Chapter 1: The Scientific Method
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Order
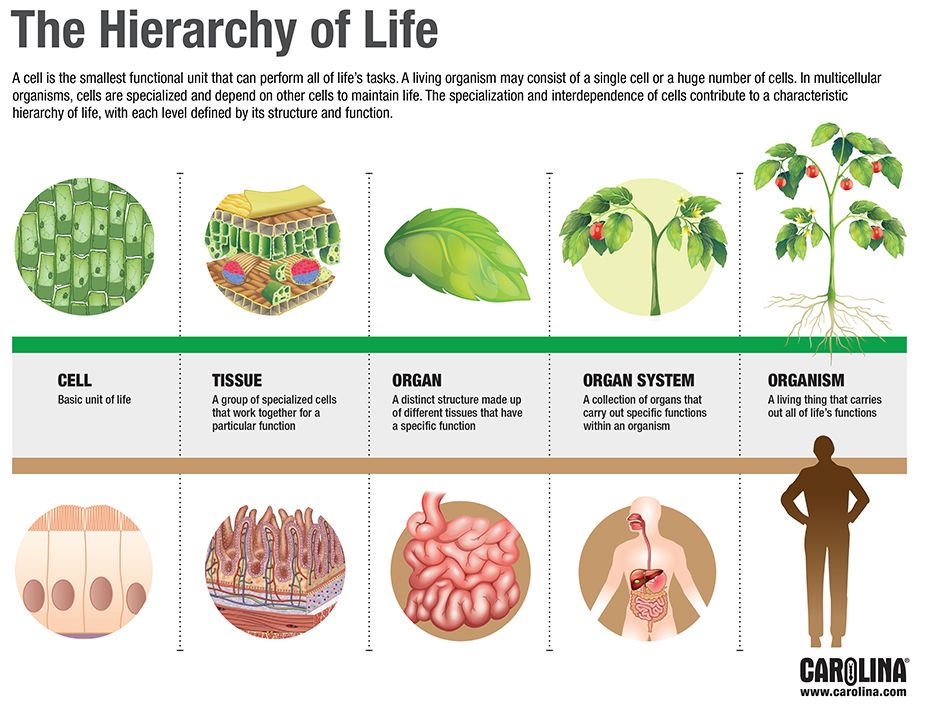
Organisms are highly organized structures that consist of one or more cells.
Multicellular organisms have an advantage over single-celled organisms since their cells can be specialized to perform specific functions.
Atoms —> molecules —> cells —> tissues —> organs —> organ systems —> organism
Response to Stimuli
Living organisms detect and respond to changes in their environment, such as light, heat, sound, and chemical/mechanical contact.
Example: Plants can bend toward a source of light or respond to touch
Positive Response
Movement toward a stimulus
Negative response
Movement away from a stimulus
Reproduction
The process by which organisms produce new individuals, passing DNA to offspring.
Single-celled organisms reproduce by first replicating their DNA, and then divide it equally to form two new daughter cells; While multicellular organisms produce specialized reproductive cells to form offspring.
Adaptation
The ability of an organism to evolve and develop favorable traits for survival in its environment.
Driven by natural selection or survival of the fittest
Adaptations enhances an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce
Growth and Development
The process of cell division and differentiation leading to the formation of an adult organism.
Organisms grow and develop along a specific sequence based on the instructions present in their genes.
Regulation/Homeostasis
Mechanisms that maintain a stable internal environment necessary for life.
All organisms require regulatory mechanisms to coordinate internal functions.
Cells require appropriate conditions, such as proper temperature, pH, and concentration of diverse chemicals.
Energy Processing
The use of energy from various sources for metabolic activities in an organism.
Example: Organisms, like autotrophs, perform photosynthesis to convert sunlight into chemical energy that they can use as a source of food.
Evolution
The process by which species change over time due to mutations and natural selection.
Mutations allow organisms to adapt to environmental changes, helping them to become well suited for their environment and give them a better chance at survival.
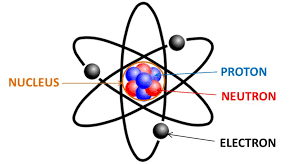
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element.
Consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons
Atoms form molecules
Molecule
A chemical structure consisting of at least two atoms bonded together.
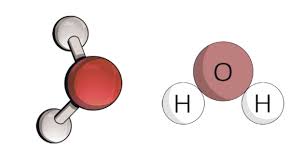
Macromolecule
These are the most important molecules biologically.
They are large molecules that are formed by combining smaller units called monomers.
Example: DNA is a macromolecule that contains instructions for an organism’s functioning that contains it.
Organelles
Specialized structures within cells that perform specific functions.
They are aggregates of macromolecules, surrounded by membranes
Cell
The smallest fundamental unit of structure and function in living organisms.
Prokaryotes
Single-celled organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles, and do not have nuclei surrounded by nuclear membranes.
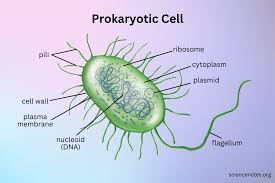
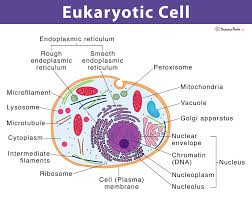
Eukaryotes
Organisms that have membrane-bound organelles and nuclei.
Tissues
Groups of similar cells working together to perform a specific function.
In most multicellular organisms, cells combine to make tissues.
Organs
Collections of tissues grouped together based on a common function.
Present in both animals and plants
Organ System
A higher level of organization consisting of functionally related organs.
Example: The circulatory system includes multiple organs like the heart and blood vessels.
Organisms
Individual living entities, including single-celled and multicellular forms.
Single-celled organisms are considered as microorganisms.
Example: Each tree in a forest is an organism.
Population
All individuals of a species living in a specific area.
Example: A forest may include many white pine trees; all of these pine trees represent the population of white pine trees in this forest.

Community
The set of populations inhabiting a particular area.
Example: All of the trees, flowers, insects, and other populations in a forest form a community.
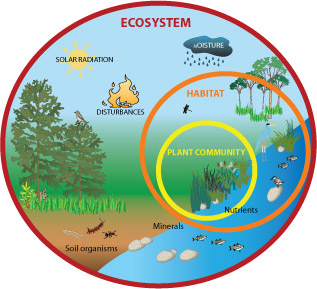
Ecosystem
All living things (biotic) and nonliving things (abiotic) in an environment, such as nitrogen in the soil or rainwater.
Biosphere
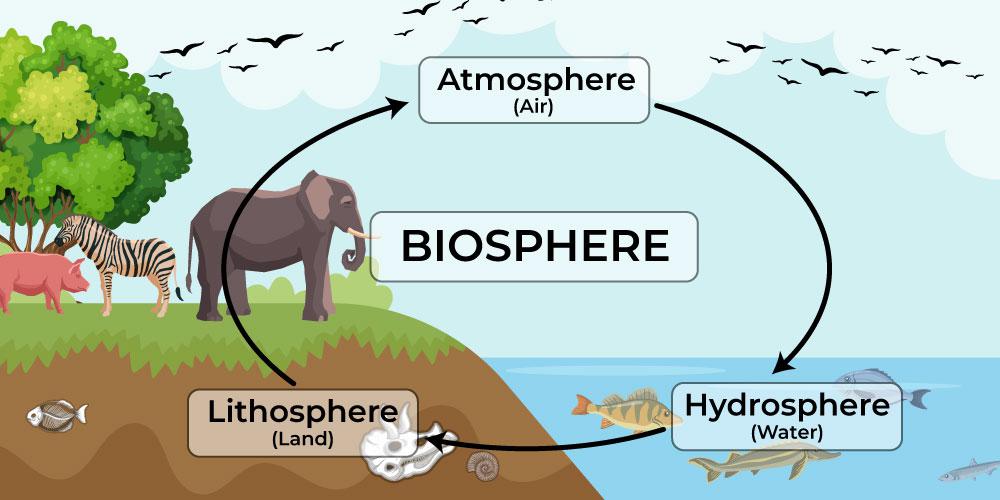
The collection of all ecosystems, representing the zone of life on Earth.
Highest level of organization
Includes land, water, and portions of the atmosphere.
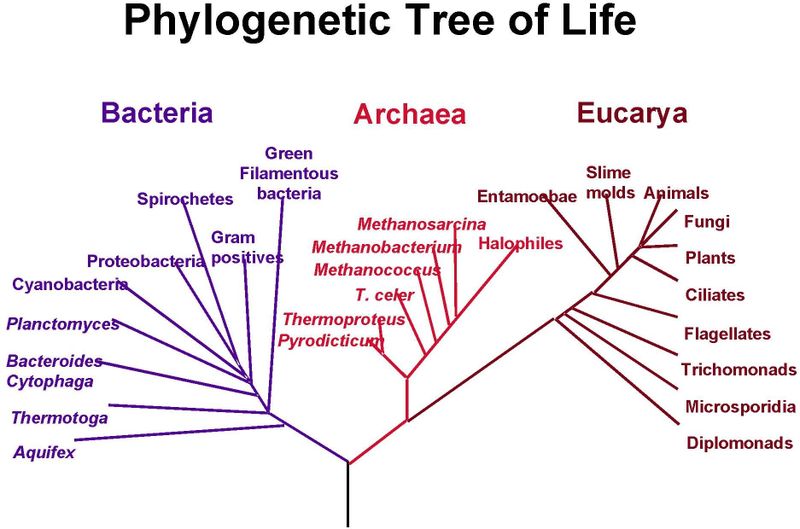
Domains
The three major classifications of life: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
Further divided into kingdoms, phylum, class, order, genus, and species
Example: Humans are a part of Eukarya
Binomial Naming System
A scientific method of naming organisms using genus and species names.
The first letter of the genus is capitalized and specie name is all lowercase.
Underline when writing and italicize when typing.
Example: The scientific name for humans is Homo sapiens.
Scientific Method
A systematic approach to generating knowledge through observation and experimentation.
Helps to answer questions based on observations and logical reasoning in our findings.
Validates data to support conclusions.
Hypothesis
A testable and falsifiable explanation for a phenomenon.
Steps of the Scientific Method (9 Steps)
Make observations.
Ask questions.
Create a hypothesis that is testable/falsifiable.
Make a prediction (specific expectation) (if-then statement).
Collect data for testing hypothesis.
Conduct an experiment with: A control group (placebo) and experimental group (actual treatment), large study, random assignment of subjects, and double-blind.
Analyze results.
Conclusion.
Publication after being peer-edited and repeated testing.
Scientific Theory
An explanation supported by extensive evidence and repeated testing.
Variables
Any part of an experiment that can change or vary.
Independent Variable
The variable that is manipulated or tested in an experiment.
Example: Blood pressure drug
Dependent Variable
The variable that is measured in response to changes in the independent variable.
Example: Blood pressure measurement
Control Variable
A variable that remains constant throughout an experiment.
Example: Age of subjects, health status, etc.
Graphs and Data
Visual diagrams that help you interpret data.
X-axis (horizontal) includes the independent variable.
Y-axis (vertical) includes the dependent variable.
Natural Sciences
Fields of science related to the physical world and its phenomena.
Astronomy, chemistry, computer science, biology, etc.
Life Sciences
The study of living organisms, primarily biology.
Physical Sciences
The study of nonliving matter, including fields like chemistry and physics.
Applied Science
The use of scientific knowledge to solve real-world problems.
Example: Finding a cure for a disease, development of vaccine, etc.