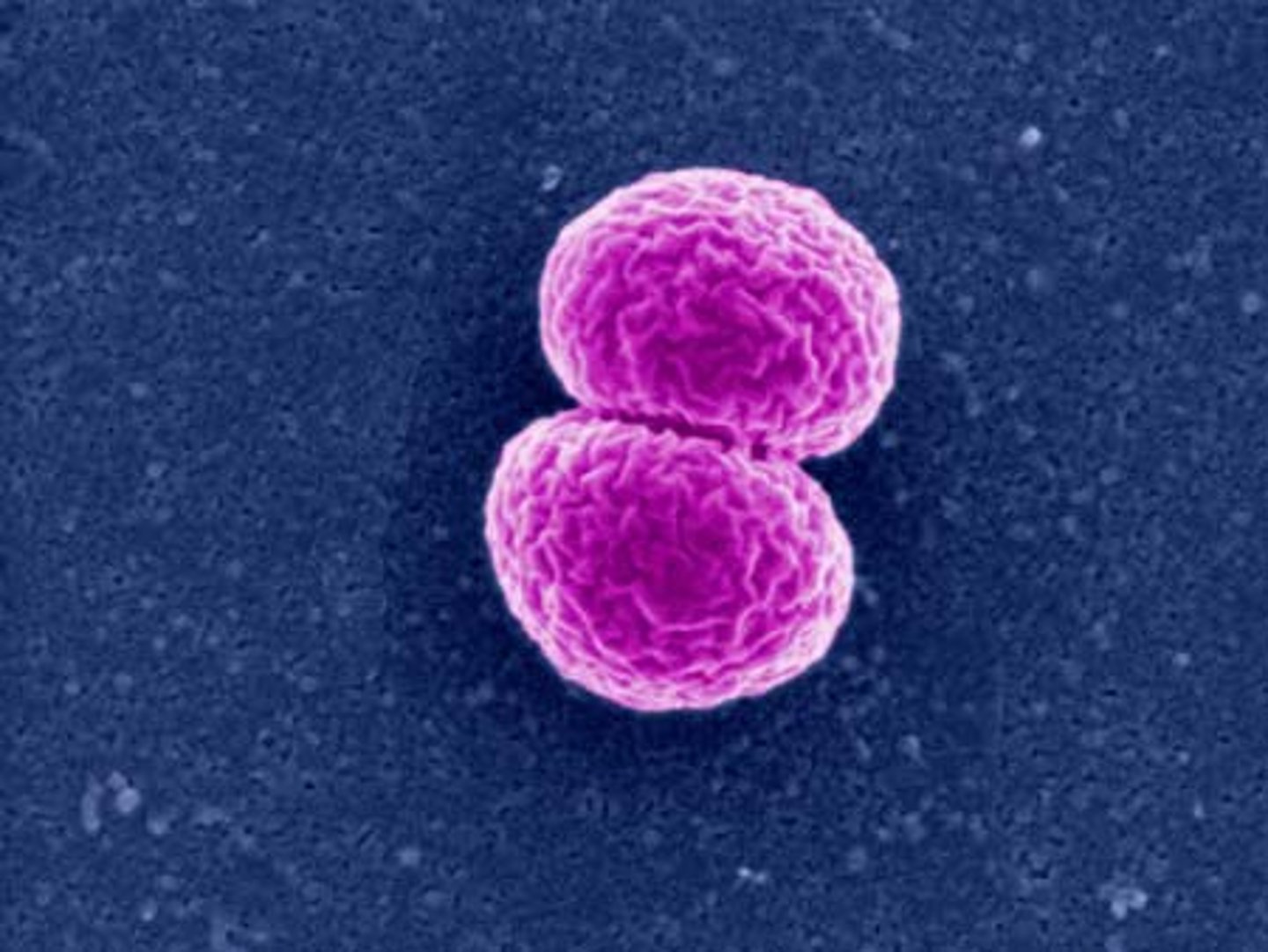
diplo
double
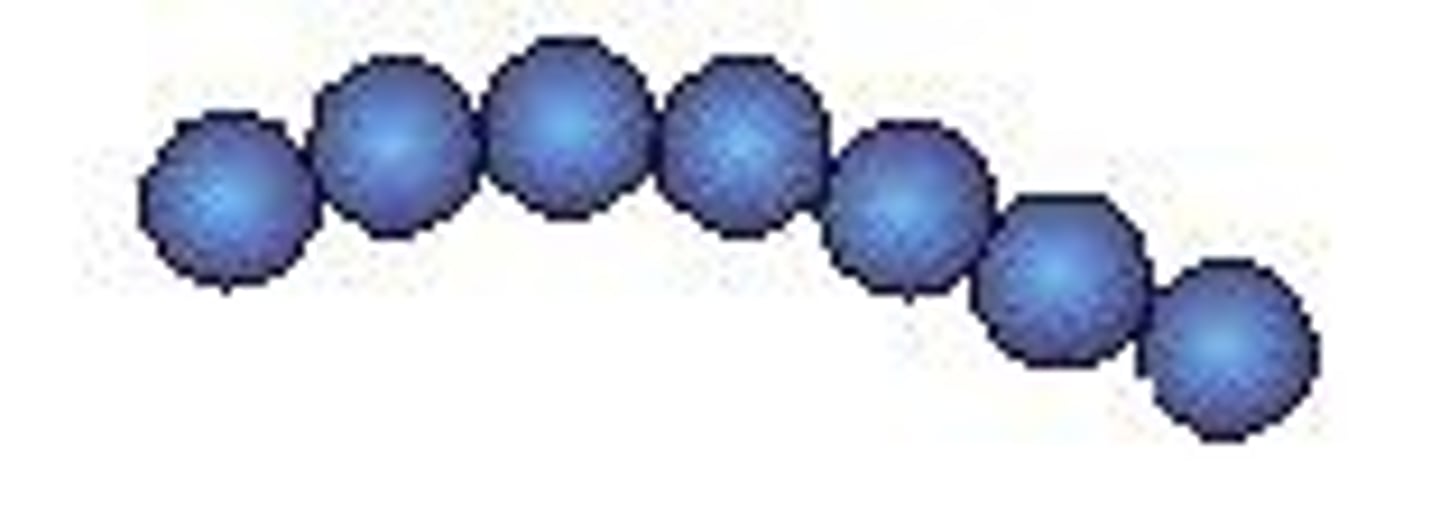
strepto
twisted chains; streptococci
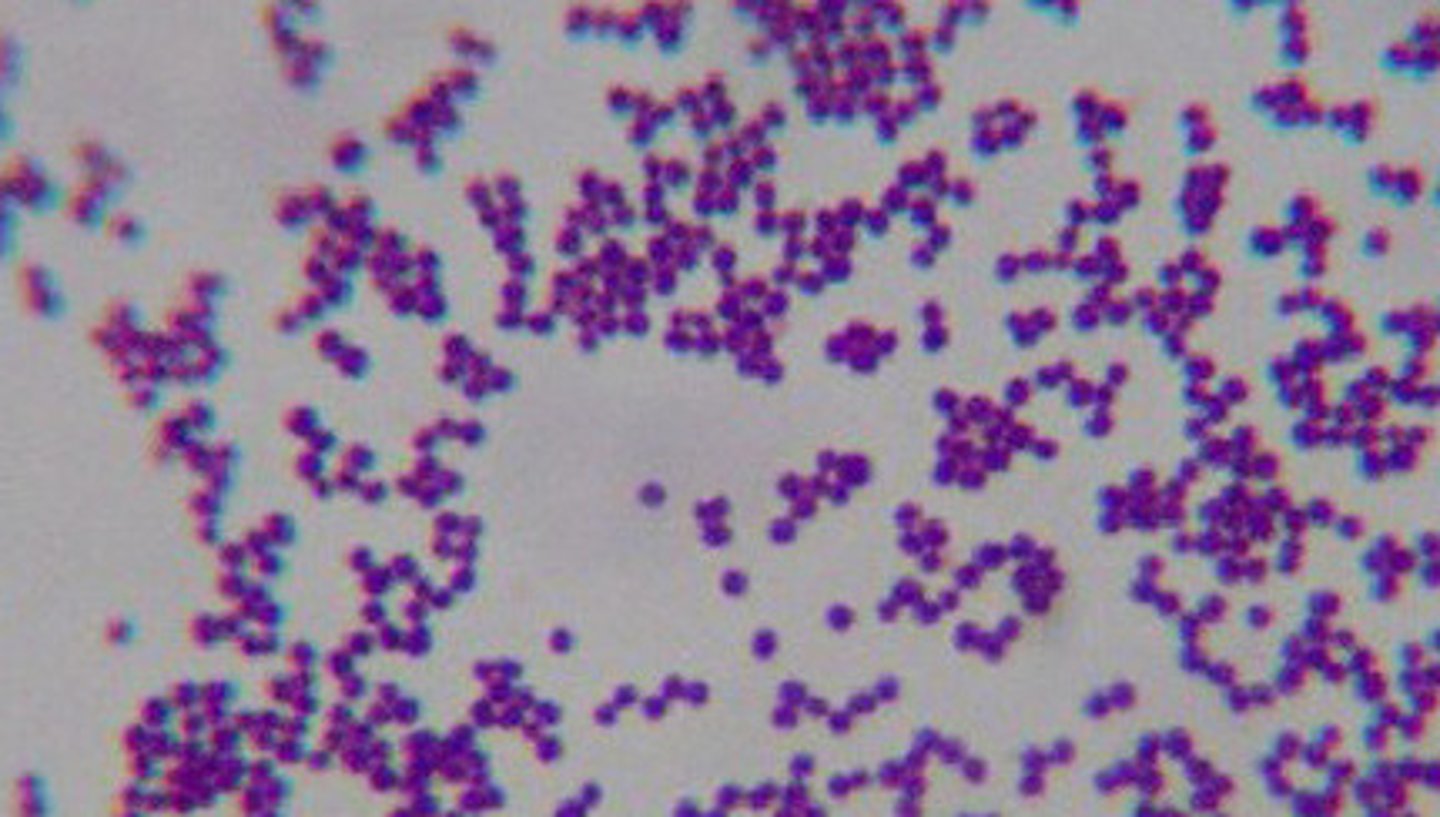
Staphylococcus aureus
a form of staphylococci that commonly infects wounds and causes serious problems such as toxic shock syndrome or produces food poisoning
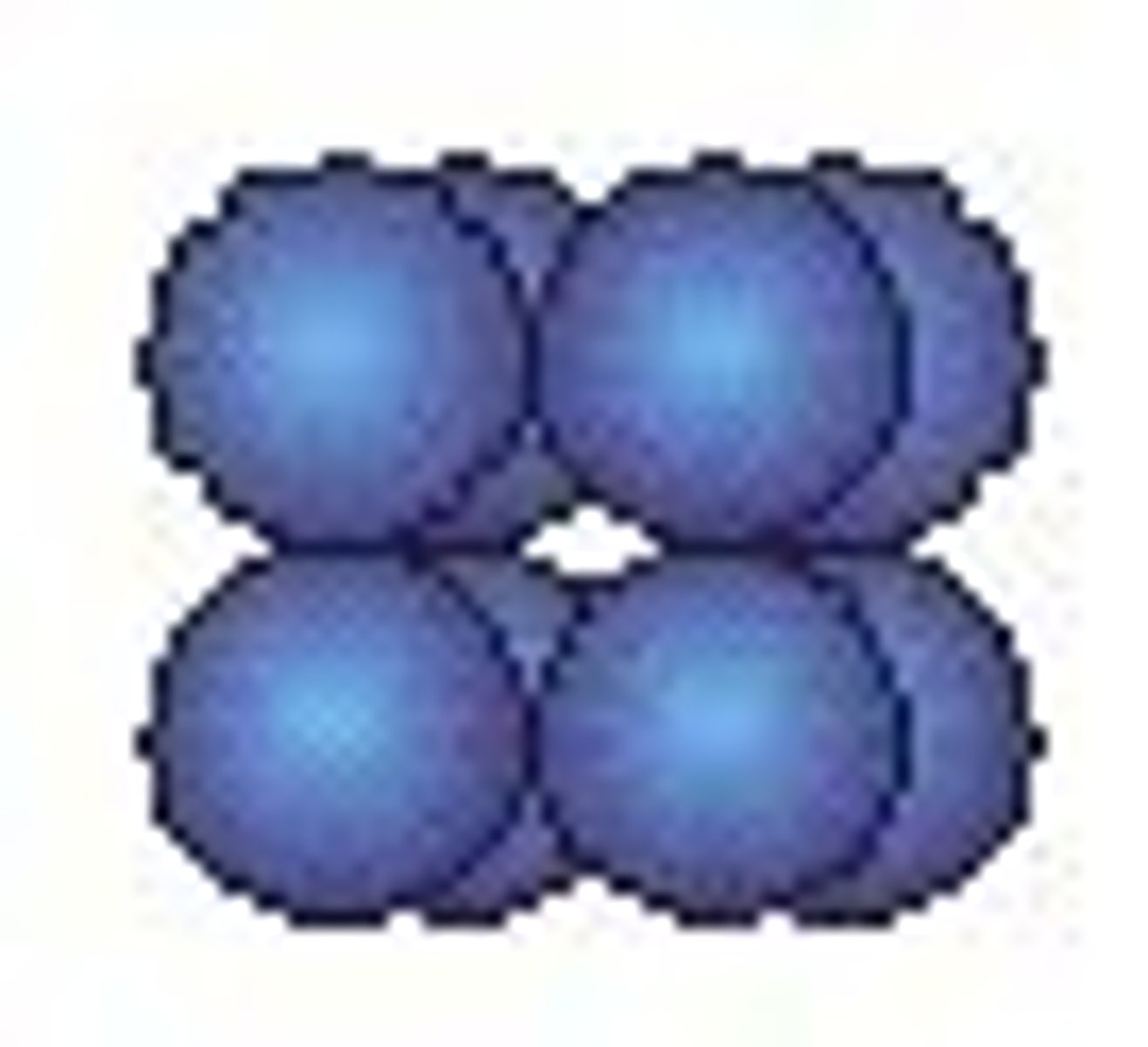
sarcina
cubical packet of 8, 16, or more cells
Tetrad
structure containing 4 chromatids that forms during meiosis

Palisade
a fence made of stakes
What are the two major groups of extracellular structures in bacteria?
Flagella and Axial Filaments; provide motility. Fimbriae and Pili help attachment points and channels
Flagella
whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
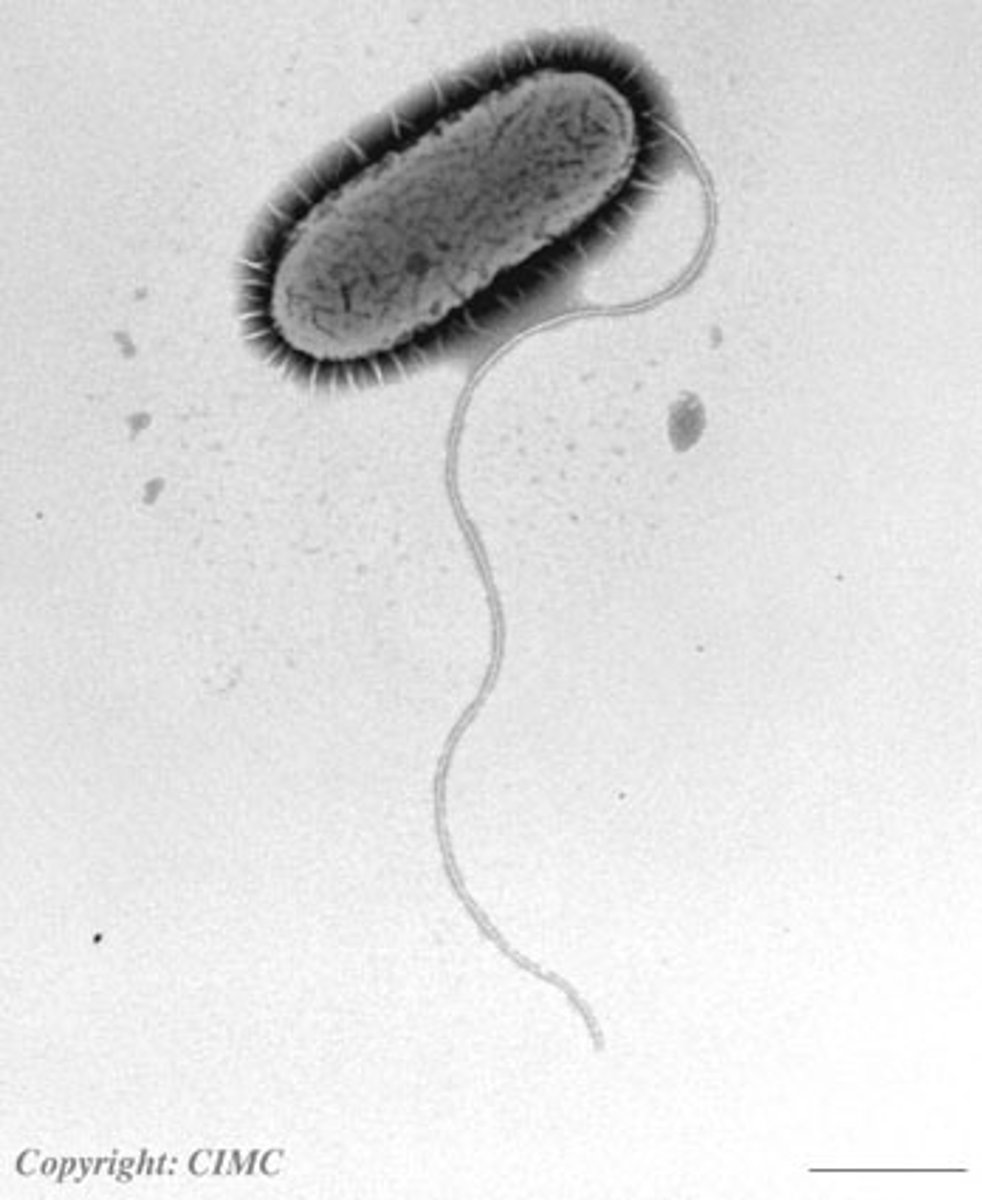
axial filaments
-also called endoflagella. -in spirochetes. -anchored at one end of a cell. -rotation causes cell to move
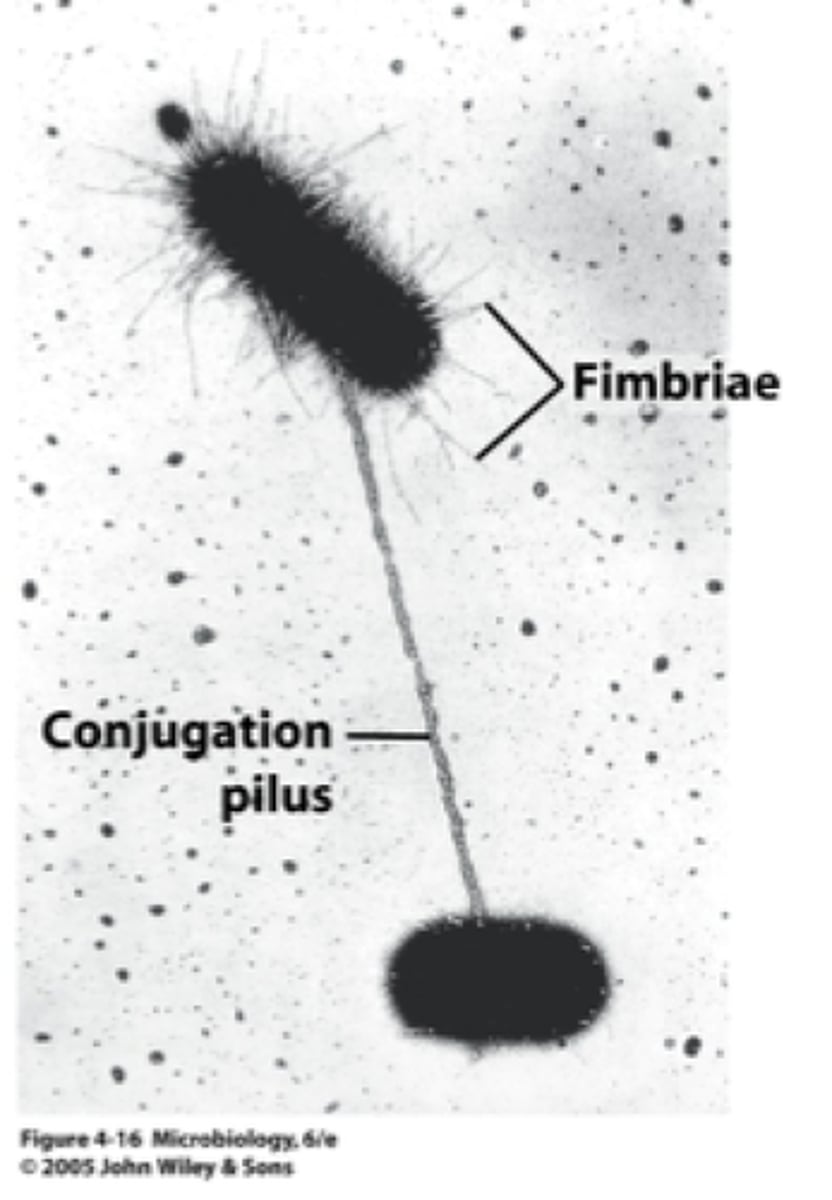
Fimbriae
finger or fringe like projections at the end of the fallopian tubes
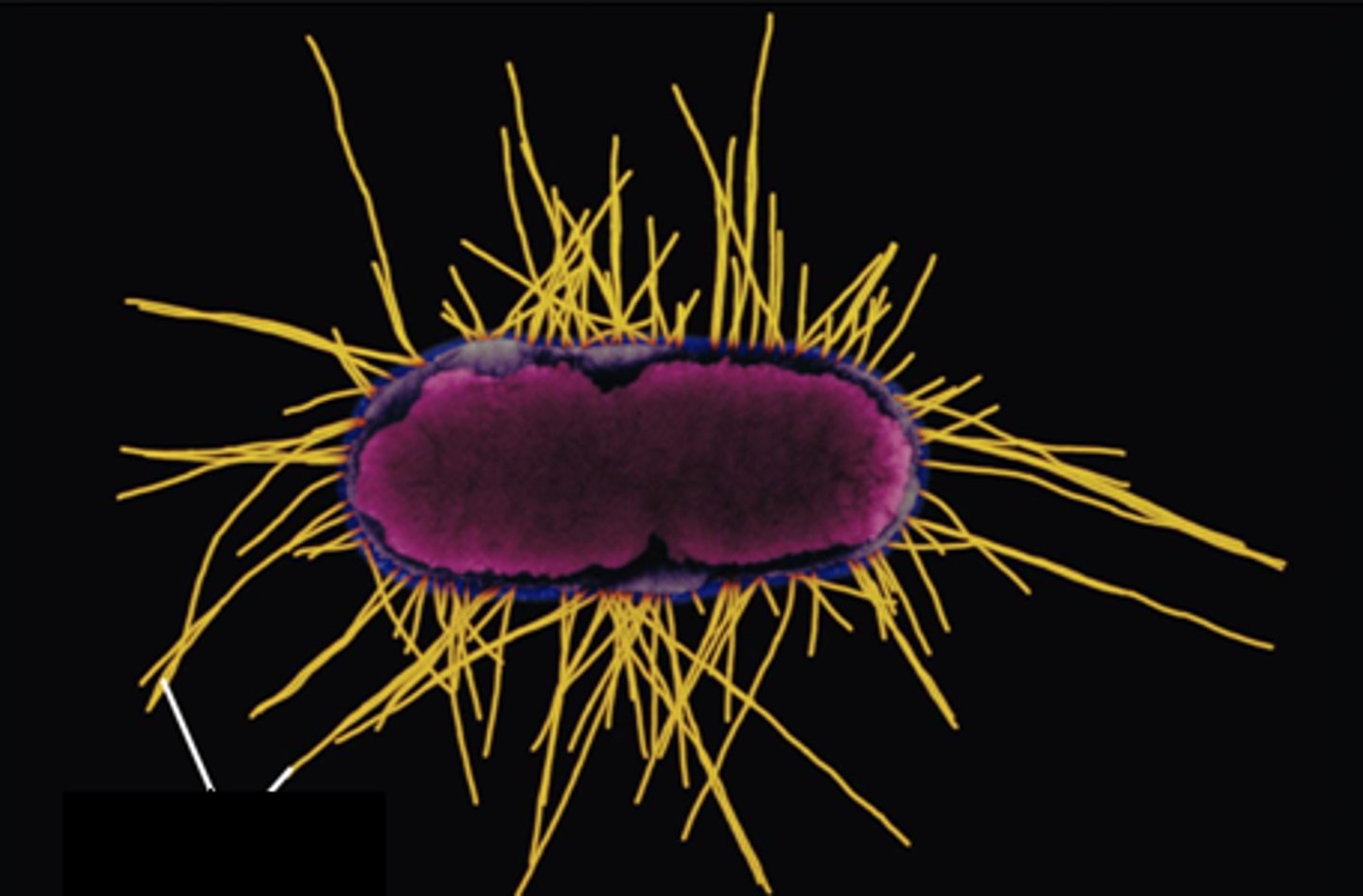
Pili
Appendages that allow bacteria to attach to each other and to transfer DNA
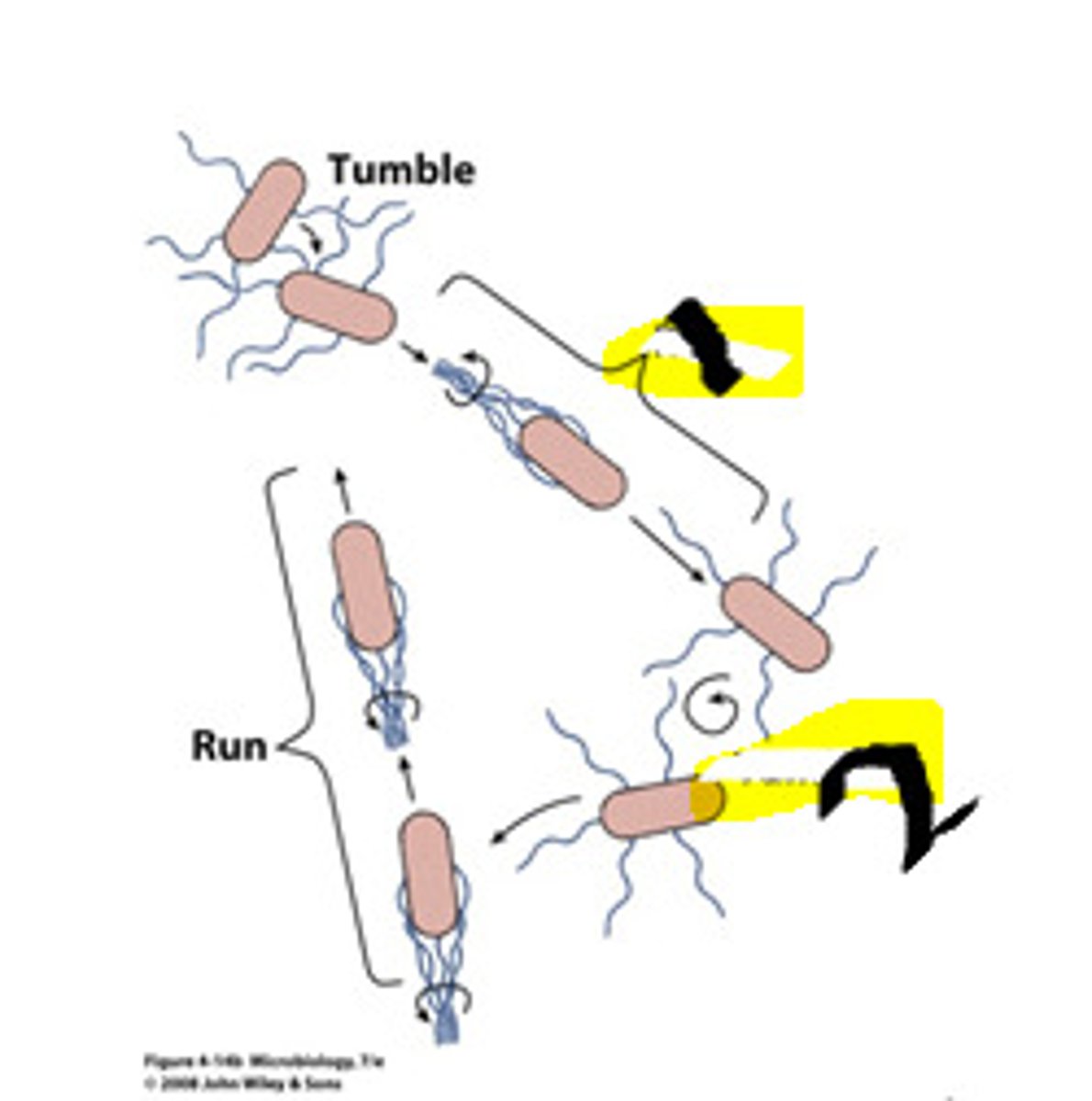
run and tumble motility
flagella can move forward and backward.
-backward = random movement
-have receptors to tell it where to go
Positively chemotaxis
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism towards a higher concentration of a chemical.
Negatively chemotaxis
occurs when there is lower concentration of chemicals
positive phototaxis
movement towards light
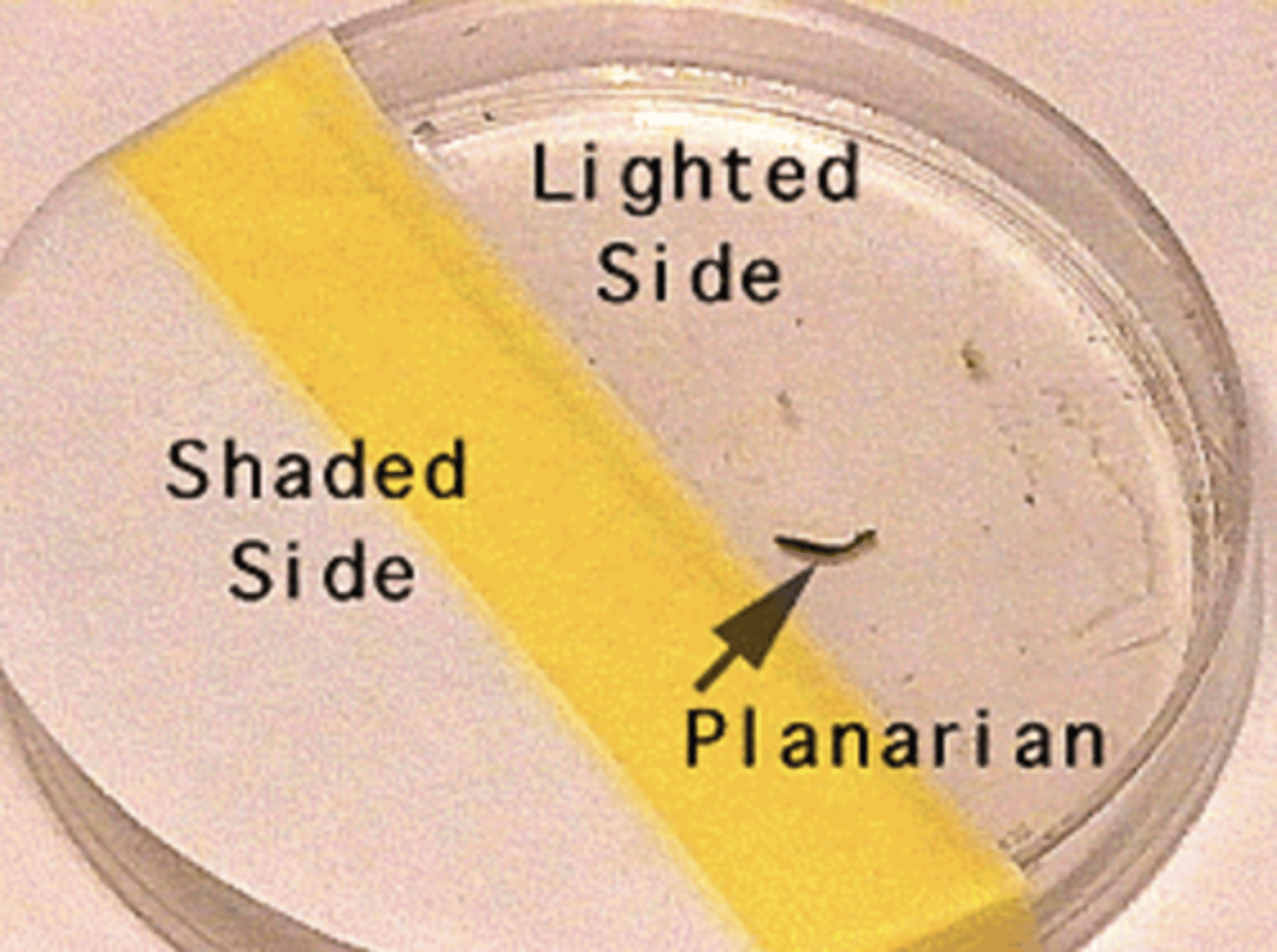
negative phototaxis
movement away from light
Compare and contrast s layers and capsules/glycocalyces.
A slime layer is loosely associated with the bacterium and can be easily washed off, whereas a capsule is attached tightly to the bacterium and has definite boundaries. The glycocalyx is a sticky, gelatinous material that forms outside of bacteria's cell wall. A layer on top of the existing one. A capsule is formed when this layer has tightly adhered to the cell's surface. The glycocalyx is called a slime layer when it is dispersed randomly
How can you visualize if a bacterium has a capsule?
the best way to visualize them is to stain the background using an acidic stain and to stain the cell itself using a basic stain.
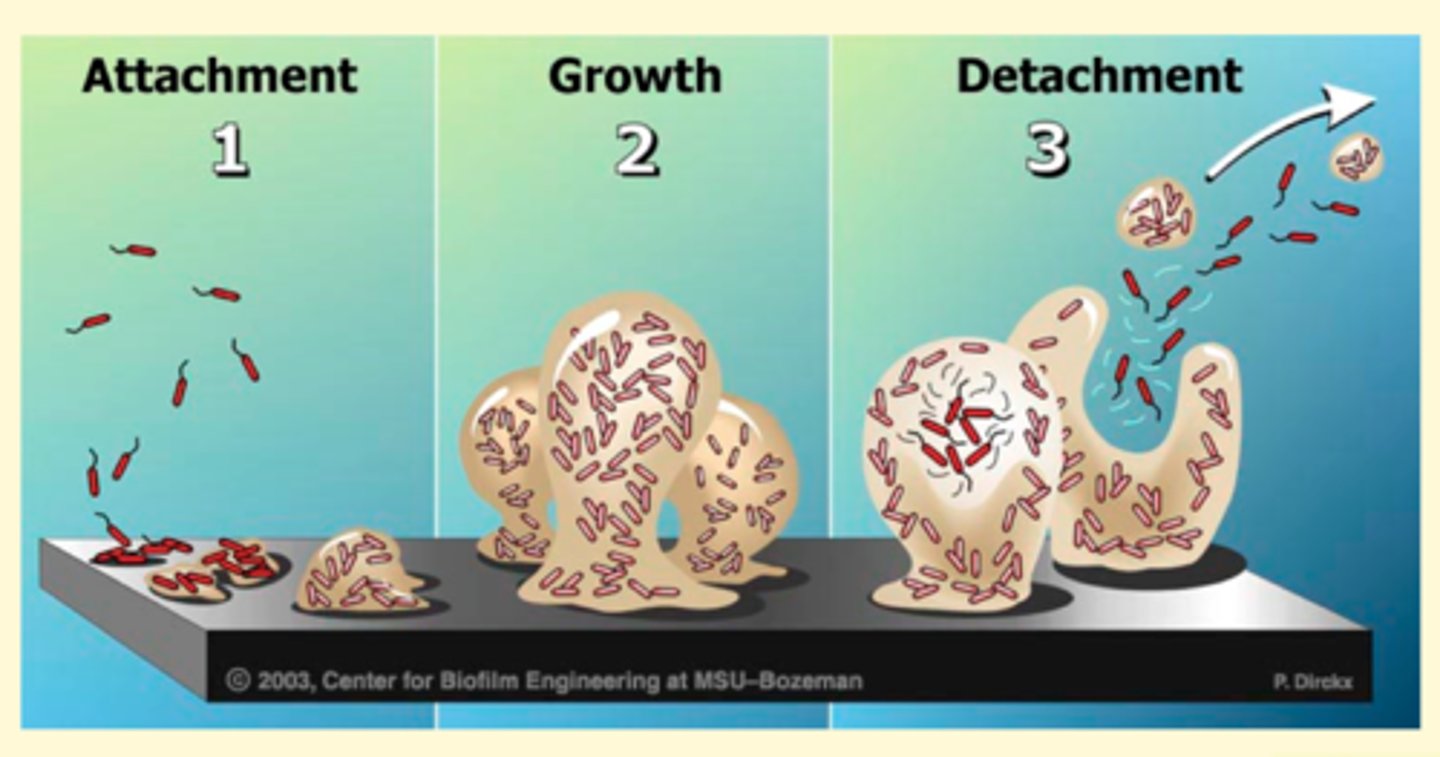
formation of biofilm
A "pioneer" colonizer initially attaches to a surface.
Other microbes then attach to those bacteria, or a polymeric sugar or protein substance secreted by the microbial colonizers.
Attached cells are stimulated to release chemicals as the cell population grows.
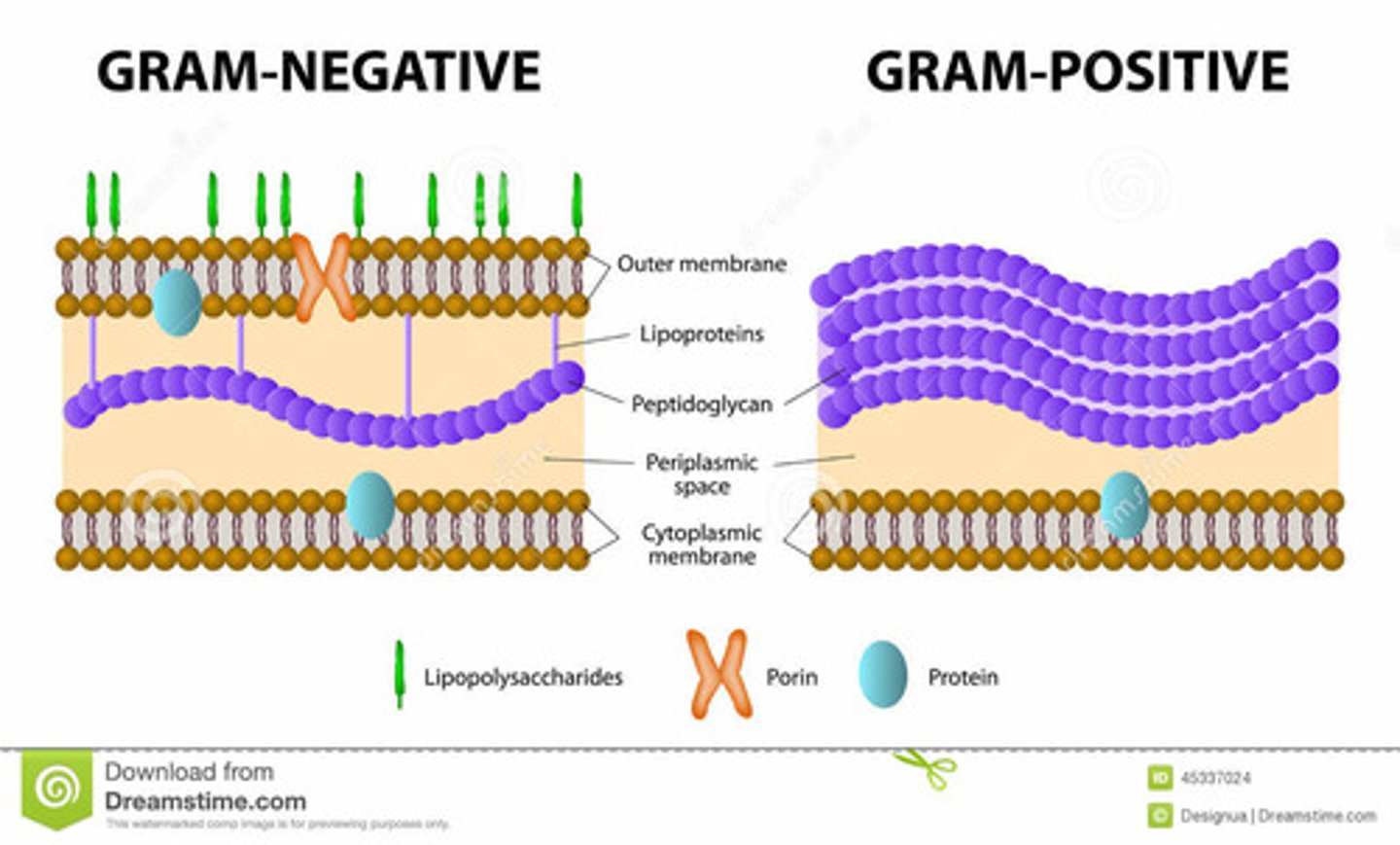
cell envelope (gram negative)
Three Layers: Thin outer layer
-Cell wall
-Cytoplasmic membrane
-Outer membrane
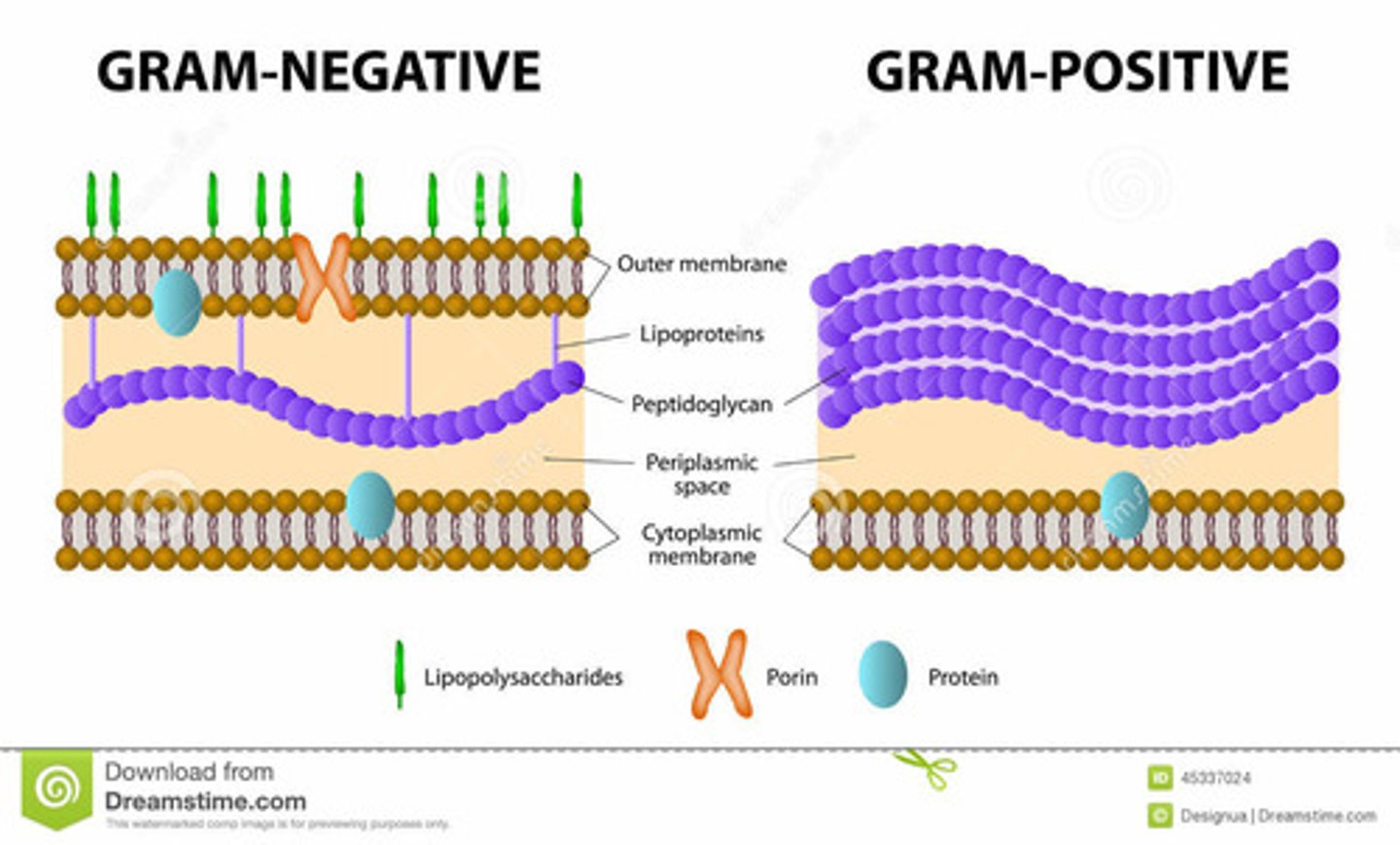
cell envelope of gram positive
Two Layers: Thick outer layer
-Cell wall
-Cytoplasmic membrane
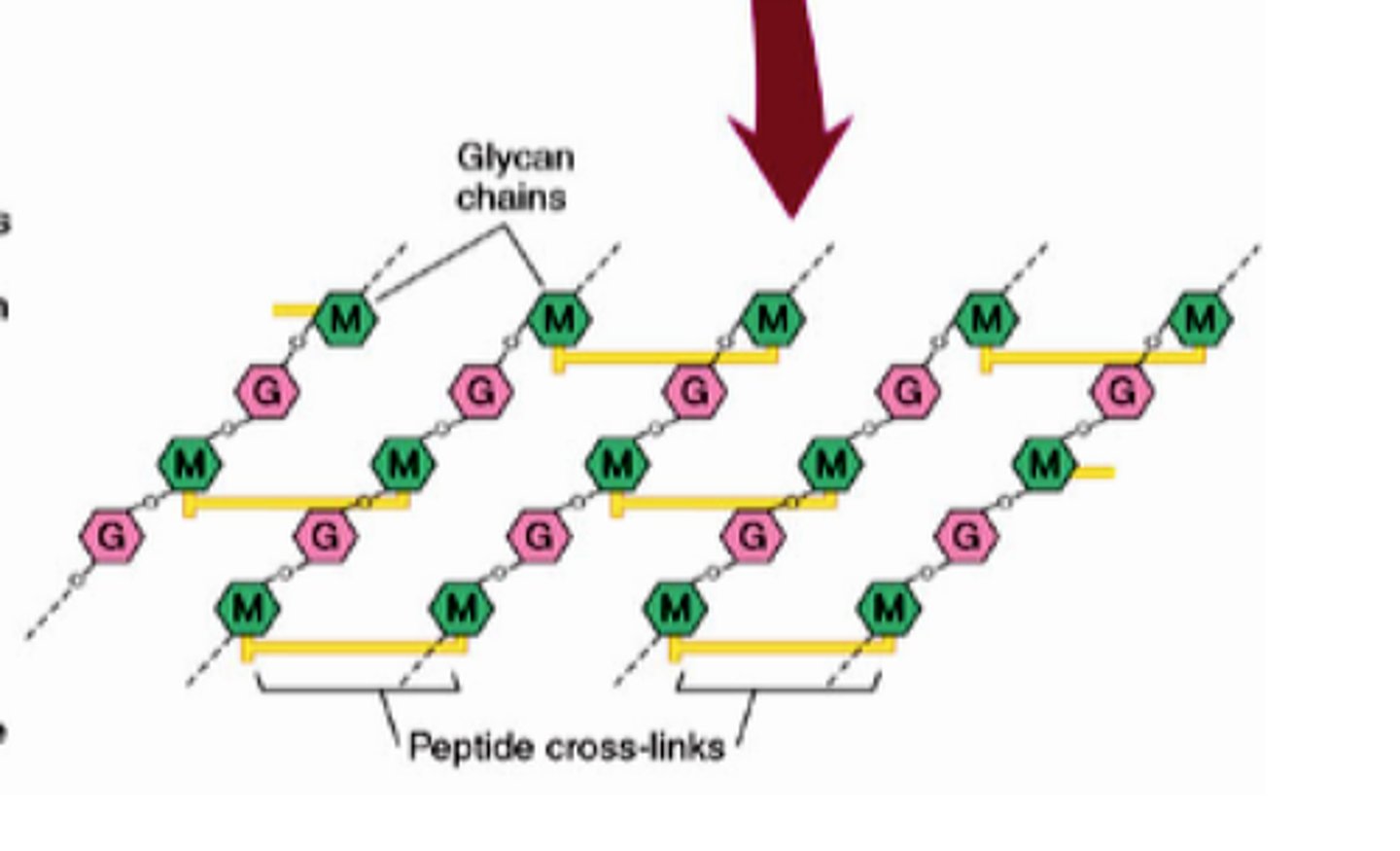
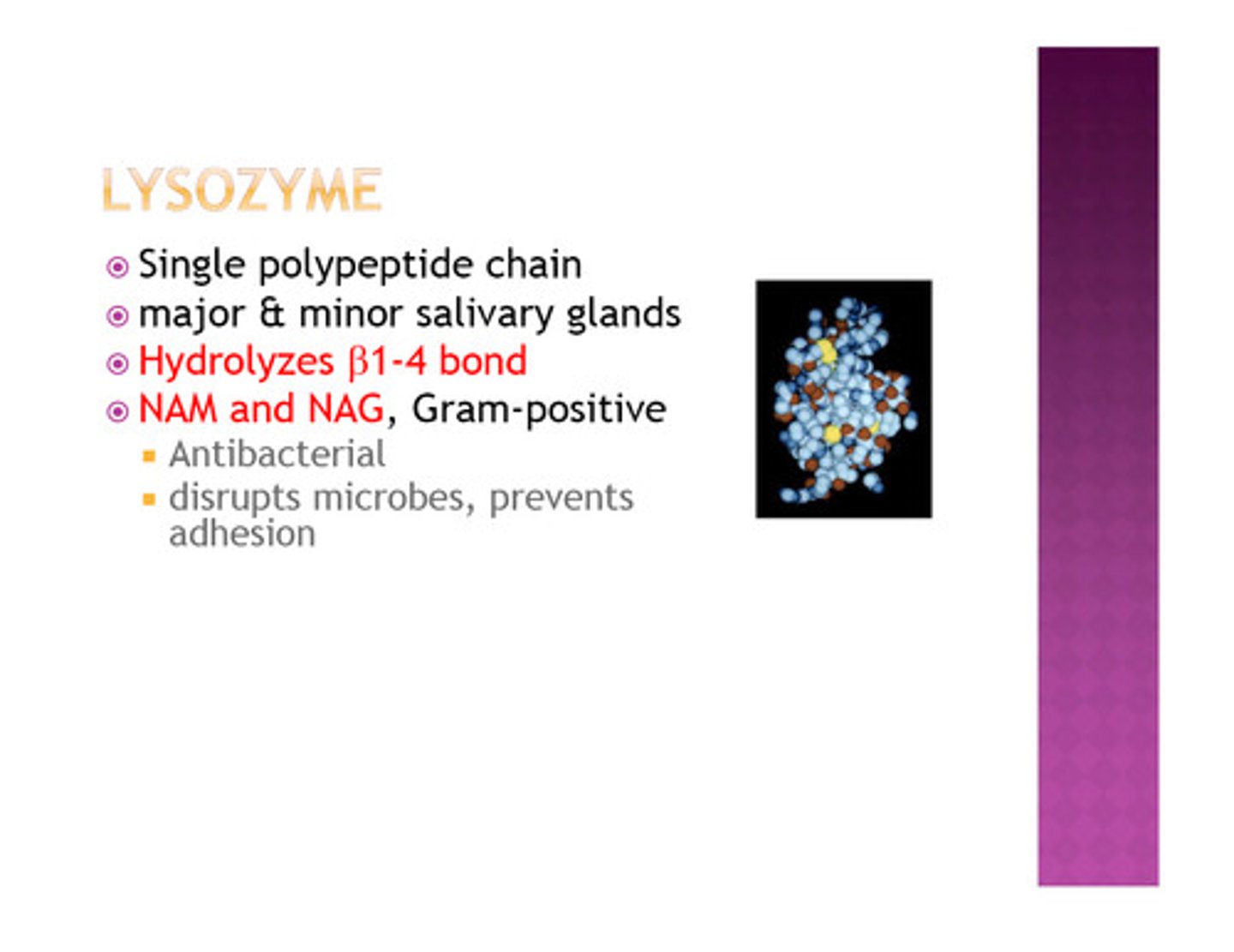
Structure of peptidoglycan
Polysaccharide chain made up of two sugars NAG and NAM linked through glycosidic bonds and then cross-linked by peptide bridges to produce a strong lattice structure
Antibiotic that targets peptidoglycan
penicillin
Enzyme that digests peptidoglycan
lysozyme
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.

Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
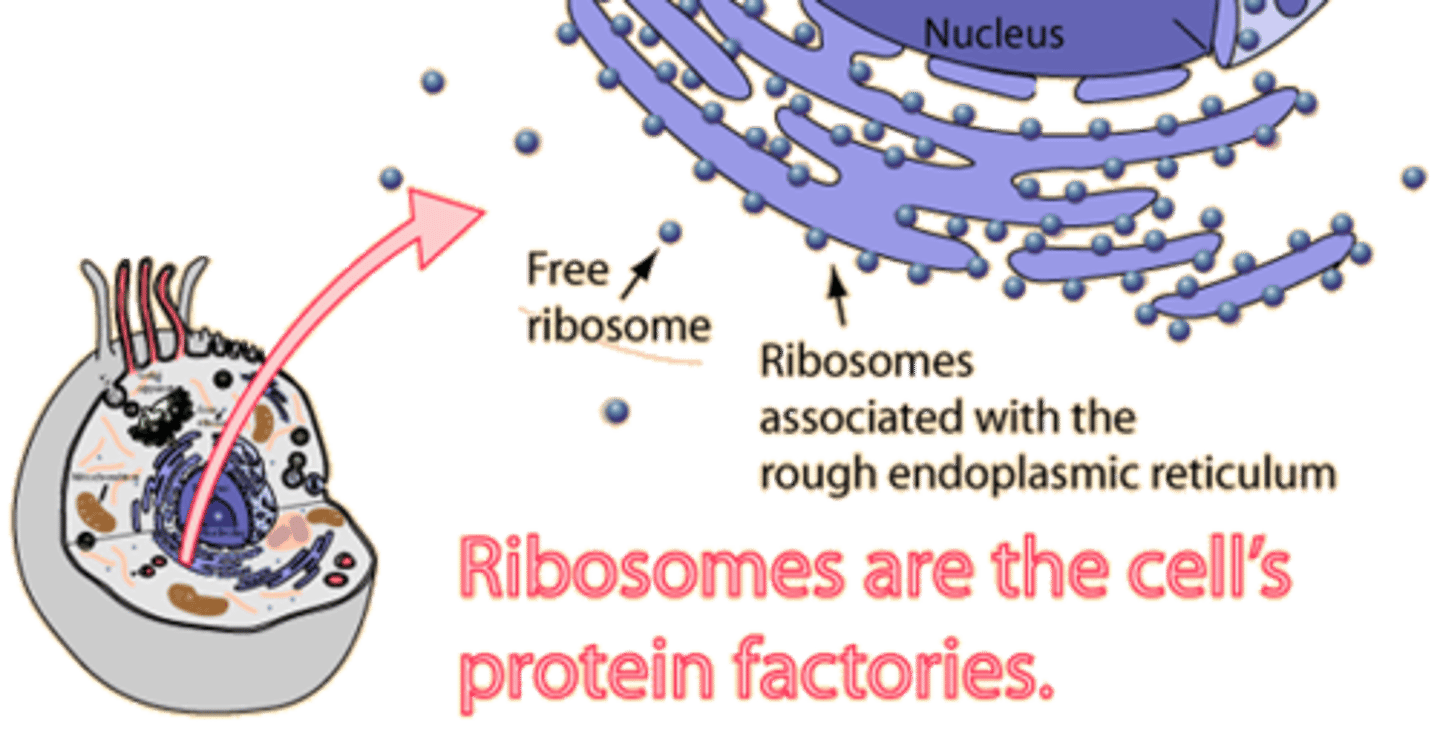
Ribosomes
protein synthesis
inclusion bodies
compacted masses of viruses or damaged cell organelles in the nucleus and cytoplasm
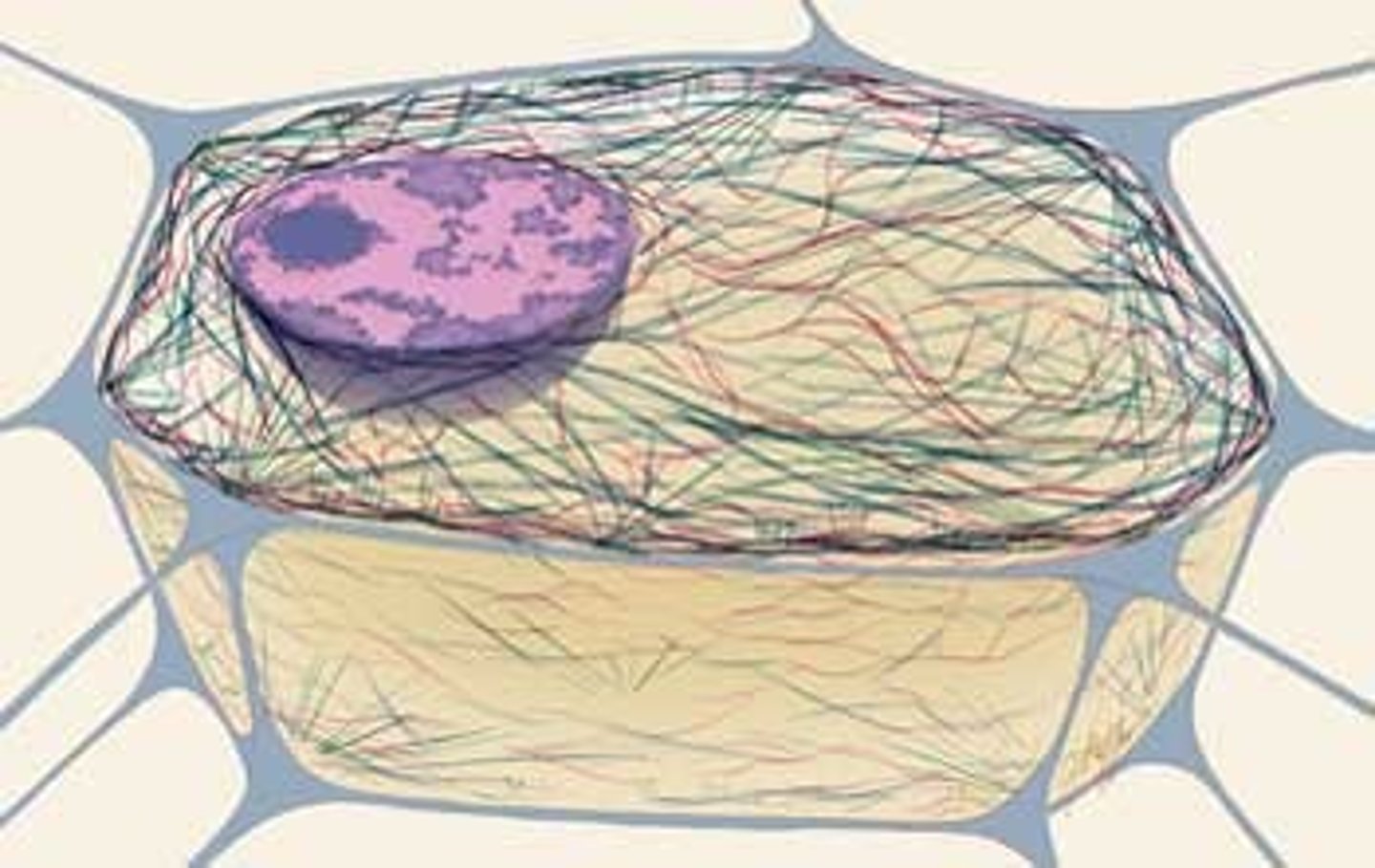
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
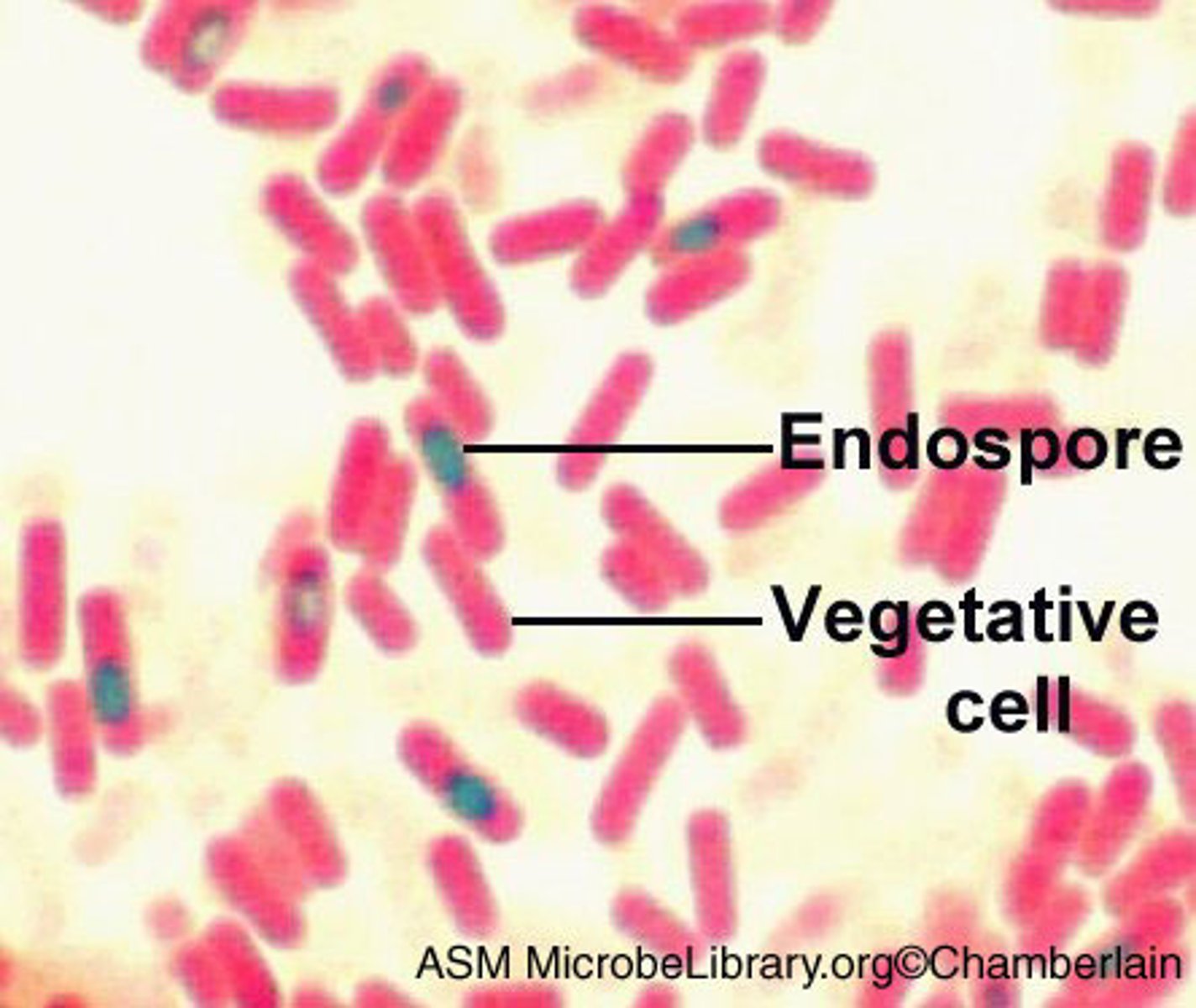
Endospore
A thick-walled protective spore that forms inside a bacterial cell and resists harsh conditions.
extremophiles
Archaea that live in extreme environments.

Methogens
prokaryotes that produce methane gas that live in oxygen free environments
Halophiles
"salt-loving" archaea that live in environments that have very high salt concentrations

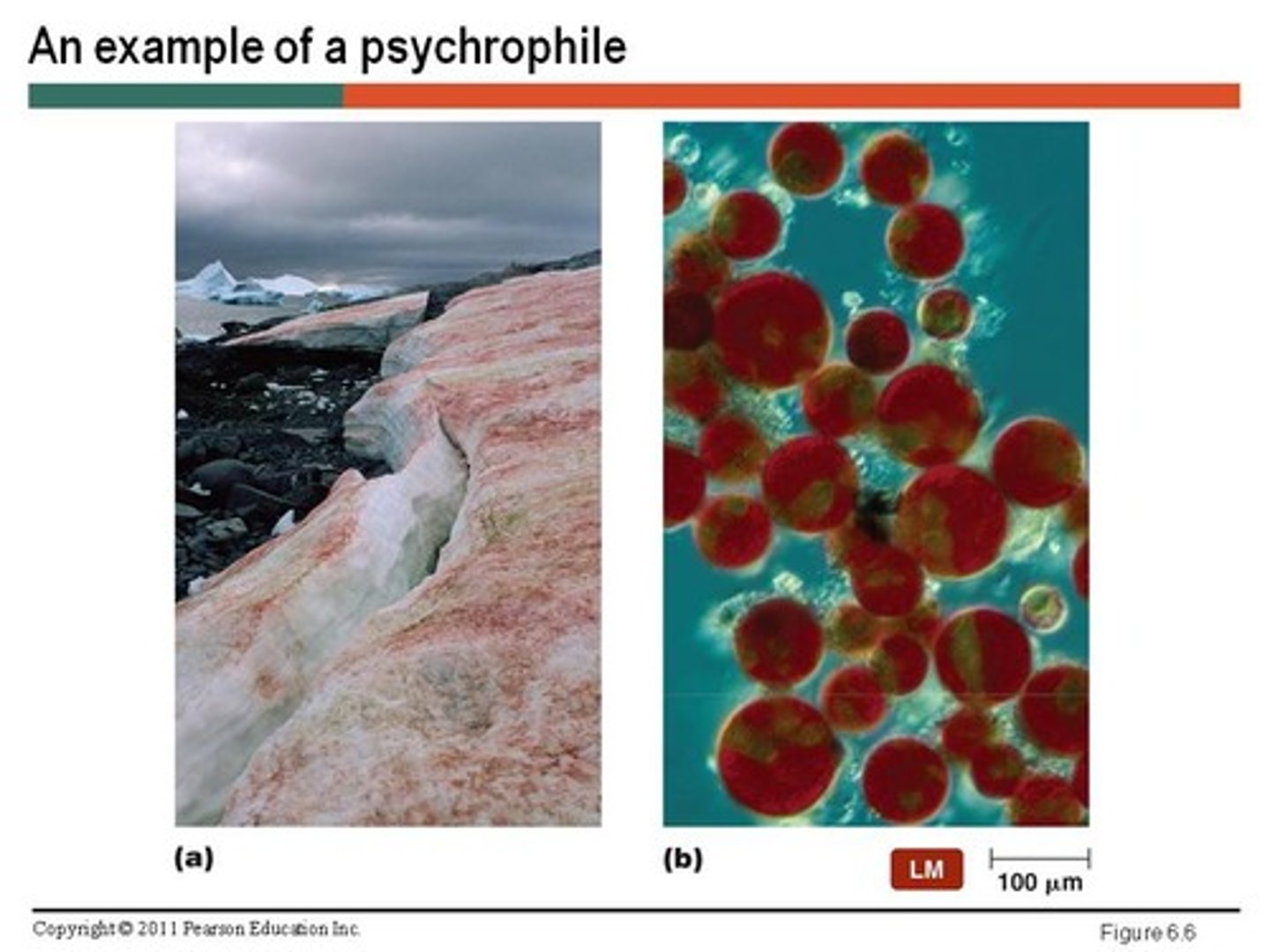
Psychrophiles
cold-loving microbes
Hyperthermophiles
Organisms that grow in extremely high temperatures (90 degrees C)

Domains of life
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
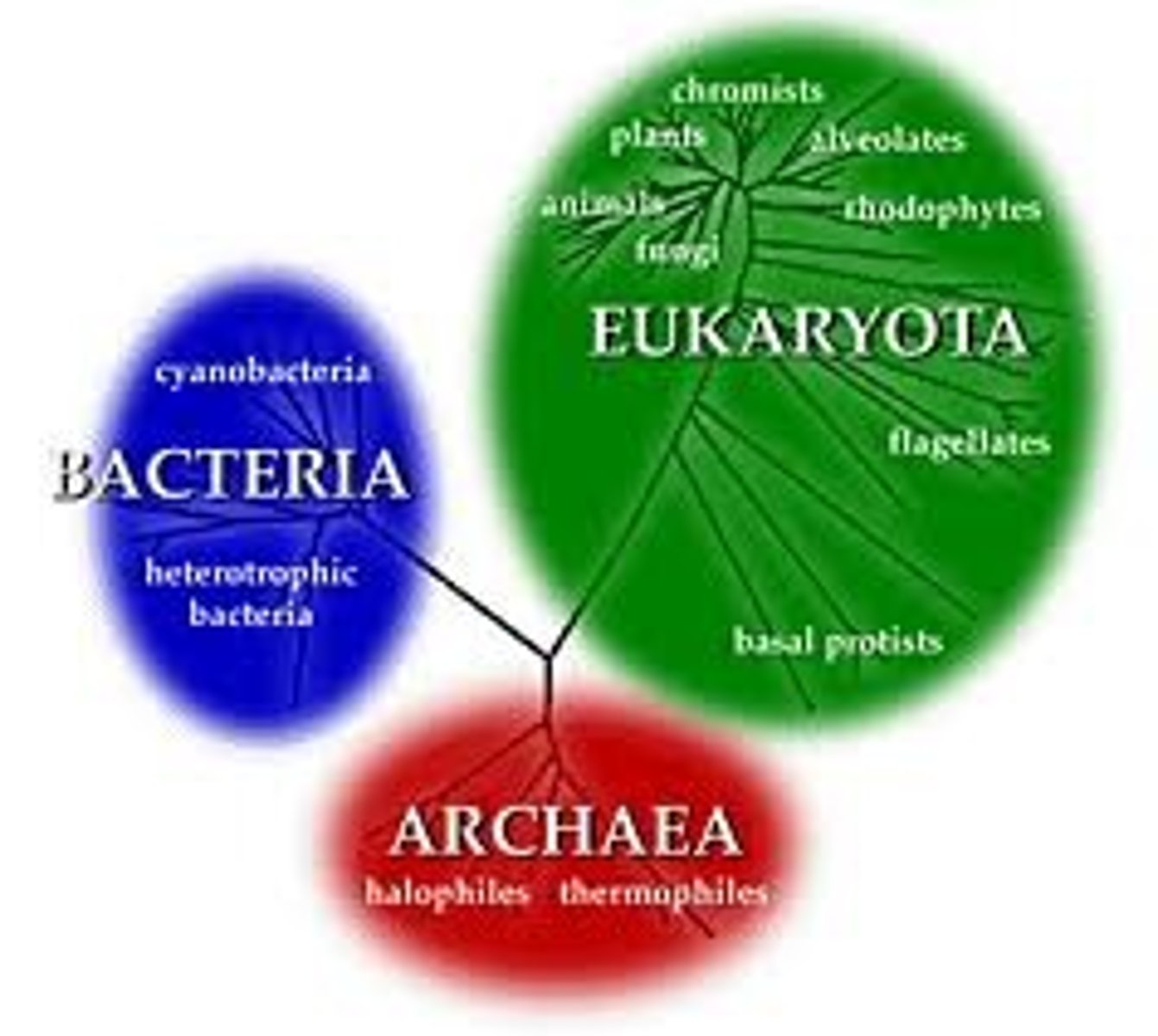
What domain is most closely related to eukarya ?
Archaea
bacterial strain
subgroup of a bacterial species that has distinguishing characteristics
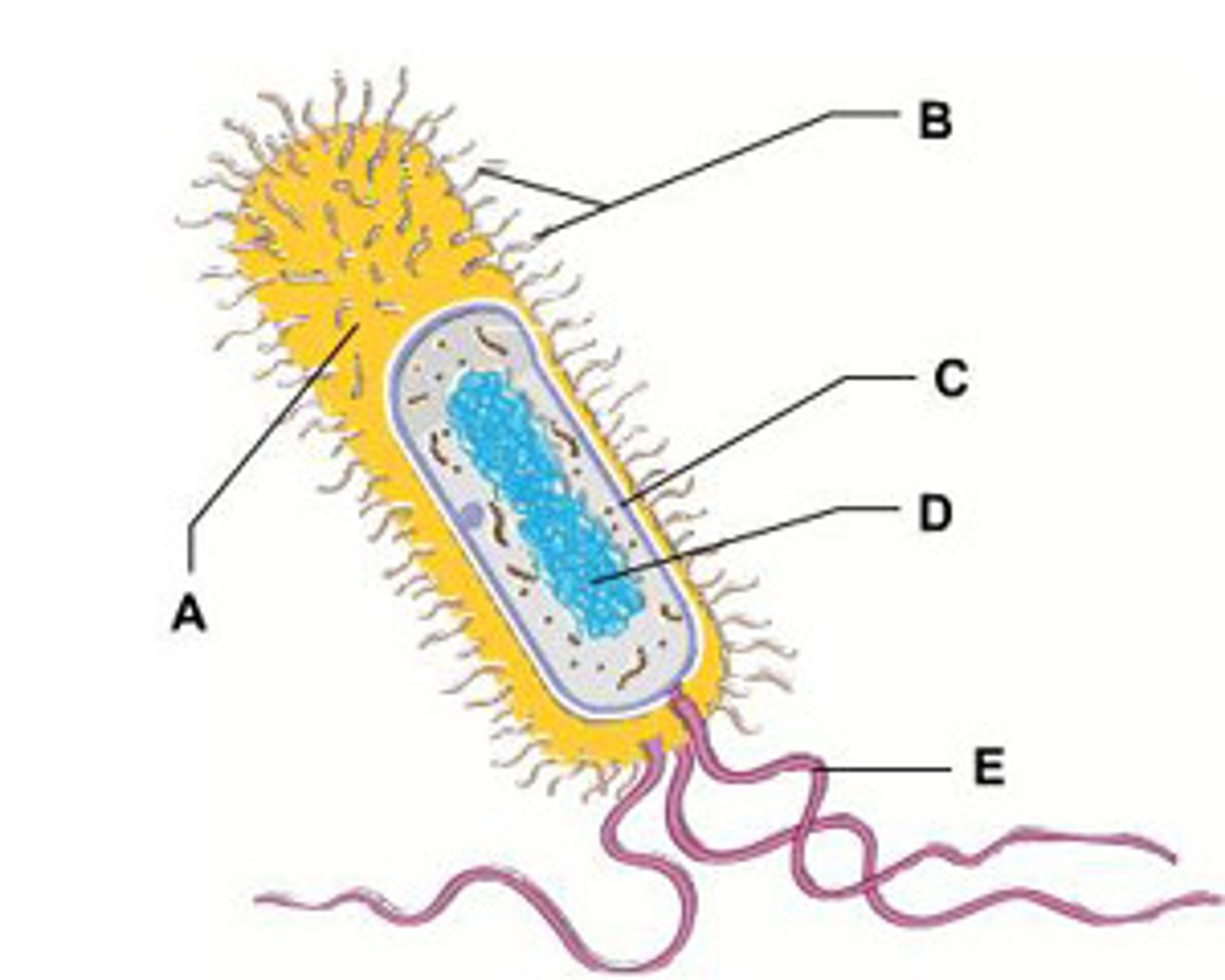
bacterial species
A collection of bacterial cells which share an overall pattern of similar traits