Super Important Core IB Physics Knowledge (Topics 1-8)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:27 PM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
1
New cards
Work
The transfer of energy, measured in joules. W = ΔE
2
New cards
Power
The rate of the transfer of energy, measured in joules per second. P = ΔE/Δt
3
New cards
Unit definition of a Watt
1 W = 1 J/s (Joule per second)
4
New cards
Unit definition of a Volt
1 V = 1 J/C (Joule per Coulomb)
5
New cards
Formula for the weight of an object
W = mg (AKA Fg = mg, only works on Earth's surface)
6
New cards
Internal energy
Total random kinetic and potential energy of the particles in a substance
7
New cards
Specific heat capacity
Energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 K
8
New cards
Defining property of SHM
Acceleration is proportional to negative displacement (proportional to displacement and restorative)
9
New cards
What type of wave is sound?
Longitudinal
10
New cards
Resistance
Ratio of potential difference across a device to current through the device (R=V/I) (NOT a gradient!)
11
New cards
Emissivity
Ratio: Power radiated by an object per unit area / Power radiated per unit area by a black body at the same temperature
12
New cards
Potential Difference
Work done per unit charge in moving a charge between 2 points in an E field (1 V = 1 J/C)!
13
New cards
Velocity vs. time graph - how do you find acceleration?
Gradient (slope of the tangent line)
14
New cards
Velocity vs. time graph - how do you find displacement?
Area under the curve
15
New cards
Moderator
Slows neutrons in a fission reactor to allow further reactions to take place (water is a common moderator)
16
New cards
Heat
Thermal energy (Q), measured in Joules - can be transferred between two objects in thermal contact until they reach thermal equilibrium
17
New cards
Most used energy source overall
Oil
18
New cards
Specific energy
Energy per unit mass for a fuel source
19
New cards
Mass defect
Difference between the mass of a nucleus and the total mass of its individual nucleons
20
New cards
Efficiency of a coal power plant
30-35%
21
New cards
How do you place an ammeter in a circuit, and what is its resistance?
In series, 0
22
New cards
Transverse wave
Particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave
23
New cards
Free fall
Gravitational force is the only force acting on an object
24
New cards
Renewable energy
Rate of consumption < rate of production
25
New cards
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocity (a = Δv/Δt, AKA dv/dt) (definitely NOT v/t)
26
New cards
Energy density
Energy per unit volume for a fuel source
27
New cards
Energy density
Energy per unit volume for a fuel source
28
New cards
Electric field strength
Electric force per unit charge at a point in space, on a small test charge
29
New cards
What provided evidence for atomic energy levels?
Emission / absorption spectra
30
New cards
What's an alpha particle?
Helium nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutrons)
31
New cards
State Newton's Second Law
The resultant (net) force on an object is equal to its rate of change of momentum (F \= ∆p/∆t)
32
New cards
State the law of conservation of momentum
Momentum in a system does not change unless a net external force acts on the system
33
New cards
Albedo
Fraction / percent of incoming radiation that is reflected back into space
34
New cards
Define 1 electron volt, and state its value
The energy gained by an electron moving through a potential difference of 1 volt (1 eV \= 1.6 x 10^-19 J)
35
New cards
Gravitational field strength
Gravitational force per unit mass at a point in space on a small test mass
36
New cards
How do you place a voltmeter in a circuit, and what is its resistance?
In parallel, infinite resistance
37
New cards
What type of wave is light?
EM wave/Transverse wave (electromagnetic wave)
38
New cards
Charge of an alpha particle
+2e
39
New cards
Elastic collision
Momentum AND kinetic energy are conserved
40
New cards
Most used energy source in electrical energy generation
Coal
41
New cards
Unified atomic mass unit (u)
1/12 the rest mass of carbon-12 in its ground state
42
New cards
Rank the 3 fossil fuels in order of increasing efficiency
Coal < Oil < Natural gas
43
New cards
Control rods
Moveable rods that absorb neutrons to control the rate of the fission reaction in a nuclear reactor
44
New cards
When do you get constructive interference?
When 2 waves meet in phase at a point in space / When the path difference is n*(wavelength)
45
New cards
emf of a battery
The work done by the battery per unit charge in powering the entire circuit, including the energy dissipated as heat inside of the battery due to its internal resistance. (Stands for electromotive force, but it's not a force!!)
46
New cards
Polarization
Direction of oscillation of the E field in an EM wave
47
New cards
State Newton's Third Law
When two bodies A and B interact, the force that A exerts on B is equal and opposite to the force that B exerts on A
48
New cards
Half-life
Average time taken for half a parent nuclei to decay
49
New cards
Systematic error
Error that skews all data points in the same direction away from the "true" value
50
New cards
Outline the process of the greenhouse effect
\-Solar radiation (mainly visible & UV) passes through the atmosphere
\-Radiation is absorbed by the Earth
\-Earth radiates its own EM radiation as a black body, mainly as infrared
\-Some IR radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases due to RESONANCE
\-GHG re-radiates IR radiation randomly / in all directions
\-Some IR radiation directed back towards the surface of Earth, further heating the planet
\-Radiation is absorbed by the Earth
\-Earth radiates its own EM radiation as a black body, mainly as infrared
\-Some IR radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases due to RESONANCE
\-GHG re-radiates IR radiation randomly / in all directions
\-Some IR radiation directed back towards the surface of Earth, further heating the planet
51
New cards
List the regions of the EM spectrum, low to high frequency
Radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray, gamma
52
New cards
Order of magnitude of the wavelength of visible light
10^-7 m
53
New cards
What macroscopic property of a substance is related to potential energy?
Phase
54
New cards
Define the temperature of a substance
Measure of the average kinetic energy of its molecules
55
New cards
When do you get destructive interference?
2 waves arrive at a point in space out of phase / the path difference is (n + 1/2)*(wavelength)
56
New cards
Photovoltaic cells
Convert light to electrical energy
57
New cards
Optically active substance
Substance (e.g. sugar water) that rotates the plane of polarization of incident polarized light
58
New cards
How do you calculate average velocity?
Total displacement / Total time
59
New cards
Beta particle
Electron (beta minus) or positron (beta plus), charge of -e or +e
60
New cards
Current
Rate of flow of electrical charge, measured in coulombs per second. I \= Δq/Δt
61
New cards
What macroscopic property of a substance is related to kinetic energy?
Temperature
62
New cards
Impulse
The change in momentum of an object (Δp). Equal to the product of net force and duration of collision (Δp \= FΔt)
63
New cards
State Newton's 1st Law
An object will maintain a state of translational equilibrium unless acted upon by a net external force.
64
New cards
Longitudinal wave
Particles oscillate parallel to the direction of propagation
65
New cards
Main use of pumped hydroelectric systems
Store energy for later use (uses gravitational potential energy)
66
New cards
How can you graphically determine impulse?
Area under the curve for a force vs. time graph
67
New cards
Solar constant
Amount of solar energy incident per second on an area of 1 m^2 above Earth's atmosphere that is at right angles to the Sun's rays (~1360 W/(m^2) [in the data booklet!])
68
New cards
Glaciers role in Earth's climate
Reflect incoming light, increase albedo
69
New cards
List the main greenhouse gases
Water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide
70
New cards
Properties of a standing wave
\-Does not transfer energy
\-Has nodes (points of 0 amplitude)
\-All points have different amplitudes
\-Two points are either completely in phase (0°) or completely out of phase (180°)
\-Has nodes (points of 0 amplitude)
\-All points have different amplitudes
\-Two points are either completely in phase (0°) or completely out of phase (180°)
71
New cards
Define random error
Error that causes measurements to skew randomly about the "true" value
72
New cards
Efficiency of an oil power plant
35-40%
73
New cards
Solar constant is ~1400 W/(m^2). Why is the average solar intensity on Earth's surface much less? ~350 W/(m^2)
Energy spreads over the sphere of Earth's surface. Solar constant is expressed in terms of circular cross section... π(r^2) vs. 4π(r^2)
74
New cards
When can you use P \= Fv?
Constant speed against a resistive force
75
New cards
Frequency of the first harmonic of a string fixed at both ends
v/2L
76
New cards
Assumption of LUG
Masses act as point masses
77
New cards
Fission
Heavy nucleus splits into 2 lighter nuclei, releases energy (right side of binding energy curve)
78
New cards
When is momentum NOT conserved in a collision?
When a net external force acts on the system
79
New cards
Efficiency of a natural gas power plant
~45%
80
New cards
Limitation of suvat
Constant acceleration
81
New cards
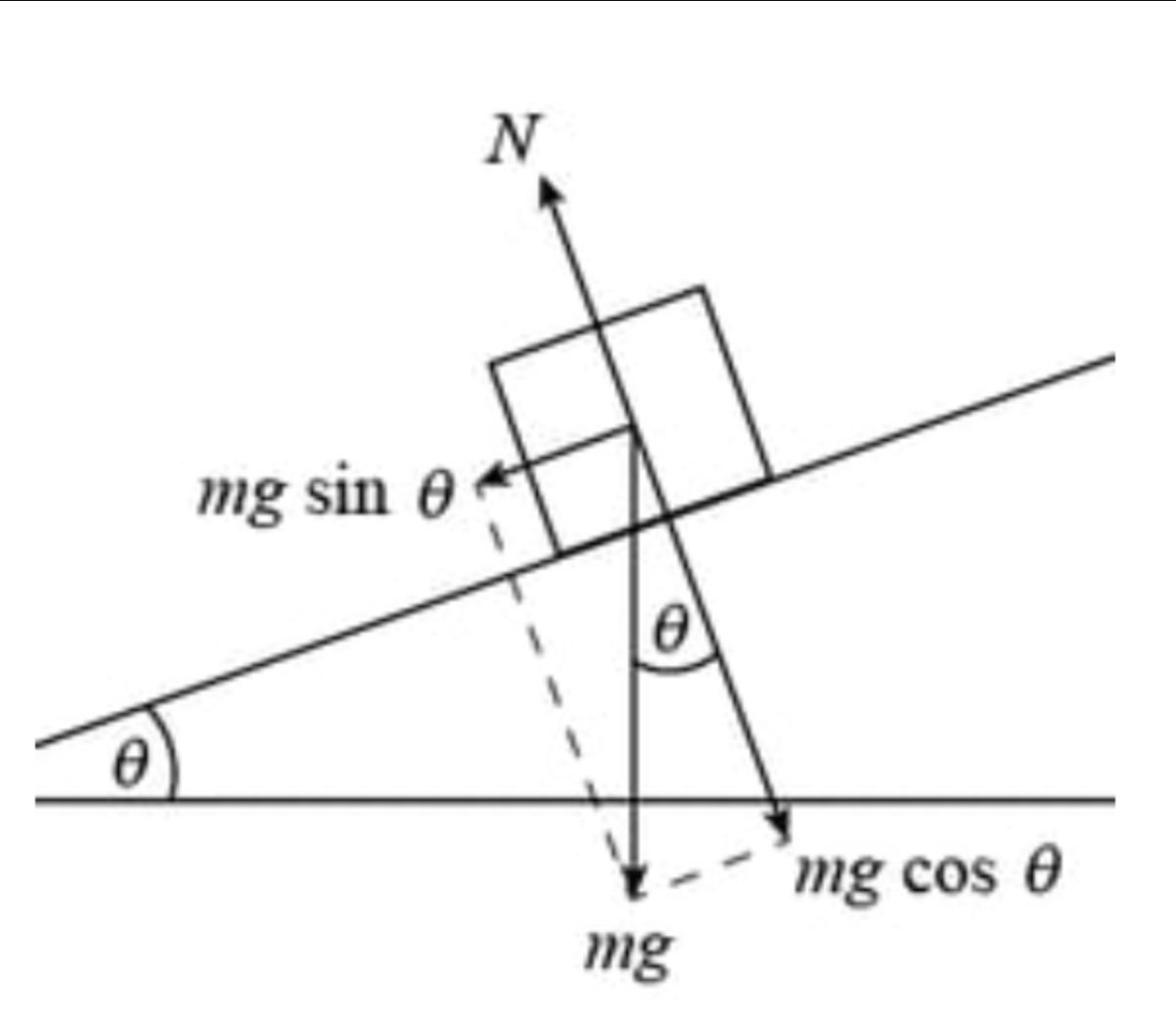
Object is sliding down a ramp. Normal force is equal in magnitude to what other force?
Component of weight perpendicular to the ramp (=mgcosθ)
82
New cards
Ohm's law
Current flowing through a conductor is proportional to the potential difference, providing the temperature remains constant / Resistance of a conductor is constant, providing the temperature remains constant
83
New cards
Order of magnitude: Size of a nucleus
10^-15 m
84
New cards
Frequency of the first harmonic of a pipe open at both ends
v/2L
85
New cards
7 base units
kilogram, meter, second, ampere, mole, kelvin, candela
86
New cards
Inelastic collision
Momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy is not
87
New cards
Centrifugal force
NO SUCH THING!
88
New cards
Difference between amplitude & displacement
Amplitude is the maximum displacement of an oscillating particle
89
New cards
Thermistor
Resistor whose resistance depends on temperature (usually decreases with increasing temperature)
90
New cards
Wind equation limitation / assumption
Equation gives the available power from a cross section of wind - all the wind can't be captured (or the wind would stop!) Betz limit gives maximum theoretical efficiency of a wind turbine, ~59%
91
New cards
Why do greenhouse gases heat the Earth? (property responsible)
RESONANCE allows them to absorb and re-radiate IR radiation
92
New cards
Frequency of the first harmonic for a pipe closed at one end (open at the other)
v/4L
93
New cards
Fusion
2 light nuceli combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy (left side of binding energy curve)
94
New cards
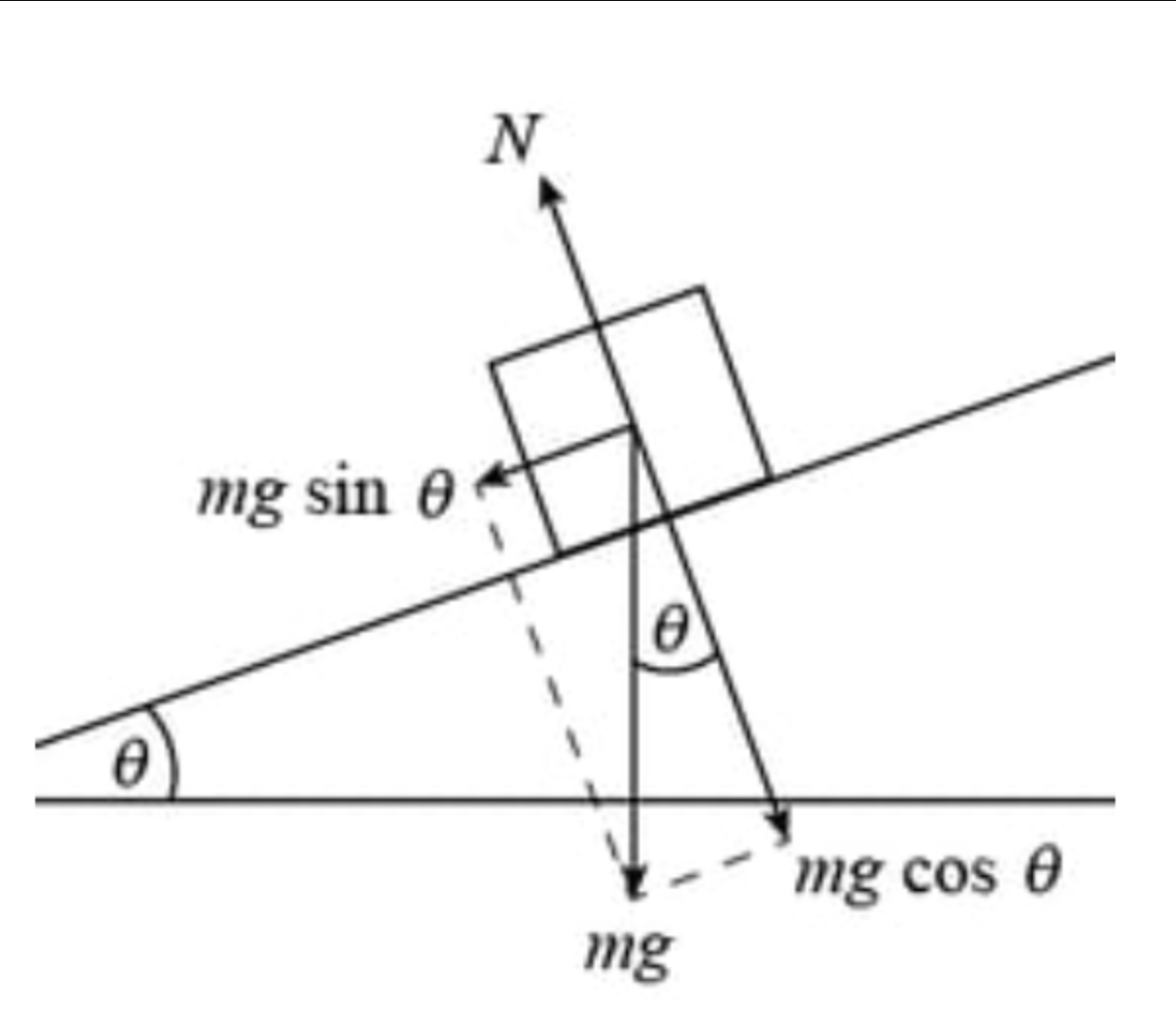
An object slides down a ramp at constant speed. The frictional force is equal in magnitude to…
the component of weight parallel to the ramp (\=mgsinθ)
95
New cards
LDR
Light dependent resistor. Resistance increases with increasing intensity
96
New cards
Besides using a polarizer, how can light become polarized?
Reflect off a surface (e.g. water)
97
New cards
Which experiment provided evidence for the nucleus?
Geiger-Marsden experiment (AKA Rutherford-Geiger-Marsden)
98
New cards
Right hand rule #1
\-Pointer finger = v (or I)
\-Middle finger = B
\-Thumb = F on a + charge
\-Middle finger = B
\-Thumb = F on a + charge
99
New cards
Right hand rule #2 (both ways)
\-Point thumb in direction of current, fingers curl to show direction of circular B field
\-Curl fingers in direction of circular current (for a coil) to get thumb as direction of B field inside coil
\-Curl fingers in direction of circular current (for a coil) to get thumb as direction of B field inside coil
100
New cards
An object in UCM moves with constant speed, why is it accelerating?
The direction of v is constantly changing, so velocity is changing, therefore it is accelerating.