Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics
11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel
The Experiments of Gregor Mendel
The scientific study of this biological inheritance is genetics
The modern science of genetics was started by a monk named Gregor Mendel
- Mendel used garden pea plants in his studies partly because peas are small, easy to grow, can make hundreds of offspring, and have many traits that are easy to see
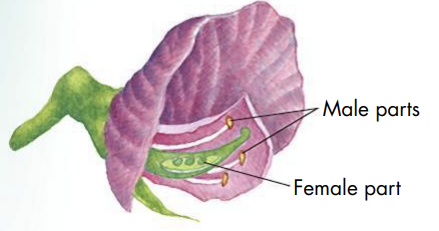
The male part of each flower makes sperm-containing pollen and the female part of each flower makes eggs
- Fertilization is the process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells join to form a new cell
- A plant grown from a seed made by self-pollination has just one parent because both reproductive cells came from the same plant
@@True-breeding plants are self-pollinating and they make offspring identical to themselves@@
- The traits (a specific characteristic, such as seed color or plant height, of an individual) in each generation are the same
To learn more about how traits are passed from parent to offspring, Mendel used pollen from one stock of plants to fertilize the female parts of flowers from other stocks of plants
- This process is called cross-pollination and produces a plant that has different parents
- The offspring of crosses between parents with different traits are called hybrids
When a yellow-seed plant was crossed with a green-seed plant, all the offspring produced yellow seeds; Mendel drew two conclusions from this
- @@First, Mendel found that an individual’s characteristics are controlled by genes that are passed from parent to offspring@@
- Each of the traits Mendel studied was controlled by a single gene that existed in two different forms called alleles
- @@Mendel’s second conclusion is called the principle of dominance and it states that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive@@
- An organism with at least one dominant allele for a form of a trait will show that form of the trait
- An organism with a recessive allele for a form of a trait will show that form only when the dominant allele for the trait is not there
Segregation
- When doing genetic crosses, we call each original pair of plants the P, or parental, generation, and their offspring are called the F1 generation
- To find out if the recessive alleles had simply disappeared or if they were still in the new plants, Mendel crossed the F1 generation with itself to make the F2 offspring
- Mendel found that the traits controlled by the recessive alleles reappeared in about one-fourth of the second generation
- Gametes are the sperm and egg cells that combine during fertilization; when gametes are made, the two alleles of each gene separate so that each gamete carries only a single copy of each gene
- Segregation refers to the separation of alleles
11.2 Applying Mendel’s Principles
Probability and Punnett Squares
Mendel figured out that the principles of probability (the likelihood that a particular event will occur) could be used to explain the results of his genetic crosses
- For example, when flipping a coin, there are only two possible outcomes: the coin can land either heads up or tails up.
- The chance, or probability, of either outcome is the same, so, the probability that a single coin flip will land heads up is 1 chance in 2; this can be described as a probability of 1/2, or 50 percent
Organisms with the same characteristics can have different combinations of alleles
For example, the tall pea plants could be either TT or Tt
- If an organism has two identical alleles of a gene, then the organism is homozygous
- The tall (TT) plants are homozygous because they have two identical alleles (TT) for a gene; the short plants are also homozygous because they have two identical alleles (tt) for a gene
- If an organism has two different alleles for the same gene, then the organism is heterozygous
- The parents in this cross are heterozygous because they have two different alleles (Tt) for that gene
Although three different combinations of the alleles t and T are possible: Tt, TT, and tt, only two different forms of the plant are possible
- Plants with the combinations TT and Tt are tall, and plants with the combination tt are short
- Mendel noticed that all of the tall pea plants had the same phenotype, or physical traits, but they did not, however, have the same genotype, or genetic makeup
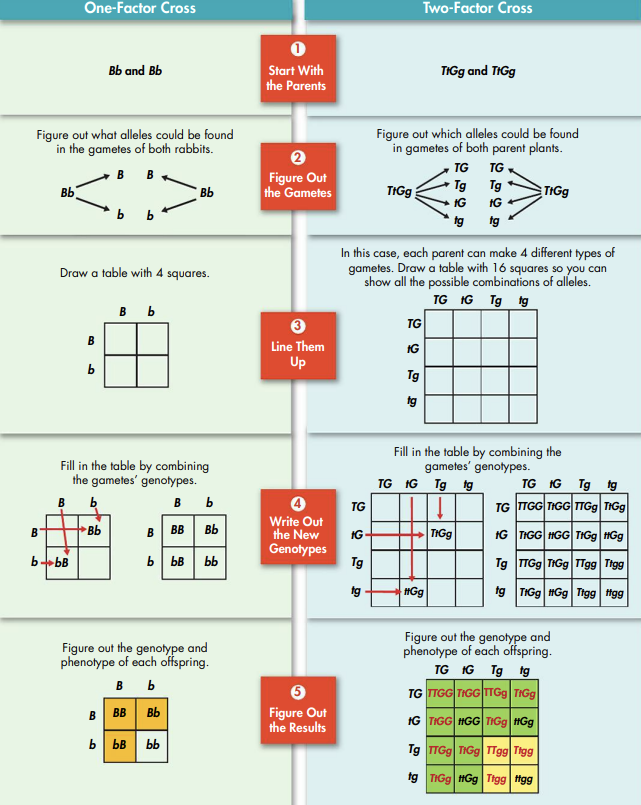
Punnett squares use probability to predict combinations of alleles in a genetic cross
Independent Assortment
- Independent assortment is one of Mendel’s principles that states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
- Genes that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance
- Independent assortment helps explain the many genetic variations we see in all living things
A Summary of Mendel’s Principles
- Mendel’s principles of heredity form the basis of modern genetics, including:
- Biological characteristics are inherited through units called genes, which are passed from parents to offspring
- Sometimes there are two or more forms (alleles) of a gene for a single trait; some forms of a gene may be dominant and others may be recessive
- In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene. Organisms get one copy from each parent. These alleles segregate from each other when gametes are made.
- Alleles for different genes usually segregate independently of each other
11.3 Other Patterns of Inheritance
Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles
- Most genes have more than two alleles, and many traits are controlled by more than one gene
- Sometimes neither allele is dominant over the other; if alleles have codominance, the phenotypes made by both alleles show up at the same time
- Cases where one allele is not completely dominant are called incomplete dominance, in which the heterozygous phenotype lies somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes
- A gene with more than two alleles is said to have multiple alleles
- Two individuals having two different alleles each could together have four different alleles for the same gene
- Many traits are controlled by several genes at work at the same time; traits controlled by two or more genes are said to be polygenic traits
- In multiple alleles, many different alleles exist for a gene in a population; however, an individual organism only has a single pair of these alleles
- In polygenic traits, each individual organism has many different gene pairs that all work together on one trait
- Environmental conditions can change gene expression and influence genetically controlled traits
11.4 Meiosis
Chromosome Number
Chromosomes are strands of DNA and protein inside the cell nucleus, and they are the carriers of genes; genes are located in specific places on chromosomes
Homologous is the term used to refer to chromosomes in which one set comes from the male parent and one set comes from the female parent
Diploid is the term used to refer to a cell that contains two sets of homologous chromosomes
Haploid is the term used to refer to a cell that contains only a single set of genes
- Haploid cells are made by meiosis
Meiosis is a process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell
- Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division, called meiosis I and meiosis II
- The result of meiosis is 4 haploid cells that are genetically different from one another and from the original cell
- Interphase: Cells undergo a round of DNA replication, forming duplicate chromosomes
- Prophase I: Each chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome to form a tetrad, which has four chromosomes
- Next, they undergo a process called crossing-over, in which the chromatids of the homologous chromosomes cross over one another
- Crossing-over produces new combinations of alleles on each chromatid
- Metaphase I: Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes
- Anaphase I: The fibers pull the homologous chromosomes to opposite ends of the cell
- Telophase I and Cytokinesis: Nuclear membranes form and the cell separates into two cells
- Prophase II: Meiosis I results in two haploid (N) daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell
- Metaphase II: The chromosomes line up in a similar way to the metaphase stage of mitosis
- Anaphase II: The sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell
- Telophase II and Cytokinesis: Meiosis II results in four haploid daughter cells
The haploid cells made by meiosis II are gametes, such as eggs and sperm, that join in fertilization to form a zygote, which has new combinations of alleles
- The zygote undergoes cell division by mitosis and grows into an organism

@@Mitosis can be a form of asexual reproduction@@
- Mitosis does not change the number of chromosomes
- Meiosis makes two identical diploid cells
@@Meiosis is a step in sexual reproduction@@
- Meiosis cuts the chromosome number in half
- Meiosis makes four genetically different haploid cells
Gene Linkage and Gene Maps
- Alleles of different genes tend to be inherited together when those genes are on the same chromosome
- Chromosomes are made of many genes linked together; gene maps show how far apart these genes are from each other
- Linked genes are not always inherited together
- If crossing-over happens during meiosis, then linked genes can be separated
- The farther apart genes are on a chromosome, the more likely crossing-over will separate them
- This trend means that the rate of crossing-over can be used to locate and even map genes on a chromosome